Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (8): 1667-1675.doi: 10.12307/2025.334
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis
Wang Qiuyue1, Jin Pan2, Pu Rui1, 3
- 1College of Education and Physical Education, 2Health Science Center, 3Human Science Laboratory, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-04-03Accepted:2024-05-11Online:2025-03-18Published:2024-07-06 -
Contact:Pu Rui, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, College of Education and Physical Education, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; Human Science Laboratory, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Jin Pan, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Health Science Center, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Wang Qiuyue, Master candidate, College of Education and Physical Education, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860386 (to JP); Jingzhou Medical and Health Science and Technology Project, No. 2022HC36 (to JP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
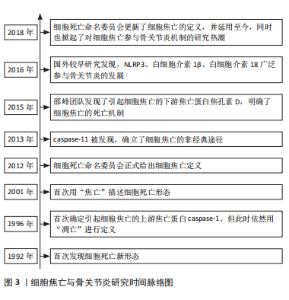
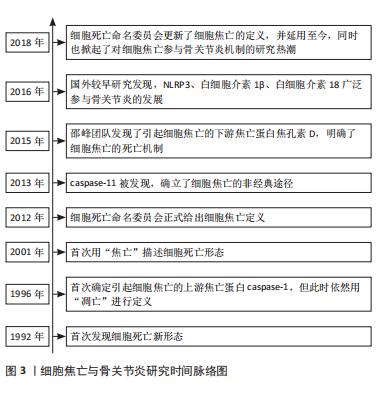
2.1 细胞焦亡概述 2.1.1 细胞焦亡的发现 1992年,ZYCHLINSKY等[8]在革兰阴性细菌病原体福氏志贺氏菌诱导巨噬细胞自杀过程中发现的新型细胞死亡机制,与以往细胞凋亡的形态学特征不一致,表现为侵入性细菌性病原体可诱导宿主细胞自杀。2001年,COOKSON等[9]首次将细胞不断膨胀至破裂,从而引发机体免疫反应的细胞炎症性程序死亡描述为“焦亡”。2015年邵峰团队发现了GSDMD,其作为caspase的底物是细胞膜形成膜孔的关键物质,参与细胞焦亡的下游通路[10]。2018年,细胞死亡命名委员会将细胞焦亡的定义更新为“一种调控性细胞死亡”,即由炎症刺激物引发的机体免疫反应,促使细胞程序性的死亡方式[11]。细胞焦亡与骨关节炎研究时间脉络图,见图3。"
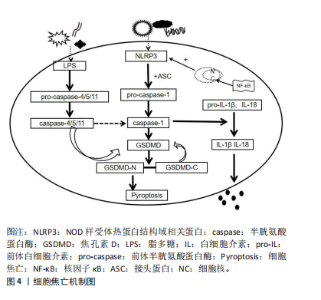
2.1.2 细胞焦亡的信号通路 细胞焦亡与其他细胞死亡形式不同,主要依赖于炎性小体刺激。炎性小体是胞质多分子复合物,可感知细胞内微生物危险信号和代谢扰动[12]。细胞焦亡经典途径依赖于caspase-1的激活,而非经典途径依赖于caspase-4/5/11。 经典细胞焦亡途径:在典型的炎症小体通路中,病原相关分子模式和损伤相关分子模式均能激活炎症小体。当处于病原相关分子模式时,细胞膜上的受体被炎症小体激活,诱导核因子κB进入细胞核[13-14],进而促进炎症小体NLRP3和caspase-1以及白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的前体转录[13];随后激活细胞质中的NLRP3炎症小体与接头蛋白ASC结合,通过募集前体caspase-1并将其激活为成熟的caspase-1,接着通过蛋白水解作用将前体白细胞介素1β和前体白细胞介素18加工成熟并释放到细胞外[14]。此外,成熟的caspase-1裂解效应蛋白GSDMD,产生N末端和C末端结构,N末端结构转移到细胞膜释放焦孔素并形成小孔,导致细胞肿胀和细胞膜突起,而C末端结构则返回原位[14]。同时,细胞外液中的电离子、水等小分子物质由于浓度差进入细胞内不断膨胀至破裂,细胞内的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18流向细胞外,从而产生炎症反应,引发细胞焦亡经典途径。细胞焦亡的机制见图4。"
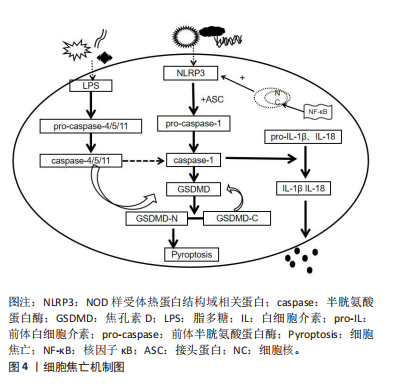
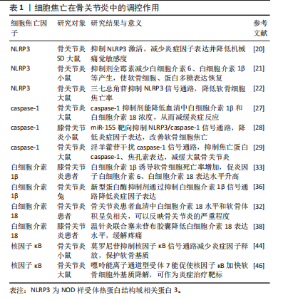
非经典细胞焦亡途径:不同于经典细胞焦亡途径,人caspase-4、caspase-5与小鼠caspase-11属于同系物,其与革兰阴性菌的脂多糖和脂质A具有高特异性亲和力,相互结合启动激活程序[15];它们与前体caspase-4/5/11结合,成熟的caspase-4/5/11活化GSDMD并与GSDMD-N端结合,转移到细胞膜上形成穿孔并产生气泡,而这一过程并不依赖于caspase-1。细胞膜破裂释放的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18扩大炎症信号,募集免疫细胞并刺激T细胞增殖;同时体液中的水分和小分子物质不断进入细胞内,使得细胞持续增大直至破裂,细胞内容物和炎性因子不断流出,从而引发细胞焦亡非经典途径。此外,caspase-11可通过caspase-1途径间接调控白细胞介素1β/caspase-4/5/11信号通路以激活泛连接通道蛋白1排出钾离子,进而激活NLRP3炎症小体,协同发挥细胞焦亡途径[16]。 2.2 细胞焦亡与骨关节炎 近年来,骨关节炎治疗领域中关于细胞焦亡调控的实证研究逐渐增多。NLRP3、caspase-1/4/5/11、白细胞介素1β/18以及核因子κB均参与细胞焦亡引发炎症。因此,细胞焦亡信号途径可能成为骨关节炎的潜在干预靶点。 2.2.1 NLRP3与骨关节炎 NLRP家族中NLRP1和NLRP3受到研究者的广泛关注,尤其是NLRP3在机体免疫防御方面发挥着至关重要的作用[17]:一方面,NLRP3引发细胞焦亡的经典途径,通过募集前体caspase-1,进而通过激活caspase-1,促进细胞释放炎症因子;另一方面,NLRP1或NLRP3炎症小体介导非经典途径的成纤维细胞样滑膜细胞焦亡[18]。