Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 572-578.doi: 10.12307/2025.116
Previous Articles Next Articles
Constructing a model of degenerative scoliosis using finite element method: biomechanical analysis in etiology and treatment
He Kai1, Xing Wenhua2, Liu Shengxiang2, Bai Xianming2, Zhou Chen2, Gao Xu2, Qiao Yu3, He Qiang1, Gao Zhiyu1, Guo Zhen1, Bao Aruhan1, #br# Li Chade1
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; ²Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; ³Hohhoo People’s Hospital, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-12-11Accepted:2024-02-04Online:2025-01-28Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Xing Wenhua, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:He Kai, Master candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Zhiyuan” Talent Program Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. ZY0110016 (to XWH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Kai, Xing Wenhua, Liu Shengxiang, Bai Xianming, Zhou Chen, Gao Xu, Qiao Yu, He Qiang, Gao Zhiyu, Guo Zhen, Bao Aruhan, Li Chade. Constructing a model of degenerative scoliosis using finite element method: biomechanical analysis in etiology and treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 572-578.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
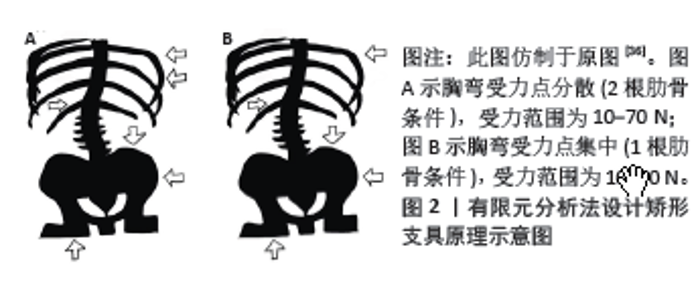
2.1 有限元法在DS病因中的应用 骨质疏松的老年患者在外力的作用下易发生骨折,如老年人因乘坐颠簸车辆发生脊柱压缩性骨折,据此推测颠簸环境产生的振动因素可能是老年人脊柱骨骼变形的病因之一,继而导致DS的发生。XU等[27]有相似的发现,直升飞机驾驶员和卡车司机比普通人更容易患DS和腰疼,他们由此猜测脊柱的循环振动可催化脊柱组织疲劳、椎间盘退变,最终导致脊柱异常畸形。他们通过运用有限元法构建了5例健康人和5例退变性脊柱侧弯受试者的脊柱模型,对最上方椎体的上终板施加轴向、大小40 N、频率范围1-25 Hz的力模拟共振反应,结果显示,5例健康人在纵向、横向、前后方向上的最大共振振幅均显著小于5例脊柱侧弯受试者,由此得出结论:脊柱侧凸比健康脊柱对振动更敏感。 不同DS患者在X射线正位片上测得Cobb角、顶椎位置相近,但同一神经根支配的感觉区所引发的疼痛程度却相差很大,出现这种情况的主要原因很可能是其他的变量因素,比如冠状面上不明显的矢状面和水平轴面的构造差异,KIM等[7]对此进行了相关研究,探索了DS的弯曲模式与神经根症状之间的关系,该研究建立了两种脊柱侧弯曲线模式的有限元模型(孤立侧弯曲线,侧弯合并旋转曲线),计算侧弯弧形最大的顶椎两侧(左、右)神经根的应力。在不旋转的侧弯曲线中,顶椎凹侧的神经根压应力大于凸侧的拉应力;相反,在侧弯曲线上加入椎体的节段性旋转时,凸侧的拉应力明显增大,凹侧的压应力明显减小。综上所述,旋转脱位可能是脊柱凸侧神经症状发生的重要病理机制。 关节突关节的不对称应力载荷是体内试验得出的DS进展的因素之一[28]。WANG等[29]运用有限元法对DS小关节力进行了深入研究——左右两侧小关节对DS的演变有重要作用。他们发现,在左右弯曲的情况下,Cobb角越小,凸侧关节突关节受力越大,当Cobb角大于20°时,凹侧关节突关节受力大,关节突关节的不对称负荷发生在DS早期阶段,并受到脊柱侧弯曲线等级的影响;在轴向旋转情况下,同侧关节突关节的应力远小于同一水平的对侧关节突关节应力。总的来看,DS使关节突关节承受不对称载荷。在偏心性压应力作用下,凹侧小关节面出现压缩变形,凸侧小面关节受载荷作用的剪切力限制椎体旋转和滑移的作用减弱。关节突关节接触力的不对称负荷会加速腰椎退变,导致失去平衡。 一些不当的动作经常会造成脊柱的损伤。郑杰等[30]做了DS的生物力学有限元分析,发现过度的后伸和旋转运动会增大退行性侧弯脊柱的椎体、椎间盘、关节突关节的应力。此外,他们还对椎间盘和关节突关节在DS发生发展中产生的作用进行了研究[31],发现椎间盘和关节突关节的退变都会使脊柱的旋转增加,但DS的发生发展主要是由椎间盘非对称的退变导致的。HOMMINGA等[32]运用有限元法发现退变的椎间盘若同时合并椎体后方剪切力会使椎体的扭转刚度显著下降,易发生DS。具体来说,扭转刚度下降的主导因素是纤维环和韧带因高度降低出现松弛,而不是髓核失水萎缩。由此得出结论,纤维环和韧带退化结合椎体后方的剪切力是DS的病因之一。 DS患者的影像学上椎体左右楔形变表现最严重的往往是顶椎,由此可以推测稳定性最差的顶椎可能与DS发展有关。周仕炼等[33]进行了退行性腰椎侧弯6种工况运动下的生物力学有限元分析,研究发现DS的整体刚度增强,运动范围下降;各个椎间盘的外侧纤维环的应力远大于内侧髓核的应力;侧弯的所有节段中,顶椎体(如L2)的应力最小,顶椎间盘(如L2-3)的应力最大,顶椎的应力绝大程度上转移到了顶椎间盘,加快了顶椎间盘的退变,这也可能是DS进展的主要原因。 