Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 995-1002.doi: 10.12307/2025.249
Previous Articles Next Articles
Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study
Ding Zhili1, 2, 3, Huang Jie3, Jiang Qiang3, Li Tusheng3, Liu Jiang1, 2, 3, Ding Yu1, 2, 3
- 1Naval Clinical College, Anhui Medical University, Beijing 100048, China; 2The Fifth Clinical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Division of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
-
Received:2023-12-22Accepted:2024-02-22Online:2025-02-18Published:2024-06-03 -
Contact:Ding Yu, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Naval Clinical College, Anhui Medical University, Beijing 100048, China; The Fifth Clinical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Division of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
About author:Ding Zhili, Master, Naval Clinical College, Anhui Medical University, Beijing 100048, China; The Fifth Clinical College of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Division of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sixth Medical Center, PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274637 (to DY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Zhili, Huang Jie, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Liu Jiang, Ding Yu. Constructing rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration models by different methods under X-ray guidance: a comparative study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 995-1002.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
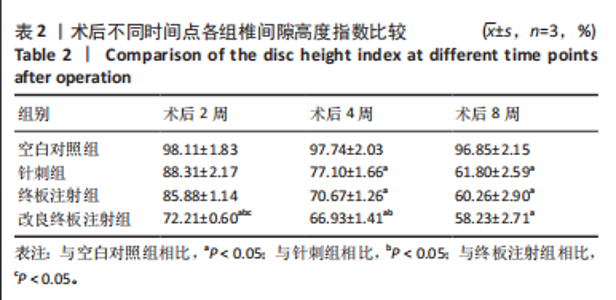
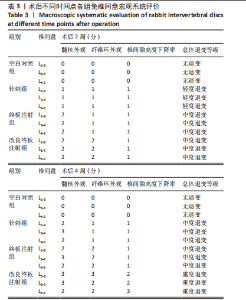
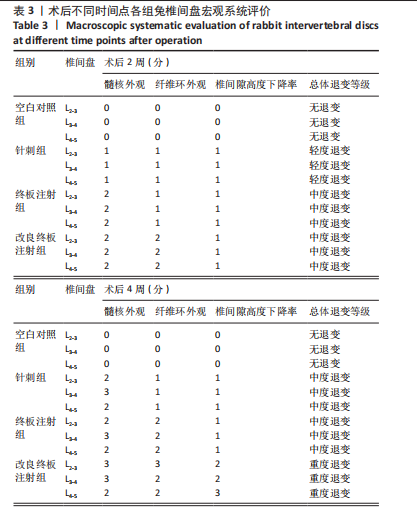
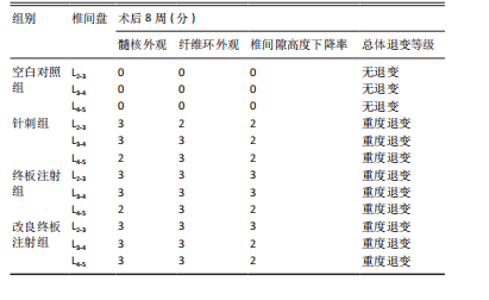
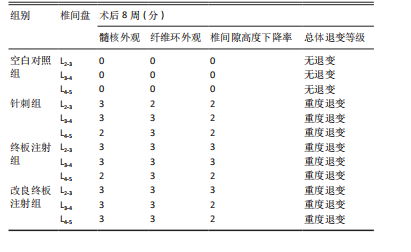
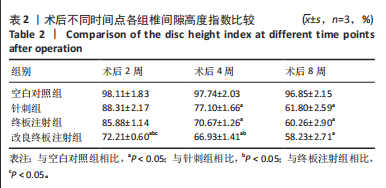
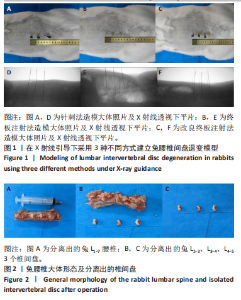
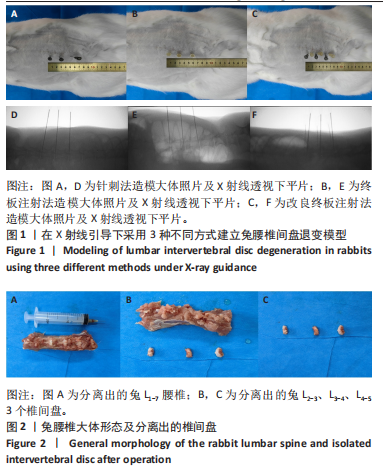
2.1 实验动物数量分析 18只实验兔中,选取2只用于术前解剖学分析,剩余16只随机分成以下4组:空白对照组、针刺组、终板注射组、改良终板注射组,每组4只。术中针刺组有1只兔因损伤脊髓出现瘫痪,终板注射组有1只兔因术中少量无水乙醇注射至椎旁静脉丛出现慢性酒精中毒症状,于术后2周死亡。术后各时间点(2,4,8周)随机从各组选取1只进入影像学数据统计分析,麻醉处死后做病理学检查及免疫组织化学检测。 2.2 解剖学分析 见图4。正常兔椎间盘髓核呈现白色胶冻状。从术后2周起,各模型组均有不同程度的颜色改变,主要表现为纤维环有明显的突出变暗或变黄,髓核不再呈现正常形态的胶状,占椎间盘面积降低,髓核含水量减低而形态发生改变。针刺组主要表现为纤维环破损,整个椎间盘含水量降低导致皱缩。终板注射组主要表现为整个椎间盘结构混乱,可见髓核,但与纤维环无明显边界。改良终板注射组主要表现为整个椎间盘严重受损,髓核无完整形态,纤维环出现较大程度的变性。 2.3 X射线片影像学表现 术后2周,与空白对照组相比,针刺组和终板注射组椎间隙高度下降不明显(P > 0.05),改良终板注射组出现明显下降(P < 0.05)。术后4周,针刺组、终板注射组、改良终板注射组相较于空白对照组椎间隙高度均有明显下降(P < 0.05),改良终板注射组相较于针刺组椎间隙高度有明显下降(P < 0.05),而与终板注射组无统计学差异(P > 0.05),针刺组相较于终板注射组椎间隙高度降低无统计学差异(P > 0.05)。术后8周,针刺组、终板注射组及改良终板注射组相对于空白对照组椎间隙高度均有明显下降(P < 0.05),针刺组相较于终板注射组及改良终板注射组椎间隙高度指数无统计学差异 (P > 0.05),见表2。 "