此外,NLRP3作为一种炎症小体可加重滑膜炎症,进一步导致骨关节炎的恶化[19]。上述研究提示,NLRP3不仅会引发细胞焦亡的发生,还会加重滑膜炎症的出现。由此可见,抑制NLRP3可成为调控细胞焦亡缓解骨关节炎的新靶标。 NLRP3是激活细胞焦亡程序的开端,抑制NLRP3的通路可减少细胞焦亡的发生。刘格格[20]研究发现,豆腐果苷通过下调NLRP3炎症小体激活抑制其炎症通路,进而缓解骨关节炎大鼠炎症反应,显著减轻机械性痛觉过敏现象,为调控骨关节炎提供新策略。此外,最新被确立为NLRP3抑制剂的全霉素可缓解软骨细胞炎症反应,在一定程度上增加软骨细胞数量、恢复蛋白多糖表达,进一步的研究发现,其机制可能与全霉素降低血清中白细胞介素1β、NLRP3和白细胞介素6的表达,并与抑制NLRP3/caspase-1通路的激活有关[21]。随着研究的进一步深入,中药抑制细胞焦亡也取得突破性进展。蔡猛等[22]构建骨关节炎大鼠模型并通过三七总皂苷干预,发现软骨细胞焦亡率和NLRP3阳性细胞率均显著降低,进一步研究发现这可能与三七总皂苷抑制NLRP3信号通路有关。综上所述,抑制NLRP3信号通路可降低软骨细胞焦亡,从而延缓骨关节炎发展,证实了NLRP3在骨关节炎中调节细胞焦亡的关键作用。 2.2.2 caspase-1与骨关节炎 前期对caspase的研究主要集中于免疫防御领域,近年来发现caspase-1在细胞焦亡中也发挥重要作用。caspase-1在软骨细胞和滑膜细胞发生焦亡时将前体白细胞介素1β和前体白细胞介素18加工成熟,同时切割GSDMD产生膜孔,引发细胞内容物流出,导致炎症反应。caspase-1在细胞焦亡中发挥了重要作用,在骨关节炎中也会导致大量炎症因子的释放[23]。有研究显示,caspase-1在颞下颌关节骨关节炎滑膜细胞中高表达,说明caspase-1与颞下颌关节骨关节炎发展密切相关,提示caspase-1可作为骨关节炎诊断的生物标记物[24]。高迁移率族蛋白B1是巨噬细胞的下游产物,可加重骨关节炎的炎症反应。XIAO等[25]研究发现,骨关节炎大鼠滑膜细胞中高迁移率族蛋白B1和焦亡蛋白caspase-1、NLRP3表达水平明显升高。这一研究说明依赖于caspase-1途径的滑膜细胞焦亡增加了骨关节炎中高迁移率族蛋白B1分泌水平,为减少骨关节炎期间滑膜细胞炎症反应提供新的思路。上述研究提示,caspase-1在骨关节炎患者和骨关节炎小鼠模型中都呈现较高水平。但敲除caspase-1 基因的骨关节炎小鼠关节软骨更易发生退变,从而加速软骨细胞死亡和细胞外基质破坏[26]。由此可见,caspase-1在调节软骨细胞外基质稳态方面发挥作用,过度的caspase-1表达会造成软骨细胞破坏。 caspase-1抑制剂是治疗骨关节炎的潜在治疗剂,抑制caspase-1过度表达可缓解骨关节炎进程。细胞反应调节蛋白A是一种最早发现的caspase天然抑制剂[23]。随着研究的深入,caspase-1抑制剂的种类也在不断丰富,贝尔纳卡桑是caspase-1的有效抑制剂,能够降低血清中白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18浓度,已被证明具有体内外抗焦亡活性,可缓解多种焦亡相关疾病[27]。另有研究提示,抑制剂miR-155 靶向抑制NILRP3/caspase-1通路,降低caspase-1、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18水平,从而改善膝骨关节炎小鼠的软骨细胞焦亡[28]。此外,药物抑制caspase-1信号通路也取得了新进展。史纪元等[29]建立大鼠体外骨关节炎模型,发现淫羊藿苷可通过干扰caspase-1信号转导途径来缓解骨关节炎。以上研究表明,抑制caspase-1信号通路可缓解骨关节炎的病理进程。目前caspase-1抑制剂研究局限于人工合成类化合物,从天然产物抑制剂中提取的caspase-1抑制剂需要进一步研究。 2.2.3 白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18与骨关节炎 软骨细胞外基质主要由蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白组成,骨关节炎主要的致病原因是软骨细胞外基质降解。当软骨细胞或滑膜细胞发生焦亡时会释放炎症因子,导致关节液和周围组织的炎症水平升高,出现更严重的软骨降解和炎症反应[30]。有研究显示,骨关节炎患者炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶3及基质金属蛋白酶9表达水平较高[31]。另有研究发现,白细胞介素1β诱导骨关节炎模型中软骨细胞死亡增加,同时促炎因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素18表达水平升高[32]。上述研究表明,白细胞介素1β高水平表达是骨关节炎发生发展的显著特征,提示白细胞介素1β可作为骨关节炎诊疗的新靶点。 白细胞介素18作为另一种介导细胞炎症反应的因子,也参与了软骨基质降解、软骨细胞凋亡和滑膜炎症的调控。白细胞介素18能延长白细胞介素1β的作用时间,同时在体内促使前列腺素E2发挥分解作用,从而诱发关节软骨的退变。另有研究发现,骨关节炎患者血清白细胞介素18水平、前列腺素E2浓度与总软骨体积呈显著负相关,说明两项指标可以在一定程度上反映骨关节炎的严重程度[33-34]。由此可见,靶向降低白细胞介素18的表达可减缓骨关节炎患者的关节软骨损伤。此外,在膝骨关节炎兔模型中白细胞介素18水平表达显著升高,而抑制促炎性因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18释放,可以降低炎性反应,减缓膝骨关节炎进程[35]。以上研究均指出,白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18在动物模型和骨关节炎患者中高表达均加重了骨关节炎程度。 最近的研究表明,通过抑制白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的合成并减少其在软骨细胞中的积累,可能是缓解骨关节炎的有效方法。吴培刚等[36]对骨关节炎兔子注射新型蛋白酶抑制剂4周后发现,白细胞介素1β、基质金属蛋白酶9、核因子κB等炎症因子的相对表达量降低,其机制可能与抑制白细胞介素1β信号通路有关。李金磊等[37]研究发现,灯盏花素可通过调节应激激活蛋白酶信号通路抑制细胞炎症因子的表达,从而缓解骨关节炎大鼠软骨损伤。邹怡等[38]的研究发现,使用温针灸联合塞来昔布胶囊治疗膝骨关节炎患者可抑制炎症因子白细胞介素18表达水平,有效减轻疼痛,促进膝关节功能恢复。