Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 1523-1530.doi: 10.12307/2025.029
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Cao Yue1, Ye Xinjian1, 2, Li Biyao1, Zhang Yining1, Feng Jianying1
- 1School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, Zhejiang Province, China; 2Stomatology Hospital, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Clinical Research Center for Oral Disease of Zhejiang Province, Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedical Research of Zhejiang Province, Cancer Center of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310006, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-13Accepted:2024-02-18Online:2025-03-08Published:2024-06-28 -
Contact:Feng Jianying, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Cao Yue, School of Stomatology, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou 310053, Zhejiang Province, China -
Supported by:Zhejiang University Students’ Science and Technology Innovation Program (New Talent Program), No. 2023R410033 (to CY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
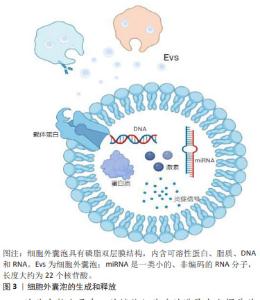
2.1 细胞外囊泡在口腔鳞状细胞癌诊断和预后中的应用 在早期阶段诊断的口腔鳞状细胞癌通常具有更好的预后效果,并且治疗干预的需求相对较低。然而,一项长期观察性研究显示,多数口腔鳞状细胞癌患者在疾病晚期才得到确诊[11],因此,提高口腔鳞状细胞癌的早期诊断准确率对于改善治疗效果和预后至关重要[12]。在寻找早期诊断方法的过程中,细胞外囊泡的研究提供了新的视角。细胞外囊泡是由细胞产生并释放的微小囊泡结构,其外层被脂质双层包裹,这些囊泡在细胞间通讯中扮演着重要角色,通过传递蛋白质、脂质及核酸等分子信息,调控其他细胞的行为[13]。特别是在口腔鳞状细胞癌中,细胞外囊泡可能承担类似于旁分泌的角色,通过从癌细胞向周围微环境释放信号分子(如miRNAs及蛋白质等),影响相邻细胞的行为和特性,促进肿瘤的生长和扩散。同时,细胞外囊泡也有可能通过类似于内分泌的机制在体内传播,通过血液或其他生物流体到达远处的组织,影响肿瘤的远处转移和整体病理过程。故而,在口腔鳞状细胞癌唾液活检中,细胞外囊泡的检测不仅有助于理解肿瘤的局部微环境变化,也可能提供有关肿瘤全身性影响的信息[14]。它们参与肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭以及与免疫系统的相互作用[15],影响肿瘤的进展和治疗反应[16]。因此,深入理解细胞外囊泡在口腔鳞状细胞癌发展中的作用,尤其是它们在唾液活检中的潜在应用,可能为早期诊断提供新的生物标志物和治疗靶点[17]。 2.1.1 细胞外囊泡作为口腔鳞状细胞癌生物标志物的潜力 细胞间的信号传递是维持组织健康和功能的关键机制,它不仅保证了组织的稳定性,而且在肿瘤的扩散与发展中起到了重要作用。因此,全面理解口腔鳞状细胞癌中细胞间通讯的信号介质对其诊断和预后具有重要价值[18]。细胞间的信号传导可能涉及细胞外囊泡的释放和摄取,而细胞外囊泡携带了多种类型的生物分子,包括可溶性蛋白(如细胞因子、趋化因子、炎症信号递质[19]、激素)、脂质、DNA和RNA,见图3。"
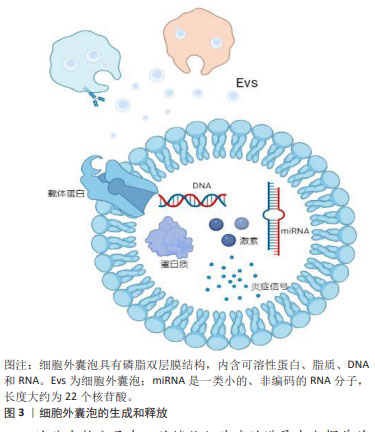
这些生物分子在口腔鳞状细胞癌的进展中发挥着关键作用,尤其是在细胞增殖、凋亡、DNA修复、代谢、血管生成和免疫反应等多个生物过程中[20]。近期研究,例如PANVONGSA等[21]的工作,显示含有EV-miRNA的液体活检(例如血液和唾液样本)在口腔鳞状细胞癌的早期筛查和诊断中表现出色。特别值得注意的是,在口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的血浆中,可以检测到大量的致癌性miRNA(如miR-21和miR-27),这一发现大幅提高了口腔鳞状细胞癌早期诊断的可行性[22]。除此之外,细胞外囊泡中的其他生物标志物,如特定蛋白质,已被证明是唾液中的稳定且具有特异性的生物标志物来源,这些标志物有望提高液体活检的敏感性[23]。采用SWATH-MS 技术对细胞外囊泡中的蛋白质组成进行定量分析显示,细胞外囊泡富含多种特定蛋白质,其中一些蛋白质(如S100蛋白和LCN2)被认为是肿瘤诊断和预后的关键生物标志物[18–21]。 2.1.2 口腔鳞状细胞癌唾液活检中的细胞外囊泡携带的miRNA可作为诊断标志物 miRNAs是细胞外囊泡中常见的遗传物质[27],它们是长度约为22个核苷酸的非编码RNA小分子,充当编码基因的调控员。miRNA的表达具有组织特异性,其表达变化在不同组织中与疾病状态紧密相关,它们能够通过与mRNA的互补配对来调节mRNA的翻译或降解,从而影响基因表达。miRNA可以通过细胞外囊泡传输或与蛋白质结合形成蛋白质-miRNA复合物。在细胞外囊泡中的miRNA释放后更为稳定,不易被酶降解,因此,它们具有成为癌症诊断和预后的新型生物标志物的潜力[28]。在口腔鳞状细胞癌中,上调的miRNAs通过靶向肿瘤抑制基因来促进肿瘤的发生,被称为肿瘤促进miRNAs(OncomiRs),而下调的miRNAs则被视为肿瘤抑制miRNAs(TSmiRs)[29],文章总结了与口腔鳞状细胞癌诊断和预后相关的miRNA生物标记物[29-33],见表1。"
