Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 765-771.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology
Li Yonghua1, Feng Qiang1, Tan Renting1, Huang Shifu1, Qiu Jinlong1, Yin Heng2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Danzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Danzhou 571700, Hainan Province, China; 2Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-14Revised:2020-02-24Accepted:2020-03-25Online:2021-02-18Published:2020-12-01 -
Contact:Feng Qiang, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Danzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Danzhou 571700, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Li Yonghua, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Danzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Danzhou 571700, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81973878
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
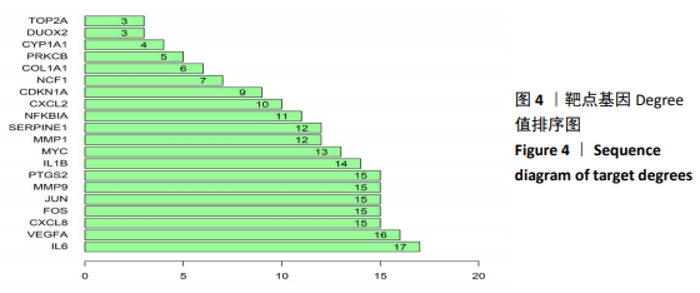
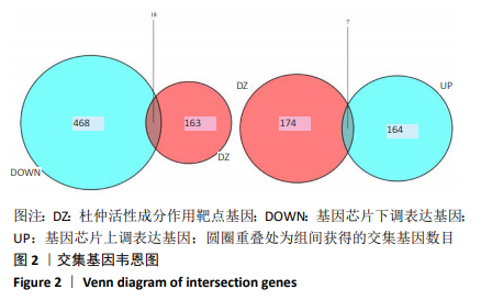
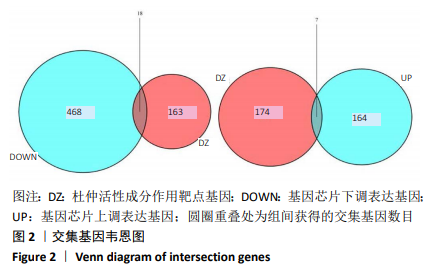
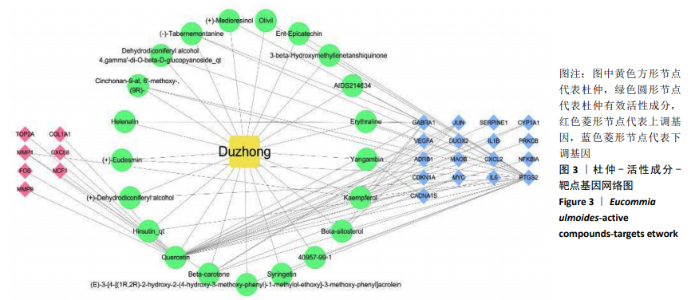
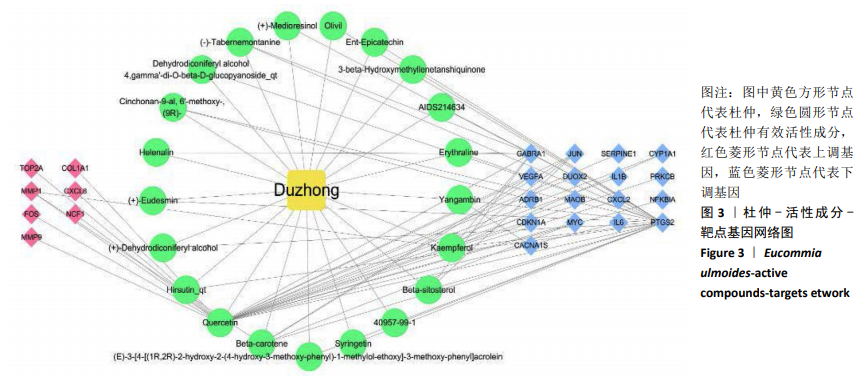
2.5 靶点基因互作网络关键基因筛选 将杜仲有效活性成分作用滑膜炎症病变差异表达基因25个上传至STRING网站,设置物种为“Homo sapiens”(人类),最小互作分数为0.4,运行靶点基因蛋白互作关系分析,将结果以TSV格式下载保存。通过R语言对靶点基因蛋白互作关系网络中靶点Degree值进行计算并排序,以条形图形式展现Degree值从高到低排名前20位的靶点基因及其Degree值,结果见图4。经计算,在差异基因互作网络中Degree值最高的是白细胞介素6(IL6),其次为血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、细胞趋化因子8(CXCL8)、FOS、JUN、基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP9)、PTGS2等,可能是杜仲活性成分调控膝骨关节炎滑膜炎症病变的关键基因。"
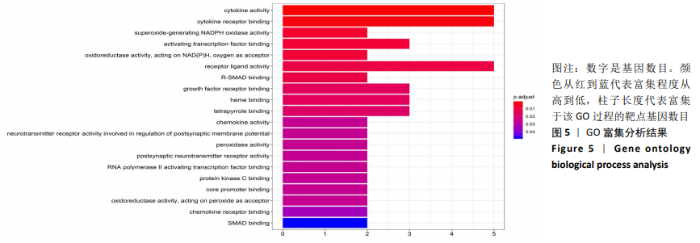
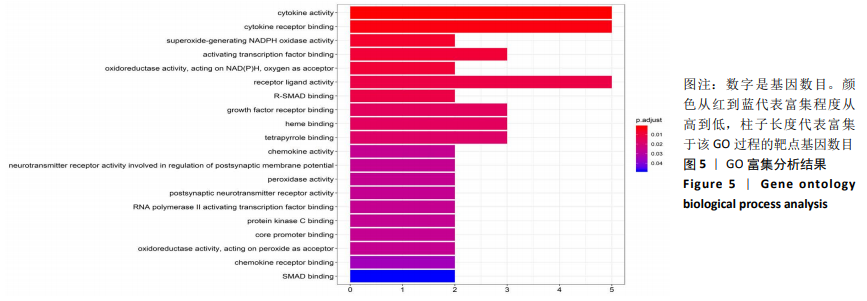
2.6 靶点基因GO富集分析 对杜仲有效活性成分作用滑膜炎症靶点基因进行整理,运行R语言Bioconductor clusterProfiler程序包对靶点基因进行GO富集分析[21],筛选检验统计P < 0.05的基因产物注释过程,并按照P值从小到大进行排序,展示排名前20的生物学过程,见图5。GO富集分析结果显示,靶点基因主要富集于细胞因子活性(Cytokine activity)、细胞因子受体结合(Cytokine receptor binding)、超氧化物-生成NADPH氧化酶活性(Superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activity)、激活转录因子结合(Activating transcription factor binding)、受体配体活性(Receptor ligand activity)、R-SMAD 结合(R-SMAD binding)、生长因子受体结合(Growth factor receptor binding)、血红素结合(Heme binding)等生物学过程。"
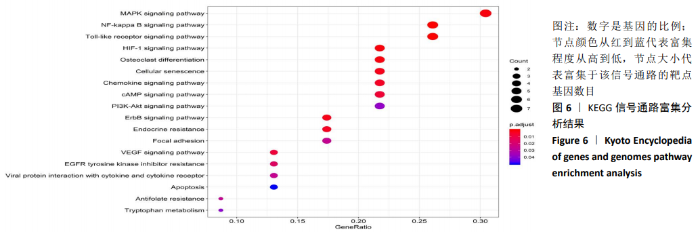
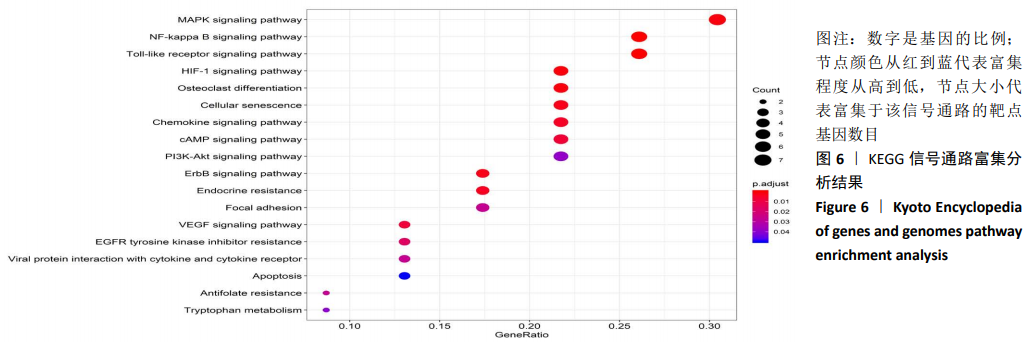
