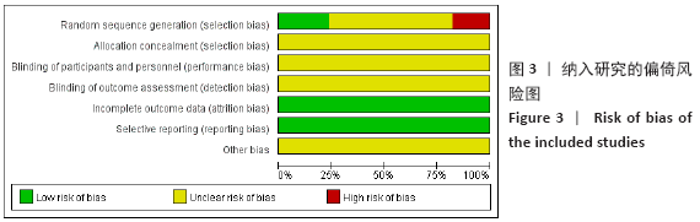
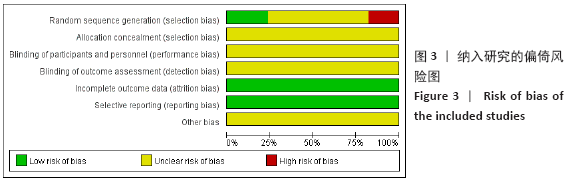
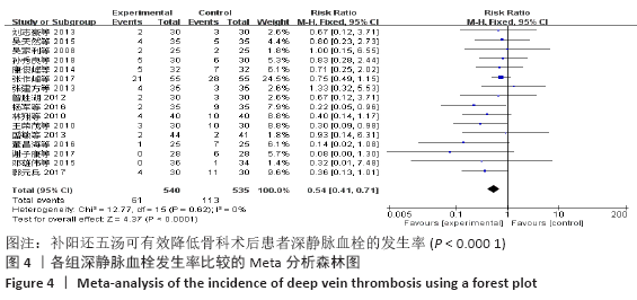
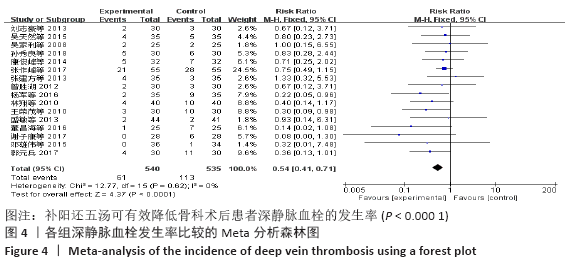
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 3267-3274.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3201
Previous Articles Next Articles
Buyang Huanwu Decoction in prevention of deep venous thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Jing Jinpeng1, Zhang Yue2, Liu Xiaomin3, Liu Yi1
- 1First Clinical Medicine School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Peripheral Vascular Disease, 3Department of Orthopedics for Athletic Injuries, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-20Revised:2020-05-21Accepted:2020-06-12Online:2021-07-18Published:2021-01-18 -
Contact:Zhang Yue, Chief physician, Department of Peripheral Vascular Disease, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jing Jinpeng, Master candidate, Physician, First Clinical Medicine School, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 81774311 (to