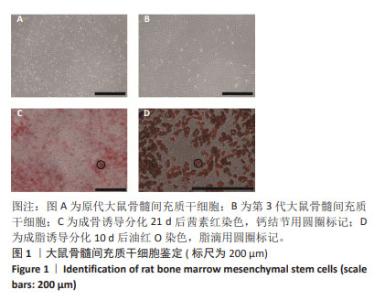
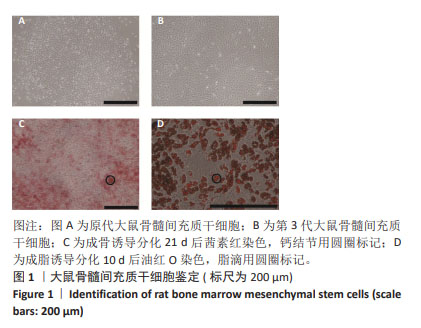
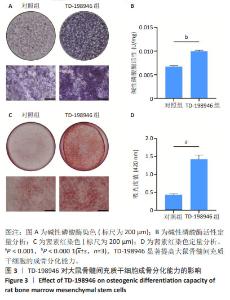
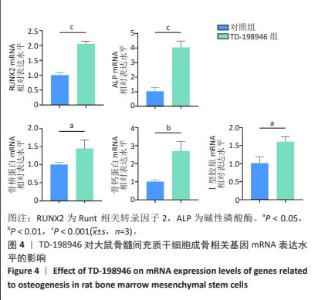
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2648-2654.doi: 10.12307/2025.060
Previous Articles Next Articles
Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Yang Chao, Luo Zongping
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Institute of Orthopedics of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-20Accepted:2024-04-13Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Luo Zongping, MD, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Institute of Orthopedics of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Yang Chao, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Institute of Orthopedics of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32071307 (to LZP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
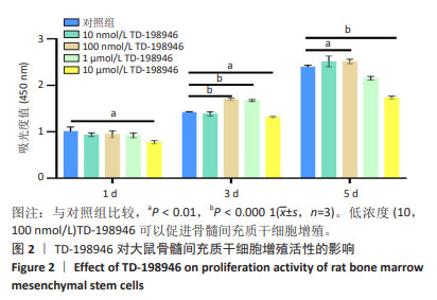
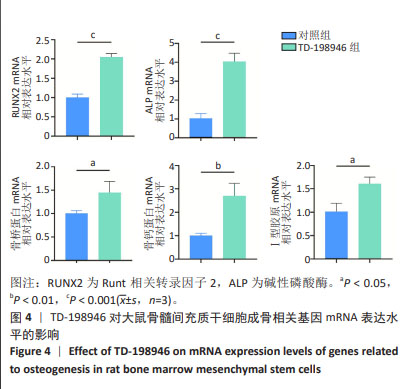
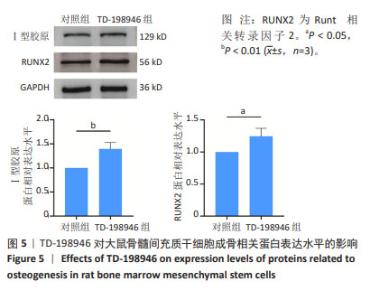
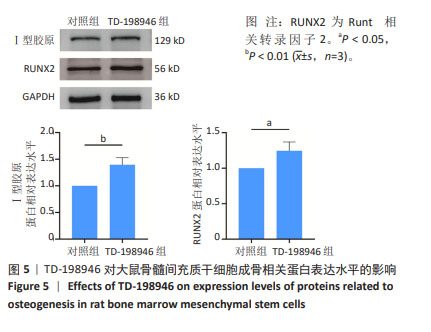
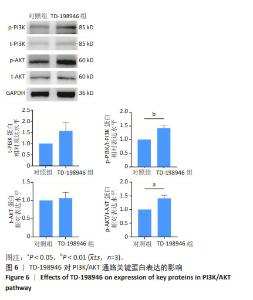
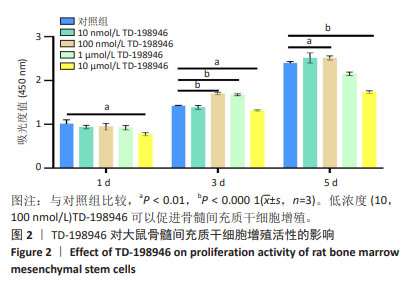
2.2 TD-198946对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响 第1天时,10 000 nmol/L TD-198946抑制细胞增殖;第3天时,100,1 000 nmol/L TD-198946促进细胞增殖,10 000 nmol/L TD-198946抑制细胞增殖;第5天时,100 nmol/L TD-198946促进细胞增殖,10 000 nmol/L TD-198946抑制细胞增殖,见图2。说明低浓度(10,100 nmol/L)TD-198946可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖,但随着浓度升高,TD-198946抑制作用也逐渐显现。因此,在后续实验中选择100 nmol/L TD-198946进行处理。"
| [1] ZHAO H, DING Y, YANG J, et al. Efficacy and safety of bisphosphonates on childhood osteoporosis secondary to chronic illness or its treatment: a meta-analysis. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022;13:20406223221129163. [2] CHANG X, XU S, ZHANG H. Regulation of bone health through physical exercise: Mechanisms and types. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:1029475. [3] PRADA D, CRANDALL CJ, KUPSCO A, et al. Air pollution and decreased bone mineral density among Women’s Health Initiative participants. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;57:101864. [4] DE SIRE A, LIPPI L, APRILE V, et al. Pharmacological, Nutritional, and Rehabilitative Interventions to Improve the Complex Management of Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Narrative Review. J Pers Med. 2022;12(10):1626. [5] WANG W, LIU H, LIU T, et al. Insights into the Role of Macrophage Polarization in the Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2485959. [6] ZHOU J, CHENG J, LIU L, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus (LA) Fermenting Astragalus Polysaccharides (APS) Improves Calcium Absorption and Osteoporosis by Altering Gut Microbiota. Foods. 2023;12(2):275. [7] TONK CH, SHOUSHRAH SH, BABCZYK P, et al. Therapeutic Treatments for Osteoporosis-Which Combination of Pills Is the Best among the Bad? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1393. [8] JAFARI A, QANIE D, ANDERSEN TL, et al. Legumain Regulates Differentiation Fate of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Is Altered in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Stem Cell Reports. 2017; 8(2):373-386. [9] MASTROLIA I, GIORGINI A, MURGIA A, et al. Autologous Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Driving Bone Regeneration in a Rabbit Model of Femoral Head Osteonecrosis. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(10):2127. [10] CAMPBELL TM, DILWORTH FJ, ALLAN DS, et al. The Hunt Is On! In Pursuit of the Ideal Stem Cell Population for Cartilage Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:866148. [11] YANO F, HOJO H, OHBA S, et al. A novel disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug candidate targeting Runx1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72(5):748-753. [12] YANO F, HOJO H, OHBA S, et al. Cell-sheet technology combined with a thienoindazole derivative small compound TD-198946 for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013;34(22):5581-5587. [13] KOBAYASHI M, CHIJIMATSU R, HART DA, et al. Evidence that TD-198946 enhances the chondrogenic potential of human synovium-derived stem cells through the NOTCH3 signaling pathway. