Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (16): 3469-3475.doi: 10.12307/2025.420
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of photoresponsive nanomaterials in bone tissue regeneration
Feng Shuqi, Zhang Shiyong, Yao Keyi, Tang Yufei, Wang Kai, Zhou Xuemei, Xiang Lin
- 1State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2School of Chemical Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-18Accepted:2024-04-29Online:2025-06-08Published:2024-09-05 -
Contact:Xiang Lin, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Feng Shuqi, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82170997, 82370996 (to XL); Sichuan Science and Technology Program, No. 2024NSFSC0537 (to XL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Shuqi, Zhang Shiyong, Yao Keyi, Tang Yufei, Wang Kai, Zhou Xuemei, Xiang Lin. Application of photoresponsive nanomaterials in bone tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3469-3475.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
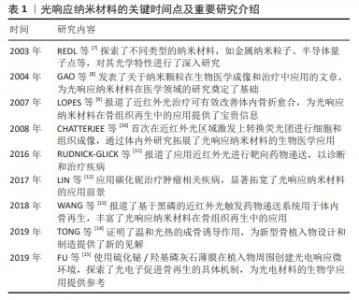
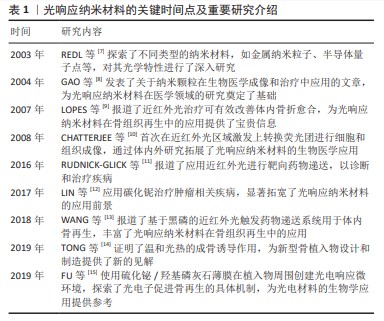
2.1 光响应纳米材料概述 2.1.1 光响应纳米材料的关键时间点及重要研究介绍 见表1。 2.1.2 光响应纳米材料的原理 在特定光源作用下光响应纳米材料被激发,将光信号转变为物理化学信号,使材料的理化性能发生变化以产生生物学效应,使光响应纳米材料在组织工程、生物成像、疾病诊断、药物递送和靶向治疗等生物医学领域广泛应用[15-19]。基于光响应纳米材料的光控疗法可通过控制光的波长、照射强度和持续时间等来实现个性化治疗,并最大程度减少对正常组织的不良反应[20]。按照波长从短到长,光可分为紫外光、可见光和近红外光[2]。大多数光响应纳米材料可响应能量较高的紫外光等短波长光,但是紫外光较低的组织穿透深度以及对生物组织较大的损伤性限制了其在生物体内的应用。与紫外光和可见光相比,位于生物组织光学窗口的近红外光对正常组织几乎没有毒性,同时在体内应用时具有更高的组织穿透深度,因而更适合生物体内应用[21]。 2.1.3 光响应纳米材料的分类 关于光响应纳米材料的分类,按照材料性质分为有机纳米材料和无机纳米材料。有机纳米材料主要包括碳基纳米材料(如石墨烯、碳纳米管等)和有机聚合物(如共轭聚合物大分子聚吡咯、小分子染料吲哚菁绿等),无机纳米材料主要包括金纳米粒子、上转换纳米粒子、金属化合物(如二氧化钛、二硫化钼、二硒化钨和硫化铋等)和单元素纳米粒子如黑磷等[22]。有机材料通常具有更好的生物相容性,但是光稳定性差,而无机纳米材料则具有较高的光稳定性,但需要改性以提高其生物降解能力[23]。 2.2 光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生中的优势 光响应纳米材料的两大特性是其发挥功能的基础:①作为纳米材料,光响应纳米材料具有独特的理化和生物学特性,包括较高稳定性、良好生物相容性、设计灵活性、高效载药能力以及接近生物分子的纳米级尺寸等[24]。除此之外,在应用形式方面,纳米材料可根据不同的治疗目标采用多种形式,如直接注射、表面涂层、生物活性支架成分以及药物递送系统组分等发挥其功能[21]。②光响应纳米材料具有光响应特性,光源本身具有可控、无创以及时空精准控制性等优势,更重要的是在特定光源(尤其是近红外光)照射下,光响应纳米材料表现出优异的光热效应、光动力学效应、光电效应以及光控药物递送的能力[21-22]。 除上述两大特性之外,部分光响应纳米材料如黑磷还具有组织矿化作用,其降解后形成的磷酸盐能与周围环境中的游离钙离子结合,具有局部矿化作用,可促进原位骨组织修复,在骨组织再生中受到广泛关注[25]。这些特性使得光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生领域具有巨大的应用潜力。 "
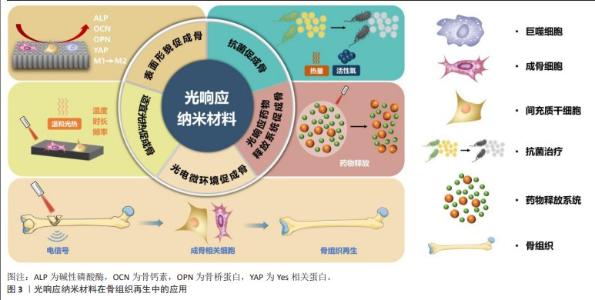
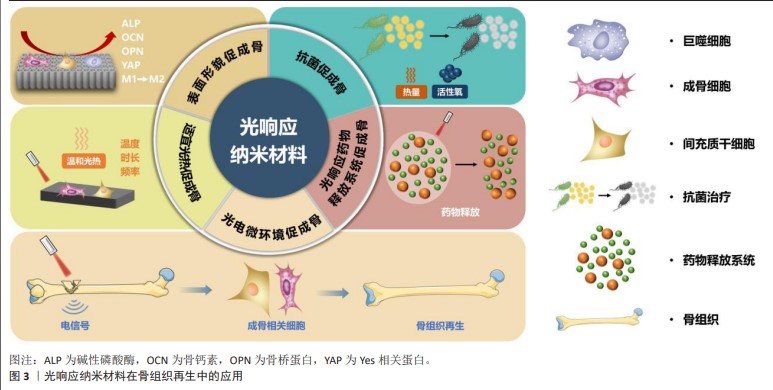
2.3 光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生中的应用 见图3。 2.3.1 表面形貌促成骨 光响应纳米材料表面为特有的纳米表面形貌。研究表明,与微米表面形貌相比,纳米表面形貌更有助于细胞黏附和成骨分化,因而更有利于促进骨组织再生[26-27]。以光响应纳米材料二氧化钛纳米管为代表来探究其内在机制。据报道,二氧化钛纳米管可诱导成骨细胞形成良好的细胞伸展并形成大量的丝状伪足,进一步探究其基因表达情况发现,二氧化钛纳米管表面的成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨相关基因如骨钙素、骨桥蛋白等表达增强;此外,二氧化钛纳米管表面的血管内皮细胞活性升高,表明该材料还有可能促进骨结合过程中的血管生成[28]。