Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3085-3090.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0276
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hemostatic agents in total knee arthroplasty: safety, curative efficacy and cost-effectiveness
Gao Cheng-zhe, Qu Yan-long
- Third Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Qu Yan-long, M.D., Chief physician, Associate professor, Third Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Gao Cheng-zhe, Master candidate, Third Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Cheng-zhe, Qu Yan-long . Hemostatic agents in total knee arthroplasty: safety, curative efficacy and cost-effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 3085-3090.
share this article
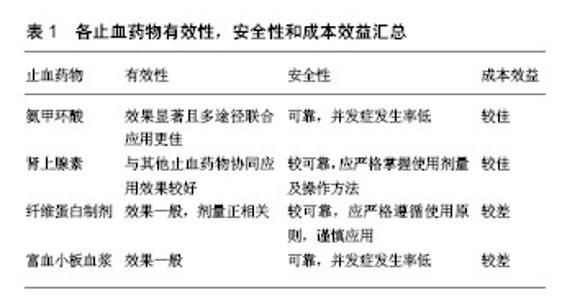
2.1 氨甲环酸 全膝关节置换围置换期失血直接原因是由手术创伤所致。然而与全髋关节置换不同,全膝关节置换过程中为保证术野清晰,常需使用止血带阻止置换区渗血,便于操作。虽然减少了置换过程中的出血,但止血带的使用破坏了纤溶-凝血间的平衡,进一步增强了纤溶作用[10]。故止血带应用所致的纤溶亢进也间接增加了全膝关节置换围置换期失血。因此,为恢复纤 溶-凝血间的动态平衡关系,减少全膝关节置换围置换期失血,使用纤溶抑制剂开始受到临床医生关注。 氨甲环酸作为一种纤溶抑制剂,最初被美国食品药品监督管理局批准用于减少血友病患者口腔手术过程中的出血,随后又普遍应用于心胸外科、妇产科等领域[11]。直到2010年,一项长达5年的全球性大规模临床研究,证实氨甲环酸可降低出血性创伤患者的死亡风险,可考虑将其应用于出血性创伤患者[12]。如今,氨甲环酸已广泛应用于骨科,特别是在人工关节置换术围置换期的应用。 氨甲环酸是一种合成的赖氨酸类似物,能竞争性的阻断纤溶酶原、纤溶酶和组织纤溶酶原激活物的赖氨酸结合位点,从而延缓了由纤溶酶介导的纤维蛋白分解,发挥抗纤溶作用,以此稳定膝关节腔内形成的血凝块不被纤溶酶分解,达到止血及减少出血的目的[13]。目前大量临床研究及Meta分析已经证实,全膝关节置换围置换期使用氨甲环酸对减少置换后出血量、降低输血率具有显著疗效,但对于氨甲环酸的最佳用药途径、剂量及时间,仍未形成统一标准,且对其使用的安全性也充满争议[14]。 2.1.1 氨甲环酸止血作用的有效性 由于静脉内用药能迅速增加并维持氨甲环酸的药物浓度,故氨甲环酸最常见的用法多为置换开始前或松止血带前静脉滴注10-30 mg/kg,置换后3 h再次于静脉内应用相同剂量的氨甲环酸。黄子达等[14]采用前瞻性自身对照方法分析静脉应用氨甲环酸的有效性,结果表明,松止血带前 10 min内静脉滴注10 mg/kg氨甲环酸能有效减少围置换期失血量、降低输血量及输血率。Xie等[15]设计了随机对照试验发现,通过全膝关节置换中作切口前静脉滴注氨甲环酸20 mg/kg联合置换后3,6 h分别再次使用氨甲环酸10 mg/kg除能显著减少隐性失血外,还能获得更小的血红蛋白下降幅度,更少的炎症反应、疼痛及膝关节肿胀,更好的膝关节功能和更短的住院时间。一项Meta分析证明,与安慰剂相比,静脉滴注氨甲环酸可以显著降低总失血量,并减少需要输血的患者数量,其中每位患者的同种异体输血量显著降低了平均144.85 mL[16]。与静脉用药相比,关节腔局部用药因其操作简便、定位可控及药物易集中到手术部位,正逐渐受到临床关注。Chen等[17]筛选了12个符合标准的随机对照试验进行分析研究,结果显示,与静脉使用氨甲环酸相比,局部应用氨甲环酸在置换后总失血量、引流量、输血率均产生了相似的结果。Lee等[18]设计了一项随机对照试验发现,对比静脉和局部应用氨甲环酸对置换后出血量的影响,结果表明,局部应用氨甲环酸后出血量比静脉应用更少,分别为(633±205) mL和(764±217) mL,均未有输血事件发生。Yozawa等[19]通过回顾性分析研究也证实了局部用药的优势。鉴于局部用药在止血方面产生了相似甚至更优的效果,并且为了能找到进一步减少出血的方法,有学者将两种用药途径结合来探讨氨甲环酸对全膝关节置换围手术期出血量的影响,发现这些临床试验均支持静脉与局部联合应用氨甲环酸,在减少全膝关节置换后总失血量、降低输血率、延缓血红蛋白下降程度及缩短住院日方面,显现了更优的临床效果[20-21]。 2.1.2 氨甲环酸止血作用的安全性 氨甲环酸理论上具有形成血栓的潜在风险,故使用氨甲环酸是否会增加静脉血栓形成风险一直备受争议。接受全膝关节置换的患者中有一部分曾有过静脉血栓栓塞的病史,这些既往病史往往令临床医生在使用氨甲环酸时变得更加谨慎。Sabbag等[22]回顾性分析了1 262例伴有静脉血栓栓塞病史的全髋关节置换或全膝关节置换患者,结果显示,与未使用氨甲环酸(1.8%;25/1 262;P=0.6)相比,在接受氨甲环酸(2.3%;6/258)的患者中,静脉血栓栓塞复发率并没有显著增加。作者进一步将31例复发性静脉血栓栓塞患者与对照组作2∶1匹配病例对照研究,得出结论,静脉应用氨甲环酸与增加的复发性静脉血栓栓塞风险(OR=0.9;P=0.9)无相关性,说明静脉使用氨甲环酸具有良好的安全性。