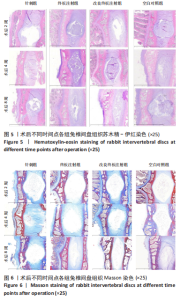
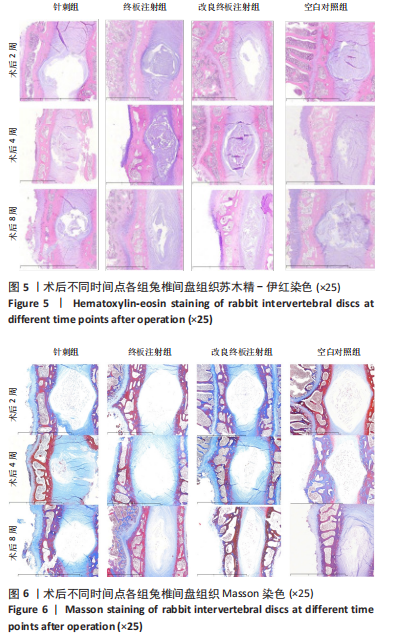
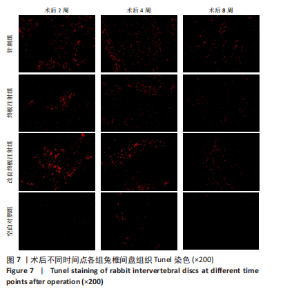
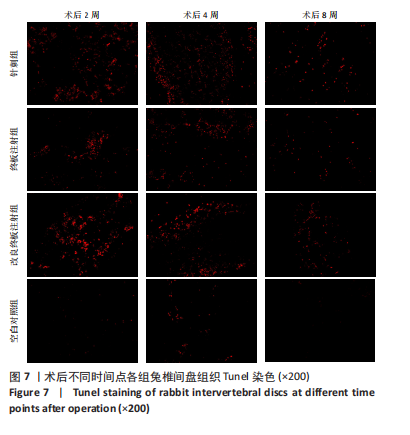
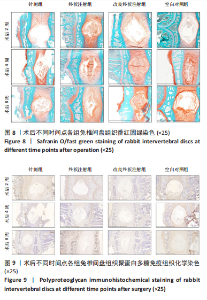
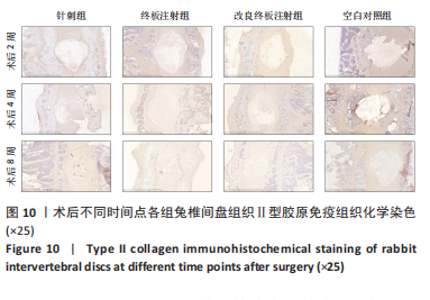
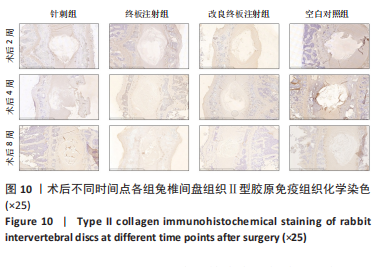
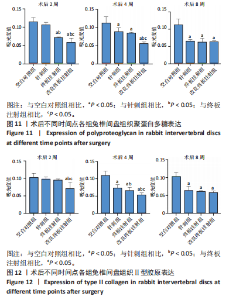
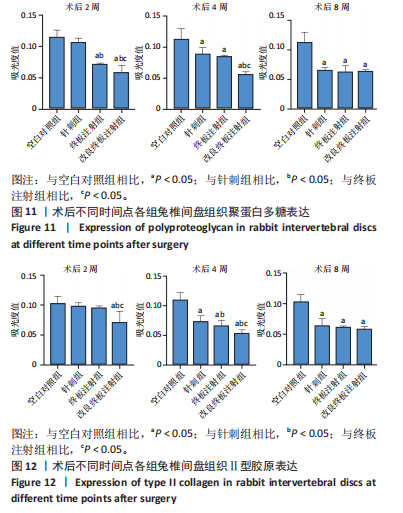
点内未观察到明显结构变化,髓核表现为完整的类圆形,外周纤维环组织呈环形排列,显示出大量脊索细胞和较少的类软骨细胞,与髓核分界清晰。模型组椎间盘髓核和纤维环随时间推移呈现退变趋势。术后2周,针刺组表现为纤维环内层向椎间盘弯曲凸入,与髓核分界不明显,髓核内出现裂隙,纤维软骨细胞逐渐替代了脊索细胞,同时伴有炎性细胞的浸润;终板注射组表现为纤维环损伤不明显,但髓核与纤维环边界不清晰;改良终板注射组表现为纤维环出现破损,与纤维环边界稍不清晰。术后4周,针刺组表现为髓核与纤维环融合,椎间盘结构已发生改变;终板注射组表现为髓核局部破裂,与纤维环无界限区分;改良终板注射组表现为整个椎间盘的失水和萎缩,髓核出现破损后失水。术后8周,3组均无正常椎间盘结构,结构混乱。针刺组髓核消失转变为其他组织,终板注射组髓核有少量残留,纤维环结构出现混乱。改良终板注射组表现为髓核与纤维环均发生退变,并融合为无序组织。 2.4.2 Masson染色 见图6。经Masson染色后,椎间盘组织显示多种颜色,其中胶原纤维呈蓝色,髓核细胞呈深红色或褐色,细胞质呈红色。术后2周,模型组髓核细胞染色均浅于空白对照组,与纤维环边界不清,纤维环结构混乱;终板注射组出现较为明显的终板破裂和排列混乱及细胞核丢失;改良终板注射组椎间盘面积明显较针刺组与终板注射组改变。术后4周,模型组椎间盘内胶原纤维均增多,且改良终板注射组增加最多,这表示髓核退变向胶原纤维开始转化。术后8周,改良终板注射组椎间盘损伤最大,表现为终板细胞大部分缺失,胶原纤维增多,与纤维环分辨不清,排列混乱成团状,细胞堆叠,新生血管长入,细胞核丢失。针刺组表现为胶原纤维仍呈环状,终板注射法胶原纤维为不规则分布。 2.4.3 Tunel 染色 见图7。空白对照组在各时间点均无明显变化,其余各组在术后2周时均有明显的细胞凋亡;针刺组在3个时间点均有小幅度下降趋势;终板注射组术后4-8周变化较术后2-4周更为明显;改良终板注射组在3个时间点均出现较多的细胞凋亡,说明改良终板注射法干预能力较针刺组和终板注射组更强。 2.4.4 番红固绿染色 见图8。针刺组纤维环结构出现破损,第4周破损最明显,髓核、纤维环边界不清,周围少见髓核细胞。终板注射组主要为软骨终板出现明显缺损,层次混乱,番红染色变浅,软骨终板细胞呈肥大空泡状,周围固绿染色颜色加深,范围明显增加,表明软骨终板中胶原蛋白含量降低,出现明显退变。改良终板注射组主要表现为整体椎间盘结构紊乱,髓核脱水,纤维环混乱,髓核、纤维环无明显边界。 2.5 椎间盘免疫组织化学检测结果 见图9-12。术后2周,除针刺组外,其余组Ⅱ型胶原、聚蛋白多糖表达均降低,改良终板注射组相较于终板注射组吸光度值明显下降(P < 0.05),Ⅱ型胶原呈阳性染色,自髓核至纤维环,其染色强度逐渐减弱,纤维环外层无染色。术后4周,随着造模时间的延长,针刺组椎间盘纤维环内层及髓核中Ⅱ型胶原吸光度值明显降低,与终板注射组无统计学差异(P > 0.05),可见髓核呈淡黄色,改良终板注射组与针刺组及终板注射组均存在统计学差异(P < 0.05)。术后8周,各造模组髓核染色加深,呈黄色,Ⅱ型胶原、聚蛋白多糖吸光度值持续降低,与空白对照组存在统计学差异(P < 0.05),各造模组之间无统计学差异(P > 0.05),这表明随着术后时间推移,Ⅱ型胶原、聚蛋白多糖含量减少,导致椎间盘退变。"