另一项研究在钛植入物表面制造微图案,在体内外测试了二氧化钛纳米管表面形貌对成骨性能的影响,体外研究发现,线状图案表面的人间充质干细胞呈现细长形态和平行线性排列,并且其成骨分化能力在该表面形貌下显著增强;除了在体外上调关键骨特异性功能基因的表达外,其在体内还可加速植入物和宿主骨之间的骨结合,进一步的机制研究表明,线状图案表面可促进细胞骨架伸展,并最终激活Yes相关蛋白介导的机械转导途径,促进人间充质干细胞成骨分化[29]。因此,材料表面形貌可作为细胞外机械信号传递到细胞内并调节细胞行为,增强成骨相关细胞的成骨能力。 除了直接的物理信号外,纳米材料的表面形貌还可通过调控免疫相关细胞的功能间接促进骨组织再生。巨噬细胞是重要的免疫相关细胞,在体内复杂的微环境中具有连续的表型极化谱,其中M1(经典活化)、M2(选择性活化)表型相关标记物与局部组织修复命运高度相关[30-31]。据报道,骨免疫微环境中的巨噬细胞表现出优越的可塑性,可响应于局部可变的环境而极化为M1和M2表型[32]。通过抑制巨噬细胞的M1促炎型极化、促进M2促修复型极化可促进骨组织再生[33]。研究表明,二氧化钛纳米管表面的巨噬细胞倾向于极化为M2表型,有利于组织修复,同时体内RNA测序结果进一步表明,二氧化钛纳米管表面细胞的炎症相关信号通路表达下降、代谢相关信号通路表达增加,有利于组织修复再生[34]。因此,光响应纳米材料的表面形貌可通过直接调节成骨细胞及间接调节免疫相关细胞的基因表达及生物学行为来促进骨组织再生。 2.3.2 抗菌促成骨 光响应纳米材料具有特定光源照射下的光热抗菌、光动力抗菌的能力,在感染性骨缺损中备受关注。 光热抗菌疗法是指光响应纳米材料在光照下将光能转换为热能,使局部温度升高以破坏细菌细胞膜的完整性,通过高温使细菌内的蛋白质变性而导致不可逆转的细菌损伤,从而达到有效杀菌的目的。以光响应碳化钛纳米片复合水凝胶支架为例,其具有较高的光热转换效率,因而具有良好的抗菌效果,同时还可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,以实现控制感染和促进骨再生的目的[35]。有序促进抗菌和成骨的光响应复合材料可实现功能的逐步调节,以满足感染性骨缺损不同阶段的需求。一项研究在钛植入物表面合成碳酸锶/硫化镍复合涂层,该涂层可通过光热效应进行灭菌,然后逐渐降解并释放出镍离子,以加速骨缺损中血管生成;此外,富含锶的碳酸锶纳米棒可促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化,加速钛植入物的骨结合[36]。研究表明,以光响应纳米材料黑磷为核心的多功能植入物涂层或集成骨支架,在近红外光照射下早期通过抗菌光热治疗减少局部感染,之后通过适宜的光热温度和促生物矿化离子释放等来增强骨组织再生[37-38];进一步探究潜在机制发现,黑磷经近红外光照射后可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,并上调成骨通路的表达来促进感染性骨缺损中的骨再生[38]。 光动力抗菌疗法是指光响应纳米材料在光照下发生光化学反应和氧化还原过程,诱导单线态氧或其他自由基的产生,从而破坏细菌细胞膜和蛋白质,最终使细菌死亡,具有可控性好、毒性小和不使细菌产生耐药性等优点[39-40]。研究表明,氢化二氧化钛纳米管/钛箔复合材料在光照射下具有较强的抗菌能力和促成骨能力:一方面,通过光催化产生活性氧以抑制变异链球菌和牙龈卟啉单胞菌的增殖,为成骨提供有利环境;另一方面,其纳米结构可加速初始蛋白质的黏附,促进成骨细胞前体细胞的增殖[41]。 光热抗菌和光动力抗菌的抗菌效应可减少局部感染,从而降低炎症反应,为骨缺损修复创造有利微环境。然而,为达到理想的抗菌效果,光热抗菌通常需要较高温度,而光动力抗菌则需要产生大量的活性氧,这可能会对周围的正常组织造成损伤[42]。目前的研究联合利用光热抗菌和光动力抗菌,以达到高效抗感染、减少不良反应的目的,并最终实现感染条件下良好的成骨效果。一项研究合成了掺杂碳点的二氧化钛纳米棒阵列,由于光热和光动力疗法的联合作用,该材料可在660 nm可见光和808 nm近红外光的共同照射下对金黄色葡萄球菌表现出优异的体内外抗菌效果,同时促进骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附和扩散,具有促进成骨的能力[43]。同样地,另一项研究在钛植入物表面制备了以光响应红磷为核心的复合材料,其在808 nm 近红外光照射下通过热量和活性氧的协同作用清除体内生物膜,并表现出优异的成骨性能,这种兼具抗菌和成骨特性的骨植入物在临床骨科上具有良好应用前景[42]。 "

2.3.3 适宜光热促成骨 基于光响应纳米材料的光热疗法可诱导产生轻微局部光热效应,并且具有损伤小、准确度高的特点,近年来已被广泛用于辅助促进骨组织再生[44]。研究表明,光响应纳米材料经近红外光照射后可产生适度的热量(比正常人体温度高3-5 ℃),有助于骨组织再生[37,45]。TONG等[14]利用黑磷和聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物合成的新型骨科植入材料具有良好的光热效应,该材料在40-42 ℃的适宜光热刺激下可促进骨缺损部位的骨组织修复。除温度之外,光热治疗的频率和时长对于骨组织再生也同样重要。研究表明,周期性的适宜光热治疗(41 ℃,1次/周,1 h/次)可增强碱性磷酸酶的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[46]。然而,当光热疗法以较高温度(> 55 ℃)进行长时间照射(> 10 min)时,会对周围组织造成不可逆转的损伤,对骨组织再生产生不利影响[47]。因此,控制光热疗法的温度、频率和时长对促进骨组织再生具有重要意义。 从机制层面来看,适宜的光热治疗促进骨组织再生可能与细胞行为、基因和蛋白质表达等密切相关。据报道,温和的局部热量(40-43 ℃)可通过诱导间充质干细胞的早期分化和促进成骨细胞的成熟来促进骨缺损的修复[46]。研究表明,光响应纳米材料黑磷、碳纳米管可通过光热效应上调热休克蛋白和碱性磷酸酶的表达、促使成骨相关基因的表达增高,从而促进骨组织再生,以实现“光热促成骨”的效果[48-49]。ZHANG等[50]合成的多孔银钯合金纳米颗粒可用于光热疗法进行原位骨再生,RNA测序结果表明其在近红外光照射下产生的温和局部热量可通过激活Wnt信号通路促进骨再生。因此,温和的光热刺激可通过上调成骨相关基因、蛋白质的表达和功能性成骨来有效增强成骨作用,促进骨缺损修复。 2.3.4 光电微环境促成骨 光响应纳米材料的光电响应特性在骨组织再生中起到重要作用。