随着局部用药方式的流行,也有学者通过研究发现,与静脉应用氨甲环酸相比,局部用药的系统吸收率可降低70%,可最大限度的减少静脉应用氨甲环酸可能带来的潜在系统并发症[1]。 无论是静脉、关节腔内局部还是两种途径联合应用,氨甲环酸均显现出良好的安全性,但曾有静脉应用氨甲环酸出现过敏反应的个案报道[23]。为了规避这种风险,口服用药似乎是一种新的尝试,不仅达到了静脉用药的止血效果,也最大限度的降低了静脉血栓形成的潜在风险[24]。Kayupov等[25]对89例接受全髋关节置换的患者随机分为口服氨甲环酸组和静脉滴注氨甲环酸组,结果也表明,2组置换后血红蛋白降低程度相似,在平均总失血量方面结果也相当,且2组均未发生静脉血栓栓塞事件。 2.1.3 氨甲环酸应用的成本效益 自氨甲环酸成功应用于全膝关节置换围手术期后,大量研究证实全膝关节置换后失血量明显降低,对于输血的需求也大幅度缩减,这不仅减少了患者在院期间并发症的发生率,也节约了医疗成本、提高了患者对手术效果的满意度[26]。与静脉及局部用药相比,口服氨甲环酸费用更加低廉、方便。 总的来说,氨甲环酸是一种成本低、效益高的止血药物。但是关于氨甲环酸的使用方案目前仍没有形成统一标准,更多的是根据医生的习惯来确定使用方法,结合多位学者的研究及临床经验,多阶段、多途径、多次数使用氨甲环酸能够更加有效的达到治疗目的[27-28]。尚需要更多的高质量临床试验确定最佳的使用方案,以让患者在承担最小的风险、更低的成本下获得更有效的治疗效果。 2.2 肾上腺素 研究表明,肾上腺素作为一种常见血管收缩剂,临床常利用其收缩局部血管的功能,配合其他药物使用以达到延长其他药物疗效的目的[29]。另有学者发现,肾上腺素能通过激活α2受体促进血小板聚集,继而促使血液凝固,减少局部失血[30]。考虑到肾上腺素的这些有利作用,越来越多的学者开始研究局部应用肾上腺素是否能减少全膝关节置换后失血,甚至有将稀释肾上腺素与其他止血药物联用来研究其对全膝关节置换置换期失血、输血率的影响[31]。 2.2.1 肾上腺素止血作用的有效性 Lombardi等[29]对2001年至2012年行全膝关节置换的171例患者(197膝)使用“鸡尾酒”(局麻药物、血管收缩剂等药物混合而成的镇痛制剂)减少置换后出血的有效性进行了评价。置换中将0.25%的布比卡因、肾上腺素、吗啡混合液注射到膝关节软组织及关节腔内,结果显示,试验组失血量明显低于对照组,并且认为这种简单、低廉的止血方案可以作为全膝关节置换围置换期失血管理的一种有效辅助手段。与之相反,Malone等[31]认为关节腔内灌注稀释肾上腺素对全膝关节置换后出血并无明显影响。Teng等[32]筛选了符合标准的4个随机对照试验和1个非随机对照试验进行分析,结果显示在人工关节置换中使用肾上腺素可显著降低置换后出血量。除了发现单独使用“鸡尾酒”具有减少置换后出血的潜能外,有学者研究全膝关节置换中将稀释肾上腺素与氨甲环酸联合局部应用的止血效果,Gao等[33]对100例行初次单侧全膝关节置换患者进行随机对照双盲试验研究,结果显示,稀释肾上腺素联合氨甲环酸在膝关节腔内的局部应用能显著降低全膝关节置换总体失血量(P=0.006)、隐性失血量(P=0.000)和输血率(0% vs.4%)。之后时利军等[34]也证实了稀释肾上腺素联合氨甲环酸在关节腔内局部应用的良好止血效果,不管在总失血量、隐性失血量以及置换后异体输血率等方面,联合用药组都明显优于单纯局部应用氨甲环酸组。 2.2.2 肾上腺素止血作用的安全性 作为血管收缩剂,应用肾上腺素理论上会有皮肤坏死、升高血压、形成血栓等风险[35]。Tanaka等[36]认为膝关节腔内局部注射稀释肾上腺素不但止血效果不显著,且长时间应用有增加伤口周围皮肤坏死的风险。Yu等[37]对5项随机对照试验的荟萃分析结果证实,目前这些研究( 5个临床随机对照试验,共493例患者)并不能证实稀释肾上腺素联合氨甲环酸会增加静脉血栓栓塞的风险。综上,通过一定比例的稀释及掌握正确的应用方法(避免注射至皮下),全膝关节置换中局部应用肾上腺素能够较安全的且有效的达到止血目的。 2.2.3 肾上腺应用的成本效益 全膝关节置换围置换期镇痛管理已逐渐受到临床医师的关注,其中应用“鸡尾酒”镇痛是目前全膝关节置换围置换期镇痛比较流行的方法之一。据报道,将“鸡尾酒”注射到膝关节滑膜、关节囊等部位具有止痛效果好、易操作、成本效益高、不良反应少等优势[38-39]。虽然关于“鸡尾酒”药物配方的黄金标准尚未成立,但肾上腺素因其收缩血管作用良好且价格低廉、应用方便等因素,是最常见的配方之一。故合理利用“鸡尾酒”行关节周围注射不仅实现了镇痛管理也达到了止血目的,极大的降低了医疗成本,具有良好的成本效益。 虽然全膝关节置换中应用肾上腺素具有一定可行性,但目前关于肾上腺素临床应用的统一标准还未得到专家共识,仍需更多前瞻性对照试验来完善。 2.3 纤维蛋白制剂 纤维蛋白制剂近几年逐渐扩展到骨科领域,用于减少出血和输血,促进创口愈合,加速术后康复,正逐渐被人工关节置换领域所关注[40]。目前临床上应用的纤维蛋白制剂种类繁多,如纤维蛋白封闭剂、止血基质等。纤维蛋白封闭剂是最常用的一种局部纤维蛋白制剂,主要由两部分构成即机械成分(凝胶基质)和化学成分(人源纤维蛋白源和凝血酶)。纤维蛋白封闭剂的作用机制是通过机械成分起到黏附、封闭出血点;同时通过化学成分再现凝血步骤中最后环节即当纤维蛋白原与凝血酶两种成分混合时,纤维蛋白原被转化成纤维蛋白单体,继而在凝血因子ⅩⅢa和纤维连接蛋白的作用下,纤维蛋白单体交联成网,稳定凝血块,共同达到止血、促进创口愈合的作用。 2.3.1 纤维蛋白制剂止血的有效性 Notarnicola等[41]对90例接受全膝关节置换的患者随机分为3组(低剂量纤维蛋白制剂、高剂量纤维蛋白制剂、对照组),结果表明,与对照组相比,纤维蛋白制剂组能有效延缓置换后血红蛋白下降,显著降低输血率,然而低剂量与高剂量组间在减少出血、降低输血率方面并无显著差异。Wang等[42]筛选了8个符合标准的随机对照试验进行分析研究,结果表明,在全膝关节置换中应用纤维蛋白制剂可显著减少置换后引流量、延缓置换后血红蛋白下降及降低输血需求。