| [1] DANIELS J, BINCH AA, LE MAITRE CL. Inhibiting IL-1 signaling pathways to inhibit catabolic processes in disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2017; 35(1):74-85. [2] ZHANG J, SUN J, CHEN D, et al. Suppression of matrix degradation and amelioration of disc degeneration by a 970-nm diode laser via inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway in a rabbit model. Lasers Med Sci. 2023;38(1):58. [3] LIPSON SJ, MUIR H. Vertebral osteophyte formation in experimental disc degeneration. Morphologic and proteoglycan changes over time. Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23(3):319-324. [4] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14. [5] ELMOUNEDI N, BAHLOUL W, GUIDARA AR, et al. Establishment of an Animal Model of Disk Degeneration by Intradiskal Injection of Monosodium Iodoacetate. World Neurosurg. 2023;173:e532-e541. [6] SUDO T, AKEDA K, KAWAGUCHI K, et al. Intradiscal injection of monosodium iodoacetate induces intervertebral disc degeneration in an experimental rabbit model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):297. [7] YANG K, SONG Z, JIA D, et al. Comparisons between needle puncture and chondroitinase ABC to induce intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(10):2788-2800. [8] 陈明珏,曹惠玲,肖国芝.几种椎间盘退变动物模型的建立和应用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2022,38(4):401-409. [9] 贺庆,李兵,邓燕青,等.构建腰椎三维图像模型兔的特点分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(12):1889-1893. [10] YAMAGUCHI T, GOTO S, NISHIGAKI Y, et al. Microstructural analysis of three-dimensional canal network in the rabbit lumbar vertebral endplate. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(2):270-276. [11] 孟祥玉,巴穆登,艾尔肯•阿木冬.两种方法建立兔腰椎间盘退变模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4):564-568. [12] LUO TD, MARQUEZ-LARA A, ZABARSKY ZK, et al. A percutaneous, minimally invasive annulus fibrosus needle puncture model of intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(3):2309499018792715. [13] 谭伟伟,何升华,孙志涛,等.微创针刺旋切制备兔椎间盘退变模型[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(3):343-347. [14] WILKE HJ, ROHLMANN F, NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, et al. Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6):720-730. [15] KIRNAZ S, CAPADONA C, LINTZ M, et al. Pathomechanism and Biomechanics of Degenerative Disc Disease: Features of Healthy and Degenerated Discs. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(s1):10-25. [16] ELMOUNEDI N, BAHLOUL W, AOUI M, et al. Original animal model of lumbar disc degeneration. Libyan J Med. 2023;18(1):2212481. [17] MOON CS, LIM TH, HONG J, et al. Assessment of a Discogenic Pain Animal Model Induced by Applying Continuous Shear Force to Intervertebral Discs. Pain Physician. 