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(2):103-115. [14] KUSHIOKA J, KAITO T, CHIJIMATSU R, et al. The small compound, TD-198946, protects against intervertebral degeneration by enhancing glycosaminoglycan synthesis in nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):14190. [15] WANG J, WU H, PENG Y, et al. Hypoxia adipose stem cell-derived exosomes promote high-quality healing of diabetic wound involves activation of PI3K/Akt pathways. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1): 202. [16] LIU X, WANG J, FAN Y, et al. Particulate Matter Exposure History Affects Antioxidant Defense Response of Mouse Lung to Haze Episodes. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(16):9789-9799. [17] KENT LN, RUMI MA, KUBOTA K, et al. FOSL1 is integral to establishing the maternal-fetal interface. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(23):4801-4813. [18] ZHANG W, LI X, ZHANG W, et al. The LncRNA CASC11 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration by Adsorbing miR-646 and miR-381-3p to Upregulate Their Target RAB11FIP2. Front Oncol. 2021;11:657650. [19] ZHAO B, PENG Q, POON EHL, et al. Leonurine Promotes the Osteoblast Differentiation of Rat BMSCs by Activation of Autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:615191. [20] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020; 28(4):400-409. [21] CHEN X, CHEN W, AUNG ZM, et al. LY3023414 inhibits both osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis through the PI3K/Akt/GSK3 signalling pathway. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(4):237-249. [22] CHO SW, SUN HJ, YANG JY, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing RANK-Fc or CXCR4 prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Mol Ther. 2009;17(11):1979-1987. [23] HUANG J, PARK J, JUNG N, et al. Hydrothermally treated coral scaffold promotes proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells and enhances segmental bone defect healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1332138. [24] WAESE EY, KANDEL RA, STANFORD WL. Application of stem cells in bone repair. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(7):601-608. [25] PIPINO C, PANDOLFI A. Osteogenic differentiation of amniotic fluid mesenchymal stromal cells and their bone regeneration potential. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(4):681-690. [26] 马明明,徐宏光,张艺凡,等.小分子药物TD-198946对终板软骨退变具有保护作用[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2015,20(8): 871-875. [27] YE C, ZHANG W, HANG K, et al. Extracellular IL-37 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10(10):753. [28] LIU X, BRUXVOORT KJ, ZYLSTRA CR, et al. Lifelong accumulation of bone in mice lacking Pten in osteoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(7):2259-2264. [29] LI H, LI T, FAN J, et al. miR-216a rescues dexamethasone suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(12):1935-1945. [30] ZHOU X, XI K, BIAN J, et al. Injectable engineered micro/nano-complexes trigger the reprogramming of bone immune epigenetics. Chem Eng J. 2023;462:142158. [31] SHANG J, YU Z, XIONG C, et al. Resistin targets TAZ to promote osteogenic differentiation through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. iScience. 2023;26(7):107025. |
| [1] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [2] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [3] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [4] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [5] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [6] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [7] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [8] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [9] | Li Tingyue, Guo Qian, He Wenxi, Wu Jiayuan. Long noncoding RNA TP53TG1 promotes odontogenic and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7776-7782. |
| [10] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [12] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [13] |
Li Yunzhe, Niu Zefan, Wang Zirou, Ai Chongyi, Chen Gang, Wang Xinxing.
Asperosaponin VI promotes osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells under hypoxia environment #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7481-7489.
|
| [14] | Liu Chengyuan, Guo Qianping. Differential effects of kartogenin on chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of rat and rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7490-7498. |
| [15] | Tang Haoxu, Liang Yingjie, Li Ce, Ding Penglin, Qian Minlong, Yuan Lingli. Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6821-6827. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||