Reinhardt等[43]将局部应用EVICELTM与关节周围注射肾上腺素作对照,结果表明,两者在减少总失血量方面相当,但在降低输血率及输血量方面,应用EVICELTM的效果更明显,且证实EVICELTM与QUIXILTM在减少出血量、降低输血率方面产生了相似的结果。相反,Li等[44]通过回顾性分析证实,虽然EVICELTM能够减少总出血量、引流量和降低输血率,但效果不如QUIXILTM,这可能与EVICELTM成分中缺少氨甲环酸有关。 尽管纤维蛋白制剂的止血效应在人工关节置换领域已经得到了大量研究的支持,但相当一部分学者对纤维蛋白制剂止血的有效性提出质疑。Randelli等[45]设计了一项随机对照试验,对比局部应用(EVICELTM)和安慰剂对初次全膝关节置换后出血量的影响,结果表明,两组置换后总出血量无显著差异,输血率两组间差异无显著性意义。之后Schwab等[46]进行的一项回顾性研究也得出相似的结论。 研究结果间的差异性可能与研究机构间关于纤维蛋白制剂的用药方案不同,甚至研究试验设计间的差异相关,故尚需更多高质量研究制定出统一用药方案,进而评价纤维蛋白制剂止血作用的有效性。 2.3.2 纤维蛋白制剂止血作用的安全性 由于纤维蛋白制剂理论上也存在形成血栓的风险,故不断有学者对应用纤维蛋白制剂的安全性进行分析研究。Wang等[45]通过研究发现,在全膝关节置换术中应用纤维蛋白制剂并没有增加静脉血栓栓塞、膝关节肿胀、伤口感染等形成的风险和其他相关并发症。另外,意大利药品监管局提出,使用纤维蛋白制剂时的喷洒压力控制在200- 250 kPa以内,喷洒最小距离在10-15 cm范围,并在使用过程中监测患者的生命体征[47]。 2.3.3 纤维蛋白制剂应用的成本效益 Molloy等[48]对150例行全膝关节置换的患者随机分为3组(氨甲环酸、纤维蛋白制剂、对照组),结果显示,与对照组相比,氨甲环酸和纤维蛋白制剂两组在减少置换后失血量、降低输血率方面均显示出了良好的临床效果,但两组间对比无明显差异。在药物的花费上,作者所在机构平均每个患者使用氨甲环酸花费约4英镑,而纤维蛋白制剂高达380英镑,故认为,纤维蛋白制剂虽然表现出良好的止血效果,但不具有较佳的成本效益。由于纤维蛋白制剂花费与使用剂量正相关,因此按需使用,降低医疗成本是很有必要的。 关于纤维蛋白制剂使用与否及应用方案目前仍不能得出决定性的结论,但部分学者通过研究给出了使用纤维蛋白制剂的建议: 纤维蛋白制剂作为一种支持治疗手段具有一定可行性。有研究表明,于假体安装前、冲洗关节腔后,将纤维蛋白制剂喷洒于截骨面渗血处;假体安装后、缝合关节囊前,将纤维蛋白制剂喷洒于假体凹槽、关节囊周围,可有效减少置换后出血量,特别是作为常规止血操作不充分时的一种支持治疗[49]。 2.4 富血小板血浆 富血小板血浆是获取自体全血通过离心等技术制成的富含血小板、纤维蛋白及多种生长因子的血浆制剂,如今在骨科领域多用于韧带、肌腱、关节软骨损伤及骨缺损等损伤的修复[50]。众所周知,当血管受损害时,机体出于自身保护,会启动凝血与止血机制,其中主要是血小板在起作用。血小板通过黏附、聚集、释放等功能,起到收缩血管、形成止血栓、抑制纤溶活动等作用,最终实现凝血与止血。 2.4.1 富血小板血浆止血作用的有效性 Bernasek等人[51]回顾性分析了392例行全膝关节置换的患者,这些患者被分为4组(“鸡尾酒”镇痛组、纤维蛋白制剂组、富血小板血浆组及对照组),以探讨它们对置换后引流量、血红蛋白水平及输血率的影响,结果显示,富血小板血浆虽然能减少置换后引流量,但对置换后血红蛋白、输血率无明显影响。Tingstad等[52]也认为在全膝关节置换期间使用富血小板血浆不会减少围置换期失血量。相反,Mochizuki等[53]通过全膝关节置换术中关节腔内使用富血小板血浆,置换后留置引流管并夹闭1 h的方法进行研究,结果表明,富血小板血浆可以使全膝关节置换患者围置换期出血量显著降低并延缓置换后血红蛋白下降。作者通过引流管夹闭的方式一定程度上防止了关节内富血小板血浆的流失,延缓了富血小板血浆的作用时间,这可能是其试验结果不同于其他研究结果的因素之一。 2.4.2 富血小板血浆止血作用的安全性 国内学者董佩龙等[54]通过研究发现,全髋关节置换结束时将富血小板血浆和血凝酶喷涂于创面,另喷涂同等剂量的生理盐水和血凝酶作对照,结果表明,全髋关节置换中使用富血小板血浆可减少置换后引流量同时不增加置换后皮肤相关并发症。另外,最近Ma等[55]对6篇文献中529例全膝关节置换患者置换后失血量及血红蛋白水平进行荟萃分析得出,应用富血小板血浆并未增加置换后并发症的发生。而且富血小板血浆是获取自体全血制成的血浆制剂,故不具有免疫排斥性,能较安全的在临床上应用。 2.4.3 富血小板血浆应用的成本效益 富血小板血浆目前主要应用于骨科领域包括骨、软骨、肌腱、韧带损伤等疾病的相关治疗,尽管近年来不断有研究表明富血小板血浆可以用于减少全膝关节置换后失血,但在人工关节置换领域的使用还属探索阶段,关于其临床疗效及安全性的报道仍存争议,特别是其制作环节复杂,需要额外产生医疗成本,不具有良好的成本效益,故不推荐将富血小板血浆作为全膝关节置换中止血的常规用药,其应用的可行性仍值得进一步探讨(表1)。 "