ZY); Development Foundation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology of Shandong Province, No. 2019-0149 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Buyang Huanwu Decoction in prevention of deep venous thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3267-3274.
share this article
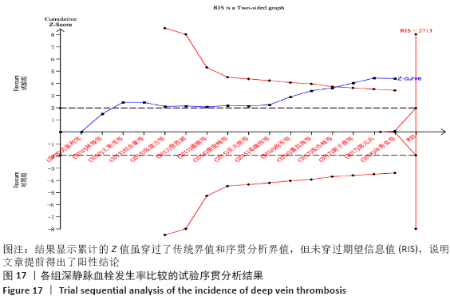
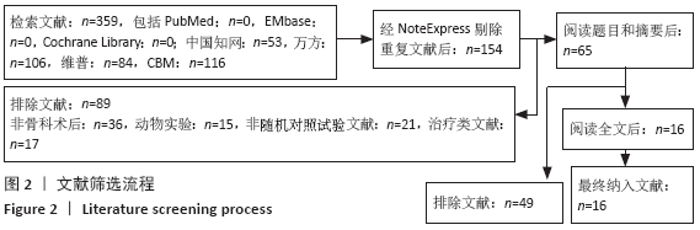
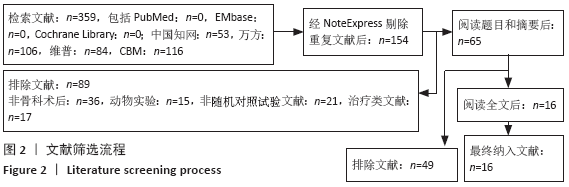
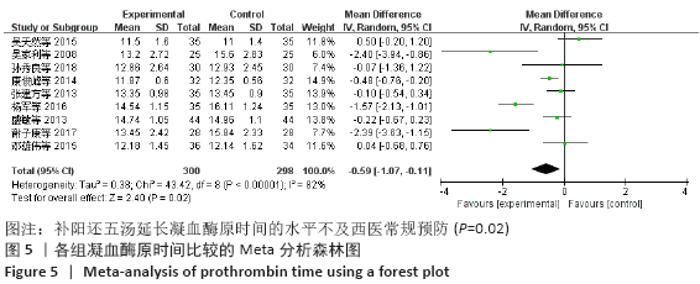
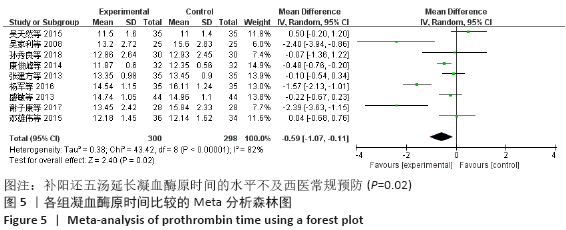
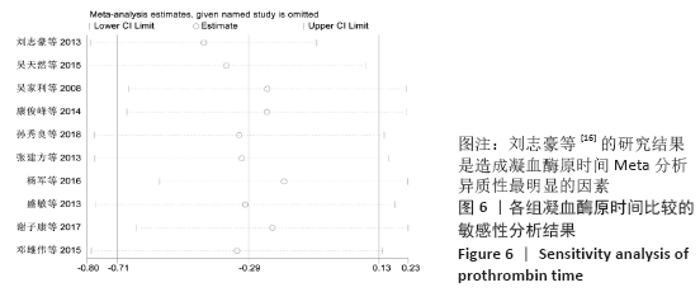
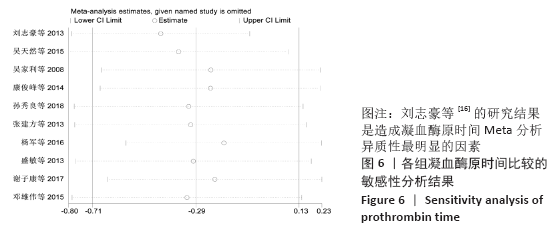
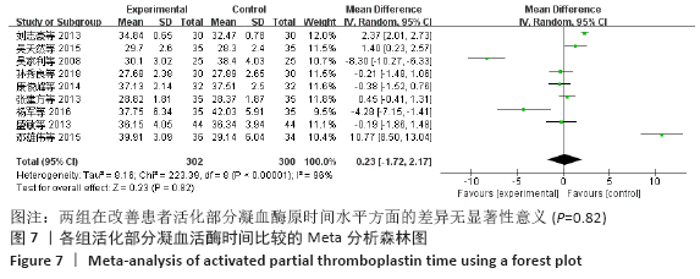
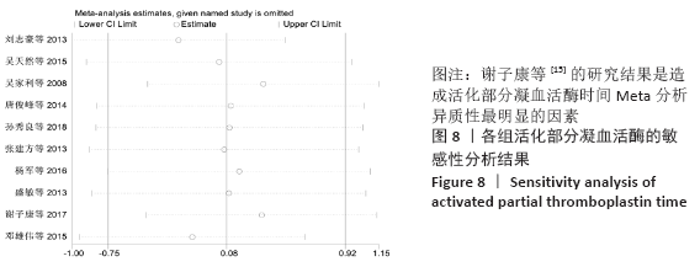
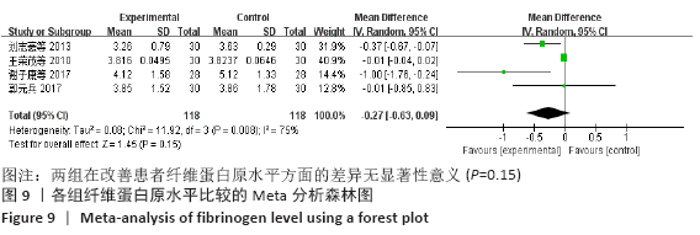
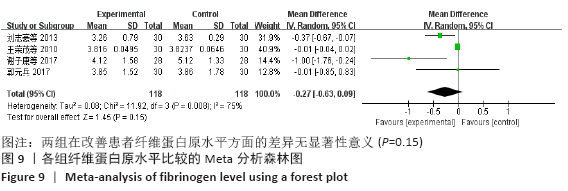
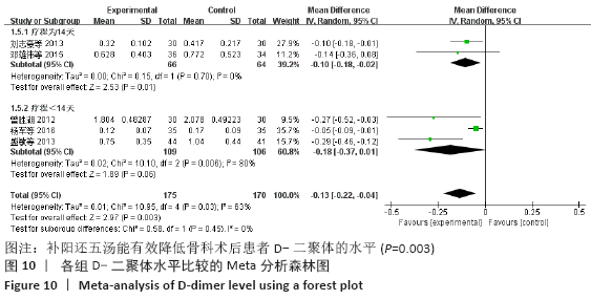
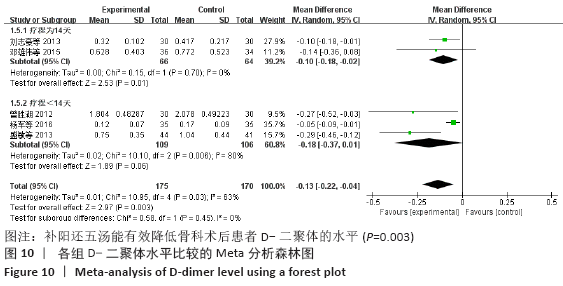
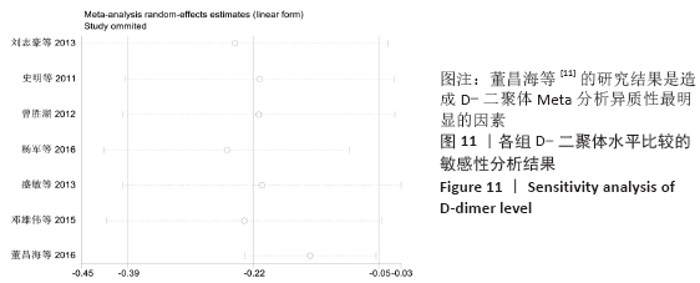
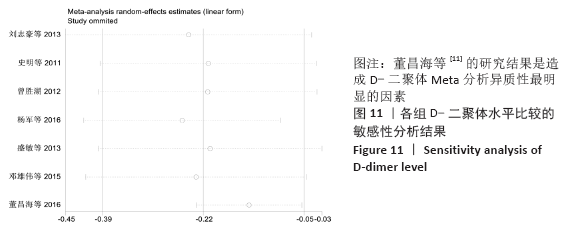
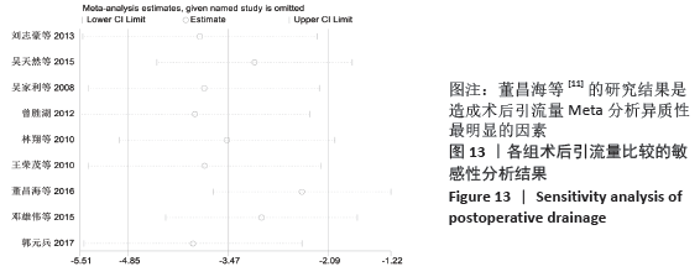
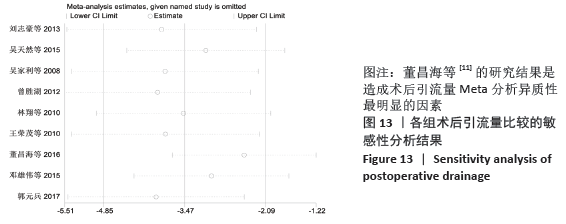
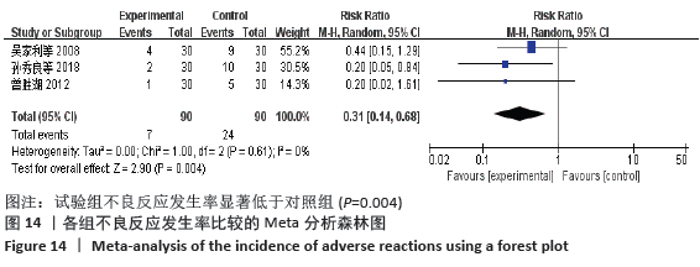
