Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 1070-1075.doi: 10.12307/2024.118
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and endoplasmic reticulum stress related pathway proteins in brain tissue of fluorosis rats
Yang Chun1, Wen Jianxia1, Feng Jianglong1, 2, Guan Zhizhong1, 2, 3, Wei Na1, 2
- 1Department of Pathology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Endemic and Minority Diseases (Guizhou Medical University), Ministry of Education, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-02-09Accepted:2023-03-14Online:2024-03-08Published:2023-07-17 -
Contact:Wei Na, MD, Associate professor, Department of Pathology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pathology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Chun, Master candidate, Department of Pathology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U1812403 (to GZZ), 81560512 (to WN); Science and Technology Program of Guizhou Province, No. Qiankehe Foundation-ZK[2022] General 439 (to WN); Open Project of the Key Laboratory of Endemic and Minority Diseases of the Ministry of Education (Guizhou Medical University), No. FZSW-2021-007 (to WN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Chun, Wen Jianxia, Feng Jianglong, Guan Zhizhong, Wei Na. Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor and endoplasmic reticulum stress related pathway proteins in brain tissue of fluorosis rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1070-1075.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
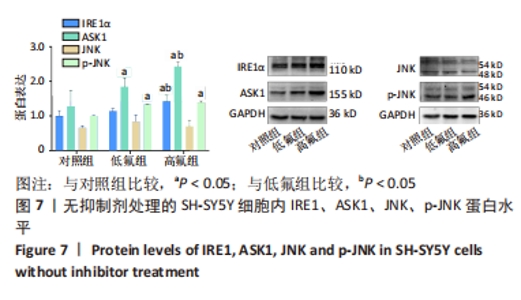
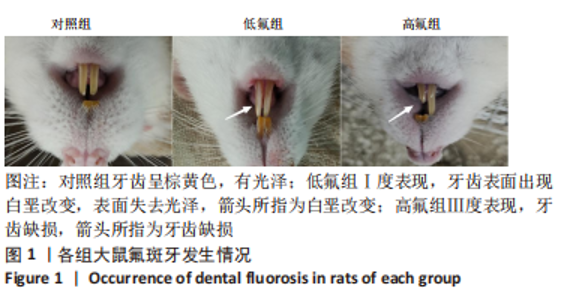
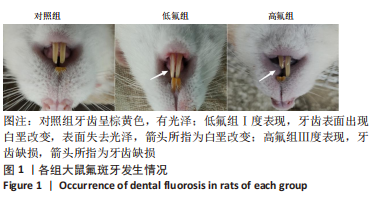
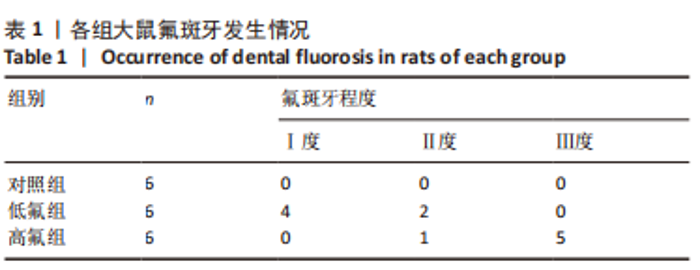
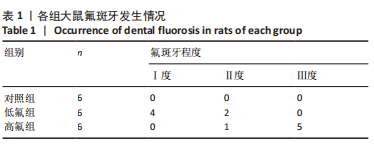
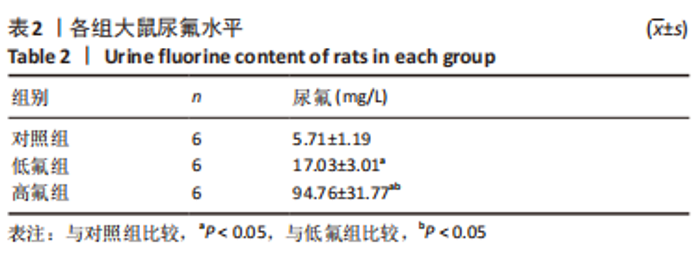
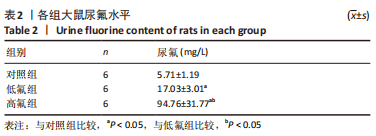
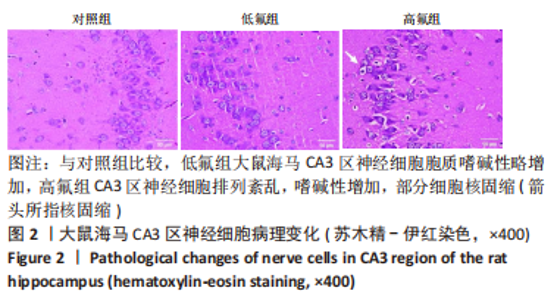
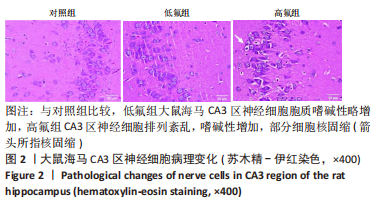
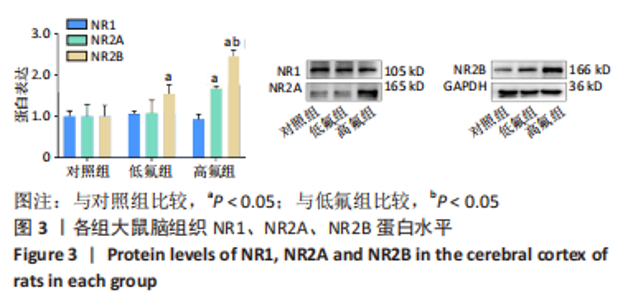
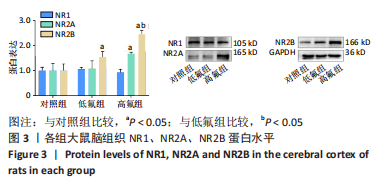
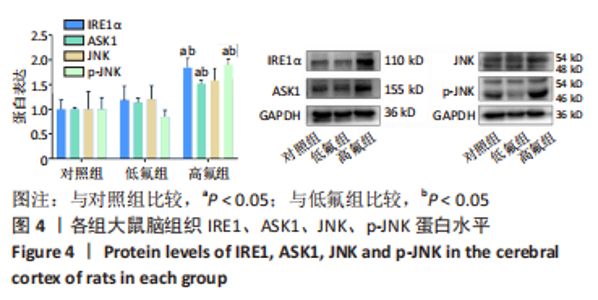
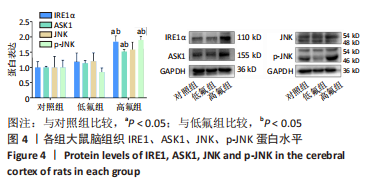
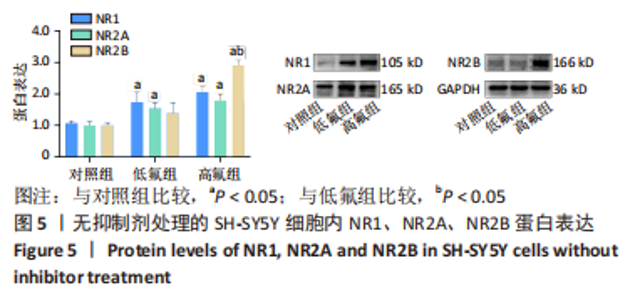
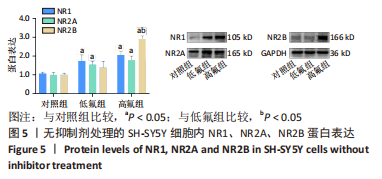
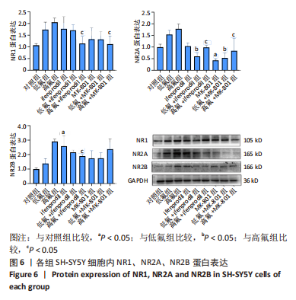
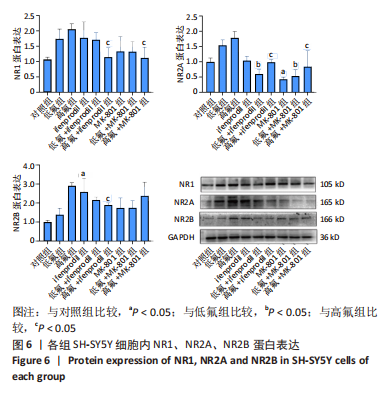
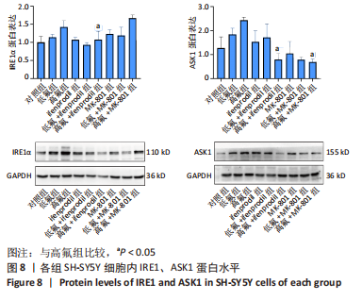
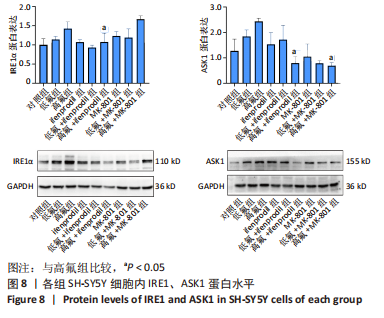
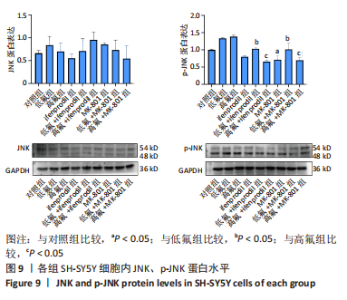
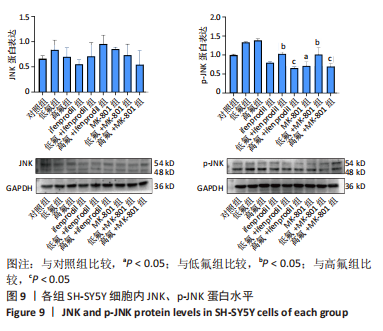
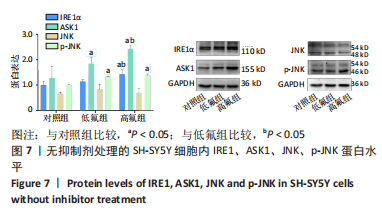
