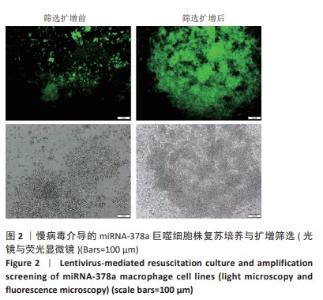
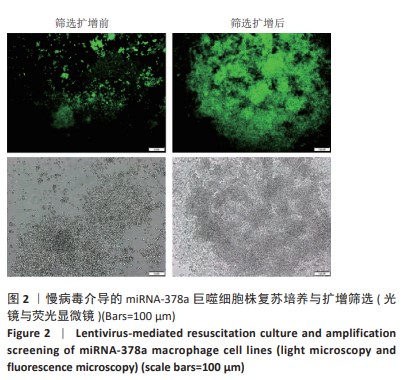
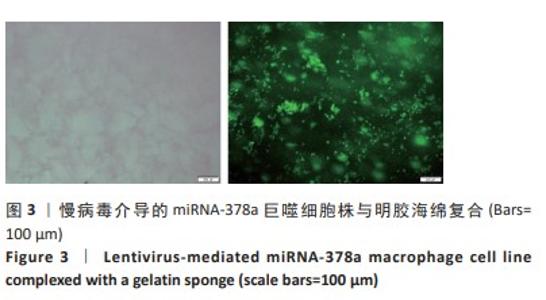
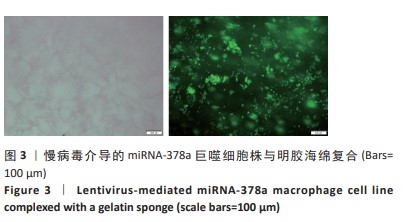
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (4): 789-799.doi: 10.12307/2025.263
Previous Articles Next Articles
miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion
Wang Sifan1, 2, He Huiyu1, 2, Yang Quan1, 3, Han Xiangzhen1, 2
- 1Department of Stomatology of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Institute of Stomatology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Urumqi Stomatological Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-12-02Accepted:2024-01-20Online:2025-02-08Published:2024-05-31 -
Contact:Han Xiangzhen, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Institute of Stomatology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Sifan, Master candidate, Department of Stomatology of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital), Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; Institute of Stomatology of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Youth Program of Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in 2021, No. 2021D01C337 (to HXZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
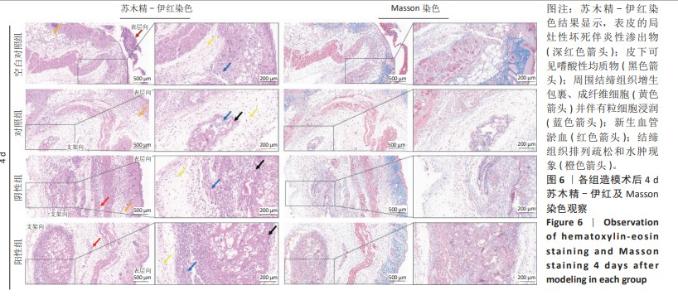
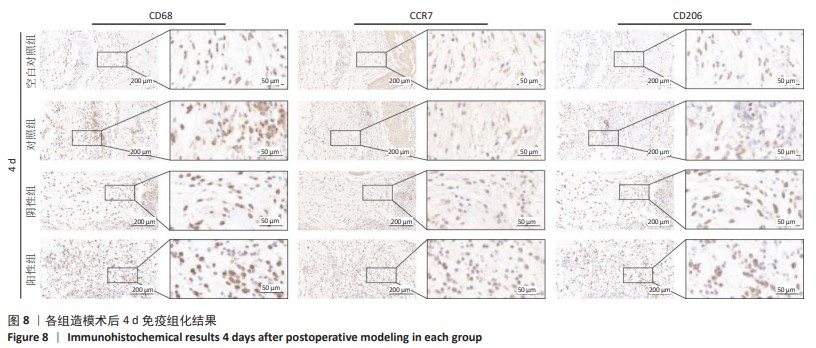
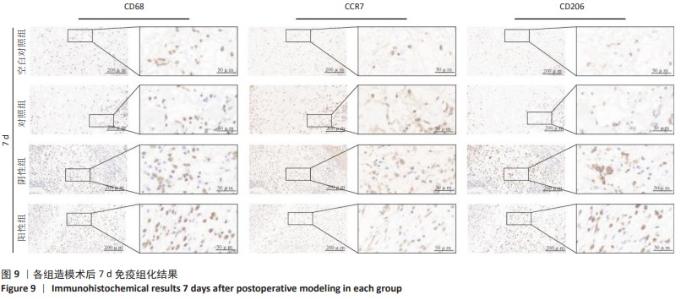
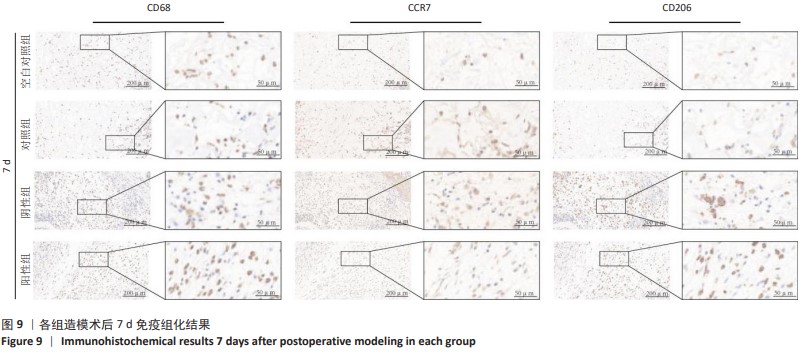
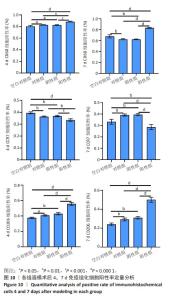
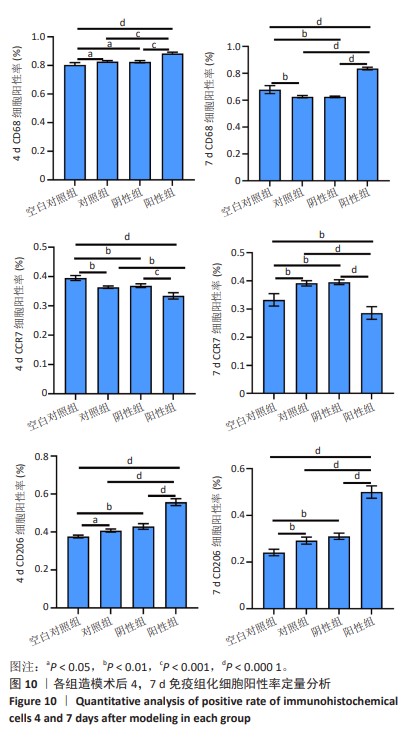
2.4 苏木精-伊红染色结果 各组4,7 d 苏木精-伊红染色观察,表皮的局灶性坏死伴炎性渗出物(深红色箭头);皮下可见嗜酸性均质物(黑色箭头);周围结缔组织增生包裹、成纤维细胞(黄色箭头)并伴有粒细胞浸润(蓝色箭头);新生血管淤血(红色箭头);结缔组织排列疏松和水肿现象(橙色箭头)。其中表皮小范围增厚、结缔组织增生、新生血管及成纤维细胞数量等现象7 d较4 d显著,阳性组 > 阴性组≈对照组 > 空白对照组;表皮的局灶性坏死伴炎性渗出物、嗜酸性均质物、粒细胞弥散性浸润、结缔组织排列疏松和水肿等现象4 d较7 d显著,阳性组 < 阴性组≈对照组 < 空白对照组。各组4,7 d Masson染色观察结果与苏木精-伊红染色结果一致,胶原纤维增生面积7 d较4 d占比更大,且阳性组 > 阴性组≈对照组 > 空白对照组;4 d时阳性组 > 阴性组≈对照组 > 空白对照组趋势不变,但差异较7 d有所减小。见图6,7。"
| [1] KALIVA M, GEORGOPOULOU A, DRAGATOGIANNIS DA, et al. Biodegradable Chitosan-graft-Poly(l-lactide) Copolymers For Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(2):316. [2] YANG P, XING J, LIU J, et al. Individual tissue-engineered bone in repairing bone defects: a 10-year follow-up study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(15-16):896-904. [3] WANG L, XU L, PENG C, et al. The effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell and nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen I/poly-L-lactic acid scaffold implantation on the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(3):2021-2028. [4] CLAIR S, DE OTEYZA DG. Controlling a Chemical Coupling Reaction on a Surface: Tools and Strategies for On-Surface Synthesis. Chem Rev. 