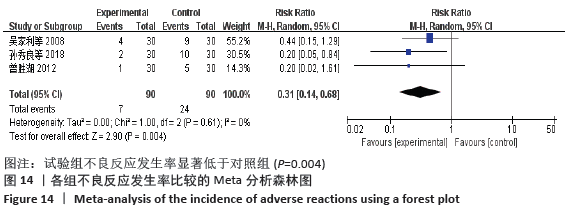
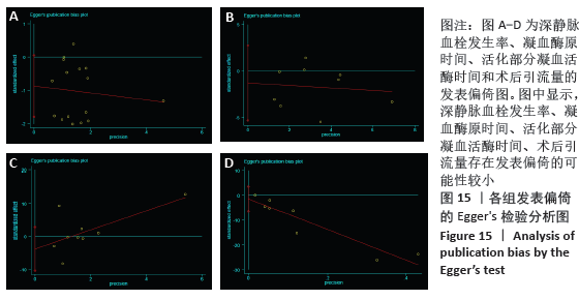
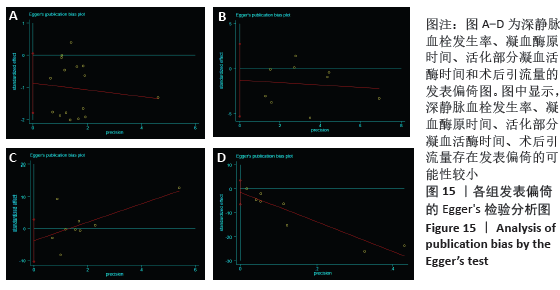
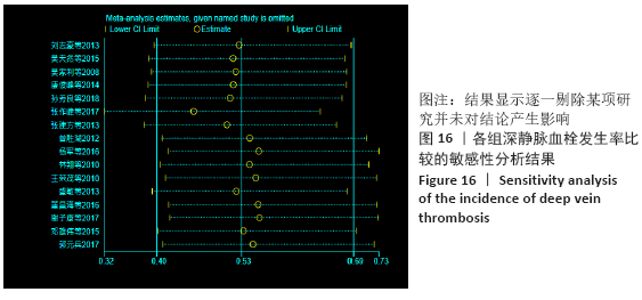
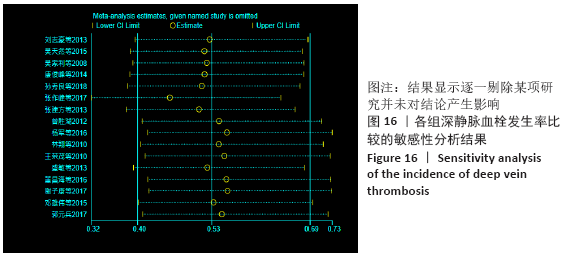
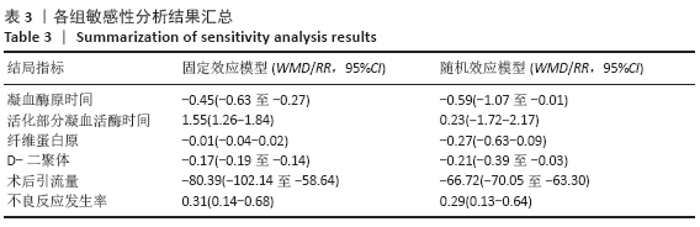
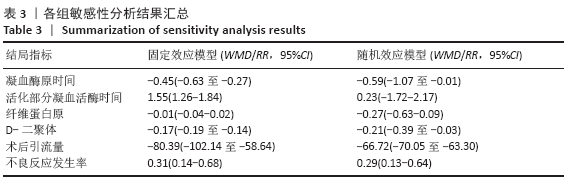
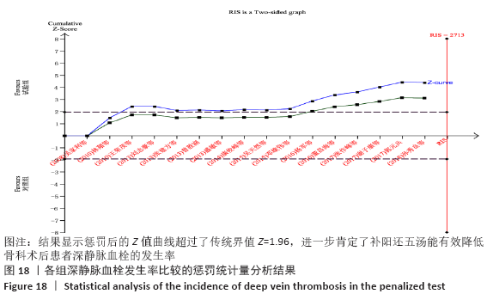
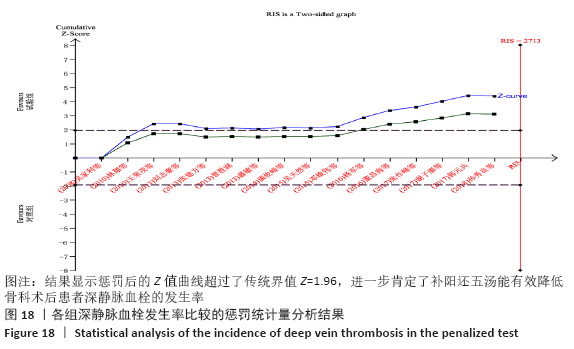
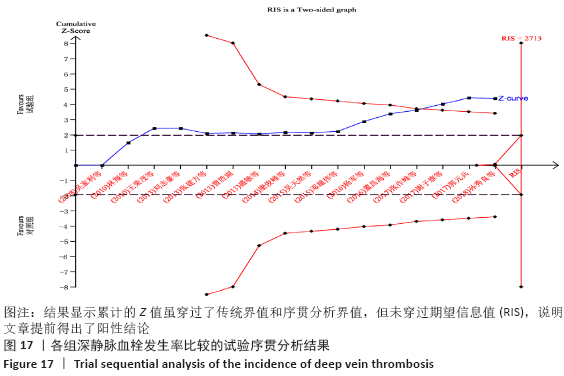
2.7 试验序贯分析结果 对报道深静脉血栓发生率的16个研究进行TSA探索分析。文章Ⅰ类错误率α=0.05,Ⅱ类错误率β=0.1,相对危险降低度(relative risk reduction,RRR)为20%,对照组相对事件发生率依据Meta分析数据定义为21.1%,信息轴设定为累积样本量,统计学效能为80%,样本量为期望信息值(RIS)。发现累计的Z值在纳入第13项研究后同时穿过了传统界值和TSA界值,未穿过RIS,提前得出了阳性结论,见图17。继续进行惩罚统计量分析,惩罚后的Z曲线超过了传统界值Z=1.96,也进一步肯定了补阳还五汤预防骨科术后患者发生深静脉血栓的临床疗效,见图18。通过比较Meta分析和TSA结果,可以发现Meta分析可能提前得出了假阳性结论,虽经TSA校正后,结论更为可信,但仍需纳入高质量的随机对照试验文献进行验证。 "
| [1] 李晓强,张福先,王深明.深静脉血栓形成的诊断和治疗指南(第三版)[J].中国血管外科杂(电子版),2017,9(4):250-257. [2] 田伟.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2):65-71. [3] HUTTON B, SALANTI G, CALDWELL DM, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions:checklist and explanations. Ann Int Med. 2015;162(11):777-784. [4] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组.