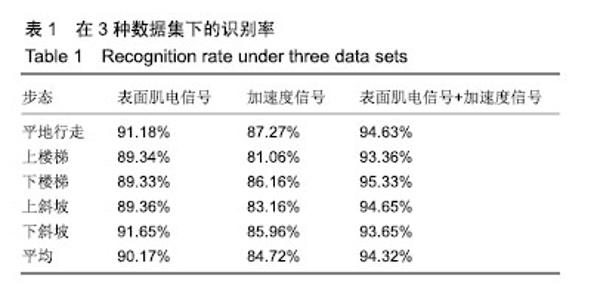
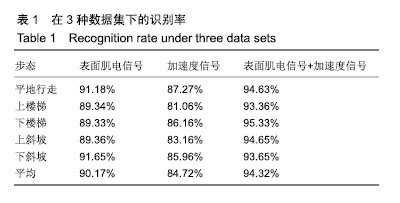
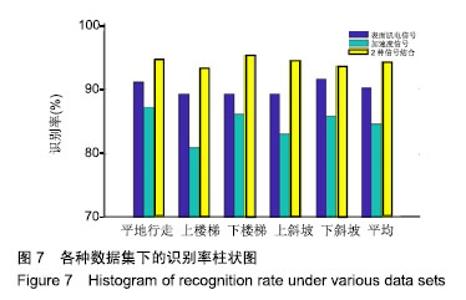
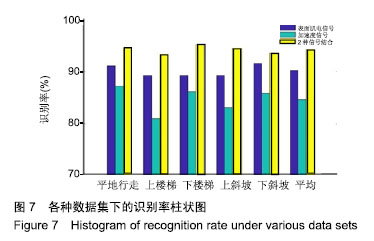
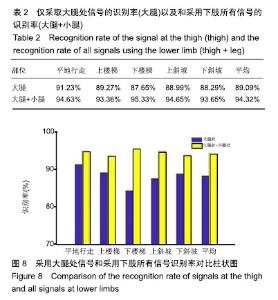
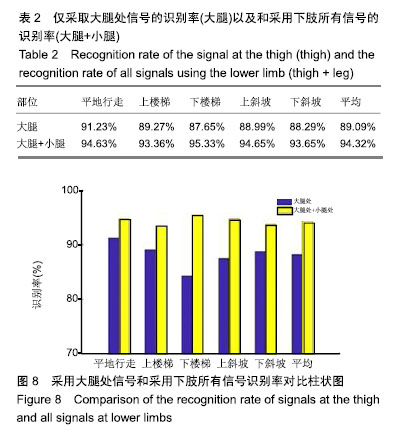
| [1] Langhorne P, Bernhardt J, Kwakkel G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet. 2011;377(9778):1693-1702. [2] 吴冬梅,孙欣,张志成,等.表面肌电信号的分析和特征提取[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(43):8073-8076. [3] Kyoung A, Huynh N. Intelligent switching control of a pneumatic muscle robot arm adopting learning vector quantization neural network. Mechatronics. 2007;17(4-5):902-905. [4] Li Z, Huang Z, He W, et al. Adaptive impedance control for an upper limb robotic exoskeleton using biological signals. IEEE Trans Industr Electr. 2017;64(2):1664-1674. [5] Capela NA, Lemaire ED, Baddour N. Improving classification of sit, stand, and lie in a smartphone human activity identification system. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA) Proceedings, 2015 :473-478. [6] Kim J, Wagner J, Rehm M, et al. Bi-channel Sensor Fusion for Automatic Sign Language Recognition. 2008 8th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition. 2008;1-2: 647-652 . [7] Li Y, Chen X, Zhang X, et al. A Sign-Component-Based Framework for Chinese Sign Language Recognition Adopting Accelerometer and sEMG Data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2012 ;59(10): 2695-2704. [8] 杨喜东.融合表面肌电和运动传感器信息的中国手语手势识别技术研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2016. [9] Roy SH, Cheng MS, Chang SS, et al. A combined semg and accelerometer system for monitoring functional activity in stroke. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2009;17(6): 585-594. [10] Zhang X, Chen X, Li Y, et al. A framework for hand gesture recognition based on accelerometer and emg sensors. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst Humans. 2011; 41(6): 1064-1076. [11] Zhuang Y, Lv B, Sheng X, et al. Towards Chinese sign language recognition using surface electromyography and accelerometers. 2017 24th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP). 2017 : 1-5. [12] 曹海婷,戎海龙,焦竹青,等.基于多特征组合的动态手势识别[J].计算机工程与设计,2018,39(6):1727-1732. [13] 张燕,郜鑫,陈玲玲,等.基于随机森林算法的地形识别系统在主动型膝上假肢控制中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(53): 8609-8614. [14] 俞毕洪. 基于表面肌电信号的穿戴式人体行为识别系统[D].杭州:浙江大学,2018. [15] 刘洪涛,曹玉珍,谢小波,等. 表面肌电信号的时变AR模型参数评估肌疲劳程度的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2007,26(4): 493-497. [16] Pei-Lin Z, Sheng L. Fault feature selection method based on wavelet and GA-PLS algorithm. J Vib Measure Diagn. 2014; 34(2): 385-391. [17] Batista P, Silvestre C, Oliveira P, et al. Accelerometer calibration and dynamic bias and gravity estimation: analysis design and experimental evaluation. IEEE Trans Contr Syst Technol. 2011; 5 :1128-1137. [18] Yang J, Pan J, Li J. sEMG-based continuous hand gesture recognition using GMM-HMM and threshold model, 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). 2017 :1509-1514. [19] Popov AA, Gultyaeva TA, Uvarov VE. Training hidden Markov models on incomplete sequences. 2016 13th International Scientific-Technical Conference on Actual Problems of Electronics Instrument Engineering (APEIE), 2016. [20] Li J, Lei T, Zhang F. An Gaussian-Mixture Hidden Markov Models for Action Recognition Based on Key Frame. 2018 11th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), 2018 : 1-5. |