2023;26(3):E181-E189. [18] 毛强,何帮剑,张圣扬,等.异常力学负荷导致椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(12):1-6. [19] 陈灿,杜梦凡,陈一仁,等.力学改变致腰椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(12):1133-1137 [20] LIANG H, LUO R, LI G, et al. The Proteolysis of ECM in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1715. [21] TAYEBI B, MOLAZEM M, BABAAHMADI M, et al. Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous and Open Surgery Approaches in The Animal Model of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Disc Degeneration. Cell J. 2023;25(5):338-346. [22] SUH HR, CHO HY, HAN HC. Development of a novel model of intervertebral disc degeneration by the intradiscal application of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) in rat. Spine J. 2022;22(1):183-192. [23] URA K, SUDO H, IWASAKI K, et al. Effects of Intradiscal Injection of Local Anesthetics on Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rabbit Degenerated Intervertebral Disc. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(9):1963-1971. [24] 杜瑞环,张警,李忠海.腰椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):847-853. [25] 陈飞,陆声,李娜,等.椎间盘退变模型建立的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(9):821-825. [26] KONG MH, DO DH, MIYAZAKI M, et al. Rabbit Model for in vivo Study of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Regeneration. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008;44(5):327-333. [27] LEI T, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Q, et al. A novel approach for the annulus needle puncture model of intervertebral disc degeneration in rabbits. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(3):900-909. [28] ROMANIYANTO F, MAHYUDIN F, UTOMO DN, et al. Effectivity of puncture method for intervertebral disc degeneration animal models: review article. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023;85(7):3501-3505. [29] KIM DW, CHUN HJ, LEE SK. Percutaneous Needle Puncture Technique to Create a Rabbit Model with Traumatic Degenerative Disk Disease. World Neurosurg. 