上述研究提示,细胞焦亡介导的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18参与骨关节炎调节,并且白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18信号通路可作为骨关节炎的治疗靶标。部分植物提取物和抗炎药物的使用可抑制白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的表达和释放,从而减轻骨关节炎的炎症反应和关节组织的损伤,为骨关节炎防治提供新的思路。 2.2.4 核因子κB与骨关节炎 核因子κB是细胞内核转录的重要因子,可参与免疫应答、新陈代谢等多种生物途径。当细胞处于静息状态时,核因子κB与其抑制酶IκB在细胞质内结合,处于抑制状态;当细胞受到炎性因子信号刺激后,细胞质内抑制酶被磷酸化,通过泛素蛋白酶进行降解;细胞质中游离的核因子κB数量增加,从细胞质转移到细胞核中,进而调控NLRP等炎症因子的转录[39]。核因子κB 信号转导通过多种模式广泛参与骨关节炎病理进程,可通过诱导前列腺素E2促进炎症因子释放,引发降解蛋白酶的表达,减少胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖的产生,从而导致炎症反应并加重骨关节炎进程[40]。此外,核因子κB通路的激活可引发一系列炎症因子的释放,如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等,可促进软骨细胞凋亡、细胞外基质降解,导致关节软骨的损伤和退化。因此,核因子κB信号通路的活化与骨关节炎的发生发展关系密切。 先前的研究已证明,青蒿琥酯[41]、独活寄生汤[42]、马钱苷等中药能够使核因子κB通路失活[43],进一步减弱软骨基质分解代谢和软骨细胞焦亡,从而减缓骨关节炎的严重程度。YU等[44]的研究发现,莫罗尼苷可以通过抑制核因子κB信号通路来抑制NLRP3的表达,从而保护软骨基质免受降解。嘌呤能离子通道型受体7是对多种信号转导过程都具有生物学效应的阳离子通道,参与NLRP3的激活过程并与疼痛密切相关[45]。LI等[46]对大鼠注射激活的嘌呤能离子通道型受体7,通过核因子κB/NLRP3的相互作用促进了骨关节炎软骨细胞中的胞外基质降解。这一研究提示,嘌呤能离子通道型受体7是炎症治疗的潜在靶标,为骨关节炎研究和治疗提供了新的途径。由此可见,抑制核因子κB通路的激活可有效改善骨关节炎软骨的病理性改变,缓解关节软骨的退变。 细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的调控作用见表1。 2.3 运动对细胞焦亡、骨关节炎的影响 现阶段,骨关节炎的临床治疗手段包括药物治疗、手术等方法。运动疗法因其经济、有效、易操作等优点已成为骨关节炎非药物治疗的重要手段。诸多研究表明,运动能够延缓细胞焦亡,在骨关节炎的防治中发挥关键作用。 2.3.1 运动与骨关节炎 运动已成为防治骨关节炎最经济有效的方法,有氧运动和无氧运动都有利于缓解骨关节炎患者的疼痛并改善关节功能[47]。在CHEUNG等[48]进行的随机对照试验中发现,无论是哈达瑜伽还是有氧强化 "
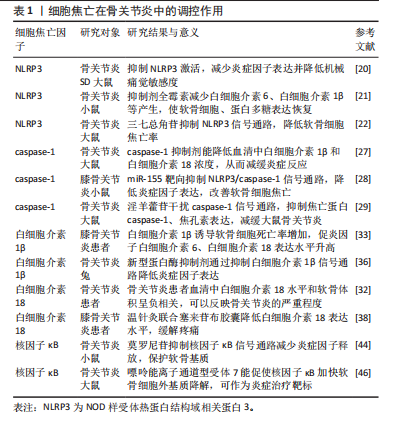

运动均能改善膝骨关节炎的症状和功能,其机制可能与有氧运动通过激活核因子κB干扰成骨细胞与破骨细胞的信号通路,影响骨代谢有关,为患者缓解骨关节炎进程提供了多元化选择。随着研究的进一步深入,OKA等[49]发现为期8周的中等强度跑台运动能够减缓小鼠炎症程度并抑制软骨降解;深入分析发现,有氧运动可抑制基质金属蛋白酶13和肿瘤坏死因子α并降低炎症因子的表达,从而缓解半月板损伤。此外,具有浓郁民族特色的中华传统运动疗法是以中医为理论依据、康复养生为核心的有氧运动,其中包括五禽戏、太极拳、八段锦等项目,特点在于动作缓慢、强度适中,尤其适合老年人,也是骨关节炎患者的优等选择。 除此之外,水中运动作为有氧运动的补充有重要的潜在价值。水的阻力可以在比较慢的速度下消耗相同的能量,水的浮力可以减少关节摩擦、减少疼痛,其物理特征使得水中运动适合各个年龄段的人群。因此,水中运动被认为是一种非常有效且安全的运动方式。此外,与陆地台阶测试相比,水中台阶测试更适合下肢无力和膝骨关节炎患者用以提高肌肉力量[50]。黄晓倩[51]的研究发现,为期16周的水中运动可显著减轻膝骨关节炎超重女性的膝疼痛和僵硬、肿胀的症状,并且高强度水中运动优于低强度水中运动,但对于改善膝关节日常功能几乎没有影响,提示水中运动可作为治疗骨关节炎的有用辅助手段。 无氧运动不仅能直接减轻疼痛,还能通过提高肌肉质量进一步改善骨健康。抗阻训练是无氧运动的一种形式,也是提高肌肉力量的有效方式。研究表明,高强度间歇训练能够减轻骨关节炎大鼠的疼痛,深入探究发现运动通过抑制钙亚基通道蛋白缓解疼痛敏感度[52]。高强度间歇训练能够提高有氧能力、肌肉力量和生活质量[53]。但MESSIER等[54]的研究发现,对于骨关节炎患者,高强度力量训练在18个月的随访中并未显著改善疼痛状况,并且比低强度力量训练有更大的风险,故力量训练对骨关节炎的改善作用还需进一步商榷。此外,BABUR等[55]的研究发现,进行抗阻训练后的膝骨关节炎患者瘦体质量增加,并且没有出现疼痛或不良事件。另有研究指出,骨关节炎患者持续3-6个月的抗阻运动干预可改善身体功能,并指出改善效果与运动量无关或依从性无关[56]。因此,抗阻运动能够增强肌肉质量进而改善骨关节炎。 2.3.2 运动介导细胞焦亡调控骨关节炎 运动作为一种重要的生活方式被广泛认为可以对细胞焦亡起到积极的调节作用,最近有研究揭示了有氧运动调控细胞焦亡的新机制。卞学鹏等[57]的研究发现,递增负荷的有氧运动能够显著降低胰岛素抵抗小鼠海马细胞焦亡相关蛋白NLRP3、GSDMD、GSDMD-N和炎症因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18以及核因子κB的表达,从而抑制细胞焦亡,而空白组胰岛素抵抗小鼠核因子κB蛋白水平显著升高,炎症小体表达水平均有上升趋势。有研究表明,有氧运动可以抑制NLRP3的活化,从而抑制焦亡接头蛋白、caspase-1和白细胞介素1β的下游通路。此外,有氧运动结合姜黄素的干预效果最佳[58]。上述研究提示,有氧运动可通过不同途径抑制细胞焦亡,从而发挥改善疾病的有益效应。此外,4周跑台运动显著降低细胞焦亡经典途径中NLRP3、caspase-1、GSDMD蛋白的表达,减少大鼠缺血侧脑组织中焦亡下游炎性因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的释放,减轻脑梗死程度[59]。但运动预处理如何调控NLRP3炎症小体活化产生影响细胞焦亡的具体机制尚未明确。