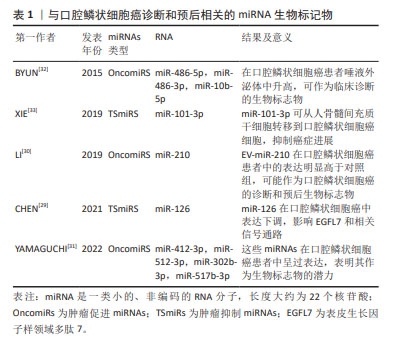
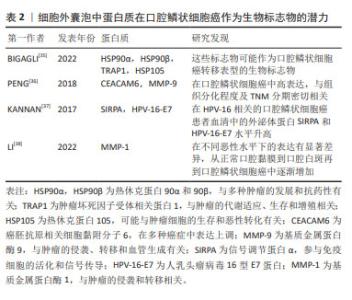
表1可见,不同研究对口腔鳞状细胞癌中miRNAs的角色进行了深入探讨,强调了它们在诊断和治疗中的潜在价值。在口腔鳞状细胞癌的病理机制中,miRNAs扮演着关键角色。不同的miRNAs在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的表达模式与疾病的发展和进展密切相关,为早期诊断和治疗提供了新的可能性。特别是在细胞外囊泡miRNAs的研究中,它们在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的高表达或低表达模式揭示了潜在的生物标志物的角色。这些miRNAs不仅有助于揭示肿瘤的生物学特征,而且可能指导未来的治疗策略。例如,高表达的miRNAs可能促进肿瘤的发展和侵袭性,而低表达的miRNAs则可能指示肿瘤抑制过程的激活。此外,这些研究也凸显了miRNAs在肿瘤微环境中的作用,特别是它们如何通过影响血管生成、细胞增殖和迁移等关键生物学过程来调控肿瘤的行为。通过细胞外囊泡介导的miRNA转移,特别是在抑制口腔鳞状细胞癌进展中显示出了重要的治疗潜力。 总之,miRNAs在口腔鳞状细胞癌的生物学研究中提供了新的视角,不仅在疾病的生物标志物研究中占据重要地位,也为开发新的治疗方法提供了基础。未来的研究将进一步阐明这些小分子在肿瘤生物学中的复杂角色,为口腔鳞状细胞癌的管理和治疗提供新的策略。 2.1.3 口腔鳞状细胞癌唾液活检中的细胞外囊泡携带的蛋白质可作为诊断标志物 在讨论口腔鳞状细胞癌的生物标志物时,除了miRNAs外,细胞外囊泡中的蛋白质也显示出极大的潜力。这些蛋白质,尽管在体液中存在某些局限性,例如易受蛋白酶降解且特异性相对较差[34],但细胞外囊泡提供了一个独特的解决方案。细胞外囊泡中的膜蛋白不仅帮助识别囊泡的类型和来源,而且还能保护囊泡内的蛋白质不被分解,从而提高它们作为生物标志物的稳定性和准确性。在这方面,已有研究发现了多种蛋白质在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的潜在应用,见表2。"
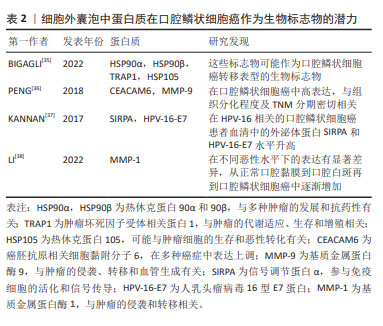
在口腔鳞状细胞癌的研究中,细胞外囊泡内的蛋白质作为生物标志物,展示了提高稳定性和特异性的独特优势,为口腔鳞状细胞癌的诊断和治疗提供了新的分子层面的见解。 关键的发现包括HSP90α及HSP90β等蛋白质与口腔鳞状细胞癌转移表型的潜在联系,以及CEACAM6和MMP-9的高表达可能反映了口腔鳞状细胞癌的组织分化程度和临床分期,这些发现不仅揭示了细胞外囊泡蛋白质在诊断口腔鳞状细胞癌中的作用,而且凸显了它们在疾病进展和临床治疗中的应用潜力。此外,细胞外囊泡中蛋白质的变化模式也为理解口腔鳞状细胞癌的分子机制提供了新视角。例如,基质金属蛋白酶1的逐渐增加反映了从正常口腔粘膜到口腔鳞状细胞癌的病理转变,这可能有助于早期诊断和监测疾病的进展。 总体而言,这些研究结果不仅增强了研究者们对口腔鳞状细胞癌分子生物学的认识,而且为开发更有效的诊断工具和治疗策略提供了重要的线索。未来的研究应进一步探索细胞外囊泡蛋白质在口腔鳞状细胞癌及其他肿瘤中的作用机制及其临床应用价值。 2.1.4 细胞外囊泡干预口腔鳞状细胞癌的疾病进程与预后 在口腔鳞状细胞癌疾病发展进程与预后上,及时的进程跟踪以及预后的复发或局部复发、远处转移等问题是口腔鳞状细胞癌诊疗的主要挑战,而细胞外囊泡及其内含的丰富的生物活性物质则为临床上提供了患者定期随访的检测指标,在口腔鳞状细胞癌进程与预后监测中发挥着显著作用[39],这一发现对于定期评估患者病情并制定相应治疗策略尤为重要。由于口腔鳞状细胞癌的高死亡率主要与疾病的复发和淋巴结转移相关,因此,对这些生物标志物的研究和应用,对于改善患者的生存率和生活质量具有深远意义。淋巴结转移可能会增加远处转移的可能性,并对总生存率产生负面影响[6]。肿瘤细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡通过诱导血管生成和淋巴管生成促进了向前哨淋巴结的转移,这与肿瘤分泌的细胞外囊泡在远端转移之前形成龛位的作用相符[40]。WANG等[41]通过对口腔鳞状细胞癌患者术后引流液中的细胞外囊泡研究发现,转移性口腔鳞状细胞癌患者(LN+组)的EHD2(EH结构域蛋白2)和CAVIN1(腔蛋白1)这2个代谢蛋白的表达在LN+组和LN-组之间存在显著差异,结果显示术后引流液中的EHD2和CAVIN1水平可能与口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的淋巴结转移有关。在一项研究中,科学家们探讨了血清中外泌体的蛋白质含量作为局部区域癌症传播,尤其是淋巴结转移的潜在指标[42]。在这项研究中,来自3组受试者(每组10例)的血清外泌体被分离出来进行分析:其中一组(口腔鳞状细胞癌)伴有淋巴结转移,一组(口腔鳞状细胞癌)无淋巴结转移,以及一组健康对照,采用液相色谱-质谱联用技术进行蛋白质组学分析,在所识别的415种蛋白质中,与健康对照组和无淋巴结转移的口腔鳞状细胞癌组相比,有淋巴结转移的口腔鳞状细胞癌组分别显示了37种和28种蛋白质的差异表达。结合组织、血清和全血样本的qPCR验证结果,研究者发现,血清外泌体中的某些蛋白质,如血小板因子4变异1 (PF4V1)、CXC趋化因子7 (CXCL7)、凝血因子Ⅷ亚单位A1 (F13A1)和载脂蛋白A1(ApoA1),可能与口腔鳞状细胞癌的淋巴结转移有关,表明这些蛋白质具有作为口腔鳞状细胞癌淋巴结转移的新型预测性生物标志物的潜力。 在口腔鳞状细胞癌的管理中,追踪疾病进展、预测复发和转移是主要挑战。细胞外囊泡及其携带的生物活性物质在监测口腔鳞状细胞癌进程和预后方面显示出显著潜力,特别是在评估淋巴结转移和总生存率方面。最新研究发现,细胞外囊泡中的特定蛋白质,如EHD2和CAVIN1,以及血清外泌体中的蛋白质,如PF4V1,CXCL7,F13A1和ApoA1,可能作为口腔鳞状细胞癌淋巴结转移的新型预测性生物标志物。这些发现为改善口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的诊断、治疗和生存率提供了重要信息。 