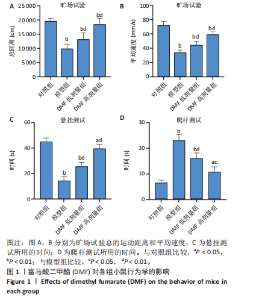
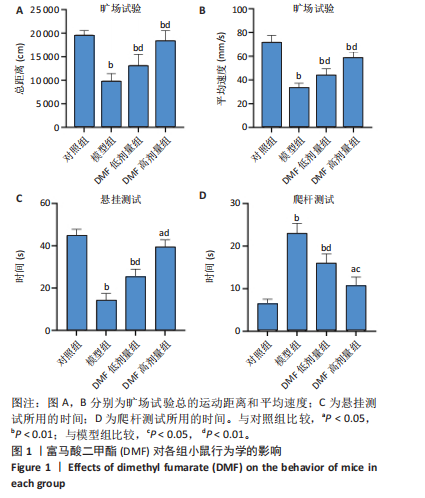
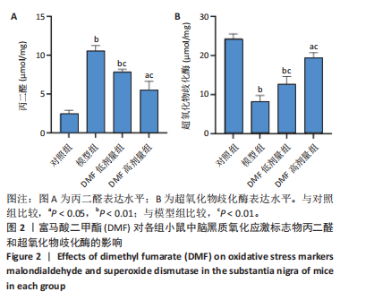
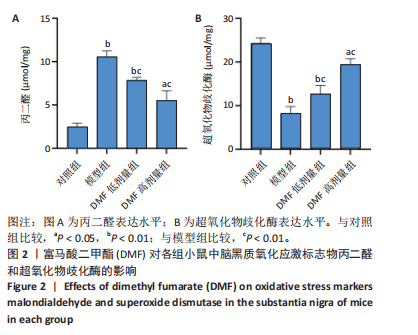
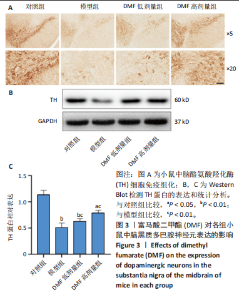
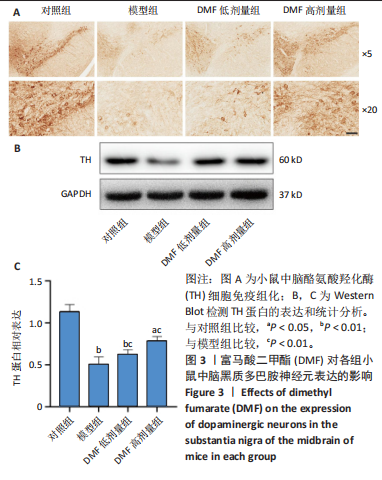
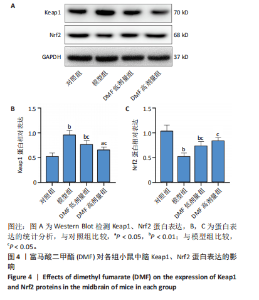
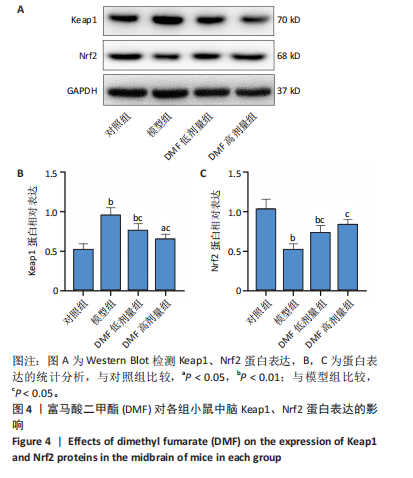
[1] BLOEM BR, OKUN MS, KLEIN C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10291): 2284-2303.
[2] Hayes MT. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Am J Med. 2019;132(7): 802-807.
[3] VÁZQUEZ-VÉLEZ GE, ZOGHBI HY. Parkinson’s Disease Genetics and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2021;44:87-108.
[4] BALL N, TEO WP, CHANDRA S, et al.Parkinson’s Disease and the Environment. Front Neurol. 2019;10:218.
[5] LI G, MA J, CUI S, et al. Parkinson’s disease in China: a forty-year growing track of bedside work. Transl Neurodegener. 2019;8:22.
[6] CRAMB KML, BECCANO-KELLY D, CRAGG SJ, et al. Impaired dopamine release in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2023;146(8):3117-3132.
[7] POSTUMA RB, LANG AE.The Clinical Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease-We Are Getting Better. Mov Disord. 2023;38(4):515-517.
[8] SVEINBJORNSDOTTIR S. The clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2016;139 Suppl 1:318-324.
[9] MORRIS HR, SPILLANTINI MG, SUE CM, et al.The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease.Lancet. 2024;403(10423):293-304.
[10] VIJIARATNAM N, SIMUNI T, BANDMANN O, et al. Progress towards therapies for disease modification in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(7): 559-572.