2019;119(7):4717-4776. [5] HUANG YJ, HUNG KC, HUNG HS, et al. Modulation of Macrophage Phenotype by Biodegradable Polyurethane Nanoparticles: Possible Relation between Macrophage Polarization and Immune Response of Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(23):19436-19448. [6] SUN J, ZHANG J, LI K, et al. Photobiomodulation Therapy Inhibit the Activation and Secretory of Astrocytes by Altering Macrophage Polarization. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(1):141-152. [7] LUO W, AI L, WANG B, et al. Eccentric exercise and dietary restriction inhibits M1 macrophage polarization activated by high-fat diet-induced obesity. Life Sci. 2020;243:117246. [8] LIU W, MIAO Y, ZHANG L, et al. MiR-211 protects cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting cell apoptosis. Bioengineered. 2020; 11(1):189-200. [9] TAN X, GUO W, PENG Z, et al. LncRNA-Malat1 down-regulates miR-211-5p expression to promote neuronal damage from cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;192:114694. [10] CHEN L, ZHU Q, LU L, et al. MiR-132 inhibits migration and invasion and increases chemosensitivity of cisplatin-resistant oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting TGF-beta1. Bioengineered. 2020;11(1): 91-102. [11] MARTINEZ B, PEPLOW PV. MicroRNAs as disease progression biomarkers and therapeutic targets in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model of multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1831-1837. [12] HAN Z, ROSEN ST, Querfeld C. Targeting microRNA in hematologic malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol. 2020;32(5):535-544. [13] HUPKES M, SOTOCA AM, HENDRIKS JM, et al. MicroRNA miR-378 promotes BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. BMC Mol Biol. 2014;15:1. [14] DONG X, LIAO B, ZHAO J, et al. METTL14 mediates m(6)a modification on osteogenic proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the processing of pri-miR-873. Mol Med Rep. 2023;28(3):166. [15] LIN S, LIU Q, LELYVELD VS, et al. Mettl1/Wdr4-Mediated m(7)G tRNA Methylome Is Required for Normal mRNA Translation and Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation. Mol Cell. 2018;71(2): 244-255. [16] ZHU Y, ZHANG X, YANG K, et al. Macrophage-derived apoptotic vesicles regulate fate commitment of mesenchymal stem cells via miR155. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):323. [17] MACHADO IF, TEODORO JS, PALMEIRA CM, et al. miR-378a: a new emerging microRNA in metabolism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(10): 1947-1958. [18] RUCKERL D, JENKINS SJ, LAQTOM NN, et al. Induction of IL-4Ralpha-dependent microRNAs identifies PI3K/Akt signaling as essential for IL-4-driven murine macrophage proliferation in vivo. Blood. 