Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (24): 3875-3881.doi: 10.12307/2021.096
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and comparison of four commonly used methods for patellar height measurement
Jie Ke1, Deng Peng2, Zeng Yirong2
- 1Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Third Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-08-26Revised:2020-09-14Accepted:2020-10-16Online:2021-08-28Published:2021-03-17 -
Contact:Zeng Yirong, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Third Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Jie Ke, Master, Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the High-Level Hospital Construction Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, No. 211010010722 (to ZYR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jie Ke, Deng Peng, Zeng Yirong. Application and comparison of four commonly used methods for patellar height measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3875-3881.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
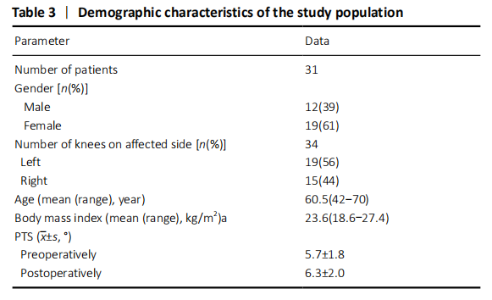
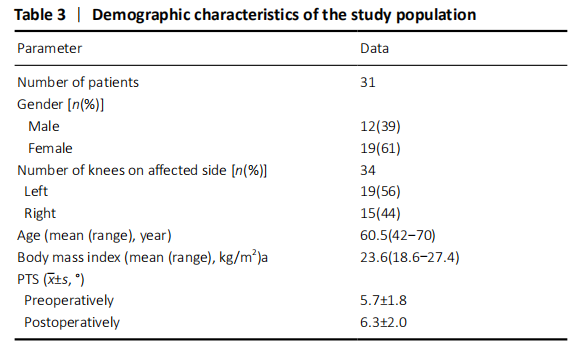