L4-L5、L5-S1是临床上腰椎间盘突出的最好发部位,由此可推测DS也可能存在常见的结构特征及进展机制。黄平[34]进行了退变性腰椎侧凸演变过程及相关生物力学机制的有限元分析,一方面研究发现在冠状面上侧弯曲线通常在腰段,少见于胸腰段,且腰段的侧弯曲线一般为“S形”双曲线,包括弧形较大的曲线和弧形较小的反向曲线,其中主弯即弧形较大的曲线常位于腰椎的近侧,弧形较小的曲线位于腰椎的远侧,前者侧凸顶点多在L2或L3椎体水平,或是L2/3、L3/4椎间隙水平,且顶椎朝向凸侧旋转;后者在远侧是由于主弯上方有胸廓连接相对固定,所以只能通过下方较为灵活的L4/5、L5/S1椎间盘代偿产生与上腰段弧形相反的弧形来恢复整个腰椎的基本力线平衡。另一方面研究总结侧凸形成和演变的基本过程是应力的破坏、腰椎的变形、力学的失衡,这三者互为因果且相互影响,并如此往复循环,直到承载力线重新恢复并且力学平衡重新获得。 2.2 有限元在DS治疗中的应用 矫形支具的使用是治疗DS有效的保守治疗方法[35],佩戴矫形支具可以有效防止侧弯进展。KARIMI 等[36]对DS患者的矫形支具运用有限元法进行了相关研究,图2A示脊柱侧凸从15°下降到了7.668°,图2B示脊柱侧凸从15°下降到了6.28°。该研究虽然是个案研究,没有进行统计学分析,但可以得出结论,这里提到的受力配置(10-70 N)对减少脊柱侧弯角度是有效的。在矫形器的生物力学中,力可以通过软组织或肋骨传递到弯曲的椎体。"

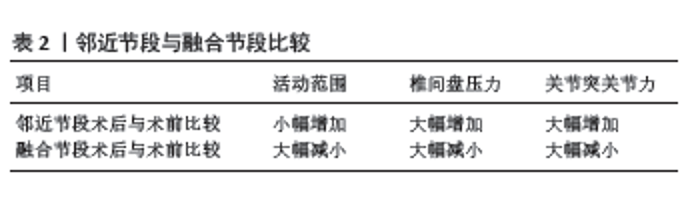
3D打印是一项通过逐层打印来构造物体的技术。郑杰等[37]做了有限元辅助3D打印技术进行个性化脊柱手术的研究,通过两组依靠3D打印和不依靠3D打印的DS手术的对比,发现3D打印组凭借术前对3D打印模型反复地进行螺钉内固定练习,实现了置钉难度更易、精确度更高、手术所用的时间更短、术中创伤更小、出血量更少、术后患者血红蛋白更高,并发症随之减少,而且研究发现,3D打印可用于术前对患者及家属介绍手术相关事宜,使术前交代更加清楚,能促进医患沟通,减少医患矛盾。 Cobb角较小但症状严重的DS患者也具备手术适应证。赵迪[38]通过有限元法建立DS模型,对其进行了后路矫形手术的应力分析研究,发现对于那些Cobb角度较小、脊柱整体平衡性较好且柔韧性灵活度更高的DS患者,短节段的融合固定也是一种较优的选择,可以获得满意的成效。 由于DS常累及多个节段,所以长节段固定融合是DS手术治疗中较多的选择,各种方式的长节段固定融合后邻接水平的活动范围、椎间盘和关节突关节的应力有何变化?郑杰等[39]进行了相关研究,发现治疗DS行长节段固定融合时所涉及的节段越多,对术后脊柱活动范围、邻椎椎间盘和关节突关节的应力影响越大。 手术方式的选择需要考虑利弊、个性化应用。马超[40]对DS患者进行了短节段和长节段融合固定的临床研究和有限元分析,发现与短节段矫形术相比,长节段矫形能力更强,但有着更大的手术创伤和更多的手术的并发症,且长节段融合固定时,位于尾端的螺钉所产生的应力较大,尤其在左右侧屈活动时螺钉产生的应力最大。此外,若长节段固定范围延伸到胸椎,会使近端区域活动范围变小,头端固定椎上方的邻椎椎体的前方应力变大而后方韧带复合体应力变小,易发生邻椎椎体的破坏。 DS的手术治疗易出现并发症,如融合失败后形成假关节,特别是腰骶交界处,假关节是L5-S1节段最常见的并发症[41]。LESZCZYNSKI等[42]建立了器械化的腰椎有限元模型并与体内试验进行了比较,他们发现钉棒、融合器置入的腰椎有限元模型与体外实验相同;由单边双棒的双边固定和L5-S1椎间融合器组成的内固定配置最大限度地减少了主棒(单边双棒中直接连接椎弓根螺钉的棒)的活动范围和应变,因此假关节的风险最低。该研究的有限元模型与已发表的实验结果一致。 邻椎退变是DS术后常见的并发症之一,已有体内实验证明应力集中是邻椎退变的主要原因[43]。HADDAS等[44]运用有限元分析法进行了相关研究。通过利用活体,CT扫描、软件导入分析,建立了20个腰椎有限元模型,每个模型施加纵向压缩载荷和6个不同的工况(向前弯曲、向后伸展、右侧弯曲、左侧弯曲、右侧轴向旋转、左侧轴向旋转),测量脊柱的活动范围、椎间盘内压力和关节突关节力。研究发现,患者术后与术前相比,邻近节段的活动范围小幅度增加,椎间盘内压力和关节突关节力显著增加,而融合节段的活动范围、椎间盘内压力和关节突关节力都显著减小,见表2。即融合对邻近节段的机械运动行为影响小,对邻近节段的机械力学行为影响大,对融合节段的机械运动、机械力学行为都影响较大。该研究不仅验证了应力集中是邻椎退变的主要原因,而且这些结果将有助于定义导致临床上邻椎恶化的变量(活动范围、椎间盘内压力、关节突关节力),这些变量通常通过下X射线摄影、计算机断层扫描和磁共振成像间接测量获得,有了这些信息,外科医生可以计划最合适的手术策略,以防止与邻椎恶化相关的中长期不良后果。"

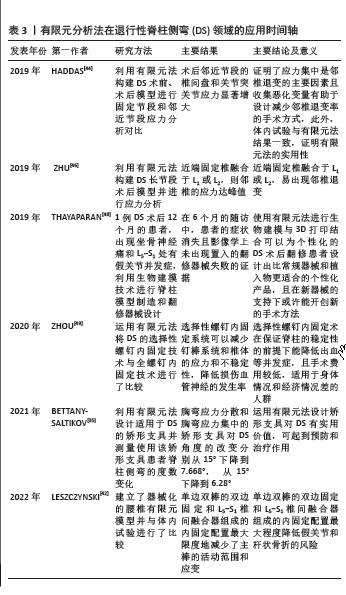
无论体内试验、还是有限元分析法都证明了应力集中是邻椎退变的主要原因,如何能在保持手术效果的同时减少应力集中?FRADET等[45]通过有限元分析法发现了在DS长节段手术中,在头端固定椎用钩形螺钉替代普通椎弓根螺钉、减少损害头端固定椎后方脊上韧带和脊间韧带及下关节突,能减少邻椎应力集中和退变。此外,ZHU 等[46]发现DS长节段手术中,若头端固定椎若融合水平在L1或L2水平,会增加邻椎的应力集中和退变。 脊柱的翻修手术是最严重的并发症之一,其中脊柱畸形手术是翻修发生率最高的手术类别[47]。THAYAPARAN 等[48]对使用生物建模和 3D 打印为退行性腰椎侧弯翻修手术设计特定的解决方案进行了探索,该研究选择1例出现坐骨神经痛和L5-S1处有假关节并发症的DS术后12个月的患者,利用生物建模技术进行脊柱模型制造和翻修器械设计,在6个月的随访中,患者的症状消失且影像学上未出现置入的翻修器械失败的证据。研究发现,术前规划与生物建模和 3D 打印相结合是一种可行的方案,它使手术技术、设备和植入物能够满足外科医生对腰椎融合手术的特定要求,通过整合患者身体的特定因素、外科医生要求和医疗保健效率,可以设计和制造与解剖学上匹配的手术工具和植入物,以补充腰椎融合手术方法。 选择性(策略性)螺钉内固定是一种使用较少螺钉,在关键部位进行螺钉内固定的技术,在特发性脊柱侧弯有较广的用途,但在DS的应用较少,ZHOU 等[49]运用有限元法将DS的选择性螺钉内固定技术与DS的全脊柱螺钉内固定术进行了比较,研究发现,螺钉数量较多的全脊柱螺钉系统推荐用于有较好身体和经济条件的DS患者。