2.2 细胞外囊泡在口腔鳞状细胞癌治疗中的应用 手术配合化疗是口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的主要和效果显著的治疗手段。然而,除了化疗在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的常见耐药性外[43],化疗药物还可能导致一些严重不良反应,包括骨髓抑制[44]、肾毒性、胃肠道不适、皮肤和舌头病变以及明显的体质量下降[45],因此,寻找替代治疗方案变得重要。来自其他细胞的细胞外囊泡可通过旁分泌机制调节一些病理生理过程,如巨噬细胞极化、血管生成和上皮间质转换来抑制口腔鳞状细胞癌的进展[46]。 2.2.1 自然来源的细胞外囊泡:利与弊的双重角色 间充质干细胞具有抑制或促进免疫反应的能力[47],可用于癌症治疗[48]。来自人类脱落乳牙(SHED)的外泌体能够减缓口腔鳞状细胞癌中的血管生成。异种移植模型显示,携带miR-100-5p和miR-1246的脱落乳牙外泌体能够抑制血管生成[49]。然而,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体被视为双刃剑,因为它也可能促进肿瘤的进展,为解决这个问题需要进行更多的研究。在口腔鳞状细胞癌的抗耐药性研究中,外泌体介导的miR-30a能通过调节Beclin1和Bcl2,诱导顺铂耐药的癌细胞的凋亡和自噬过程[50],这一发现提供了证据,支持某些外泌体miRNA可以提高口腔鳞状细胞癌患者整体存活率的观点[51]。此外,XIE等[33]在研究口腔癌时发现,富含miR-101-3p的人骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体能有效调节MMP2水平,从而在体外和体内抑制口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞的迁移和侵袭,为口腔癌的治疗提供了新的理论依据。在肿瘤生物学的研究领域,miR-21,PTEN和PD-L1构成的调控轴是肿瘤发展和免疫逃避机制的关键。miR-21的上调表达,导致PTEN的活性抑制,激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,促进肿瘤细胞增殖和生存,同时降低其对程序性细胞死亡信号的敏感性。此外,PTEN的失活还进一步导致细胞表面PD-L1的表达上调,增强肿瘤细胞通过与PD-1受体互作来逃避免疫系统监控的能力。因此,miR-21/PTEN/PD-L1轴在调控肿瘤细胞的生物学行为、免疫逃避机制及对肿瘤治疗策略的反应性方面发挥着至关重要的作用。而LI等[52]的研究进一步证实,在肿瘤微环境中,氧气压力会因肿瘤生长而发生变化,进而影响肿瘤衍生的细胞外囊泡含量,以miR-21/PTEN/PD-L1轴依赖的方式调节髓源性抑制细胞(MDSC)的功能,协调口腔鳞状细胞癌中抗肿瘤和促肿瘤γδt细胞之间的平衡。同样的,自然衍生的细胞外囊泡被认为具有双面性,因为它们也有可能促使肿瘤的发展,为应对此问题,必须进行更深入的研究探索。 2.2.2 工程化细胞外囊泡:作为口腔鳞状细胞癌靶向治疗的补充 细胞外囊泡因其生物安全性、稳定性和目标特异性被认为是肿瘤治疗的理想药物载体,代表着新一代的纳米级药物输送系统[29,32]。近期研究充分证明了细胞外囊泡的工程化能够提高药物递送效率,从而提高口腔鳞状细胞癌患者的治理效果[54-55]。“细胞外囊泡工程化”指在合适条件下使用特定技术对纯化的细胞外囊泡表面蛋白或内容进行修饰,主要分为物理和化学两种改变[56]。目前可用的物理手段包括脂质体膜融合和细胞外囊泡含量加 载[57];化学修饰主要涉及细胞外囊泡表面的转变,可分为共价和非共价修饰。共价修饰可以通过涉及细胞外囊泡和特定分子或化学连接物的化学反应来完成,非共价修饰可以在适当的温和条件下通过电-静态相互作用和脂质融合来完成[58]。通过工程化处理,可以提高细胞外囊泡在肿瘤靶向治疗和药物递送效率方面的能力[59]。文章总结了工程化细胞外囊泡提高肿瘤靶向治疗和药物递送效率方面的能力[60-63],见表3。"
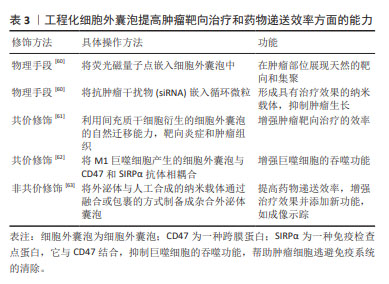
| [1] 钟来平.口腔鳞状细胞癌临床诊治的规范化和个体化:机遇与挑战[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(5):484-488. [2] WANG L, WEI Y, YAN Y, et al. CircDOCK1 suppresses cell apoptosis via inhibition of miR‑196a‑5p by targeting BIRC3 in OSCC. Oncol Rep. 2018; 39(3):951-966. [3] 董云梅,陶艳,周瑜.口腔黏膜癌变过程中血清生化标志物的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(1):43-50. [4] YU D, LI Y, WANG M, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):56. [5] LI S, MAN Q, GAO X, et al. Tissue‐derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non‐cancer diseases: present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175. [6] ZHANG Y, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous cell carcinoma: current progress and future prospect. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1149662. [7] 赵鹏程,陈莹,刘婷姣,等.