创伤骨科患者深静脉血栓形成筛查与治疗的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(12):1013-1017. [5] 侯军其,何雅鸿.补阳还五汤对老年股骨粗隆间骨折防旋股骨近端髓内钉术后血栓相关并发症的影响[J].血栓与止血学,2017,23(5):778-779. [6] 孙元隆,阮小芬,李益萍,等.辨证论治应用芪苈强心胶囊对缺血性心力衰竭疗效影响的Meta分析比较[J].中国中药杂志,2019,44(22): 4975-4984. [7] 邓雄伟,徐南云,胡和军,等.补阳还五汤预防高龄股骨粗隆间骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成36例[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2015,13(17): 51-53. [8] 吴家利,洪汉刚,卢勇,等.补阳还五汤防治关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的疗效研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2008,16(1):19-22. [9] 孙秀良,王新杰,邵柳彬.补阳还五汤预防老年粗隆间骨折患者术后下肢DVT形成的临床研究[J].中医临床研究,2018,10(19):84-86. [10] 张作峰,王献印,程平平,等.补阳还五汤预防人工膝关节置换术后DVT形成55例临床观察[J].国医论坛,2017,32(5):32-33. [11] 董昌海,梁发树,李茂瑞.补阳还五汤防治骨科术后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].光明中医,2016, 31(21):3148-3149. [12] 吴天然,陈夏平,李铭雄,等.补阳还五汤预防老年股骨粗隆间骨折外支架术后DVT的形成[J].中医临床研究,2015,7(2):4-6. [13] 王荣茂,郭元兵,石树培,等.