螺钉数量较少的选择性螺钉内固定系统可以减少钉棒系统和椎体的生物力学应力和不稳定性,降低损伤血管神经的并发症风险,所以使用较少数量螺钉的关键椎螺钉系统可以明显减少手术的并发症。策略性螺钉系统在临床实践中,能根据患者的实际情况制定合理的螺钉方案。此项研究有助于进一步研究不同情况下椎弓根螺钉固定的最佳手术方案,能最大限度地降低螺钉固定后术后并发症的风险,同时保持合理的三维固定效果。 螺钉松动是DS矫形术的并发症之一[50]。螺钉松动是因为螺钉的硬度远大于骨质,且螺钉与骨的界面是最薄弱的部位,一旦力量超过骨质所能承受的最大阈值,螺钉接触的骨质将发生破坏,破坏到一定程度便会出现螺钉松动,力量足够大甚至可能引发断钉的风险。DRISCOLL 等[51]运用有限元法对DS患者行手术治疗时2种螺钉的生物力学进行了比较,这两种螺钉分别是普通万向螺钉和新型万向螺钉,新型万向螺钉的U型钉尾灵活度更高、卡槽更长,较长的卡槽使棒与螺杆的距离更远,该研究发现,新型万向螺钉比普通螺钉更能有效降低DS矫形术所需的螺钉与骨的界面力,有利于防止螺钉松动和断裂的并 发症。 有限元分析法在DS领域的应用时间轴见表3。"
| [1] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;136:104745. [2] WANG W, BARAN GR, BETZ RR, et al. The Use of Finite Element Models to Assist Understanding and Treatment For Scoliosis: A Review Paper. Spine Deform. 2014;2(1):10-27. [3] NAOUM S, VASILIADIS AV, KOUTSERIMPAS C, et al. Finite Element Method for the Evaluation of the Human Spine: A Literature Overview. J Funct Biomater. 2021;12(3):43. [4] CAI XY, SANG D, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519. [5] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285. [6] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5): 301-317. [7] KIM HJ, CHUN HJ, KANG KT, et al. A validated finite element analysis of nerve root stress in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(6):599-605. [8] WEI W, ZHANG T, YANG J, et al. Material sensitivity of patient-specific finite element models in the brace treatment of scoliosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111449. [9] WANG R, WU Z. Recent advancement in finite element analysis of spinal interbody cages: A review. FrFront Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1041973. [10] SAKTI YM, SARASWATY RW, PRATAMA BY, et al. Functional outcomes following surgical treatment in patient with primary degenerative adult scoliosis. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;84:106095. [11] ZHANG H, YU H, ZHANG M, et al. Selection of spinal surgery and hip replacement sequence in patients with both degenerative scoliosis and hip disease. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(12):300060520959224. [12] CHEN K, ZHAO J, YANG Y, et al. Global research trends of adult degenerative scoliosis in this decade (2010-2019): a bibliometric study. Eur Spine J. 2020; 29(12):2970-2979. [13] SUN W, GAO J, ZHU L, et al. Effect of spinal manipulation on degenerative scoliosis. J Tradit Chin Med. 2020;40(6):1033-1040. [14] DIEBO BG, SHAH NV, BOACHIE-ADJEI O, et al. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet. 2019;394(10193):160-172. [15] DIEBO BG, LAVIAN JD, MURRAY DP, et al. The Impact of Comorbid Mental Health Disorders on Complications Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery With Minimum 2-Year Surveillance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018; 43(17):1176-1183. [16] DIEBO BG, CHERKALIN D, JALAI CM, et al. Comparing psychological burden of orthopaedic diseases against medical conditions: Investigation on hospital course of hip, knee, and spine surgery patients. J Orthop. 