Characteristics of subjects Digital radiographs of 34 knees (31 patients) were evaluated in this study, including 12 male patients and 19 female patients. The mean age was 60.8 years (ranging from 42 to 68 years), and the mean body mass index was 23.6 kg/m2 (ranging from 18.6 to 27.4 kg/m2). There was no difference between preoperative and postoperative posterior tibial slope (PTS). Patients’ demographic data and PTS were listed in Table 3."
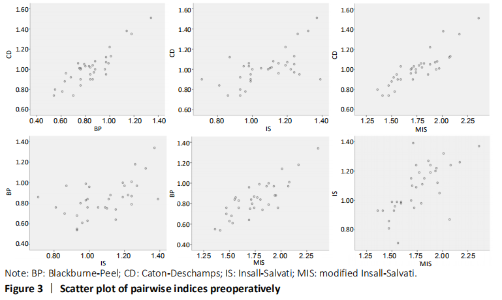
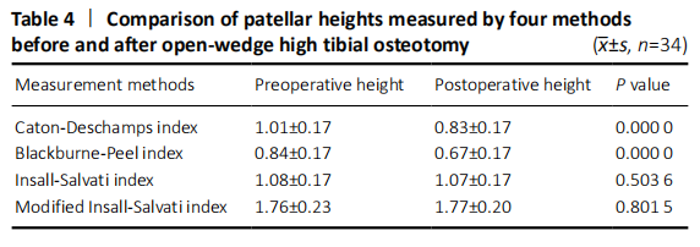
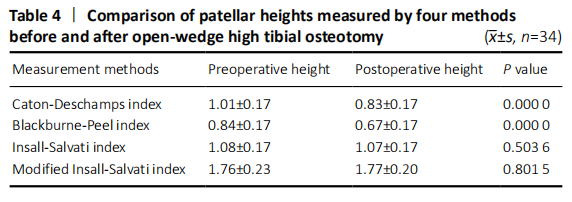
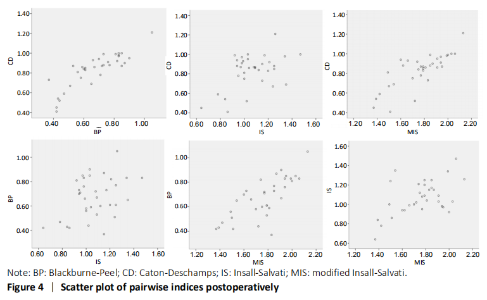
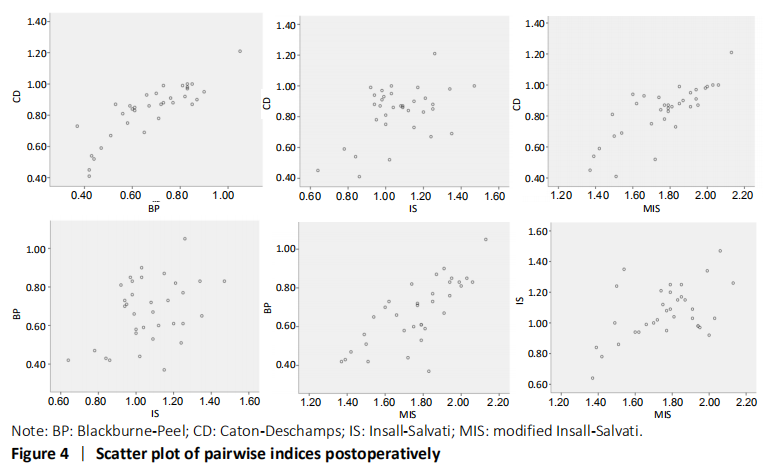
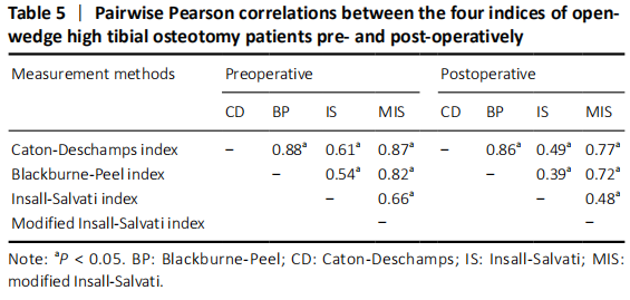
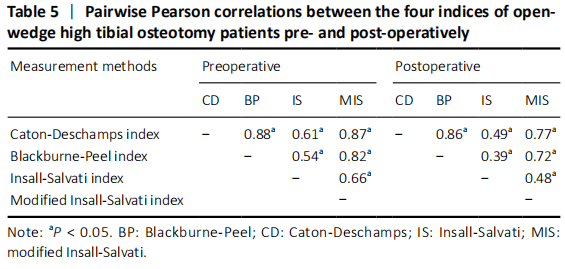
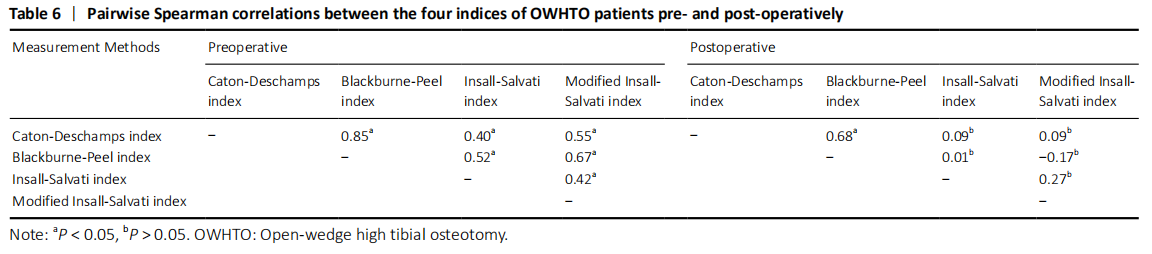
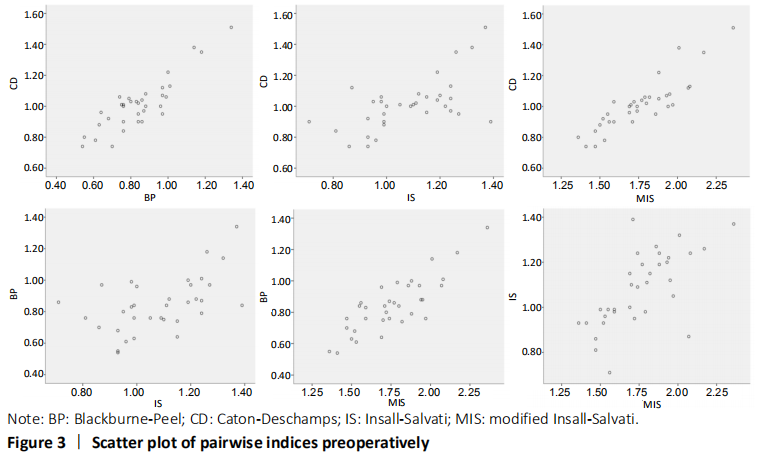
In the quantitative correlations using the Pearson correlation, significant difference between two arbitrary methods was found pre- and post-operatively (P < 0.05; Table 3). We found that BP and CD (r = 0.88), MIS and CD (r = 0.87), MIS and BP (r = 0.82) presented an excellent correlation with each other preoperatively. Moreover, only CD and BP (r = 0.86) found excellent correlation with each other postoperatively (Table 5). The scatter plots were shown in Figures 3 and 4."
