Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (29): 4598-4604.doi: 10.12307/2022.881
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of hypoxic exercise on skeletal muscle energy metabolism of rats with alimentary obesity
Wu Juhua1, Yang Yanan2, Weng Xiquan3, Zhao Fangfang4, Xu Guoqin3, Lin Wentao3, 4
- 1School of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou 545006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangdong Provincial Football Center, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Sports and Health, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China; 4Zhuhai College of Science and Technology, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-27Accepted:2021-05-09Online:2022-10-18Published:2022-03-27 -
Contact:Lin Wentao, Professor, Department of Sports and Health, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China; Zhuhai College of Science and Technology, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wu Juhua, MD, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou 545006, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Sports and Health Laboratory Fund Project of Guangxi University of Science and Technology, No. GKDTYSY2003 (to WJH); Western and Frontier Project of Humanities and Social Science Research Fund for the Youth, Ministry of Education, No. 18XJCZH009 (to WJH); the Young and Middle-aged Teachers’ Capability Improvement Project in Guangxi Universities, No. 2018KY0314 (to WJH); Guangxi University of Science and Technology Doctoral Fund, No. 17083 (to WJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Juhua, Yang Yanan, Weng Xiquan, Zhao Fangfang, Xu Guoqin, Lin Wenta. Effects of hypoxic exercise on skeletal muscle energy metabolism of rats with alimentary obesity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4598-4604.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
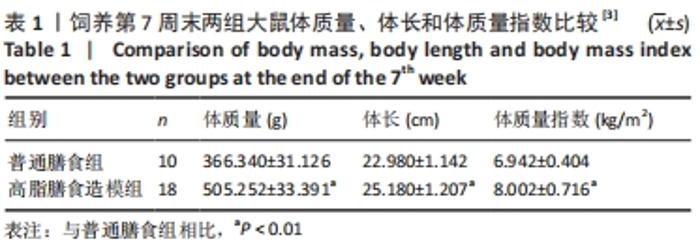
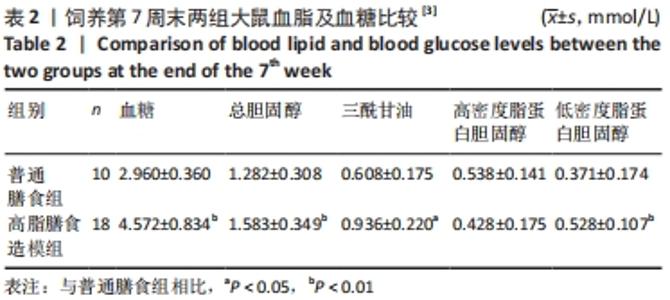
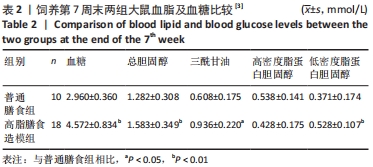
2.1 实验动物数量分析 干预结束后,剩余大鼠55只,其中常氧安静组和16.3%低氧安静组均为10只;常氧运动组、16.3%低氧运动组以及13.3%低氧安静组均为9只;13.3%低氧运动组为8只。实验中共脱失5只大鼠,其中常氧运动组1只、16.3%低氧运动组1只和13.3%低氧运动组2只均因运动时颈部折断而死亡,13.3%低氧安静组1只则因长有肿物而死亡。在进行蛋白测定时,根据G power软件进行样本量计算,得出每组n≥6即达到所需效应量。 2.2 高脂膳食诱导营养性肥胖大鼠模型建立[3] 7周高脂膳食饲养后,高脂膳食造模组大鼠的体质量、体长、体质量指数均高于普通膳食组[12],差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表1。"

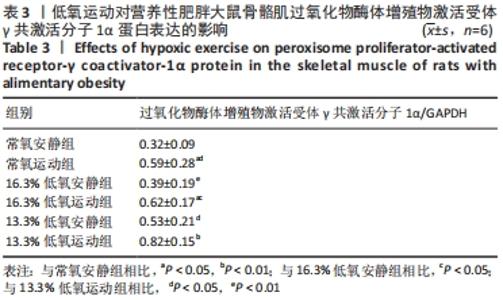
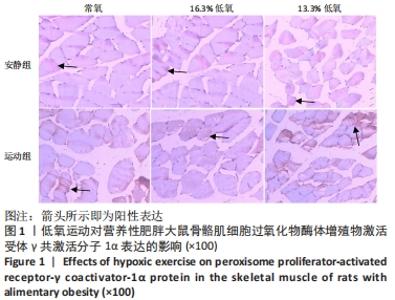
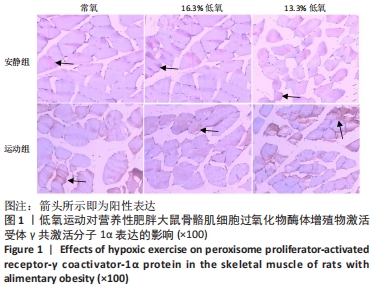
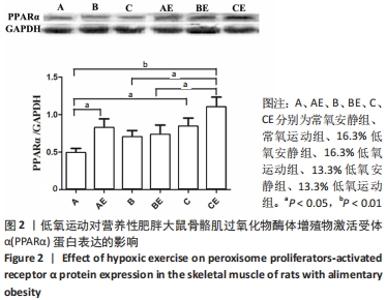
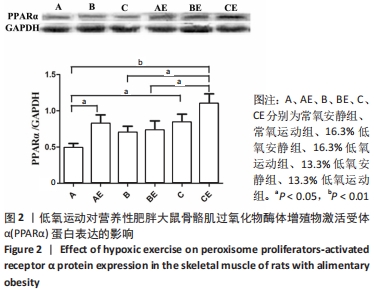
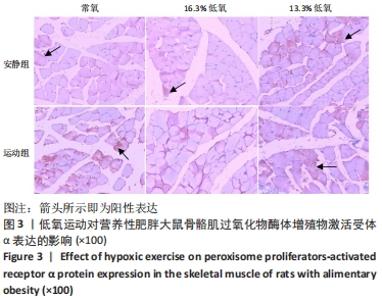
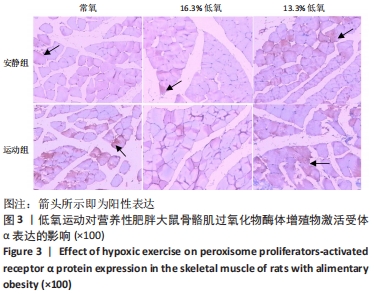
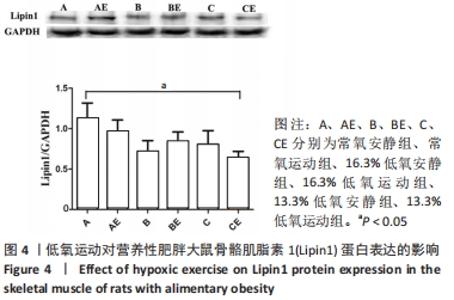
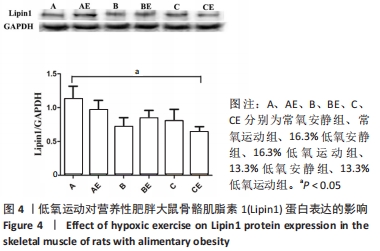
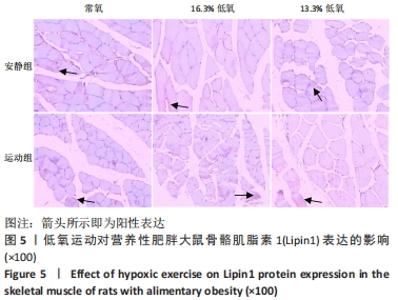
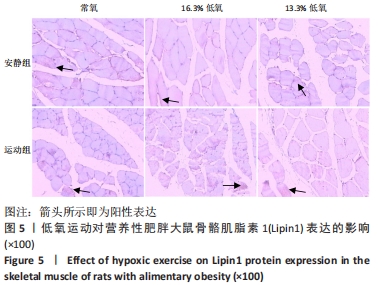
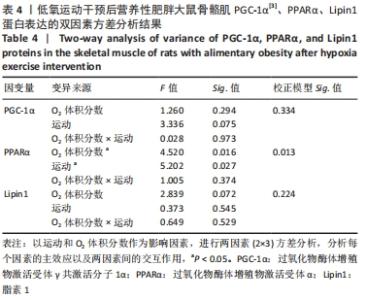
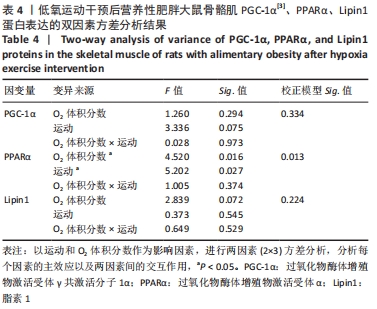
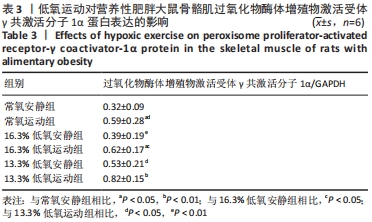
