Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (3): 336-342.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0027
Previous Articles Next Articles
Management of perioperative blood loss applied in unicompartment knee arthroplasty
Cui Ke-ke1, Yang Wei-yi2, Liu Jun2, Pan Jian-ke2, Zhang Bao-qing2, Zhang Xiao-liang1, Cao Xue-wei2
- 1School of Second Clinical Medicine of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2018-01-28Published:2018-01-28 -
Contact:Cao Xue-wei, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Cui Ke-ke, Studying for master’s degree, School of Second Clinical Medicine of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81473698; Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China, No. 20124425110004; the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, No. 2011B031700027; Project of Department of Finance of Guangdong Province, No. [2014]157; Traditional Chinese Medicine Bureau of Guangdong Province, No. 20164020; Science Research Project of Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, No. YK2013B2N19 and YN2015MS15
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cui Ke-ke, Yang Wei-yi, Liu Jun, Pan Jian-ke, Zhang Bao-qing, Zhang Xiao-liang, Cao Xue-wei. Management of perioperative blood loss applied in unicompartment knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(3): 336-342.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
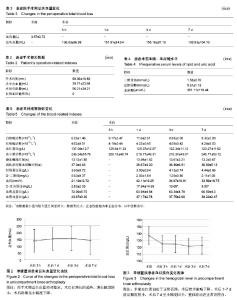
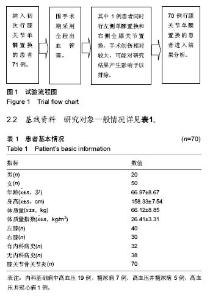
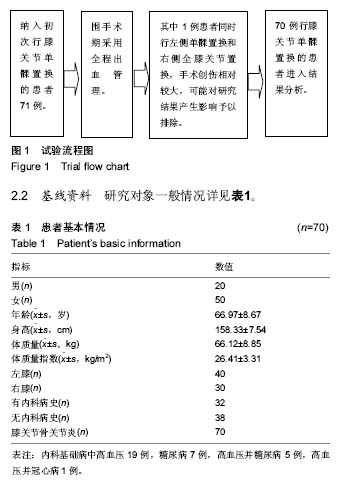
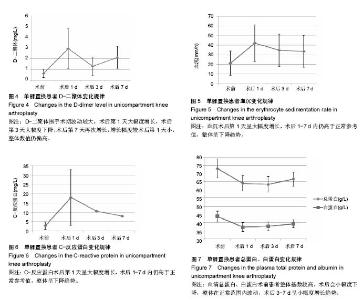
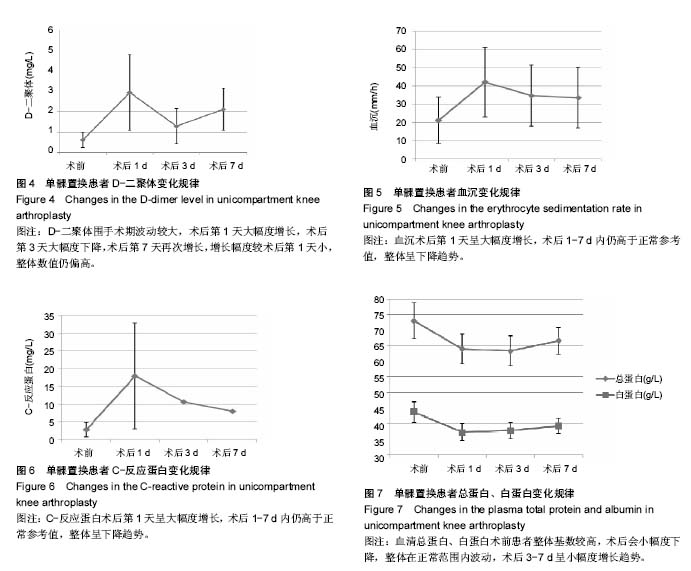
2.3 手术时间与出血量、术后引流量的影响 患者手术时间?术中出血量?术后引流量?术中自体血回输率情况详见表2?手术时间对术中出血量的影响,假设t 检验结果,t=0.406 5,P=0.685 7 > 0.05,无统计学意义,提示手术时间与术中出血无明显相关性;手术时间对术后引流量的影响,假设t 检验结果,t=-2.351 3,P=0.021 6 < 0.05,有统计学意义,提示手术时间与术后引流量存在相关性;患者围手术期动态血液检测?临床症状和体征无进行性失血及贫血表现,所有研究对象住院期间均未进行术中自体血回输及异体血回输,总输血率为0。 2.4 血容量与术后总失血量 单髁置换患者血容量?术后总失血量变化详见表3及图2,经检验,术后3 h?1 d?3 d和7 d总出血量之间对比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)?单髁置换围手术期总失血量相对稳定,术后3 d内有进一步增长的趋势,增长幅度较小,3 d后呈小幅度下降,提示微创膝关节单髁置换出血量小、总失血量少。 2.5 术前血脂、尿酸水平 研究对象术前三酰甘油?总胆固醇和血尿酸值偏高,详见表4。检验术前三酰甘油水平对术后1,3,7 d总失血量的影响,假设t 检验,结果P=0.257 9,0.249 5,P=0.967 8,均 > 0.05,差异无显著性意义;总胆固醇水平对术后1,3,7 d总失血量的影响,假设t 检验,结果P=0.740 5,0.989 8,0.462 5 ,均 > 0.05,差异无显著性意义? 2.6 其他观察指标及变化规律 术前?术后白细胞计数、红细胞计数、红细胞比积、血小板计数、C-反应蛋白、血沉、凝血3项、D-二聚体、总蛋白、白蛋白情况详见表5及图3-7。单髁置换患者围手术期白细胞计数术后1-7 d较术前增多,术后1 d增长幅度稍大,术后3-7 d仍稍高于术前,整体呈下降趋势;血小板计数围手术期轻微波动于正常范围内,术后7 d基本可恢复至术前水平;凝血酶原时间?活化部分凝血活酶时间?纤维蛋白原术后较术前会有小幅度波动,基本波动于正常范围内,纤维蛋白原术后3-7 d较术前、术后1-3 d有增长趋势。所有研究对象术前血红蛋白处于正常范围,均无纠正贫血治疗,术后红细胞计数和血红蛋白变化情况基本相符,术后较术前略下降,术后1-7 d波动幅度较小,术后7 d呈小幅度回升,整体波动在正常范围内。D-二聚体围手术期波动较大,术后第1天大幅度增长,术后第3天大幅度下降,术后第7天再次增长,增长幅度较术后第1天小,整体数值仍偏高。血沉、C-反应蛋白术后第1天呈大幅度增长,术后1-7 d内仍高于正常参考值,整体呈下降趋势。血清总蛋白?白蛋白术前患者整体基数较高,术后小幅度下降,整体在正常范围内波动,术后3-7 d呈小幅度增长趋势?"
| [1] 王一鸣, 王琦,张先龙. 膝关节单髁置换术的适应证及远期疗效综述[J]. 中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2016, 10(3): 88-92.[2] 张启栋,郭万首,刘朝晖,等. 内翻畸形膝骨关节炎软骨磨损的临床研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(23): 2345-2350.[3] Arno S, Maffei D, Walker PS, et al. Retrospective analysis of total knee arthroplasty cases for visual, histological, and clinical eligibility of unicompartmental knee arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8): 1396-403.[4] Satku K. