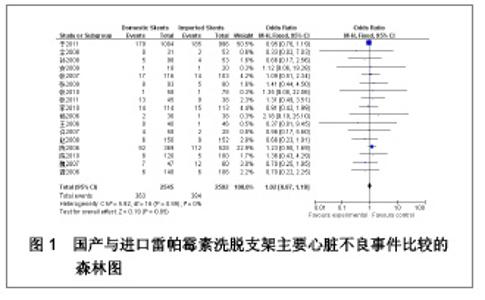
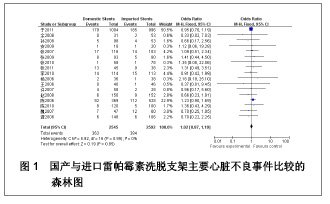
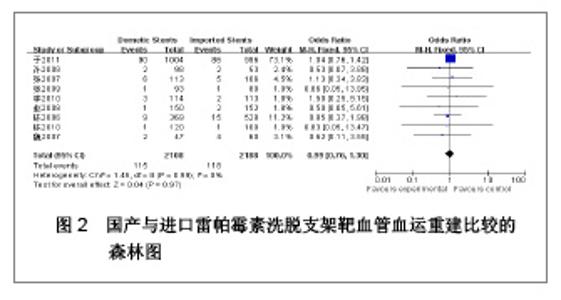
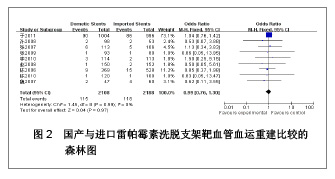
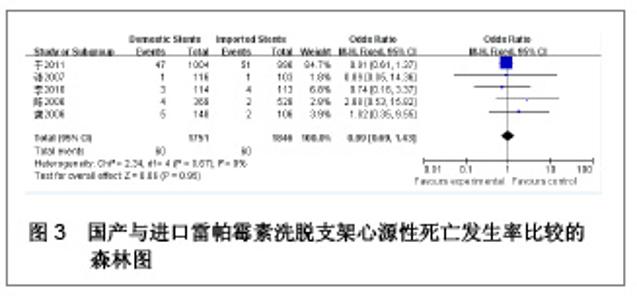
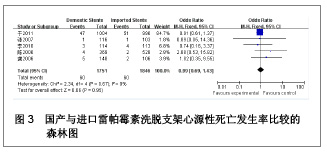
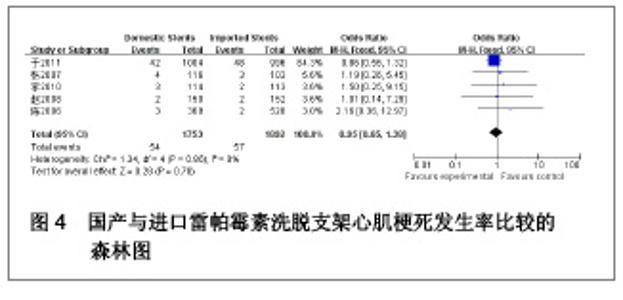
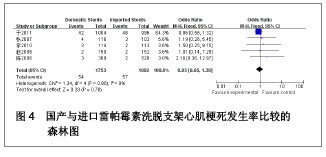
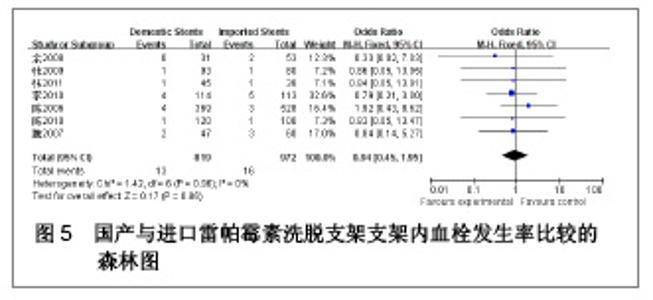
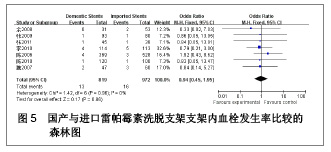
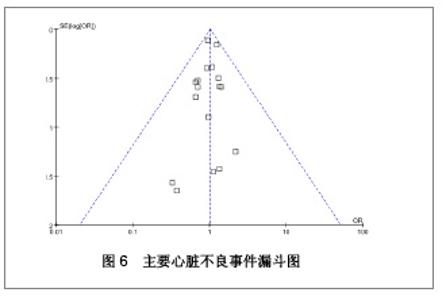
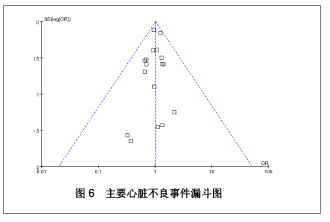
| [1] Paradis JM,Bélisle P,Joseph L,et al.Drug-Eluting or Bare Metal Stents for the Treatment of Saphenous Vein Graft Disease Clinical Perspective.Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2010;3(6): 565-576.[2] Jadad AR,Moore RA,Carrol D,et al.Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials is blinding necessary.Control Clin Trials.1996;17(1): 1-12.[3] 孙雨华,甘舜进,张海滨,等. Firebird支架治疗急性冠脉综合征临床对比观察[J]. 基层医学论坛,2008,12(1): 23-25.[4] 龚佩华,邱建平,陆纪德,等. 冠状动脉原发病变应用国产与进口雷帕霉素洗脱支架的临床比较[J].中原医刊,2006,33(13): 4-6.[5] 陈世忠,韦金儒,银剑斌,等. 国产Firebird支架对急性冠脉综合征的疗效观察[J]. 右江民族医学院报,2010,32(4): 502-504.[6] 许敏,郭金成,王国忠,等. 国产和进口雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗急性心肌梗死的疗效比较[J].基层医学论坛,2007,11(17): 773-776.[7] 张正海,郭金成,张学坤,等.国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架在急性冠脉综合征的临床研究[J].实用心脑血管病杂志,2009,17(12): 1031-1032.[8] 张庆华,闫华,李莉,等.国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗走过心绞痛的疗效观察[J]. 实用医学杂志,2011,27(15): 2833-2835.[9] 魏文斌.国产与进口雷帕霉素洗脱支架的近期临床观察[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2007,6(6): 51-53.[10] 余华, 马礼坤, 冯克福, 等. 国产与进口雷帕霉素洗脱支架的临床应用研究[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2008, 11(4): 365-367.[11] 陈方,高阅春,何继强,等. 