| [1] Wong J, Abrishami A, El Beheiry H, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces rostoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(15):2503-2513.[2] Carling MS, Jeppsson A, Eriksson BI, et al. Transfusions and blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective observational study. J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10(1):48.[3] Wang JW, Chen B, Lin PC, et al. The efficacy of combined use of rivaroxaban and tranexamic acid on blood conservation in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty a double-blind randomized, controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3):801-806.[4] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565.[5] Sarzaeem MM, Razi M, Kazemian G, et al. Comparing efficacy of three methods of tranexamic acid administration in reducing hemoglobindrop following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(8):1521-1524. [6] Song EK, Seon JK, Prakash J, et al. Combined Administration of IV and topical tranexamic acid is not superior to either individually in primary navigated TKA. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(1):37-42.[7] Friedman R, Homering M, Holberg G, et al. Allogeneic blood transfusions and postoperative infections after total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(4):272-278.[8] Liu D, Dan M, Martinez Martos S, et al. Blood management srategies in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016; 28(3):179-187.[9] Bedard NA, Pugely AJ, Lux NR, et al. Recent trends in blood utilization after primary hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(3): 724-727.[10] Marra F, Rosso F, Bruzzone M, et al. Use of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. Joints. 2016; 04(04):202-213.[11] Napolitano LM, Cohen MJ, Cotton BA, et al. Tranexamic acid in trauma: how should we use it ? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013; 74(6): 1575-1586.[12] Shakur H, Roberts I, Bautista R, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid on death, vascular occlusive events, and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant haemorrhage (CRASH-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010; 376: 23-32.[13] Kushioka J, Yamashita T, Okuda S, et al. High-dose tranexamic acid reduces intraoperative and postoperative blood loss in posteriorlumbar interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017; 26(3):363-367. [14] 黄子达,张文明,李文波,等.氨甲环酸减少人工全膝关节置换术后失血量的自身对照研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(3): 280-283.[15] Xie J, Ma J, Yao H, et al. Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet: a randomized clinical trial. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31: 2458-2464.[16] He P, Zhang Z, Li Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in bilateral total knee replacement: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21:3634-3642.