2015;84(2):438-445. [30] XU H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A novel rat model of annulus fibrosus injury for intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2024;24(2):373-386. [31] ZHU P, KONG F, WU X, et al. A Minimally Invasive Annulus Fibrosus Needle Puncture Model of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats. World Neurosurg. 2023;169:e1-e8. [32] LI YX, MA XX, ZHAO CL, et al. Nucleus pulposus cells degeneration model: a necessary way to study intervertebral disc degeneration. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2023;82(4):745-757. [33] XIN L, XU W, WANG J, et al. Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model. Open Med (Wars). 2021;16(1):1616-1627. [34] XU HM, HU F, WANG XY, et al. Relationship Between Apoptosis of Endplate Microvasculature and Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disk. World Neurosurg. 2019;125:e392-e397. [35] VARDEN LJ, NGUYEN DT, MICHALEK AJ. Slow depressurization following intradiscal injection leads to injectate leakage in a large animal model. JOR Spine. 2019;2(3):e1061. [36] XIN L, ZHANG C, ZHONG F, et al. Minimal invasive annulotomy for induction of disc degeneration and implantation of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) plugs for annular repair in a rabbit model. Eur J Med Res. 2016;21:7. [37] IMANISHI T, AKEDA K, MURATA K, et al. Effect of diminished flow in rabbit lumbar arteries on intervertebral disc matrix changes using MRI T2-mapping and histology. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):347. [38] MIYAGI M, MILLECAMPS M, DANCO AT, et al. ISSLS Prize winner: Increased innervation and sensory nervous system plasticity in a mouse model of low back pain due to intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(17):1345-1354. [39] SAMANTA A, LUFKIN T, KRAUS P. Intervertebral disc degeneration-Current therapeutic options and challenges. Front Public Health. 2023; 11:1156749. [40] TESSIER S, RISBUD MV. Understanding embryonic development for cell-based therapies of intervertebral disc degeneration: Toward an effort to treat disc degeneration subphenotypes. Dev Dyn. 2021;250(3):302-317. |
| [1] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [2] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [3] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| [4] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [5] | Chen Chao, Hu Yaoquan, Lyu Zhengpin, He Qicong, Yangyang Zijiu, Luo Haoyan, Wu Guishuai, Zuo Qianlin, Wang Xuenan, Zhang Fan. tert-Butyl hydroperoxide can induce ferroptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6858-6865. |