光响应纳米材料能吸收光能并产生电子,进而通过调节细胞局部电位变化实现对细胞信号传导的远程及时空精确性调节,以达到无创促进骨组织再生的目的[21,51]。 光电子可通过调控成骨相关细胞的活动促进骨再生。一项研究通过在二氧化钛纳米管阵列上负载稀土元素和金纳米颗粒来设计光电响应钛植入物,通过能量上转换效应来增强光电转化效率,研究结果表明,该光电转化材料体系产生的光响应电流在体外可促进成骨细胞前体细胞的增殖和成骨分化,在体内可促进种植体骨结合[52]。类似地,一项研究合成了氧化石墨烯/二氧化钛/钛薄膜,其在适当的光照强度下产生的光诱导表面电位,表现出良好的促骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化作用[53]。 从机制层面来看,研究表明光响应纳米材料的光电转化促成骨可能通过控制电压门控钙离子通道的开放,进而调节细胞内成骨相关信号通路。一项关于光响应氮化碳纳米薄膜的研究发现,其在光照射下可发生明显的光电响应,光诱导的电荷转移可以增强胞内钙离子内流,激活成骨细胞分化相关的关键转录因子Runx2来促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化,实现高效的骨再生[54]。另有研究表明,光响应硫化铋/羟基磷灰石纳米薄膜在近红外光照射后可产生光电子,并在植入物周围快速形成光电微环境;RNA测序结果表明,当光电子转移到间充质干细胞的细胞膜时,膜电位发生去极化,细胞形状发生改变,进一步促进钙离子内流,激活Wnt/钙离子信号通路以调控成骨分化的下游基因[15]。此外,光照射产生的材料表面电位变化还可促进成骨生长因子的吸附,以达到局部促成骨的作用[53]。 2.3.5 光响应药物释放系统促成骨 基于光响应纳米材料的药物释放系统,可在特定光源照射下发生结构变化以促进药物释放,为骨组织再生提供靶向治疗策略,以提高治疗的精确性并降低对正常组织的影响。 作为骨诱导元素的锶离子具有促成骨作用,研究通过将氯化锶和黑磷结合到聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球中以构建新型光响应离子释放系统,在近红外光调控下可实现锶离子的时空精准释放,以显著促进缺损部位的骨组织再生[13]。除离子释放系统之外,按需释放骨再生相关蛋白质也可为骨组织再生提供新的策略。基于金纳米颗粒水凝胶的治疗系统可利用其近红外光响应特性实现骨形态发生蛋白2的时空控制释放,以促进新的矿化骨组织的形成[55]。光响应碳酸镁钙微球水凝胶复合材料可顺序递送抗炎药物阿司匹林和骨形态发生蛋白2,前期通过阿司匹林的快速释放减轻了骨修复早期的炎症反应,后期在近红外光照射下可控释放骨形态发生蛋白2进而上调成骨通路表达,以促进骨修复晚期的骨组织再生[56]。 总之,在光响应药物释放系统中,光响应纳米材料作为载体,光作为触发药物释放的开关,共同构成的药物释放系统可靶向传递并控制成骨相关物质的释放,以达到促进骨组织生成的目的。光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生中的代表性应用,见表2。"

| [1] SHI C, WU T, HE Y, et al. Recent advances in bone-targeted therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;207:107473. [2] ZHAO W, ZHAO Y, WANG Q, et al. Remote Light-Responsive Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Delivery: Advances and Perspectives. Small. 2019;15(45):e1903060. [3] WEI H, CUI J, LIN K, et al. Recent advances in smart stimuli-responsive biomaterials for bone therapeutics and regeneration. Bone Res. 2022; 10(1):17. [4] YANG Y, AW J, XING B. Nanostructures for NIR light-controlled therapies. Nanoscale. 2017;9(11):3698-3718. [5] YANG Y, VELMURUGAN B, LIU X, et al. NIR photoresponsive crosslinked upconverting nanocarriers toward selective intracellular drug release. Small. 2013;9(17):2937-2944. [6] ZHANG Y, HUANG L, LI Z, et al. Illuminating Cell Signaling with Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Nanomaterials. ACS Nano. 2016;10(4): 3881-3885. [7] REDL FX, CHO KS, MURRAY CB, et al. Three-dimensional binary superlattices of magnetic nanocrystals and semiconductor quantum dots. Nature. 2003;423(6943):968-971. [8] GAO X, CUI Y, LEVENSON RM, et al. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22(8): 969-976. [9] LOPES CB, PACHECO MT, SILVEIRA L JR, et al. The effect of the association of NIR laser therapy BMPs, and guided bone regeneration on tibial fractures treated with wire osteosynthesis: Raman spectroscopy study. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2007;89(2-3):125-130. [10] CHATTERJEE DK, RUFAIHAH AJ, ZHANG Y. Upconversion fluorescence imaging of cells and small animals using lanthanide doped nanocrystals. Biomaterials. 2008;29(7):937-943. [11] RUDNICK-GLICK S, COREM-SALKMON E, GRINBERG I, et al. Targeted drug delivery of near IR fluorescent doxorubicin-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol) bisphosphonate nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of primary and metastatic bone cancer in a mouse model. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016;14(1):80. [12] LIN H, GAO S, DAI C, et al. A Two-Dimensional Biodegradable Niobium Carbide (MXene) for Photothermal Tumor Eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II Biowindows. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(45):16235-16247. [13] WANG X, SHAO J, ABD EL RAOUF M, et al. Near-infrared light-triggered drug delivery system based on black phosphorus for in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;179:164-174. [14] TONG L, LIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Near-infrared light control of bone regeneration with biodegradable photothermal osteoimplant. Biomaterials. 2019;193:1-11. [15] FU J, LIU X, TAN L, et al. Photoelectric-Responsive Extracellular Matrix for Bone Engineering. ACS Nano. 2019;13(11):13581-13594. [16] MENG X, WANG X, CHENG Z, et al. Photoluminescence Lifetime of Black Phosphorus Nanoparticles and Their Applications in Live Cell Imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(37):31136-31145. [17] PERUMAL V, SIVAKUMAR PM, ZARRABI A, et al. Near infra-red polymeric nanoparticle based optical imaging in Cancer diagnosis. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019;199:111630. [18] HE X, YANG X, LI D, et al. Red and NIR Light-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for On-Demand Drug Delivery. Curr Med Chem. 2020; 27(23):3877-3887. [19] CHEN H, ZHAO Y. Applications of Light-Responsive Systems for Cancer Theranostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(25):21021-21034. [20] OLEJNICZAK J, CARLING CJ, ALMUTAIRI A. Photocontrolled release using one-photon absorption of visible or NIR light. J Control Release. 2015;219:18-30. [21] WAN Z, ZHANG P, LV L, et al. NIR light-assisted phototherapies for bone-related diseases and bone tissue regeneration: A systematic review. Theranostics. 2020;10(25):11837-11861. [22] SON J, YI G, YOO J, et al. Light-responsive nanomedicine for biophotonic imaging and targeted therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;138:133-147. [23] 徐静,吕慧欣,鲍鑫,等.