细胞外囊泡miRNA在口腔鳞癌中的研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2021,35(3):200-203. [8] LU Y, ZHENG Z, YUAN Y, et al. The emerging role of exosomes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;22:9:628103. [9] ABAK A, ABHARI A, RAHIMZADEH S. Exosomes in cancer: small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics. Peer J. 2018;6:e4763. [10] ALMERIA C, WEISS R, ROY M, et al. Hypoxia conditioned mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles induce increased vascular tube formation in vitro. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;23:7:292. [11] SEOANE-ROMERO JM, VAZQUEZ-MAHIA I, SEOANE J, et al. Factors related to late stage diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012:e35-e40. [12] 蒋宇磊,夏斌,饶南荃,等.外泌体在口腔鳞状细胞癌恶性进展及诊疗应用的研究[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(6):711-717. [13] 毛露珈,史恩宇,王瀚平,等.细菌外膜囊泡在抗肿瘤治疗方面的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(5):100-105. [14] STADLER ZK,THOM P, ROBSON ME, et al. Genome-wide association studies of cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010;28(27): 4255-4267. [15] AHMADI M, ABBASI R, REZAIE J. Tumor immune escape: extracellular vesicles roles and therapeutics application. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22(1):9. [16] 肖博林,张伟,陈刚.细胞外囊泡与口腔肿瘤免疫[J].口腔医学, 2023,43(9):769-774. [17] 吴若怡,王晓宁,翟培淞,等.上皮癌来源细胞外囊泡亚群蛋白质谱分析[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2023,21(4):326-331. [18] GONDALIYA P. Extracellular vesicle RNA signaling in the liver tumor microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2023;558:216089. [19] LI R, ZHOU Y, ZHANG M, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived EVs promote tumor progression by regulating inflammatory cytokines and the IL-17A-induced signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;118:110094. [20] 廖立,田卫东.间充质干细胞来源胞外囊泡在牙及颌面部组织再生中的研究与展望[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2022,40(1):7-13. [21] PANVONGSA W, PEGTEL DM,VOORTMAN J. More than a bubble: extracellular vesicle microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers. 2022;14(5):1160. [22] MOMEN-HERAVI F, BALA S. Extracellular vesicles in oral squamous carcinoma carry oncogenic miRNA profile and reprogram monocytes via NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget. 2018;9(78):34838-34854. [23] KACZOR-URBANOWICZ KE, MARTIN CARRERAS-PRESAS C, ARO K, et al. Saliva diagnostics - Current views and directions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(5):459-472. [24] RAHIMI S, ROUSHANDEH AM, AHMADZADEH E, et al. Implication and role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in cancer: lipocalin-2 as a potential novel emerging comprehensive therapeutic target for a variety of cancer types. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(3):2327-2346. [25] ARGYRIS PP, SLAMA Z M, ROSS KF, et al. Calprotectin and the Initiation and Progression of Head and Neck Cancer. J Dent Res. 2018;97(6):674-682. [26] RAIMONDI L, DE LUCA A, AMODIO N, et al. Involvement of multiple myeloma cell-derived exosomes in osteoclast differentiation. Oncotarget. 