综上,7周高脂膳食饲养后,高脂膳食造模组大鼠形态学变化表现为体质量、体质量指数、体长显著高于普通膳食组,且体质量增长高于普通膳食组大鼠20%;血液生化相关指标表现为血糖、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、三酰甘油水平显著高于普通膳食组,提示高脂膳食诱导营养性肥胖大鼠模型建立成功[11]。 2.3 低氧运动对营养性肥胖大鼠骨骼肌细胞PGC-1α蛋白表达的影响[3] 常氧安静组和常氧运动组、常氧安静组和16.3%低氧运动组、常氧运动组和13.3%低氧运动组、16.3%低氧安静组和16.3%低氧运动组、13.3%低氧安静组和13.3%低氧运动组大鼠骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白表达水平相比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);常氧安静组和13.3%低氧运动组、16.3%低氧安静组和13.3%低氧运动组大鼠骨骼肌PGC-1α蛋白表达水平相比差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。"
| [1] NAM GE, KIM YH, HAN K, et al. Obesity Fact Sheet in Korea, 2019: Prevalence of Obesity and Abdominal Obesity from 2009 to 2018 and Social Factors. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2020;29(2):124-132. [2] CELIK O, YILDIZ BO. Obesity and physical exercise. Minerva Endocrinol (Torino). 2021; 46(2):131-144 [3] 吴菊花, 钟红梅, 杨亚南, 等. 低氧运动对营养性肥胖大鼠骨骼肌AMPK-PGC-1α的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(6):486-492. [4] PARK HY, KIM J, PARK MY, et al. Exposure and Exercise Training in Hypoxic Conditions as a New Obesity Therapeutic Modality: A Mini Review. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2018;27(2):93-101. [5] BENSAAD K, FAVARO E, LEWIS CA, et al. Fatty acid uptake and lipid storage induced by HIF-1α contribute to cell growth and survival after hypoxia-reoxygenation. Cell Rep. 2014;9(1):349-365. [6] OU LC, LEITER JC. Effects of exposure to a simulated altitude of 5500 m on energy metabolic pathways in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004;141(1): 59-71. [7] FINCK BN, KELLY DP. PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(3):615-622. [8] PARK JS, HOLLOSZY JO, KIM K, et al. Exercise Training-Induced PPARβ Increases PGC-1α Protein Stability and Improves Insulin-Induced Glucose Uptake in Rodent Muscles. Nutrients. 2020;12(3):652. [9] SOORI R, ZADEH MM, GHRAM A, et al. Effects of Hypoxic and Normoxic Training in Altitude on HIF-1α and PGC-1α Levels in Elite Endurance Runners. J Exerc Sci Med. 2019;11(1):61-70. [10] CHANDLER PC, VIANA JB, OSWALD KD, et al. Feeding response to melanocortin agonist predicts preference for and obesity from a high-fat diet. Physiol Behav. 2005;85(2):221-230. [11] 汤锦花, 严海东. 营养性肥胖大鼠模型的建立及评价[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2010,31(1):32-34. [12] ALTUNKAYNAK ME, OZBEK E, ALTUNKAYNAK BZ, et al. The effects of high-fat diet on the renal structure and morphometric parametric of kidneys in rats. J Anat. 2008;212(6):845-852. [13] KELEHER MR, ZAIDI R, SHAH S, et al. Maternal high-fat diet associated with altered gene expression, DNA methylation, and obesity risk in mouse offspring. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0192606. [14] ISLAM H, HOOD DA, GURD BJ. Looking beyond PGC-1α: emerging regulators of exercise-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and their activation by dietary compounds. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(1):11-23. [15] WANG HT, ZHANG YC, XU MY, et al. Research progresses on PGC-1α, a key energy metabolic regulator. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2020;72(6):804-816. [16] HU G, XU L, MA Y, et al. Chronic exercise provides renal-protective effects with upregulation of fatty acid oxidation in the kidney of high fructose-fed rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020;318(3):F826-F834. [17] WEI D, LIAO L, WANG H, et al. Canagliflozin ameliorates obesity by improving mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation via PPARα in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 2020;247:117414. [18] CHUNG N, PARK J, LIM K. The effects of exercise and cold exposure on mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017;21(2):39-47. [19] DENG H, ZHANG W, RUAN D, et al. The Combination of Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Induces Weight Loss via the PGC-1α/Irisin/UCP-1 Pathway. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2019;9(10):1388-1394. [20] QI X, WANG J. Melatonin improves mitochondrial biogenesis through the AMPK/PGC1α pathway to attenuate ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7299-7312. [21] 王慧婷, 张岩晨, 徐梦怡, 等. 能量代谢关键调控因子PGC-1α的研究进展[J]. 生理学报,2020,72(6):804-816. [22] DIXON ED, NARDO AD, CLAUDEL T, et al. The Role of Lipid Sensing Nuclear Receptors (PPARs and LXR) and Metabolic Lipases in Obesity, Diabetes and NAFLD. Genes (Basel). 2021;12(5):645. [23] NAJT CP, KHAN SA, HEDEN TD, et al. Lipid Droplet-Derived Monounsaturated Fatty Acids Traffic via PLIN5 to Allosterically Activate SIRT1. Mol Cell. 2020; 77(4):810-824. [24] BARROSO E, RODRÍGUEZ-CALVO R, SERRANO-MARCO L, et al. The PPARβ/δ activator GW501516 prevents the down-regulation of AMPK caused by a high-fat diet in liver and amplifies the PGC-1α-Lipin 1-PPARα pathway leading to increased fatty acid oxidation. Endocrinology. 2011;152(5):1848-1859. [25] 陈毅. 白藜芦醇通过激活AMPK-Lipin1信号通路改善酒精性脂肪肝[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2015. [26] ARAI T, TANAKA M, GODA N. HIF-1-dependent lipin1 induction prevents excessive lipid accumulation in choline-deficient diet-induced fatty liver. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14230. [27] BOUGARNE N, WEYERS B, DESMET SJ, et al. Molecular Actions of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(5):760-802. [28] QI ZG, ZHAO X, ZHONG W, et al. Osthole improves glucose and lipid metabolism via modulation of PPARα/γ-mediated target gene expression in liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle in fatty liver rats. Pharm Biol. 2016; 54(5):882-888. [29] PHUA WWT, WONG MXY, LIAO Z, et al. An aPPARent Functional Consequence in Skeletal Muscle Physiology via Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1425. [30] TAHRI-JOUTEY M, ANDREOLETTI P, SURAPUREDDI S, et al. Mechanisms Mediating the Regulation of Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation by PPARα. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8969. [31] RUSSELL AP, FEILCHENFELDT J, SCHREIBER S, et al. Endurance training in humans leads to fiber type-specific increases in levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 2003; 52(12):2874-2881. [32] WANG TY, WANG XH. Effects of aerobic exercise on PPARα signaling in diabetes rats and its association with PPARγ. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020;36(4):312-317. [33] 路瑛丽, 谢敏豪, 冯连世, 等. 高住高练对肥胖大鼠腓肠肌脂肪酸氧化的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(11):1060-1068. [34] 李格, 张缨. 低氧训练诱导AMPK对小鼠骨骼肌PPARα表达的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2013,29(5):40-46. [35] SHARMA S, TAEGTMEYER H, ADROGUE J, et al. Dynamic changes of gene expression in hypoxia-induced right ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286(3):H1185-H1192. [36] REUE K. The role of lipin 1 in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism. Novartis Found Symp. 2007;286:58-68. [37] ISHIMOTO K. Lipin 1 in lipid metabolism. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011;131(8): 1189-1194. [38] HAUSMAN GJ, BASU U, DU M, et al. Intermuscular and intramuscular adipose tissues: Bad vs. good adipose tissues. Adipocyte. 2014; 3(4):242-255. [39] FINCK BN, GROPLER MC, CHEN Z, et al. Lipin 1 is an inducible amplifier of the hepatic PGC-1alpha/PPARalpha regulatory pathway. Cell Metab. 2006; 4(3):199-210. [40] PHAN J, REUE K. Lipin, a lipodystrophy and obesity gene. Cell Metab. 2005; 1(1):73-83. [41] PHAN J, PÉTERFY M, REUE K. Lipin expression preceding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is critical for adipogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(28):29558-29564. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | FAN Yaru, LI Ruixin , LI Fengji, LUO Rui, LIU Hao, YAN Yingbin. Characterization and photothermal effect of indocyanine green encapsulated poly lactic acid-co-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [3] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [4] | Bao Xianguo, Gao Zengxin, Wu Zhanpo, Chen Youmin, Cheng Qinghua, Lu Haitao, Guo Changzheng, Xu Shuai. Correlation between lumbar posterior muscle and local kyphosis in patients with degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1418-1423. |
| [5] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [6] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [7] | Gu Zhengqiu, Xu Fei, Wei Jia, Zou Yongdi, Wang Xiaolu, Li Yongming. Exploratory study on talk test as a measure of intensity in blood flow restriction training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1154-1159. |
| [8] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [9] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [10] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [11] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [12] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [13] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||