[17] Chen T, Chen Y, Jiao J, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):11.[18] Lee S Y, Chong S, Balasubramanian D, et al. What is the ideal route of administration of tranexamic acid in TKA? a randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017; 475(8):1987-1996. [19] Yozawa S, Ogawa H, Matsumoto K, et al. Peri-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and the necessity for allogeneic transfusion after total knee arthroplasty using autologous transfusion: a retrospective observational study. J Arthroplasty.2017;33(1):86-89. [20] Li JF, Hang L, Hui Z, et al. Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):22.[21] Zhang XQ, Ni J, Ge WH,et al.Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total joint arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Surg.2017;38:15-20.[22] Sabbag OD, Abdel MP, Amundson AW, et al. Tranexamic acid was safe in arthroplasty patients with a history of venous thromboembolism: a matched outcome study. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9):S246-S250.[23] Lucas-Polomeni MM, Delaval Y, Menestret P, et al. A case of anaphylactic shock with tranexamic acid (Exacyl). Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2004; 23:607-609.[24] Fillingham Y A, Kayupov E, Plummer D R, et al. The James A. Rand young investigator's award: a randomized controlled trial of oral and intravenous tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: the same efficacy at lower cost? J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(9):26-30.[25] Kayupov E, Fillingham Y A, Okroj K, et al. Oral and intravenous tranexamic acid are equivalent at reducing blood loss following total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99(5):373-378.[26] Gillette BP, Maradit Kremers H, Duncan CM, et al. Economic impact of tranexamic acid in healthy patients undergoing primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty, 2013, 28(8):137-139.[27] Iwai T, Tsuji S, Tomita T, et al. Repeat-dose intravenous tranexamic acid further decreases blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(3):441-445.[28] Lei Y, Xie J, Xu B, et al. The efficacy and safety of multiple-dose intravenous tranexamic acid on blood loss following total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2017;41(10):2053-2059.[29] Lombardi AV, Berend KR, Mallory TH, et al. Soft tissue and intra-articular injection of bupivacaine, epinephrine, and morphine has a beneficial effect after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428:125-130.[30] Yun-Choi HS, Park KM, Pyo MK. Epinephrine induced platelet aggregation in rat platelet-rich plasma. Thromb Res. 2000; 100(6):511-518.