由此可见,NLRP3、caspase-1、GSDMD等焦亡蛋白下调可缓解细胞焦亡,表明有氧运动对细胞焦亡的信号通路有重要的调控作用。 FU等[60]发现32周的负重跑可改变大鼠身体成分,并且负重运动组NLRP3、Caspase-1和GSDMD呈现较低表达,说明负重运动通过抑制焦亡蛋白表达来缓解炎症。此外,活性氧可触发NLRP3炎症小体的激活。另有研究显示,12周的跑台运动通过抑制活性氧降低小鼠体内NLRP3水平,抑制细胞焦亡发生[61]。骨骼肌在运动时会诱导产生新型脂肪因子镍纹样蛋白,并通过抑制NLRP3和caspase-1改善软骨细胞焦亡。JAVAID等[62]的研究结果显示,有氧运动能够显著增强镍纹样蛋白的表达水平,进一步的体外分析发现,镍纹样蛋白抑制骨髓来源巨噬细胞中白细胞介素1β的分泌,这一研究提示,有氧运动通过调节镍纹样蛋白对NLRP3的修饰来抑制炎症反应。成纤维细胞生长因子21是反映动脉粥样硬化的一种重要因子。有氧运动不仅可以降低血清中成纤维细胞生长因子21水平,还能减少NLRP3炎症小体介导的焦亡相关标志物在主动脉中的表达。此外,有氧运动还能有效减轻体质量,调节血糖、血脂和炎症水平,为预防和控制动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病提供了新的思路[63-64]。上述研究表明,有氧运动已被证明有利于减缓细胞焦亡的发生,这为预防疾病和维持健康提供了重要的参考。现阶段有氧运动在动物研究中取得了显著进展,但在临床实践中需要进一步验证其有效性。此外,有关无氧运动与细胞焦亡之间尚缺乏足够的研究数据支撑,若进一步探讨无氧运动对细胞焦亡的影响,可对运动调节细胞焦亡促进健康的机制进行更完整的阐述。运动对细胞焦亡的影响见表2。"
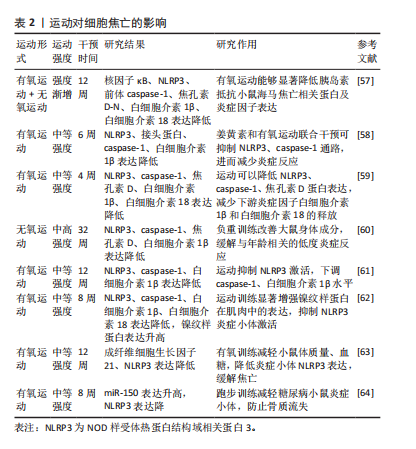

有氧运动调控细胞焦亡为骨关节炎的预防和诊疗提供更多的靶向治疗方案。先前的研究已表明,有氧运动可通过调节焦亡蛋白的表达抑制细胞焦亡的发生,也可通过调控细胞焦亡的信号通路减少炎症因子的产生。基质金属蛋白酶是参与各种细胞基质的蛋白酶,可促使软骨细胞外基质降解,从而加重骨关节炎的病理进程。SABER等[65]指出,游泳运动能下调骨关节炎大鼠关节内核因子κB、基质金属蛋白酶1及基质金属蛋白酶13等因子的分泌,提示有氧运动通过抑制细胞焦亡发生减少炎症因子的表达,进而缓解骨关节炎。另有研究通过对比低、中、高强度有氧运动发现,中等强度运动组软骨细胞死亡、软骨破坏严重程度显著降低,中等强度运动通过下调嘌呤能离子通道型受体7抑制软骨细胞自噬,保护关节软骨[66]。此外,负荷递增的有氧运动使大鼠滑膜中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶13含量减少,软骨保护性标志物白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和润滑素表达增加,提示中等强度有氧运动干预骨关节炎的效果优于低等强度有氧运动,中等强度有氧运动能够对滑膜和软骨产生最佳保护作用[67],与SHEN等[68]、WANG等[69]研究结果相同。由此可见,中等强度有氧运动治疗骨关节炎的效果最佳。 运动因子是机体在运动过程中产生的代谢产物,在调节代谢和改善炎症反应方面发挥重要作用。新型脂肪肌因子镍纹样蛋白在骨关节炎软骨细胞中发挥其抗炎作用,同时伴有Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达的恢复,通过抑制NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD级联反应来改善软骨细胞焦亡。中等强度运动会增加镍纹样蛋白的释放,从而抑制核因子κB 和NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD 联级反应,改善炎症和细胞焦亡[70]。鸢尾素是另一种在运动过程中产生的肌因子。JIA等[71]的研究发现,相较于低、高强度跑步运动,中等强度跑步运动通过增加鸢尾素水平改善大鼠骨关节炎的效果最为显著,鸢尾素通过抑制核因子κB通路来减弱NLRP3/caspase-1的表达,从而改善软骨细胞的焦亡。上述研究提示,中等强度有氧运动改善骨关节炎的效果最佳。但目前关于不同运动类型、运动强度及运动时间调节细胞焦亡影响骨关节炎的影响的研究尚少,若对此进行深入研究,可为运动调控细胞焦亡促进机体健康提供更科学的理论支持。运动介导细胞焦亡调控骨关节炎的研究总结,见表3。"

| [1] CHEN X, TANG H, LIN J, et al. Temporal trends in the disease burden of osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019, and projections until 2030. PLoS One. 2023;18(7):e0288561. [2] XIA B, DI CHEN, ZHANG J, et al. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: a review of molecular mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;95(6):495-505. [3] LUBBERS R, VAN SCHAARENBURG RA, KWEKKEBOOM JC, et al. Complement component C1q is produced by isolated articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):675-684. [4] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257. [5] 杨小瑞,曹林忠,胡康一,等.细胞焦亡在骨代谢异常疾病中的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(1):124-128. [6] LOVELESS R, BLOOMQUIST R, TENG Y. Pyroptosis at the forefront of anticancer immunity. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 2021;40(1):264. [7] 陈翔,汪萍萍.透骨消痛胶囊抑制大鼠骨性关节炎作用研究[J].