2.7 靶点基因KEGG通路富集分析 继续使用R语言Bioconductor clusterProfiler程序包对靶点基因进行KEGG通路富集分析,筛选出P < 0.05的富集信号通路,根据P 值从小到大排序,对排名前20的信号通路进行可视化展示,见图6。KEGG通路富集分析结果显示,靶点基因主要富集于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(MAPK signaling pathway)、核因子κB信号通路(NF-kappa B signaling pathway)、Toll样受体信号通路(Toll-like receptor signaling pathway)、缺氧诱导因子1信号通路(HIF- 1 signaling pathway)、破骨细胞分化信号通路(Osteoclast differentiation)、 细胞衰老信号通路(Cellular senescence)等通路。"
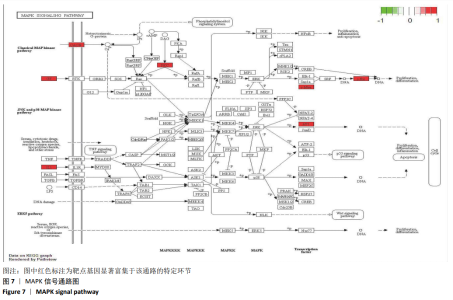
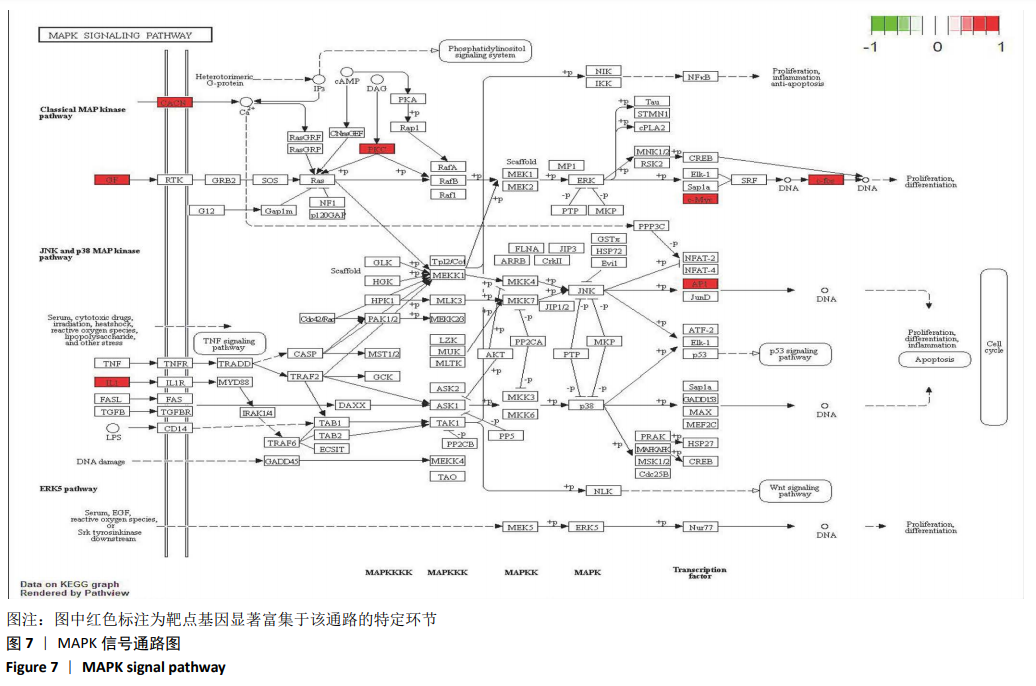
使用R语言Bioconductor Pathview程序包对靶点基因富集的KEGG信号通路进行细节展示[22],将P < 0.05的信号通路内容可视化,以便进一步了解靶点基因在各信号通路的各个阶段参与的信号转导过程。见图7,对靶点基因富集程度最高的MAPK信号通路细节展示,靶点基因CACNA1S、MYC、IL1B、FOS等分别富集于MAPK信号通路的不同环节,参与MAPK信号通路上下游的信号转导,调控基因转录、胞内外离子代谢等环节,并与肿瘤坏死因子信号通路(TNF signal pathway)、细胞增殖分化(Proliferation differentiation)、炎症(Inflammation)、细胞周期(Cell cycle)等产生级联信号转导沟通。"
| [1] CAI W, LI H, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis. Peer J.2020; 8(8390):1-18 [2] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18. [3] MIAO CG, YANG YY, HE X, et al. Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling. Cell Signal. 2013;25(10):2069-2078. [4] LI N, XU Q, LIU Q, et al. Leonurine attenuates fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 2017; 56(8): 1417-1427. [5] 陈卫衡,刘献祥,童培建,等.膝骨关节炎中医诊疗专家共识(2015年版) [J].中医正骨, 2015, 27(07): 4-5. [6] 梁子聪,易艾晶.基于文献数据挖掘调节膝骨关节炎炎症指标的中药内服方药用药规律研究[J]. 黔南民族医专学报, 2018, 31(2): 90-94. [7] 刘磊, 张舒, 周悦悦. 复方杜仲健骨颗粒联合硫酸氨基葡萄糖治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2019, 34(11): 3343-6. [8] 杨亚旭.蜂毒素联合杜仲黄酮治疗类风湿关节炎的实验研究[D].扬州:扬州大学, 2017. [9] 张彦琼,李梢.网络药理学与中医药现代研究的若干进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2015, 29(6): 883-92. [10] LIU H, WANG J, ZHOU W, et al. Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines: an example using licorice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;146(3): 773-793. [11] XU X, ZHANG W, HUANG C, et al. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13(6):6964-6982. [12] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines.J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [13] WANG S, WANG H, LU Y. Tianfoshen oral liquid: a CFDA approved clinical traditional Chinese medicine, normalizes major cellular pathways disordered during colorectal carcinogenesis.Oncotarget.2017;8(9): 14549-14569. [14] RITCHIE