加味补阳还五汤预防膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,18(8):16-18,21. [14] 林翔,王荣茂,郭元兵,等.加味补阳还五汤预防人工全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓的研究[J].山西中医学院学报,2010,11(2):6-27. [15] 谢子康,杨晓峰,彭立波,等.补阳还五汤加减预防髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的效果分析[J].中国继续医学教育,2017,9(19):176-178. [16] 刘志豪,肖学峰,贾琼.补阳还五汤加味防治骨科术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].国际中医中药杂志,2013,35(11):982-984. [17] 盛敏,胡仕其,黄品强,等.中药预防高龄髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的临床观察[J].浙江中医杂志,2013,48(11):849-850. [18] 郭元兵.加味补阳还五汤预防下肢人工关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成[D].福州:福建中医学院,2007. [19] 康俊峰,张斌,陈健,等.加减补阳还五汤预防髋关节周围骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].中国保健营养(中旬刊),2014,24(3): 1271-1272. [20] 杨军,冯丽娜,贺自克.补阳还五汤对高龄股骨转子间骨折患者髋关节置换术后凝血与血液流变学指标的影响研究[J].世界中医药,2016, 11(6):1023-1026. [21] 张建方,金国强,姚航军,等.补阳还五汤加减预防髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].中医正骨,2013,25(2):19-21, 24. [22] 曾胜湖.中药预防全髋关节置换术后并发下肢深静脉血栓的临床研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2012. [23] 张玥.