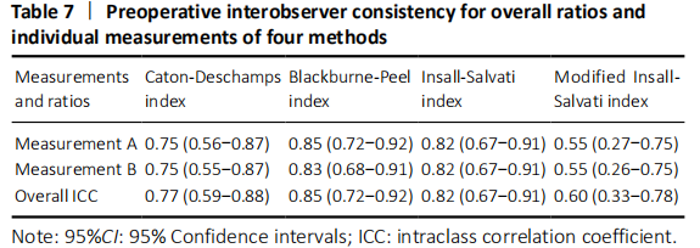
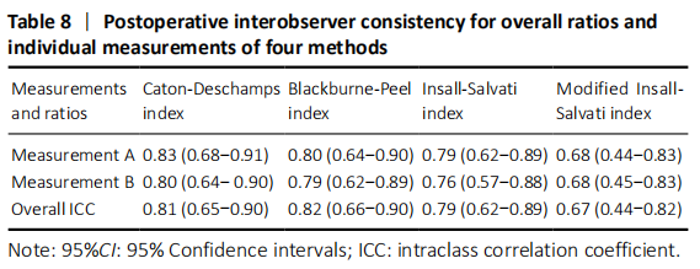
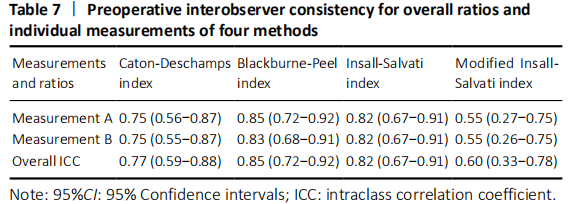
There was both good interobserver and intraobserver consistency preoperatively and postoperatively except MIS index which only had medium consistency (Tables 7 and 8). Among overall methods, BP showed the highest ICC preoperatively and postoperatively (0.85 and 0.82, respectively); CD and IS showed the second-highest ICC preoperatively (0.77 and 0.82, respectively) and postoperatively (0.81 and 0.79, respectively)."