[11] LI J, PAN L, PAN W, et al. Recent progress of oxidative stress associated biomarker detection. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023;59(48):7361-7374.
[12] ZHU Y, WANG K, JIA X, et al. Antioxidant peptides, the guardian of life from oxidative stress. Med Res Rev. 2024;44(1):275-364.
[13] PALMA FR, GANTNER BN, SAKIYAMA MJ, et al. ROS production by mitochondria: function or dysfunction?. Oncogene. 2024;43(5):295-303.
[14] SARNIAK A, LIPIŃSKA J, TYTMAN K, et al. Endogenous mechanisms of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016;70(0):1150-1165.
[15] HEMMATI-DINARVAND M, SAEDI S, VALILO M, et al. Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease: conflict of oxidant-antioxidant systems. Neurosci Lett. 2019;709:134296.
[16] IMBRIANI P, MARTELLA G, BONSI P, et al. Oxidative stress and synaptic dysfunction in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2022; 173:105851.
[17] DONG-CHEN X, YONG C, YANG X, et al. Signaling pathways in Parkinson’s disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):73.
[18] MOEZZI D, DONG Y, JAIN RW, et al. Expression of antioxidant enzymes in lesions of multiple sclerosis and its models. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):12761.
[19] YU C, XIAO JH.The Keap1-Nrf2 System: A Mediator between Oxidative Stress and Aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6635460.
[20] HE F, RU X, WEN T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4777.
[21] ULASOV AV, ROSENKRANZ AA, GEORGIEV GP, et al.Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling: Towards specific regulation. Life Sci. 2022;291:120111.
[22] URUNO A, YAMAMOTO M.The KEAP1-NRF2 System and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023;38(13-15):974-988.
[23] HØJSGAARD CHOW H, TALBOT J, LUNDELL H, et al. Dimethyl fumarate treatment of primary progressive multiple sclerosis: results of an open-label extension study.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2023;70:104458.
[24] VAVOUGIOS G, ZAROGIANNIS SG, DOSKAS T. The putative interplay between DJ-1/NRF2 and Dimethyl Fumarate: A potentially important pharmacological target. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2018;21:88-91.
[25] QI D, CHEN P, BAO H, et al. Dimethyl fumarate protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by alleviating ferroptosis via the NRF2/SLC7A11/HO-1 axis.Cell Cycle. 2023;22(7):818-828.
[26] JACKSON-LEWIS V, PRZEDBORSKI S.Protocol for the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Protoc. 2007;2(1):141-151.
[27] MAJKUTEWICZ I. Dimethyl fumarate: A review of preclinical efficacy in models of neurodegenerative diseases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022:926:175025.
[28] SCUDERI SA, ARDIZZONE A, PATERNITI I, et al. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effect of Nrf2 Inducer Dimethyl Fumarate in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(7):630.
[29] Dernie F. Mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenesis to treatment target. Neurochem Int. 2020;138:104756.
[30] HOULDSWORTH A. Role of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders: a review of reactive oxygen species and prevention by antioxidants. Brain Commun. 2024;6(1):fcad356.
[31] POLISSIDIS A, PETROPOULOU-VATHI L, NAKOS-BIMPOS M, et al. The Future of Targeted Gene-Based Treatment Strategies and Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease.Biomolecules. 2020;10(6):912.
[32] JAYARAM S, KRISHNAMURTHY PT. Role of microgliosis, oxidative stress and associated neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson?s disease: The therapeutic role of Nrf2 activators. Neurochem Int. 2021;145:105014.
[33] ROY A, BANERJEE R, CHOUDHURY S, et al. Novel inflammasome and oxidative modulators in Parkinson’s disease: A prospective study. Neurosci Lett. 2022;786:136768.
[34] SUZUKI T, TAKAHASHI J, YAMAMOTO M. Molecular Basis of the KEAP1-NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Mol Cells. 2023;46(3):133-141.
[35] KASAI S, SHIMIZU S, TATARA Y, et al. Regulation of Nrf2 by Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Physiology and Pathology. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):320.
[36] YAO Y, LI P, JIANG S, et al. A Mechanism Study on the Antioxidant Pathway of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Inhibiting Ferroptosis in Dopaminergic Neurons. Curr Mol Med. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0115665240266555231120044938.
[37] KHAN Z, ALI SA. Oxidative stress-related biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Iran J Neurol. 2018;17(3):137-144.
[38] BAIRD L, YAMAMOTO M.The Molecular Mechanisms Regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 Pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2020;40(13):e00099-20.
[39] TU W, WANG H, LI S, et al. The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway in Chronic Diseases.Aging Dis. 2019;10(3):637-651.
[40] KOPACZ A, KLOSKA D, FORMAN HJ, et al. Beyond repression of Nrf2: An update on Keap1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;157:63-74.
[41] YUAN H, XU Y, LUO Y, et al. Role of Nrf2 in cell senescence regulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(1):247-259.
[42] ZHAO M, WANG B, ZHANG C, et al. The DJ1-Nrf2-STING axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of Withaferin A in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(8):2517-2535. |