2.8 SH-SY5Y细胞中IRE1、ASK1、JNK、p-JNK蛋白的表达 与对照组比较,高氟组IRE1、ASK1蛋白明显升高(P < 0.05);与高氟组比较,高氟+Ifenprodil组IRE1、ASK1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05)。与高氟组比较,高氟+MK-801组ASK1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),见图7,8。各染氟组JNK蛋白表达与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但低氟组及高氟组SH-SY5Y细胞内p-JNK蛋白表达明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),与低氟组和高氟组比较,低氟+Ifenprodil组、低氟+MK-801组、高氟+Ifenprodil组、高氟+MK-801组p-JNK蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),见图7,9。"
| [1] JOHNSTON NR, STROBEL SA. Principles of fluoride toxicity and the cellular response: a review. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94(4):1051-1069. [2] VALDEZ-JIMÉNEZ L, SORIA FREGOZO C, MIRANDA BELTRÁN ML, et al. Effects of the fluoride on the central nervous system. Neurologia. 2011;26(5):297-300. [3] GRANDJEAN P. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: an updated review. Environ Health. 2019;18(1):110. [4] ŻWIEREŁŁO W, MARUSZEWSKA A, SKÓRKA-MAJEWICZ M, et al. Fluoride in the Central Nervous System and Its Potential Influence on the Development and Invasiveness of Brain Tumours-A Research Hypothesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2): 1558. [5] NAGENDRA AH, BOSE B, SHENOY PS. Recent advances in cellular effects of fluoride: an update on its signalling pathway and targeted therapeutic approaches. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(7):5661-5673. [6] DEC K, ŁUKOMSKA A, SKONIECZNA-ŻYDECKA K, et al. Chronic Exposure to Fluoride Affects GSH Level and NOX4 Expression in Rat Model of This Element of Neurotoxicity. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):422. [7] BOOKER SA, WYLLIE DJA. NMDA receptor function in inhibitory neurons. Neuropharmacology. 2021;196:108609. [8] CHENG F, DU L, KIM JJ, et al. NMDA and AMPA receptor physiology and role in visceral hypersensitivity: a review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;34(5):471-477. [9] ALKADHI KA. NMDA receptor-independent LTP in mammalian nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;200:101986. [10] PHILLIPS BP, GOMEZ-NAVARRO N, MILLER EA. Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;65:96-102. [11] PARK SJ, LI C, CHEN YM. Endoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Homeostasis in Kidney Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Am J Pathol. 2021;191(2):256-265. [12] ZHANG IX, RAGHAVAN M, SATIN LS. The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Calcium Homeostasis in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Endocrinology. 