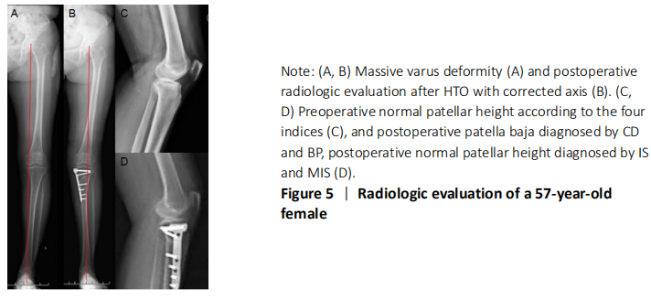
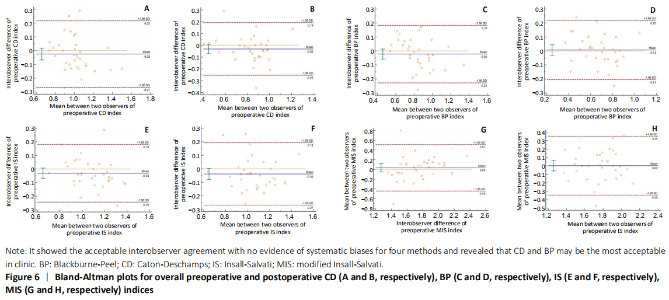
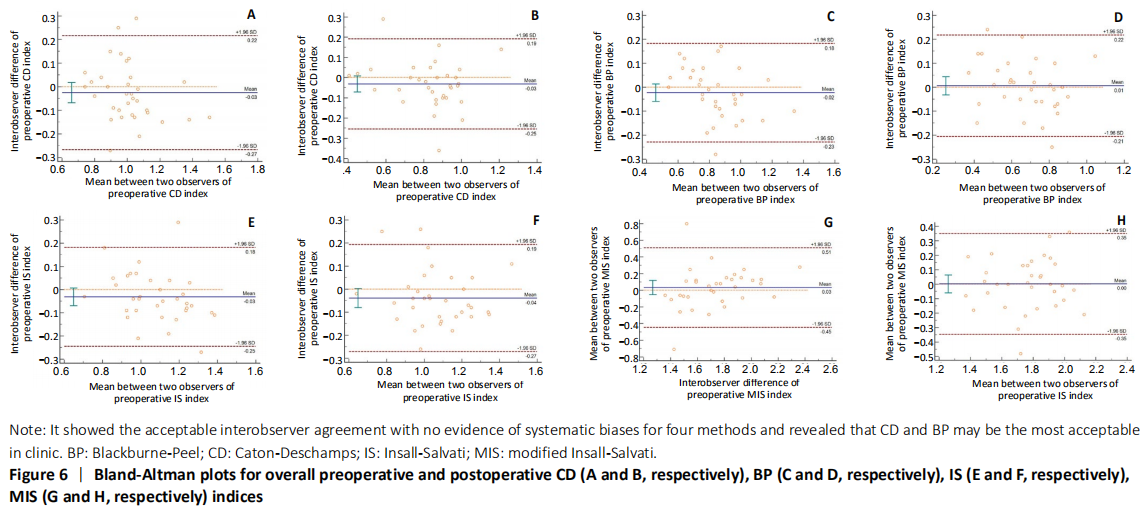
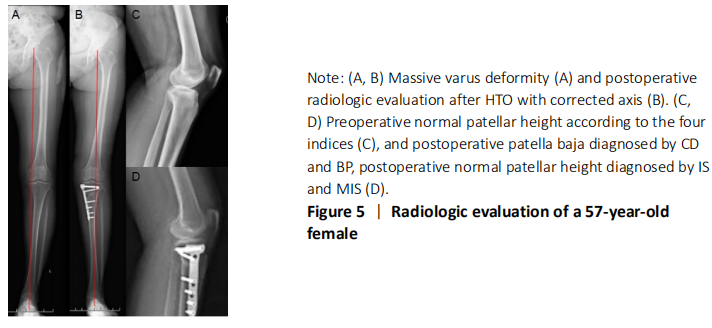
The statistics calculated by Bland-Altman plots showed acceptable interobserver agreement with no evidence of systematic biases for four methods (Figures 5 and 6). Furthermore, the maximum moduli of differences were 0.21 and 0.21 for CD, 0.19 and 0.21 for BP, 0.21 and -0.26 for IS, 0.39 and 0.33 for MIS (preoperative index and postoperative index, respectively), which revealed CD and BP may be the most acceptable in clinic. Adverse reactions and biocompatibility Tomofix plate fixation treatment has no obvious adverse reactions, and its biocompatibility is good. "
| [1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182): 1745-1759. [2] HUI C, SALMON LJ, KOK A, et al. Long-term survival of high tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(1):64-70. [3] SCHUSTER P, GEßLEIN M, SCHLUMBERGER M, et al. Ten-Year Results of Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy and Chondral Resurfacing in Severe Medial Osteoarthritis and Varus Malalignment. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(6):1362-1370. [4] DAY M, WOLF BR. Medial Opening-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Medial Compartment Arthrosis/Overload. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(3):331-349. [5] KIM JI, KIM BH, LEE KW, et al. Lower Limb Length Discrepancy After High Tibial Osteotomy: Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial of Lateral Closing Versus Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(12):3095-3102. [6] DUIVENVOORDEN T, VAN DIGGELE P, REIJMAN M, et al. Adverse events and survival after closing- and opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a comparative study of 412 patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(3):895-901. [7] Otsuki S, Murakami T, Okamoto Y, et al. Risk of patella baja after opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(3):614462772. [8] GOOI SG, CHAN CXY, TAN MKL, et al. Patella Height Changes Post High Tibial Osteotomy. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51:545-551. [9] KIM KI, KIM DK, SONG SJ, et al. Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy May Adversely Affect the Patellofemoral Joint. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(4):811-816. [10] FERNER F, LUTTER C, DICKSCHAS J, et al. Medial open wedge vs. lateral closed wedge high tibial osteotomy - Indications based on the findings of patellar height, leg length, torsional correction and clinical outcome in one hundred cases. Int Orthop. 2019;43(6):1379-1386. [11] TANAKA T, MATSUSHITA T, MIYAJI N, et al. Deterioration of patellofemoral cartilage status after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1347-1354. [12] PARK H, KIM HW, KAM JH, et al. Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Distal Tubercle Osteotomy Lessens Change in Patellar Position. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4636809. [13] KAYA H, DASTAN AE, BICER EK, et al. Posteromedial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy to Avoid Posterior Tibial Slope Increase. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(10):2710-2717. [14] GUPTA A, TEJPAL T, SHANMUGARAJ A, et al. Surgical Techniques, Outcomes, Indications, and Complications of Simultaneous High Tibial Osteotomy and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Revision Surgery: A Systematic Review. HSS J. 2019;15(2):176-184. [15] ZAMPOGNA B, VASTA S, PAPALIA R. Patient Evaluation and Indications for Osteotomy Around the Knee. Clin Sports Med. 2019;38(3):305-315. [16] CATON J, DESCHAMPS G, CHAMBAT P, et al. Patella infera. Apropos of 128 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1982;68(5):317-325. [17] BLACKBURNE JS, PEEL TE. A new method of measuring patellar height. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977;59(2):241-242. [18] GRELSAMER RP, MEADOWS S. The modified Insall-Salvati ratio for assessment of patellar height. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;(282):170-176. [19] INSALL J, SALVATI E. Patella position in the normal knee joint. Radiology. 1971;101(1):101-104. [20] MINIACI A, BALLMER FT, BALLMER PM, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy. A new fixation device. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(246):250-259. [21] FUJISAWA Y, MASUHARA K, SHIOMI S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979;10(3):585-608. [22] STAUBLI AE, DE SIMONI C, BABST R, et al. TomoFix: a new LCP-concept for open wedge osteotomy of the medial proximal tibia--early results in 92 cases. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 2:B55-62. [23] LANDIS JR, KOCH GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-174. [24] BARTKO JJ. The intraclass correlation coefficient as a measure of reliability. Psychol Rep. 1966;19(1):3-11. [25] LEE OS, AHN S, LEE YS. Changes of Sagittal and Axial Alignments of Patella after Open- and Closed-Wedge High-Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(7):625-634. [26] PHILLIPS CL, SILVER DA, SCHRANZ PJ, et al. The measurement of patellar height: a review of the methods of imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(8):1045-1053. [27] LEE YS, LEE SB, OH WS, et al. Changes in patellofemoral alignment do not cause clinical impact after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):129-133. [28] BITO H, TAKEUCHI R, KUMAGAI K, et al. Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy affects both the lateral patellar tilt and patellar height. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(7):955-960. [29] MOGHTADAEI M, OTOUKESH B, BODDUHI B, et al. Evaluation of Patellar Position before and After Medial Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: Radiographic and Computed Tomography Findings. Med Arch. 2016;70(4):293-295. [30] BIN SI, KIM HJ, AHN HS, et al. Changes in Patellar Height After Opening Wedge and Closing Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(11):2393-2400. [31] LAPRADE RF, ORO FB, ZIEGLER CG, et al. Patellar height and tibial slope after opening-wedge proximal tibial osteotomy: a prospective study. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(1):160-170. [32] WANG Z, ZENG Y, SHE W, et al. Is opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy superior to closing-wedge high tibial osteotomy in treatment of unicompartmental osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2018;60:153-163. [33] SCHUBERT I, FERNER F, DICKSCHAS J. The effect of open-wedge and closed-wedge high tibial osteotomies on the tibial posterior slope-a study of two hundred seventy-nine cases. Int Orthop. 2020;44(6):1077-1082. [34] NOYES FR, GOEBEL SX, WEST J. Opening wedge tibial osteotomy: the 3-triangle method to correct axial alignment and tibial slope. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(3):378-387. [35] HINTERWIMMER S, BEITZEL K, PAUL J, et al. Control of posterior tibial slope and patellar height in open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(4):851-856. [36] HERNIGOU P, MEDEVIELLE D, DEBEYRE J, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(3):332-354. [37] WU KL, YE PC, FENG WJ, et al. Effect of Correction Angle on Posterior Tibial Slope and Patella Height in OWHTO. Shiyong Guke Zazhi. 