药物评价研究,2020,43(1):61-65. [8] ZYCHLINSKY A, PREVOST MC, SANSONETTI PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992;358(6382):167-169. [9] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114. [10] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526(7575): 660-675. [11] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death:recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541. [12] RUSSO AJ, BEHL B, BANERJEE I, et al. Emerging Insights into Noncanonical Inflammasome Recognition of Microbes. J Mol Biol. 2018;430(2):207-216. [13] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19: 477-489. [14] MAN SM, KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;277:61-75. [15] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 2014;514(7521):187-192. [16] KAYAGAKI N, WARMING S, LAMKANFI M, et al. Non canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature. 2011;479:117-121. [17] PLATNICH JM, MURUVE DA. NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: a review of their canonical and non canonical signaling pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019;670:4-14. [18] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:5463-5469. [19] MCALLISTER MJ, CHEMALY M, EAKIN AJ, et al. NLRP3 as a potentially novel biomarker for the management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2018;26:612-619. [20] 刘格格.豆腐果苷抑制NLRP3炎症小体改善大鼠骨关节炎炎症和疼痛反应[D].芜湖:皖南医学院,2023. [21] PAN D, YIN P, LI L, et al. Holomycin, a novel NLRP3 inhibitor,attenuates cartilage degeneration and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023;657:59-68. [22] 蔡猛,张永宁.三七总皂苷调控TLR4/NLRP3/Caspase-1信号通路对骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞焦亡的影响[J].中医药信息,2023,40(2):11-17. [23] 龚明,邱波.Caspase-1与骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中国医药导报, 2016,13(20):30-33. [24] 李艳艳,冯亚平,柯金,等.NLRP3和Caspase-1在颞下颌关节骨关节炎滑膜中的表达[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,31(2):81-84. [25] XIAO Y, DING L, YIN S, et al. Relationship between the pyroptosis of fibroblast‑like synoviocytes and HMGB1 secretion in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):97-107. [26] CLEMENTS KM, PRICE JS, CHAMBERS MG, et al. Gene deletion of either interleukin-1beta, interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme, inducible nitric oxide synthase,or stromelysin 1 accelerates the development of knee osteoarthritis in mice after surgical transection of the medial collateral ligament and partial medial meniscectomy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(12):3452-3463. [27] 齐曼曼,王旭鹏,郑维朝,等.Caspase-1选择性抑制剂VX-765在大鼠急性肾损伤相关性肺损伤中的作用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2021, 37(6):629-634. [28] LI G, XIU L, LI X, et al. miR-155 inhibits chondrocyte pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis by targeting SMAD2 and inhibiting the NLRP3/Caspase-1pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):48-59. [29] 史纪元,姬乐,武世勋,等.淫羊藿苷通过抑制NLRP3炎性小体和Caspase-1通路减轻骨关节炎[J].