近红外光响应水凝胶在组织工程领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):486-492. [24] CHOI HS, FRANGIONI JV. Nanoparticles for biomedical imaging: fundamentals of clinical translation. Mol Imaging.2010;9(6):291-310. [25] HUANG K, WU J, GU Z. Black Phosphorus Hydrogel Scaffolds Enhance Bone Regeneration via a Sustained Supply of Calcium-Free Phosphorus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(3):2908-2916. [26] GUI N, XU W, MYERS DE, et al. The effect of ordered and partially ordered surface topography on bone cell responses: a review. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(2):250-264. [27] KULKARNI M, MAZARE A, GONGADZE E, et al. Titanium nanostructures for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology. 2015;26(6):062002. [28] WU B, TANG Y, WANG K, et al. Nanostructured Titanium Implant Surface Facilitating Osseointegration from Protein Adsorption to Osteogenesis: The Example of TiO(2) NTAs. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1865-1879. [29] LOU Y, SUN M, ZHANG J, et al. Ultraviolet Light-Based Micropattern Printing on Titanium Surfaces to Promote Early Osseointegration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(21):e2203300. [30] HUANG P, XU J, XIE L, et al. Improving hard metal implant and soft tissue integration by modulating the “inflammatory-fibrous complex” response. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:42-52. [31] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969. [32] LAWRENCE T, NATOLI G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(11):750-761. [33] DAI X, HENG BC, BAI Y, et al. Restoration of electrical microenvironment enhances bone regeneration under diabetic conditions by modulating macrophage polarization. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):2029-2038. [34] BAI L, ZHAO Y, CHEN P, et al. Targeting Early Healing Phase with Titania Nanotube Arrays on Tunable Diameters to Accelerate Bone Regeneration and Osseointegration. Small. 2021;17(4):e2006287. [35] NIE R, SUN Y, LV H, et al. 3D printing of MXene composite hydrogel scaffolds for photothermal antibacterial activity and bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Nanoscale. 2022;14(22):8112-8129. [36] LIU Z, DING H, QI L, et al. Core-Shell NiS@SrTiO(3) Nanorods on Titanium for Enhanced Osseointegration via Programmed Regulation of Bacterial Infection, Angiogenesis, and Osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c11995. [37] WU Y, LIAO Q, WU L, et al. ZnL(2)-BPs Integrated Bone Scaffold under Sequential Photothermal Mediation: A Win-Win Strategy Delivering Antibacterial Therapy and Fostering Osteogenesis Thereafter. ACS Nano. 2021;15(11):17854-17869. [38] YUAN B, ZHOU X, LI Y, et al. Black-Phosphorus-Nanosheet-Reinforced Coating of Implants for Sequential Biofilm Ablation and Bone Fracture Healing Acceleration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(41):47036-47051. [39] CAI X, XU T, DING R, et al. Oxygen self-supplying small size magnetic nanoenzymes for synergistic photodynamic and catalytic therapy of breast cancer. Nanoscale. 