2015;6(15):13772-13789. [27] 张秀丽,武曦,李昀生.干细胞源性细胞外囊泡在牙周再生治疗中的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2022,51(7):1216-1219. [28] CAVALLARI C, CAMUSSI G, BRIZZI MF. Extracellular vesicles in the tumour microenvironment:eclectic supervisors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(18):6768. [29] CHEN CM, CHU TH, CHOU CC, et al. Exosome-derived microRNAs in oral squamous cell carcinomas impact disease prognosis. Oral Oncol. 2021;120:105402. [30] LI W, HAN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Oral mucosal mesenchymal stem cell‑derived exosomes: a potential therapeutic target in oral premalignant lesions. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(5):1567-1578. [31] YAMAGUCHI K, YAMAMOTO T, CHIKUDA J, et al. Impact of non-coding RNAs on chemotherapeutic resistance in oral cancer. Biomolecules. 2022;12(2):284. [32] BYUN JS, HONG SH, CHOI JK, et al. Diagnostic profiling of salivary exosomal microRNAs in oral lichen planus patients. Oral Dis. 2015; 21(8):987-993. [33] XIE C, DU LY, GUO F, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-101-3p-overexpressing human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress oral cancer cell proliferation, invasion,and migration. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;458(1-2):11-26. [34] CRISTALDI M, MAUCERI R, DI FEDE O, et al. Salivary biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and follow-up: current status and perspectives. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1476. [35] BIGAGLI E, LOCATELLO LG, DI STADIO A, et al. Extracellular vesicles miR‐210 as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and survival prediction of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022; 51(4):350-357. [36] PENG Q, ZHANG J, ZHOU G. Differentially circulating exosomal microRNAs expression profiling in oral lichen planus. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(9):2848-2858. [37] KANNAN A, HERTWECK KL, PHILLEY JV, et al. Genetic mutation and exosome signature of human papilloma virus associated oropharyngeal cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):46102. [38] LI S, HAN Y, LU M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-exosome-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 1 participates in oral leukoplakia and carcinogenesis by inducing angiogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022; 51(7):638-648. [39] FENG J, XIAO BL, ZHANG LZ, et al. Simultaneous detection of two extracellular vesicle subpopulations in saliva assisting tumor t staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anal Chem. 2023;95(19):7753-7760. [40] WANG J, MAN QW, FU QY, et al. Preliminary extracellular vesicle profiling in drainage fluid after neck dissection in OSCC. J Dent Res. 2023;102(2):178-186. [41] WANG J, JING J, ZHOU C, et