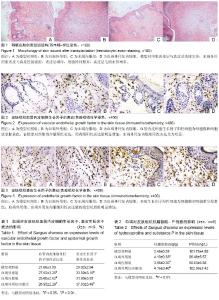
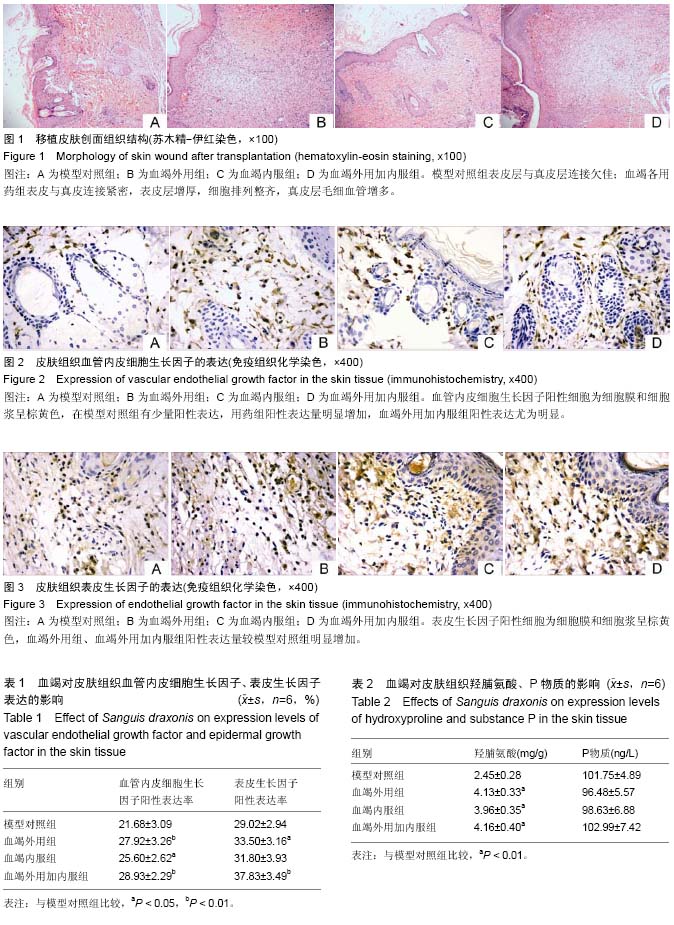
| [1] 何兰,王竹红,屠鹏飞,等.龙血树属植物化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J].中草药,2004,2 (2):221-228.
[2] 黄树莲,陈学芬,陈晓军.广西血竭的活血化瘀研究[J].中药材,1994,17(9):37-39.
[3] 向金莲,张路晗,程睿,等.血竭消炎止痛作用研究[J].时珍国医国药,2001,12(2):110-111.
[4] 陈德利,高青云,施伟民,等.中药中活血化瘀药对皮肤创伤愈合的影响[J].上海医学,2000,23 (3):145-147.
[5] 张平.龙血竭胶囊治疗褥疮临床观察[J]. 实用中医药杂志, 2014,30(6):554.
[6] 厉建胜.中药血竭在体表创伤、烧伤中的应用体会[J].哈尔滨医药,2001,21(2):70-71.
[7] 楼朝飞.龙血竭外敷治疗下肢慢性溃疡36例疗效观察[J].中国医药导报,2008,5(27):60-63.
[8] 谢龙炜,顾在秋,蔡良良.柏竭珍珠膏治疗烧伤残余创面[J].长春中医药大学学报,2014,30(5):925-927.
[9] 余海珠,吴剑,罗金丹.龙血竭联合湿润烧伤膏治疗Ⅱ~Ⅲ期压疮的效果观察[J].护理与康复,2013,12(12): 1155-1156.
[10] Sangamesh G,Kumbar,Syam P,et al. Electrospun poly (lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds for skin tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2008;29(30):4100-4107.