2018; 24(10):894-898,903. [38] ISHIMATSU T, TAKEUCHI R, ISHIKAWA H, et al. Hybrid closed wedge high tibial osteotomy improves patellofemoral joint congruity compared with open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1299-1309. [39] OGAWA H, MATSUMOTO K, YOSHIOKA H, et al. Distal tibial tubercle osteotomy is superior to the proximal one for progression of patellofemoral osteoarthritis in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(10):3270-3278. [40] JAWHAR A, SOHONI S, SHAH V, et al. Alteration of the patellar height following total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134(1):91-97. [41] VAN DUIJVENBODE D, STAVENUITER M, BURGER B, et al. The reliability of four widely used patellar height ratios. Int Orthop. 2016;40(3):493-497. |
| [1] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [2] | Liu Yafei, Wang Yalin, Zuo Yanping, Sun Qi, Wei Jing, Zhao Lixia. Structural changes of the temporomandibular joint in adolescents with skeletal Class III malocclusions after maxillary protraction: an X-ray measurement analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1154-1159. |
| [3] | Liu Zhengpeng, Wang Yahui, Zhang Yilong, Ming Ying, Sun Zhijie, Sun He. Application of 3D printed interbody fusion cage for cervical spondylosis of spinal cord type: half-year follow-up of recovery of cervical curvature and intervertebral height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [4] | Pan Qile, Zhang Hong, Zhou Huikang, Cai Guang. Comparison of the Greulich-Pyle method, the CHN method and the China 05 method for assessing bone age in children and adolescents [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 662-667. |
| [5] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [6] | Tian Yang, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Ma Fei, Zhong Dejun. Consistency and repeatability of CT and MRI in measurement of spinal canal area in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3882-3887. |
| [7] | Zhou Yuanbo, Wang Jindong. Etiology and treatment of femoral trochlear dysplasia: congenital genetic determination or stress stimulation of patella [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3908-3913. |
| [8] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [9] | Zhao Hongshun, A Jiancuo, Wang Deyuan, Xu Zhihua, Gao Shunhong. Factors affecting the height of early intervertebral space after lumbar interbody fusion via lateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3332-3336. |
| [10] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [11] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [12] | Sun Yiqiang, Xing Jianqiang, Li Xuecheng, Wang Xin, Tian Shenglan, Zhao Zihao, Geng Xiaopeng. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the elderly: a comparison of vertebral height recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2851-2855. |
| [13] | Zheng Weipeng, Wei Hewei, Liu Zhijun, Wan Lei, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao, Hu Weijian. Application of three-dimensional reconstructive CT versus X-ray in postoperative evaluation of bone tunnel and graft status after single bundle anterior cruciate ligament near-isometric reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2881-2886. |
| [14] | Du Xueting, Yang Yang, Huang Wenhua, Chen Wubiao. Clinical application and breakthrough of three-dimensional printing based on medical imaging technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2887-2894. |
| [15] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||