al. Emerging roles of exosomes in oral diseases progression. Int J Oral Sci. 2024;15;16(1):4. [42] LI C, ZHOU Y, LIU J, et al. Potential markers from serum-purified exosomes for detecting oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019;28(10):1668-1681. [43] KANG SH, OH SY, LEE KY, et al. Differential effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles on cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-876-3p. Theranostics. 2024;14(2): 460-479. [44] 黄霞,魏津钿,苏琦,等.干细胞源性细胞外囊泡经RANKL/RANK/OPG通路促进牙槽骨成骨的研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2023, 33(20):60-64. [45] HUANG Z, ZHANG Q, WANG Y, et al. Inhibition of caspase-3-mediated GSDME-derived pyroptosis aids in noncancerous tissue protection of squamous cell carcinoma patients during cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(12):4287-4307. [46] SASABE E, TOMOMURA A, LIU H, et al. Epidermal growth factor/epidermal growth factor receptor signaling blockage inhibits tumor cell-derived exosome uptake by oral squamous cell carcinoma through macropinocytosis. Cancer Sci. 2022;113(2):609-621. [47] LUO H, BIRJANDI AA, REN F, et al. Advances in oral mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in health and disease. Genes Dis. 2024;11(1):346-357. [48] LIANG W, CHEN X, ZHANG S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as a double-edged sword in tumor growth:focusing on MSC-derived cytokines. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021;26(1):3. [49] LIU T, CHEN G, SUN D, et al. Exosomes containing miR-21 transfer the characteristic of cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN and PDCD4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2017;49(9): 808-816. [50] KULKARNI B, GONDALIYA P, KIRAVE P, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of miR-30a sensitize cisplatin-resistant variant of oral squamous carcinoma cells via modulating Beclin1 and Bcl2. Oncotarget. 2020; 11(20):1832-1845. [51] XIE Q, HAO Y, LI N, et al. Cellular uptake of engineered extracellular vesicles:biomechanisms,engineered strategies, and disease treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(2):e2302280. [52] LI L, CAO B, LIANG X, et al. Microenvironmental oxygen pressure orchestrates an anti- and pro-tumoral γδ T cell equilibrium via tumor-derived exosomes. Oncogene. 2019;38(15):2830-2843. [53] ZHANG F,GUO J,ZHANG Z, et al. Application of engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted tumor therapy. J Biomed Sci. 2022;29(1):14. [54] DE ABREU RC, FERNANDES H, DA COSTA MARTINS PA, et al. Native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for cardiovascular therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(11):685-697. [55] LI S, XU J, QIAN J, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy:recent advances and challenges in clinical translation. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(24):6978-6991. [56] KUČUK N, PRIMOŽIČ M, KNEZ Ž, et al. Exosomes engineering and their roles as therapy delivery tools, therapeutic targets, and biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9543. [57] SUN J, WANG X, DING Y, et al. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic landscape of salivary extracellular vesicles to assess OSCC therapeutical outcomes. Proteomics. 2023;23(5):e2200319. [58] YASUI T, YANAGIDA T, ITO S, et al. Unveiling massive numbers of cancer-related urinary-microRNA candidates via nanowires. Sci Adv. 2017;3(12):e1701133. [59] 雷可昕,白贺天,杨淞月,等.环状RNA与口腔鳞状细胞癌研究进展[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(4):425-430. [60] YU ZL, ZHANG W, ZHAO JY, et al. Development of a dual-modally traceable nanoplatform for cancer theranostics using natural circulating cell-derived microparticles in oral cancer patients. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(40):1703482. [61] LAW ZJ, KHOO XH, LIM PT, et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated chemoresistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2021; 8:629888. [62] NIE W,WU G, ZHANG J, et al. Responsive exosome nano‐bioconjugates for synergistic cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020;59(5): 2018-2022. [63] 芦晓红,赵源,何军.杂合外泌体囊泡作为药物递送载体的研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2023,54(7):1020-1025. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [3] | Weng Zongqin, Zhao Hailong. Mechanism of exosomal miRNA involved in tumor chemotherapy resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1504-1511. |
| [4] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [5] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [6] | Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002. |
| [7] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [8] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [9] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [10] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [11] | Yu Shuangqi, Ding Fan, Wan Song, Chen Wei, Zhang Xuejun, Chen Dong, Li Qiang, Lin Zuoli. Effects of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer/lysine-grafted graphene oxide nanoparticle composite scaffolds on osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 707-712. |
| [12] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [13] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [14] | Guo Jia, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Huang Jing, Shang Wenya, Yang Yike, Liu Huiyao. Action mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in improving spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [15] | Zhou Yang, Liu Kexin, Wang Deli, Sun Zhang. Regenerative effects of engineered extracellular vesicles on repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||