世界中医药,2021,16(18): 2706-2713. [30] AN S, HU H, LI Y, et al. Pyroptosis Plays a Role in Osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1146-1157. [31] 夏雪,沈霖,凌家艳,等.加味阳和汤治疗寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎的疗效及对炎症因子的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2024,32(3): 55-58. [32] 林绪超,何文.LncRNA SNHG3/miR-423-5p对IL-1β诱导的骨关节炎软骨细胞损伤的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2023,45(9): 1312-1319. [33] 刘娉娉,周珺贤,徐健华,等.血清IL-18与膝骨关节炎关节结构改变相关性研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2023,58(11):1819-1823. [34] WASZCZYKOWSKI M, FABIŚ-STROBIN A, BEDNARSKI I, et al. Serum and synovial fluid concentrations of interleukin-18 and interleukin-20 in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee and their correlation with other markers of inflammation and turnover of joint cartilage. Arch Med Sci. 2020;18(2):448-458. [35] 李龙,刘君伟,王铎,等.温针灸对兔膝骨关节炎软骨组织中NLRP3、IL-1β和IL-18表达的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2023,45(1): 85-91. [36] 吴培刚,杨学栋,曹振昊,等.新型蛋白酶体抑制剂膝关腔内注射对兔骨关节炎的治疗作用及其机制[J]. 山东医药,2020,60(12):46-49. [37] 李金磊,殷红,刘维统,等.灯盏花素对大鼠膝骨关节炎膝关节软骨的影响[J].云南中医药大学学报,2023,46(3):76-81. [38] 邹怡,潘良,蔡素芬,等.温针灸联合塞来昔布胶囊对膝骨关节炎患者骨代谢指标和血清IL-6、IL-17、IL-18水平的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2022,22(6):1074-1078. [39] GUO Q, JIN Y, CHEN X, et al. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications.Signal Transduct Tar. 2024; 9(1):53-105. [40] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Tar. 2023;8(1): 56-86.
[41] 李亦丞.基于NF-κB及OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路探究青蒿琥酯对骨关节炎的作用及机制[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2020. [42] 张锐,马继海,柴喜平,等.独活寄生汤对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠NF-κB通路关键分子表达的影响[J]. 西部中医药,2023,36(8):15-19. [43] HU J, ZHOU J, WU J, et al. Loganin ameliorates cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis development in an osteoarthritis mouse model through inhibition of NF-κB activity and pyroptosis in chondrocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;247:112-261. [44] YU H, YAO S, ZHOU C, et al. Morroniside attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritic development by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Ethnopharmacol. 2021;266:113447. [45] LI Z, HUANG Z, BAI L. The P2X7 Receptor in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:628330. [46] LI Z, HUANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. P2X7 Receptor Induces Pyroptotic Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritis via NF-κB/NLRP3 Crosstalk. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8868361. [47] MO L, JIANG B, MEI T, et al. Exercise Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(5):23259671231172773. [48] CHEUNG C, WYMAN JF, PEDEN-MCALPINE C. Long-Term Yoga and Aerobic/Strength Exercise Adherence in Older Women with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Mixed Methods Approach. Int J Yoga Therap. 