2012; 120(11):2307-2316. [19] 杨泉, 何惠宇, 王思凡, 等. 过表达miR-378a促进巨噬细胞向M2极化且抑制巨噬细胞向M1极化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(13):2036-2041. [20] LANGER R, VACANTI JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110): 920-926. [21] LIU X, DOU G, LI Z, et al. Hybrid Biomaterial Initiates Refractory Wound Healing via Inducing Transiently Heightened Inflammatory Responses. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(21):e2105650. [22] CAO L, SU H, SI M, et al. Tissue Engineering in Stomatology: A Review of Potential Approaches for Oral Disease Treatments. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:662418. [23] LIU S, CHEN X, YU M, et al. Applications of Titanium Dioxide Nanostructure in Stomatology. Molecules. 2022;27(12):3881. [24] CHU S, WANG J, GAO F. The Application of Chitosan Nanostructures in Stomatology. Molecules. 2021;26(20):6315. [25] HAZRATI P, MIRTALEB MH, BOROOJENI H, et al. Current Trends, Advances, and Challenges of Tissue Engineering-Based Approaches of Tooth Regeneration: A Review of The Literature. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(4):473-496. [26] TAVELLI L, BAROOTCHI S, RASPERINI G, et al. Clinical and patient-reported outcomes of tissue engineering strategies for periodontal and peri-implant reconstruction. Periodontol 2000. 2023;91(1): 217-269. [27] PEIRSMAN A, NGUYEN HT, VAN WAEYENBERGE M, et al. Vascularized adipose tissue engineering: moving towards soft tissue reconstruction. Biofabrication. 2023;15(3). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/acd7a5. [28] AZARYAN E, EMADIAN RF, HANAFI-BOJD MY, et al. Dentin regeneration based on tooth tissue engineering: A review. Biotechnol Prog. 2023; 39(2):e3319. [29] SAITO MM, ONUMA K, YAMAKOSHI Y. Cementum is key to periodontal tissue regeneration: A review on apatite microstructures for creation of novel cementum-based dental implants. Genesis. 2023;61(3-4): e23514. [30] 李军, 颜杉, 许杰, 等. IL-37通过调控巨噬细胞极化抑制炎性疾病研究进展[J]. 现代医药卫生,2023,39(20):3527-3531. [31] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090. [32] MA H, SHU Q, LI D, et al. Accumulation of Intracellular Ferrous Iron in Inflammatory-Activated Macrophages. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023; 201(5):2303-2310. [33] BOUTILIER AJ, ELSAWA SF. Macrophage Polarization States in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6995. [34] YANG N, SHI N, YAO Z, et al. Gallium-modified gelatin nanoparticles loaded with quercetin promote skin wound healing via the regulation of bacterial proliferation and macrophage polarization. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1124944. [35] WU H, ZHENG J, XU S, et al. Mer regulates microglial/macrophage M1/M2 polarization and alleviates neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):2. [36] JIN GL, LIU HP, HUANG YX, et al. Koumine regulates macrophage M1/M2 polarization via TSPO, alleviating sepsis-associated liver injury in mice. Phytomedicine. 2022;107:154484. [37] WANG WB, LI JT, HUI Y, et al. Combination of pseudoephedrine and emodin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating macrophage M1/M2 polarization through the VIP/cAMP/PKA pathway. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):19. [38] CAO L, TAN Q, ZHU R, et al. LncRNA MIR4435-2HG suppression regulates macrophage M1/M2 polarization and reduces intestinal inflammation in mice with ulcerative colitis. Cytokine. 2023;170: 156338. [39] ALKAN AH, AKGUL B. Endogenous miRNA Sponges. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2257:91-104. [40] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6):613-626. [41] CUI J, LI Z, CUI K, et al. MicroRNA-20a-3p regulates the host immune response to facilitate the mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by targeting IKKbeta/NF-kappaB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;91:107286. [42] CHEN J, HUANG ZB, LIAO CJ, et al. LncRNA TP73-AS1/miR-539/MMP-8 axis modulates M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma via TGF-beta1 signaling. Cell Signal. 2020;75:109738. [43] ESSANDOH K, LI Y, HUO J, et al. MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response. Shock. 2016;46(2):122-131. [44] MOHAPATRA S, PIOPPINI C, OZPOLAT B, et al. Non-coding RNAs regulation of macrophage polarization in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2021; 20(1):24. [45] KATRILAKA C, KARIPIDOU N, PETROU N, et al. Freeze-Drying Process for the Fabrication of Collagen-Based Sponges as Medical Devices in Biomedical Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(12):4425. [46] MARKOWICZ M, KOELLENSPERGER E, STEFFENS GC, et al. The impact of vacuum freeze-drying on collagen sponges after gas plasma sterilization. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2006;17(1-2):61-75. [47] HE Y, WANG C, WANG C, et al. An Overview on Collagen and Gelatin-Based Cryogels: Fabrication, Classification, Properties and Biomedical Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(14):2299. [48] SINGH YP, DASGUPTA S. Gelatin-based electrospun and lyophilized scaffolds with nano scale feature for bone tissue engineering application: review. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022;33(13): 1704-1758. [49] SALVANTE ERG, POPOIU AV, BARB AC, et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Based Analysis of In Vivo Polymers and Collagen Scaffolds Inducing Vascularization. In Vivo. 2024;38(2):620-629. [50] NICOL L, SRIKANTH P, HENRIKSEN K, et al. Widespread disturbance in extracellular matrix collagen biomarker responses to teriparatide therapy in osteogenesis imperfecta. Bone. 2021;142:115703. [51] D’AMICO E, PIERFELICE TV, LEPORE S, et al. Hemostatic Collagen Sponge with High Porosity Promotes the Proliferation and Adhesion of Fibroblasts and Osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7749. [52] 孙皓, 蒲胤瑄, 刘佳林, 等. 过表达miR-378a修饰骨髓间充质干细胞复合胶原蛋白海绵支架对大鼠股骨缺损的修复作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2023,48(2):175-182. [53] MATTAPALLIL MJ, WAWROUSEK EF, CHAN CC, et al. The Rd8 mutation of the Crb1 gene is present in vendor lines of C57BL/6N mice and embryonic stem cells, and confounds ocular induced mutant phenotypes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(6):2921-2927. [54] BAHETI W, LV S, MA L, et al. Graphene/hydroxyapatite coating deposit on titanium alloys for implant application. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2023;21:1597502408. [55] WEI F, ZHOU Y, WANG J, et al. The Immunomodulatory Role of BMP-2 on Macrophages to Accelerate Osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(7-8):584-594. |
| [1] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [2] | Xin Yuan, Wu Xixi, Quan Liang, Zhang Hengtong, Ao Qiang. REG-augmented decellularized porcine cornea/hydroxyethyl methacrylate in situ integrated composite artificial cornea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3388-3399. |
| [3] | Wang Renzhi, Chen Yuanfen, Li Jinwei. 3D printed hollow pipe double-crosslinked hydrogel tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3432-3439. |
| [4] | Israrguli · Maimeti, Jia Sen, Liu Jia. Bone morphogenetic protein 2-loaded hydrogel induces osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3301-3310. |
| [5] | Zhou Pengfei, Lin Jing, Chen Yuying, Lin Minkui. Canine dental pulp stem cells-polyglycolic acid scaffold complex for canine periodontal tissue defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5526-5531. |
| [6] | Yu Xingge, Lin Kaili. Application of nanocomposite hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5441-5446. |
| [7] |
Ji Hangyu, Gu Jun, Xie Linghan, Wu Xiaotao.
Application of stem cells, tissue engineering scaffolds and neurotrophic factors in the treatment of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4088-4093. |
| [8] |
Feng Yuan, Han Zhiqi, Zhou Nuo.
Endothelial progenitor cells promote vasculogenesis and osteogenesis in the repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4046-4053. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||