国产与进口雷帕霉素药物洗脱支架治疗冠心病的疗效比较[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2006,34(11): 994-996.[12] 张迪,孙玲,张艳辉,等.火鸟Firebird支架与强生Cypher支架近期效果的临床观察[J].中国实用医药,2010,5(3): 47-48.[13] 于淼,周玉杰,阎赢,等. 进口与国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架一年临床疗效比较[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志,2011,19(2): 95-99.[14] 赵玉娟,李为民,周立君,等.国产替罗非班联合生物可降解支架Excel治疗急性冠脉综合征的安全性和疗效[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2009,18(8): 835-840.[15] 杨涛,王燕,张建起,等.两种药物洗脱支架的临床对照研究[J].临床荟萃,2006, 21(13): 941-942.[16] 安健,李保,杨滨,等. Partner药物洗脱支架在急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗中的临床疗效[J].中国药物与临床,2009,9(9): 806-807.[17] 李强,王乐丰,杨新春,等.可降解涂层与不可降解涂层雷帕霉素洗脱支架在急性心肌梗死直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗中的疗效比较[J].中华心血管病杂志,2010, 38(10): 886-890.[18] 张慧晶,王歆月,郭丽娟,等.国产西罗莫司洗脱冠状动脉内支架临床疗效研究[J].河北医药,2007,29(12): 1320-1321.[19] Selvendiran K,Kuppusamy ML,Bratasz A,et al.Inhibition of vascular smooth-muscle cell proliferation and arterial restenosis by HO-3867, a novel synthetic curcuminoid, through up-regulation of PTEN expression.J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2009;329(3):959-966.[20] Flueckiger A,Strahm Y,Billinger M,et al.Intimal proliferation and restenosis in paclitaxel-eluting stents with aminoparylene as carrier substance in swines.J Invasive Cardiol.2009;21(3): 128-132.[21] Marx SO,Marks AR.Bench to bedside: the development of rapamycin and its application to stent restenosis.Circulation. 2001;104(8): 852-855.[22] Verheye S,Martinet W,Kockx MM,et al.Selective clearance of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49: 706-715.[23] 陆永光,李浪,陈妍梅,等. 生物可吸收涂层和永久涂层药物支架治疗冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(51): 9549-9554. |