2024;16(8):4095-4104. [40] SOUZA BMN, MIÑÁN AG, BRAMBILLA IR, et al. Effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy with photodithazine® on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Studies in biofilms and experimental model with Galleria mellonella. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2024;252:112860. [41] ZHAO Y, LU R, WANG X, et al. Visible light-induced antibacterial and osteogenic cell proliferation properties of hydrogenated TiO(2) nanotubes/Ti foil composite. Nanotechnology. 2021;32(19):195101. [42] HUANG B, TAN L, LIU X, et al. A facile fabrication of novel stuff with antibacterial property and osteogenic promotion utilizing red phosphorus and near-infrared light. Bioact Mater. 2019;4(1):17-21. [43] HE D, ZHANG X, YAO X, et al. In vitro and in vivo highly effective antibacterial activity of carbon dots-modified TiO(2) nanorod arrays on titanium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;211:112318. [44] MA K, LIAO C, HUANG L, et al. Electrospun PCL/MoS(2) Nanofiber Membranes Combined with NIR-Triggered Photothermal Therapy to Accelerate Bone Regeneration. Small. 2021;17(51):e2104747. [45] LI W, LI S, ZHANG J, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of bone morphogenetic protein-2 microspheres coated black phosphorus nanosheets@polylactic-glycolic acid copolymers scaffold: A multifunctional antibacterial photothermal scaffold for bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;210:350-364. [46] CHEN J, SHI ZD, JI X, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by periodic heat shock in self-assembling peptide hydrogel. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(5-6):716-728. [47] JING X, XU C, SU W, et al. Photosensitive and Conductive Hydrogel Induced Innerved Bone Regeneration for Infected Bone Defect Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(3):e2201349. [48] WANG Y, HU X, ZHANG L, et al. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2829. [49] KAJIYA H, KATSUMATA Y, SASAKI M, et al. Photothermal stress triggered by near-infrared-irradiated carbon nanotubes up-regulates osteogenesis and mineral deposition in tooth-extracted sockets. Int J Hyperthermia. 2015;31(6):635-642. [50] ZHANG X, CHENG G, XING X, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Porous AuPd Alloy Nanoparticles To Produce Mild Localized Heat To Accelerate Bone Regeneration. J Phys Chem Lett. 2019;10(15): 4185-4191. [51] DONG S, ZHANG Y, MEI Y, et al. Researching progress on bio-reactive electrogenic materials with electrophysiological activity for enhanced bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:921284. [52] TANG Y, WANG K, WU B, et al. Photoelectrons Sequentially Regulate Antibacterial Activity and Osseointegration of Titanium Implants. Adv Mater. 