[11] 马列,高长有,李明忠,等. 皮肤诱导再生材料的研究进展与挑战[J].中国材料进展,2010,29(9):34-43.
[12] 方圣,陈爱军,单葵,等.人角质形成细胞体外分离与无血清培养的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2012,22(7): 26-29.
[13] 章静波.组织和细胞培养技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002:84.
[14] 韩跃东,刘玲,何黎,等.SD大鼠组织工程皮肤构建及移植的实验研究[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2008,24(4): 267-270.
[15] 杨维,崔占峰.组织工程皮肤发展现状[J].中国科学:生命科学,2015,45(5):460-470.
[16] 李啸,邱学文,王甲汉. 胶原基人工真皮的临床应用进展[J].重庆医学,2015,44(33):4721-4723.
[17] 马东东,周玉杰,路婷婷,等.组织工程皮肤研究现状[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(6):1183-1187.
[18] 李秉航,邓立欢,向萌娟,等.利用载有角质细胞生长因子微囊的组织工程皮肤修复裸鼠皮肤缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(42):6746-6752.
[19] 王楠,孙佩杰,苏秋香,等.骨髓间充质干细胞藻酸钙移植物与复合降解膜修复皮肤缺损[J].中国组织上程研究,2015, 19(32):5204-5209.
[20] 陆新.组织工程皮肤的缺陷与对策[J].医学研究生学报, 2005,18(1):74-76.
[21] 吴贞天.创伤愈合与组织修复的研究进展[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(8):21-22.
[22] Kilic U,Kilic E,Järve A,et al.Human vascular endothelial growth factor protects axotomized retinal ganglion cells in vivo by activating ERK-1/2 and Akt pathways. J Neurosci.2006;26(48):12439-12446.
[23] 靳俊峰,刘爱军,杜标炎.生肌中药对组织工程皮肤移植后 VEGF表达的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2010, 16(5): 429-432.
[24] 周凌,伍津津,朱堂友,等.组织工程皮肤分泌血管内皮细胞生长因子的初步研究[J].临床皮肤科杂志,2006,35(3): 144-146.
[25] 刘玉芳,林茂,侯彬彬,等.瘢痕疙瘩及正常皮肤中骨形态发生蛋白7、Gremlin、血管内皮生长因子、高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达[J].中国组织上程研究,2014,18(29): 4618-4624.
[26] 李晶哲,夏芸,刘柏东,等.芦荟大黄素促进皮肤创伤修复作用机理研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2011,17(11): 1260-1263.
[27] Koob TJ, Rennert R, Zabek N, et al. Biological properties of dehydrated human amnion/chorion composite graft: implications for chronic wound healing. Int Wound J.2013;10(5):493-500.
[28] 潘建西,王临青,张思胜,等.生肤灵对大鼠表皮生长因子及纤维连接蛋白影响的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2012,20(2):6-11.
[29] 吴胜,吴仲敏,傅磊冕.皮肤中的P物质及其作用[J].解剖学研究,2009,31(3):220-222.
[30] Shu B, Xie JL, Xu YB, et al. Effects of skin-derived precursors on wound healing of denervated skin in a nude mouse model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2015; 8(3): 2660-2669.
[31] 彭希亮,张玉红,倪文琼. P 物质对表皮细胞聚集、分化控制及在皮肤创伤修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(11):1538-1543.
[32] 张大维,周成霞,段嘉川,等.芦荟凝胶对美容激光致皮肤创伤修复作用研究[J].中成药,2009,31(8):1293-1295.
[33] 肖秀丽,王振宜,唐汉钧,等.复黄生肌愈创油膏对大鼠创面肉芽组织中Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原表达的影响[J].中西医结合学报,2009,7(4):366-371.
[34] Upadhyay A, Chattopadhyay P, Goyary D, et al. Ixora coccinea Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing by Upregulating the Expression of Collagen and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. ISRN Pharmacol.2014: 751824. |