深静脉血栓形成“瘀热互结”病机浅析[J].中医杂志,2009,50(11):1049-1050. [24] MIRANDA AR, HASSOUNA HI. Mechanisms of thrombosis in spinal cord injury. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14(2):401-416. [25] 李超.止血带不同充气间断时间对全膝关节置换术后患者下肢深静脉血栓及凝血功能的影响[J].重庆医学,2018,47(20):2747-2748, 2752. [26] 赵艳立,郭茜,李晓英,等.老年患者全膝关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成相关危险因素探究[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2019,11(3): 85-89. [27] 肖红卫,王素伟.骨科深静脉血栓形成危险因素及发病机制的研究进展[J].医学信息(上旬刊),2010,23(8):3046-3048. [28] 卞敬琦,牛雯颖,冯月男,等.补阳还五汤对气虚血瘀模型血小板活化影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(2):43-46. [29] 牛雯颖,袁茵,邓思瑶,等.补阳还五汤对气虚血瘀模型大鼠血小板生物学指标的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(7):3261-3265. [30] 张鸿伟,洪虹,张社强,等.探讨纤维蛋白降解产物与D二聚体相关性在D二聚体检测中的应用[J].血栓与止血学,2020,26(2):215-217. [31] 杭欣,王春光,张帅,等.彩色多普勒超声联合D-二聚体对周围型下肢深静脉血栓筛查的价值[J].医学影像学杂志,2020,30(3):475-478. [32] 黄泳清,沈洁,袁思捷,等.红细胞分布宽度、纤维蛋白原与D-二聚体预测糖尿病足发生发展风险的价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(23):3716-3721. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||