2024;36(2):e2307756. [53] LONG X, DUAN L, WENG W, et al. Light-induced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs with graphene/TiO(2) composite coating on Ti implant. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;207:111996. [54] TIWARI JN, SEO YK, YOON T, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Two-Photon Photoactivated Carbon Nitride Nanosheets. ACS Nano. 2017;11(1):742-751. [55] SANCHEZ-CASANOVA S, MARTIN-SAAVEDRA FM, ESCUDERO-DUCH C, et al. Local delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from near infrared-responsive hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;241:119909. [56] WAN Z, DONG Q, GUO X, et al. A dual-responsive polydopamine-modified hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel for sequential regulation of bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;297:120027. [57] GURUNATHAN S, KIM JH. Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1927-1945. [58] FADEEL B, GARCIA-BENNETT AE. Better safe than sorry: Understanding the toxicological properties of inorganic nanoparticles manufactured for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(3):362-374. [59] LIU Y, BHATTARAI P, DAI Z, et al. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(7):2053-2108. |
| [1] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [2] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [3] | Feng Nan, Li Yunfeng. Antibacterial piezoelectric materials: no selective killing of bacteria and no bacterial resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2105-2112. |
| [4] | Xiao Hui, Li Dongyan, Ji Jing, Wang Lizhen. Action mechanisms and application pathways of biomaterials in promoting corneal alkali burn repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2162-2170. |
| [5] | He Jing, Ao Qiang. Research hotspots in tissue decellularization method for manufacturing extracellular matrices [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5413-5420. |
| [6] | Jiang Zongrui, Zhang Zhiqi. Treatment of meniscus injury or degeneration: the effect and function of stem cells and artificial polymer scaffolds to form tissue engineering system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5421-5427. |
| [7] | Yu Xingge, Lin Kaili. Application of nanocomposite hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5441-5446. |
| [8] |
Zeng Zhaomu, Wen Xichao, Zhang Yuhao, Geng Lianting, Shen Yang, Zheng Kebin.
Role and application of exosomes-mediated miRNAs in the treatment of glioma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4073-4080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||