2022;32(2022): Article 4. doi: 10.17761/2022-D-20-00033. [49] OKA Y, MURATA K, OZONE K, et al. Treadmill Exercise after Controlled Abnormal Joint Movement Inhibits Cartilage Degeneration and Synovitis. Life (Basel). 2021;11(4):303-315. [50] SO BCL, KWOK MMY, LEE NWL, et al. Lower Limb Muscles’ Activation during Ascending and Descending a Single Step-Up Movement: Comparison between In water and On land Exercise at Different Step Cadences in Young Injury-Free Adults. Healthcare (Basel). 2023; 11(3):441. [51] 黄晓倩.水中运动对膝关节骨性关节炎超重女性的运动效益研究[D].长春:吉林体育学院,2023. [52] WANG X, SONG J, XIA P, et al. High intensity interval training attenuates osteoarthritis- associated hyperalgesia in rats. J Physiol Sci. 2023;73(1):8-17. [53] TARANTINO D, THEYSMANS T, MOTTOLA R, et al. High-Intensity Training for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Narrative Review. Sports (Basel). 2023;11(4):91-112. [54] MESSIER SP, MIHALKO SL, BEAVERS DP, et al. Effect of High-Intensity Strength Training on Knee Pain and Knee Joint Compressive Forces Among Adults With Knee Osteoarthritis: The START Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2021;325(7):646-657. [55] BABUR MN, SIDDIQI FA, TASSADAQ N, et al. Effects of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate supplementation in addition to resistance exercise training and manual therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. J Pak Med Assoc. 2022;72(7):1272-1277. [56] MARRIOTT KA, HALL M, MACIUKIEWICZ JM, et al. Are the Effects of Resistance Exercise on Pain and Function in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis Dependent on Exercise Volume, Duration and Adherence? Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. doi:10.1002/acr.25313 [57] 卞学鹏,姬瑞方,刘蓓蓓,等.有氧运动降低胰岛素抵抗小鼠海马细胞焦亡相关蛋白及炎症因子的表达 [J].生理学报,2020,72(4): 455-462. [58] 毛永强,周绮云,张馨月,等.姜黄素和/或有氧运动改善高脂血症大鼠心肌细胞焦亡的作用机制[J].食品工业科技,2022,43(2): 384-389. [59] 张美.基于Caspase-1依赖的经典焦亡途径探讨运动预处理对大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤的脑保护作用[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2023. [60] FU P, GONG L, YANG L, et al. Weight bearing training alleviates muscle atrophy and pyroptosis of middle- aged rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1202686. [61] YANG W, LIU L, WEI Y, et al. Exercise suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice with diet-induced NASH: a plausible role of adropin. Lab Invest. 2021;101(3):369-380. [62] JAVAID HMA, SAHAR NE, ZHUGE DL, et al. Exercise Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Obese Mice via the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Meteorin-like. Cells. 2021;10(12):3480-3493. [63] LI XH, LIU LZ, CHEN L, et al. Aerobic exercise regulates FGF21 and NLRP3 inflammasome - mediated pyroptosis and inhibits atherosclerosis in mice. PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0273527. [64] BEHERA J, ISON J, VOOR MJ, et al. Exercise-Linked Skeletal Irisin Ameliorates Diabetes- Associated Osteoporosis by Inhibiting the Oxidative Damage-Dependent miR-150-FNDC5/ Pyroptosis Axis. Diabetes. 