ME, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47. [15] SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498-2504. [16] LI J, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290. [17] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE A L, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1):D607-D613. [18] DE SANTIAGO I, CARROLL T. Analysis of ChIP-seq Data in R/Bioconductor.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1689:195-226. [19] DU J, YUAN Z, MA Z, et al. KEGG-PATH: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes-based pathway analysis using a path analysis model. Mol Biosyst. 2014;10(9):2441-2447. [20] PRESS OU. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D331-D338. [21] YU G, WANG L G, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters]. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287. [22] LUO W,BROUWER C.Pathview: an R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization.Bioinformatics. 2013;29(14):1830-1831. [23] 吕苏梅, 张瑞丽.中老年膝骨关节炎的流行病学研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(16):4133-5. [24] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9): 1263-1267. [25] O’NEILL TW, PARKES MJ, MARICAR N, et al. Synovial tissue volume: a treatment target in knee osteoarthritis (OA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(1):84-90. [26] ZHAI Y, GAO GD, XU SY. Basic research progress of knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(1):83-87. [27] 陈达,陈后煌,邵翔,等.乌头汤抑制骨关节炎炎症反应的作用机制探讨 [J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2016, 5(8): 62-66. [28] CENGIC T, TRKULJA V, PAVELIC SK, et al. Association of TGFB1 29C/T and IL6 -572G/C polymorphisms with developmental hip dysplasia: a case-control study in adults with severe osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2015;39(4): 793-798. [29] FUJIHASHI K, KONO Y, KIYONO H. Effects of IL6 on B cells in mucosal immune response and inflammation. Res Immunol. 1992;143(7): 744-749. [30] FRANCKHAUSER S, ELIAS I, ROTTER SOPASAKIS V, et al. Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia. 2008;51(7): 1306-1316. [31] PEARSON MJ, HERNDLER-BRANDSTETTER D, TARIQ MA, et al. IL-6 secretion in osteoarthritis patients is mediated by chondrocyte-synovial fibroblast cross-talk and is enhanced by obesity. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3451. [32] ZUPAN J, VRTACNIK P, COR A, et al. VEGF-A is associated with early degenerative changes in cartilage and subchondral bone. Growth Factors. 2018;36(5-6):263-273. [33] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain.J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924. [34] ERDEM H, PAY S, MUSABAK U, et al. Synovial angiostatic non-ELR CXC chemokines in inflammatory arthritides: does CXCL4 designate chronicity of synovitis? . Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(10):969-973. [35] YANG CC, LIN CY, WANG HS, et al. Matrix metalloproteases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in medial plica and pannus-like tissue contribute to knee osteoarthritis progression.PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79662. [36] LIN J, WU G, ZHAO Z, et al. Bioinformatics analysis to identify key genes and pathways influencing synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(6):5594-5602. [37] WANG D, QIAO J, ZHAO X, et al. Thymoquinone Inhibits IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPKs Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2015;38(6):2235-2241. [38] HASEEB A, HAQQI T M. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2013;146(3): 185-196. [39] WU L, HUANG X, LI L, et al. Insights on biology and pathology of HIF-1alpha/-2alpha, TGFbeta/BMP, Wnt/beta-catenin, and NF-kappaB pathways in osteoarthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(22):3293-3312. [40] ZHANG FJ, LUO W, LEI GH. Role of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in osteoarthritis. Joint bone spine.2015; 82(3): 144-147. [41] FERNANDEZ-TORRES J, MARTINEZ-NAVA GA, GUTIERREZ-RUIZ MC, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed. 2017;57(2):162-173. [42] NAIR A, KANDA V, BUSH-JOSEPH C, et al. Synovial fluid from patients with early osteoarthritis modulates fibroblast-like synoviocyte responses to toll-like receptor 4 and toll-like receptor 2 ligands via soluble CD14. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(7):2268-6877. [43] STANNUS O, JONES G, CICUTTINI F, et al. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(11):1441-1447. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||