2018;15(2): 297-301. [17] PETROSYAN E, FARES J, LESNIAK MS, et al. Biological principles of adult degenerative scoliosis. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29(9):740-752. [18] LI LG, GAO JH, GAO CY, et al. [Clinical observation of chiropractic manipulation in the treatment of degenerative scoliosis]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(5):442-447. [19] HADDAS R, VILLARREAL J, LIEBERMAN IH. Kinematic comparison of the use of walking sticks versus a rolling walker during gait in adult degenerative scoliosis patients. Spine Deform. 2020;8(4):717-723. [20] DONG J, LI W, JIANG Y, et al. [Selection of upper instrumented vertebra for long-segment fixation in adult degenerative scoliosis]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;36(10):1305-1311. [21] SONG Z, ZHANG Z, YANG X, et al. Mid- and Long-Term Comparison Analysis of Two Approaches for the Treatment of Level III or Higher Lenke-Silva Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: Radical or Limited Surgery? Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2006-2015. [22] CRISTANTE AF, SILVA RTE, COSTA G, et al. Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;56(1):1-8. [23] BALDAIRON F, CHARLES YP, EICHLER D, et al. Analysis of factors associated with sagittal alignment deterioration after correction of degenerative scoliosis by in situ contouring. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021;107(7):103023. [24] SHAHRESTANI S, BROWN NJ, ACHARYA N, et al. A case report of robotic-guided prone transpsoas lumbar fusion in a patient with lumbar pseudarthrosis, adjacent segment disease, and degenerative scoliosis. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022;94:106999. [25] LI B, MENG X, ZHANG X, et al. Frailty as a risk factor for postoperative complications in adult patients with degenerative scoliosis administered posterior single approach, long-segment corrective surgery: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):333. [26] FAN ZQ, YAN XA, LI BF, et al. Prevalence of osteoporosis in spinal surgery patients older than 50 years: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2023;18(5):e0286110. [27] XU M, YANG J, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite element method-based study for effect of adult degenerative scoliosis on the spinal vibration characteristics. Comput Biol Med. 2017;84:53-58. [28] ZHENG J, YANG Y, CHENG B, et al. Exploring the pathological role of intervertebral disc and facet joint in the development of degenerative scoliosis by biomechanical methods. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;70: 83-88. [29] WANG L, ZHANG B, CHEN S, et al. A Validated Finite Element Analysis of Facet Joint Stress in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. World Neurosurg. 