[31] Malone KJ, Matuszak S, Mayo D, et al. The effect of intra-articular epinephrine lavage on blood loss following total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2009; 32(2):100.[32] Teng Y, Ma J, Ma X, et al. The efficacy and safety of epinephrine for postoperative bleeding in total joint arthroplasty: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine. 2017; 96(17):e6763.[33] Gao F, Sun W, Guo W, et al. Topical Administration of tranexamic acid plus diluted-epinephrine in primary total knee arthroplasty: a randomized double-blinded controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(8): 1354-1358.[34] 时利军,白禹,高福强,等.鸡尾酒疗法减少全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,21(48):329-334.[35] Gasparini G, Papaleo P, Pola P, et al. Local infusion of norepinephrine reduces blood losses and need of transfusion in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2006; 30:253-256.[36] Tanaka N, Sakahashi H, Sato E, et al. Timing of the administration of tranexamic acid for maximum reduction in blood loss in arthroplasty of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83:702-705.[37] Yu Z, Yao L, Yang Q, et al. Tranexamic acid plus diluted-epinephrine versus tranexamic acid alone for blood loss in total joint arthroplasty:A meta-analysis. Medicine. 2017; 96(24):e7095.[38] Gibbs DM, Green TP, Esler CN, et al. The local infiltration of analgesia following total knee replacement: a review of current literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94(9):1154-1159.[39] Jiang J, Teng Y, Fan Z, et al. The efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection for postoperative pain management in total knee or hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(10):1882-1887.[40] Jackson MR, MacPhee MJ, Drohan WN, et al. Fibrin sealant: current and potential clinical applications. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.1996; 7(8): 737-746.[41] Notarnicola A, Moretti L, Martucci A, et al. Comparative efficacy of different doses of fibrin sealant to reduce bleeding after total knee arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.2012;23(4):278-284.[42] Wang H, Shan L, Zeng H, et al. Is fibrin sealant effective and safe in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9:36.[43] Reinhardt KR, Osoria H, Nam D,et al. Reducing blood loss after total knee replacement: a fibrin solution. Bone Joint J.2013;95-B (supplA):135-139.