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: is it a step in the right direction?--Surgical options for osteoarthritis of the knee. Singapore Med J. 2003;44(11): 554-556.[5] Craik JD, El Shafie SA, Singh VK, et al. Revision of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(4): 592-594.[6] Lyons MC, MacDonald SJ, Somerville LE, et al. Unicompartmental versus total knee arthroplasty database analysis: is there a winner? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1):84-90.[7] Faour-Martín O, Valverde-García JA, Martín-Ferrero MA, et al. Oxford phase 3 unicondylar knee arthroplasty through a minimally invasive approach: long-term results. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5): 833-838.[8] 景鹏举,王勇平,李兴隆,等. 膝关节单髁置换术治疗膝骨性关节炎有效性的meta分析[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2017,33(2): 180-183.[9] Longo UG, Loppini M, Trovato U, et al. No difference between unicompartmental versus total knee arthroplasty for the management of medial osteoarthtritis of the knee in the same patient: a systematic review and pooling data analysis. Br Med Bull.2015; 114(1): 65-73.[10] Arirachakaran A, Choowit P, Putananon C, et al. Is unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) superior to total knee arthroplasty (TKA)? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(5): 799-806.[11] 刘义超. 单髁置换与全膝关节置换治疗膝单间室骨关节炎围手术期出血量的对比研究[D].新疆医科大学,2016.[12] Schwab PE, Lavand'homme P, Yombi JC, et al. Lower blood loss after unicompartmental than total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;23: 1-7.[13] McGrory B, Weber K, Lynott JA, et al. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Surgical Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(8): 688.[14] Thompson SA, Liabaud B, Nellans KW, et al. Factors associated with poor outcomes following unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: redefining the "classic" indications for surgery. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(9):1561-1564.[15] 岳辰,周宗科,裴福兴,等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术围术期抗纤溶药序贯抗凝血药应用方案的专家共识[J]. 中国骨与关节外科, 2015,8(4): 281-285.[16] 徐逸生,张智勉,魏超,等. 针对性止血应用于膝关节置换术的临床观察[J]. 中国输血杂志,2016,29(2): 162-165.[17] Hong KH, Pan JK, Yang WY,et al. Comparison between autologous blood transfusion drainage and closed-suction drainage/no drainage in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:142. [18] Shen HL, Li Z, Feng ML, et al. Analysis on hidden blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in treating knee osteoarthritis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(11):1653-1656. [19] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery.1962;51(2):224-232.[20] Felson DT, Naimark A, Anderson J,et al. The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the elderly. The Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;30(8):914-918.[21] Kang X, Fransen M, Zhang Y, et al. The high prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in a rural chinese population: The Wuchuan Osteoarthritic Study (vol 61, pg 641, 2009). Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61(7):1008-1008.[22] Jiang L, Tian W, Wang Y, et al. Body mass index and susceptibility to knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine Revue Du Rhumatisme. 2012;79(79):291-297.[23] Blagojevic M, Jinks C, Jeffery A, et al. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1): 24-33.[24] Lim YZ, Wang Y, Wluka AE, et al. Association of obesity and systemic factors with bone marrow lesions at the knee: A systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43(5):600-612. [25] 薛华明,马童,文涛,等. 髌旁外侧入路外侧单髁置换术治疗膝关节外侧间室骨关节炎[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(1):19-23.[26] 邱旭升,陈东阳,徐志宏,等. 全膝关节置换术后隐性失血危险因素的分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2012, 18(6): 510-512.[27] Hu KZ, Sun HY, Sui C. Effects of five treatment regimens on blood loss and blood transfusion in total knee arthroplasty: a preliminary study in China. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;55(5):433-441. [28] Chen TP, Chen YM, Jiao JB, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):11.[29] Zhang XQ, Ni J, Ge WH. Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total joint arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2017;38:15-20.[30] 徐飞,吕永明,宋莺春,等. 氨甲环酸对膝关节置换术后血红蛋白降低的临床研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2015,31(13): 1246-1248.[31] Cid J, Lozano M. Tranexamic acid reduces allogeneic red cell transfusions in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: results of a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transfusion. 2005;45(8): 1302-1307.[32] 梁峰,许晓军,姚强,等. 全膝关节置换术后CRP和ESR变化的临床研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(1): 73-74.[33] 刘安,陈廖斌,王欣,等. 膝髋关节置换术围手术期血浆D-二聚体动态监测及临床意义[J]. 中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2013, 7(2): 145-149.[34] Rafee A, Herlikar D, Gilbert R, et al. D-Dimer in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis following total hip and knee replacement: a prospective study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008;90(2):123-126. [35] An TJ, Engstrom SM, Oelsner WK, et al. Elevated d-Dimer is not predictive of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10): 2269-2272.[36] Xie J, Ma J, Huang Q, et al. Comparison of enoxaparin and rivaroxaban in balance of anti-fibrinolysis and anticoagulation following primary total knee replacement: a pilot study. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23: 704-711.[37] Ricket AL, Stewart DW, Wood RC, et al. Comparison of postoperative bleeding in total hip and knee arthroplasty patients receiving rivaroxaban or enoxaparin. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(4):270-275.[38] Ning GZ, Kan SL, Chen LX, et al. Rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 23726.[39] 陈呈锦. 人工全膝关节置换术后早期低蛋白血症的高危因素回顾性研究[D].昆明医科大学,2014.[40] Kamath AF, Nelson CL, Elkassabany N, et al. Low albumin is a risk factor for complications after revision total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(3):269-275. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [4] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [5] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [6] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [9] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [10] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [11] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [12] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [13] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [14] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [15] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||