2016;95:126-133. [30] 郑杰, 杨永宏, 楼肃亮, 等. 退变性脊柱侧弯的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(30):5490-5496. [31] 郑杰, 杨永宏. 椎间盘和关节突关节在退变性脊柱侧凸发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(9):826-831. [32] HOMMINGA J, LEHR AM, MEIJER GJ, et al. Posteriorly directed shear loads and disc degeneration affect the torsional stiffness of spinal motion segments: a biomechanical modeling study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38(21):E1313-1319. [33] 周仕炼, 胡星新, 杨曦, 等.退变性腰椎侧凸六种工况运动下的生物力学的有限元分析[J]. 华西医学,2018,33(9):1099-1105. [34] 黄平. 退变性腰椎侧凸演变过程及相关生物力学机制的有限元分析[D]. 上海:第二军医大学,2013. [35] BETTANY-SALTIKOV J, PARK A, LING J. The experiences and effectiveness of the Spinecor brace on older adults with degenerative scoliosis: a mixed methods pilot study. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2021;280:294-295. [36] KARIMI MT, EBRAHIMI MH, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Evaluation of the influences of various force magnitudes and configurations on scoliotic curve correction using finite element analysis. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2017;40(1):231-236. [37] 郑杰, 何敏娟, 王大伟, 等. 退变性脊柱侧弯3D打印个性化减压融合[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(15):1364-1368. [38] 赵迪. 成人退变性脊柱侧凸有限元模型的建立及后路三维矫形生物力学研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2010. [39] 郑杰, 杨永宏, 张冬生, 等. 退变性脊柱侧凸不同方式长节段固定融合术后邻近节段生物力学变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011,21(9):769-773. [40] 马超. 长/短节段固定治疗成人退变性脊柱侧凸的临床研究及有限元分析[D]. 北京:中国人民解放军医学院, 2016. [41] CHO KJ, KIM YT, SHIN SH, et al. Surgical treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(3):371-381. [42] LESZCZYNSKI A, MEYER F, CHARLES YP, et al. Development of a flexible instrumented lumbar spine finite element model and comparison with in-vitro experiments. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022; 25(2):221-237. [43] HA KY, KIM YH, AHN JH. Is it real adjacent segment pathology by stress concentration after limited fusion in degenerative lumbar scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(13):1059-1066. [44] HADDAS R, XU M, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite Element Based-Analysis for Pre and Post Lumbar Fusion of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis Patients. Spine Deform. 2019;7(4):543-552. [45] FRADET L, WANG X, CRANDALL D, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Acute Proximal Junctional Failure After Surgical Instrumentation of Adult Spinal Deformity: The Impact of Proximal Implant Type, Osteotomy Procedures, and Lumbar Lordosis Restoration. Spine Deform. 2018;6(5):483-491. [46] ZHU WY, ZANG L, LI J, et al. A biomechanical study on proximal junctional kyphosis following long-segment posterior spinal fusion. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(5):e7748. [47] BARI TJ, KARSTENSEN S, SøRENSEN MD, et al. Revision surgery and mortality following complex spine surgery: 2-year follow-up in a prospective cohort of 679 patients using the Spine AdVerse Event Severity (SAVES) system. Spine Deform. 2020;8(6):1341-1351. [48] THAYAPARAN GK, OWBRIDGE MG, THOMPSON RG, et al. Designing patient-specific solutions using biomodelling and 3D-printing for revision lumbar spine surgery. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(Suppl 2):18-24. [49] ZHOU Y, XIN D, LEI Z, et al. Comparative Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of 4 Kinds of Pedicle Screw Schemes for Treatment of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e922050. [50] FASSER MR, GERBER G, PASSAPLAN C, et al. Computational model predicts risk of spinal screw loosening in patients. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(10): 2639-2649. [51] DRISCOLL M, MAC-THIONG JM, LABELLE H, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of 2 Different Pedicle Screw Systems During the Surgical Correction of Adult Spinal Deformities. Spine Deform. 2015;3(2):114-121. [52] SUN XY, KONG C, ZHANG TT, et al. Correlation between multifidus muscle atrophy, spinopelvic parameters, and severity of deformity in patients with adult degenerative scoliosis: the parallelogram effect of LMA on the diagonal through the apical vertebra. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):276. [53] TANG Y, YANG S, CHEN C, et al. Assessment of the association between paraspinal muscle degeneration and quality of life in patients with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(1):505-511. [54] TIAN L, GUO Y, GUO Z. Association between serum β-oestradiol and health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2023;98(1):91-97. |
| [1] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [2] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [3] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [4] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [5] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [6] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [7] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [8] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [9] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [10] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [11] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [12] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [13] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [14] | Liu Lu, Zhong Chang, Yu Xin, Ren Chenyuan, Gong Yangyang, Zhou Ping, Wang Yingbin. Academic progress and clinical application of in vitro synthetic microenvironment to promote maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7856-7862. |
| [15] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||