2020;161(2):bqz028. [13] SUN F, LI X, YANG C, et al. A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology. 2014;325:52-66. [14] QIU LL, PAN W, LUO D, et al. Dysregulation of BDNF/TrkB signaling mediated by NMDAR/Ca2+/calpain might contribute to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aging mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):23. [15] ZHOU L, DUAN J. The NMDAR GluN1-1a C-terminus binds to CaM and regulates synaptic function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;534:323-329. [16] WEGEHAUPT F, MENGHINI G. Fluoride Update. Swiss Dent J. 2020;130(9):677-683. [17] SRIVASTAVA S, FLORA SJS. Fluoride in Drinking Water and Skeletal Fluorosis: a Review of the Global Impact. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2020;7(2):140-146. [18] AGALAKOVA NI, NADEI OV. Inorganic fluoride and functions of brain. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020;50(1):28-46. [19] REN C, LI HH, ZHANG CY, et al. Effects of chronic fluorosis on the brain. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;244:114021. [20] WANG J, YUE B, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of exercise on microglial activation and transcriptome of hippocampus in fluorosis mice. Sci Total Environ. 2021;760:143376. [21] WEI W, PANG S, SUN D. The pathogenesis of endemic fluorosis: Research progress in the last 5 years. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4):2333-2342. [22] GU LS, WEI X, LING JQ. Etiology, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of dental fluorosis. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;55(5):296-301. [23] DA SILVA JAC, SCHRÖDER N. The Role of Ca2+ Permeable AMPA Receptors in Neurodegeneration, Neurotoxicity, and Neuroinflammation. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(5):624-633. [24] 孙丽丛, 张丹参, 景永帅. NMDA受体对中枢神经系统的影响[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2021,35(9):641. [25] CERCATO MC, COLETTIS N, SNITCOFSKY M, et al. Hippocampal NMDA receptors and the previous experience effect on memory. J Physiol Paris. 2014;108(4-6): 263-269. [26] GROENENDYK J, AGELLON LB, MICHALAK M. Calcium signaling and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2021;363:1-20. [27] WANG X, ENO CO, ALTMAN BJ, et al. ER stress modulates cellular metabolism. Biochem J. 2011;435(1):285-296. [28] HETZ C, ZHANG K, KAUFMAN RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):421-438. [29] AJOOLABADY A, LINDHOLM D, REN J, et al. ER stress and UPR in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms, pathogenesis, treatments. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(8):706. [30] GONG J, WANG XZ, WANG T, et al. Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017;18(1): 1-14. [31] DI CONZA G, HO PC. ER Stress Responses: An Emerging Modulator for Innate Immunity. Cells. 2020;9(3):695. [32] 李林江,万生芳,李荣科,等.基于ATF6/CHOP通路的红芪多糖对糖尿病胃轻瘫大鼠胃窦组织平滑肌的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(11):67-72. [33] 曹洁,姚隆 .PERK/ATF4/CHOP信号通路在饱和脂肪酸诱导肝细胞脂毒性凋亡中的作用[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2017,30(8):811-818. [34] 温建霞,何丽,冯江龙,等.不同剂量氟对大鼠肾皮质IRE1α-ASK1-JNK蛋白表达的影响[J].中华地方病学杂志,2022,41(2):100-104. [35] XU F, TONG M, TONG CSW, et al. A Combinatorial CRISPR-Cas9 Screen Identifies Ifenprodil as an Adjunct to Sorafenib for Liver Cancer Treatment. Cancer Res. 2021;81(24):6219-6232. [36] DANNENHOFFER CA, WERNER DF, VARLINSKAYA EI, et al. Adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure does not alter responsiveness to ifenprodil or expression of vesicular GABA and glutamate transporters. Dev Psychobiol. 2021;63(5):903-914. [37] ZHANG C, ZHANG Y, QIN Y, et al. Ifenprodil and Flavopiridol Identified by Genomewide RNA Interference Screening as Effective Drugs To Ameliorate Murine Acute Lung Injury after Influenza A H5N1 Virus Infection. mSystems. 2019;4(6):e00431. [38] SONG X, JENSEN MØ, JOGINI V, et al. Mechanism of NMDA receptor channel block by MK-801 and memantine. Nature. 2018;556(7702):515-519. [39] KRUK-SLOMKA M, BIALA G. Cannabidiol Attenuates MK-801-Induced Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia in the Passive Avoidance Test in Mice. Molecules. 2021;26(19):5977. [40] SAOUD H, KERESELIDZE E, EYBRARD S, et al. MK-801-induced behavioral and dopaminergic responses in the shell part of the nucleus accumbens in adult male rats are disrupted after neonatal blockade of the ventral subiculum. Neurochem Int. 2021;150:105195. |
| [1] | Bi Jintong, Hu Xin, Liu Jinshu. Wear properties of dental ceramics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 406-412. |
| [2] | Li Yangjie, Qi Rong, Zhang Xinyu, Cheng Jiaji, Zhou Ning, Cui Xue, Cheng Shuang, Wang Zhengdong, Yan Nan. Neuroprotective effects of sodium butyrate and acetylation proteomics analysis in fluorosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3151-3157. |