2022;71(12):2777-2792. [65] SABER MM, MAHMOUD MM, AMIN HM, et al. Therapeutic effects of combining curcumin and swimming in osteoarthritis using a rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 2023;166:115309. [66] LI Z, HUANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Moderate-intensity exercise alleviates pyroptosis by promoting autophagy in osteoarthritis via the P2X7/AMPK/mTOR axis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):346-364. [67] CASTROGIOVANNI P, DI ROSA M, RAVALLI S, et al. Moderate Physical Activity as a Prevention Method for Knee Osteoarthritis and the Role of Synoviocytes as Biological Key. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):511-528. [68] SHEN P, JIA S, WANG Y, Et al. Mechanical stress protects against chondrocyte pyroptosis through lipoxin A4 via synovial macrophage M2 subtype polarization in an osteoarthritis model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113361. [69] WANG Y, JIN Z, JIA S, et al. Mechanical stress protects against chondrocyte pyroptosis through TGF-β1-mediated activation of Smad2/3 and inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in an osteoarthritis model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;159:114216. [70] LIU J, JIA S, YANG Y, et al. Exercise induced meteorin-like protects chondrocytes against inflammation and pyroptosis in osteoarthritis by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;158:114118. [71] JIA S, YANG Y, BAI Y, et al. Mechanical Stimulation Protects Against Chondrocyte Pyroptosis Through Irisin- Induced Suppression of PI3K/Akt/NF -κB Signal Pathway in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:797855. |
| [1] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [2] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [4] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [5] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [6] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [7] | Sun Yaotian, Xu Kai, Wang Peiyun. Potential mechanisms by which exercise regulates iron metabolism in immune inflammatory diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
| [8] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [9] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [10] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [11] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [12] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [13] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [14] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [15] | Jiang Yang, Peng Hao, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Song Yueyu, Yin Xingxiao, Li Yanqi, Chen Qigang. Isometric exercise reduces resting blood pressure: a meta-analysis of moderating factors and dose effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 975-986. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||