| [6] | Yu Qinghe, Cai Ziming, Wu Jintao, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Wang Yakun, Lin Xiaoqin, Lin Wenping. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation of endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6391-9397. |
| [7] | Gou Yanyun, Hou Meijin, Jiang Zheng, Chen Shaoqing, Chen Xiang, Gao Yuzhan, Wang Xiangbin. Biomechanical characteristics of walking in patients with idiopathic scoliosis: cross-sectional analysis of three-dimensional motion capture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 471-477. |
| [8] | Gao Xilin, Wu Si Zhang Chao Zhu Liguo, Fu Bifeng, Wang Ping. Mechanotransduction proteins in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 579-589. |
| [9] | Xi Haixiang, Duan Jie, Xu Ping, Fei Xi, Li Xiaoping, Cao Lei, Tang Guangping, Zhang Lei. Syringin-chitosan hydrogel suppresses intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5968-5976. |
| [10] | Ma Jikun, Wang Jianru, Qi Junjie, Liu Haifei. Mechanism by which diabetes exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5907-5913. |
| [11] | Yu Qinghe, Cai Ziming, Tian He, Li Pian, Ruan Ye, Liang Jinzhu, Lin Shuhui, Lin Wenping. Formononetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5328-5334. |
| [12] | Wang Runzheng, Fu Su, Dong Chao, Li Dongzhe, Wang Yongkui. Relationship between bone mineral density and lumbar disc degeneration in middle-aged and elderly men and postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5079-5085. |
| [13] | Liu Zhaofeng, Yang Xuejun. Targeted biomarkers of single-cell RNA sequencing in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4351-4360. |
| [14] | Wang Zikun, Li Shudong, Gao Shuang, Fan Shuhao, Li Cheng, Meng Chunyang. Relationship between intervertebral disc degeneration and 473 gut microbiotas: what can be learned from big data information in the FinnGen database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4369-4378. |
| [15] | Liu Zhongyuan, Li Yang, Zhang Zhiwen . Mechanism by which KRT18 interacts with mRNA and long non-coding RNA to regulate intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 312-321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||