| [3] | Liang Weiye, Duan Qinghong. Correlation between femur bone morphogenetic protein 2 expression and bone fluoride content in fluorosis rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2675-2680. |
| [4] | Tang Yujing, Lan Fengjun, Li Guangdi, Wang Jian, Liu Riguang. Role of calcium ions in the pathogenesis of chronic fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2745-2753. |
| [5] | Zheng Pei, Xing Xinyang, Huo Hongfeng. Exercises for activating foot valgus muscle: reciprocal inhibitory effects on antagonistic muscle elasticity, tension and hardness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1149-1153. |
| [6] | Sun Honglei, Qi Fengna, Cheng Ruiqing. ICON penetrating resin for treatment of dental fluorosis: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5419-5424. |
| [7] | Ye Ting, Li Jing, Xu Lijuan, Ma Li. Skin administration of Wentong Huoxue Cream can relieve inflammation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5091-5096. |
| [8] | Ding Xue, Jia Ying, Liu Chun, Yang Shirong, Lai Lingyan, Yang Hua, Ding Qi. Displacement and rate changes of orthodontic tooth movement in Sprague-Dawley rats with chronic fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4687-4692. |
| [9] | He Lu, Li Yanlin, Meng Xuhan, Wang Guoliang, Yang Tengyun, Liao Xinyu, Zhou Xiaoxiang, Yang Guang. C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 antagonist delays the degeneration of articular cartilage in guinea pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2150-2154. |
| [10] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [11] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [12] | Xu Chaojian, Zhang Long, Cheng Caitong, Sun Xiaojuan, Lü Zhi. Disulfiram combined with cooper inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 124-129. |
| [13] | Zhang Yong, Ma Xun, Sun Lin, Zhang Li, Guan Xiaoming, Lü Cong, Chen Xu. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate edema of spinal astrocytes after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 4011-4017. |
| [14] | Zhang Wen, Zhang Lei, Ren Shouzhong, Liu Risheng . Prednisolone inhibites osteoblast apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor beta activated kinase 1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3630-3635. |
| [15] | Ye Kui. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound protects against high glucose-induced injury to human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2728-2733. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||