[44] Li Jie, Li H B, Zhao X C, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of fibrin sealant in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Int J Surg. 2016; 36(Pt A):127-137. [45] Randelli F, D’Anchise R, Ragone V, et al. Is the newest fibrin sealant an effective strategy to reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty? a randomized controlled study. J Arthroplasty.2014;29(8):1516-1520.[46] Schwab P E, Thienpont E. Use of a haemostatic matrix (Floseal®) does not reduce blood loss in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty performed under continued aspirin. Blood Transfus. 2016; 14(2):134-139.[47] Sabatini L, Trecci A, Imarisio D, et al. Fibrin tissue adhesive reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2012;13(3):145-151.[48] Molloy D, Archbold H L, Mcconway J, et al. Comparison of topical fibrin spray and tranexamic acid on blood loss after total knee replacement: a prospective, randomised controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(3):306-309.[49] Budde S, Noll Y, Zieglschmid V, et al. Determination of the efficacy of EVICELTM on blood loss in orthopaedic surgery after total knee replacement: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16(1):1-10.[50] 付维力,李棋,李箭,等.富血小板血浆在临床骨科中的应用进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(10):1311-1316.[51] Bernasek TL, Burris RB, Fujii H, et al. Effect on blood loss and cost-effectiveness of pain cocktails, platelet-rich plasma, or fibrin sealant after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8): 1448-1451.[52] Tingstad EM, Bratt SN, Hildenbrand KJ, et al. Platelet-rich plasma does not decrease blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2015;38(5):e434.[53] Mochizuki T, Yano K, Ikari K, et al. Platelet-rich plasma for the reduction of blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a clinical trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016; 26(8):901-905.[54] 董佩龙,唐晓波,王健,等.富血小板血浆对人工全髋关节置换术创面愈合的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(4):432-434.[55] Ma JH, Sun JL, Guo WH, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on reducing blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Medicine. 2017; 96(26):e726. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [6] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [7] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [8] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [9] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [12] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [13] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [14] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [15] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||