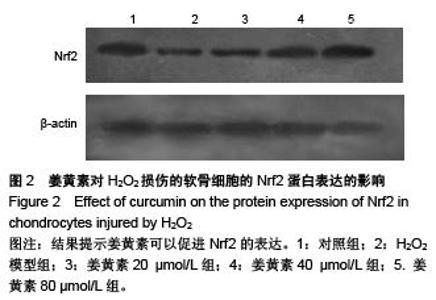
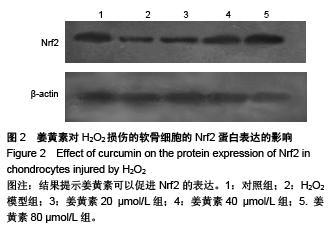
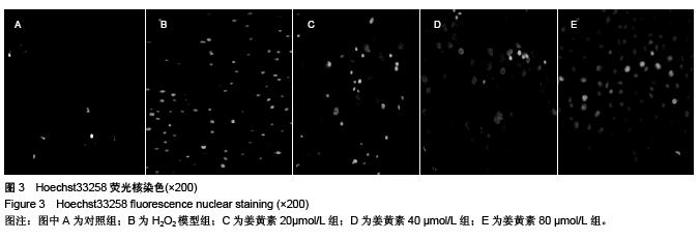
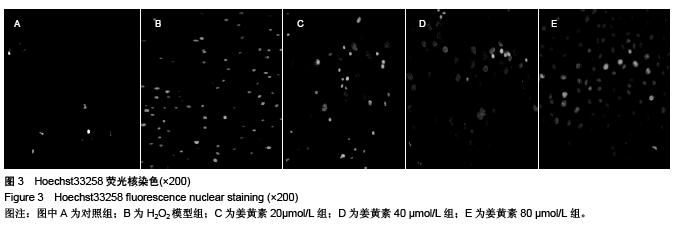
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (51): 8218-8222.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.51.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Nrf2-mediated curcumin protects chondrocytes from oxidative stress
Song Yong-zhou1, Guan Jian2, Li Ming1, Ma Wei1, Yuan He1, Wang Bin1, Tong Jiu-hui1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang, Shijiazhuang 050011, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2015-11-09Online:2015-12-10Published:2015-12-10 -
Contact:Ma Wei, M.D., Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Song Yong-zhou, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Scientific Research of Hebei Province, No. 20150666
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Yong-zhou, Guan Jian, Li Ming, Ma Wei, Yuan He, Wang Bin, Tong Jiu-hui. Nrf2-mediated curcumin protects chondrocytes from oxidative stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(51): 8218-8222.
share this article
| [1] Afonso V,Champy R,Mitrovic D,et al. Reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutases: role in joint deseases. Joint Bone Spine.2007;74(4):324-329.
[2] Que LL,Wang HX,Cao BS,et al. The regulation and functions of transcription factor Nrf2 in cancer chemoprevention and chemoresistance. J Chin Pharm Sci.2011;20(1): 5-19.
[3] Phillips J, Moore-Medlin T, Sonavane K,et al.Curcumininhibits UV radiation-induced skin cancer in SKH-1 mice.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2013;148(5):797-803.
[4] 孙宗建,何琨,张东,等.姜黄素预先给药对兔呼吸机相关性肺损伤时Nrf2蛋白表达的影响.中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(2):237-240.
[5] Shishodia S,Singh T,Chaturvedi MM. Modulation oftranscriptionfactors bycurcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007; 595:127-148.
[6] 梁莉,阙琳玲,曹宝山,等. Nrf2在姜黄素保护UVB所致细胞氧化损伤中的作用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2014,34(8): 583-587.
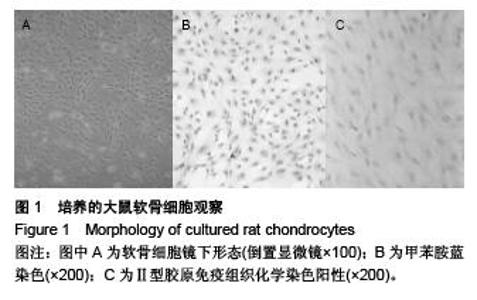
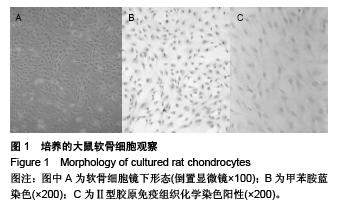
[7] 宋永周,崔慧先,吕哲,等.大鼠关节软骨细胞的培养[J].河北医科大学学报,2008,29(4):534-537.
[8] 宋永周,刘会玲,崔慧先,等.抗骨增生胶囊含药血清对软骨细胞增殖凋亡及基质金属蛋白酶分泌的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(24):4642-4646.
[9] 郑海燕,洪远,陈高.Nrf2-ARE在大鼠创伤性脑损伤模型中的表达及意义[J].中华神经外科杂志,2013,29(1):80-84.
[10] Tetik S,Ahmad S,Alturfan AA,et al.Determination of oxidant stress in plasma of rheumatoid arthritis and primary osteoarthritis patients.Indian J Biochem Biophys.2012;47(6): 353-358.
[11] Scott JL,Gabrielides C,Davidson RK,et al. Superoxide dismutase downregulation in osteoarthritis progression and end-stage disease. Ann Rheum Dis.2010;69(8):1502-1510.
[12] Olszewska-Sonina DM,Matewski D,Drewa G,et al.Oxidative equilibriuminthe prophylaxis of degenerativejoint changes: an analy-sis of pre-and postoperative activity of antioxidant enzymes in patients with hip and knee osteoarthritls.Med Sci Monit.2010;16(5):CR238-245.
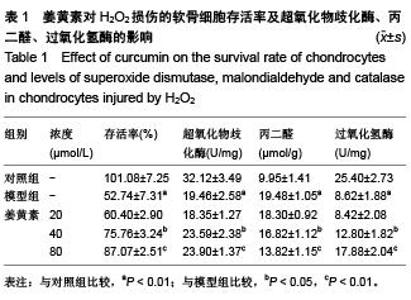
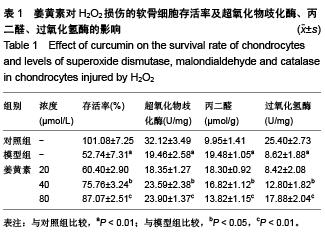
[13] 张建武,闵冬雨,周云,等. 番茄红素对H2O2致乳鼠心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(12): 160-164.
[14] He HB, Xu J, Xu YQ, et al. Cardioprotective effects of saponins from Panax japonicus on acute myocardial ischemia against oxidative stress-triggered damage and cardiac cell death in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.2012;140(1):73.
[15] McMahon M, Thomas N, Hoh K,et al. Dimerization of substrate adaptors can facilitate cullin-mediated ubiquitylation of proteins by a “tethering” mechanism: a two-site interaction model for the Nrf2-Keapl complex.J Biol Chem.2006;281: 24756-24768.
[16] Johnson JA, Johnson DA, Kraft AD, et al. The Nrf2-ARE pathway:an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2008;1147:61-69.
[17] Rahman I. Antioxidant therapeutic advances in COPD. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2008;2(6):351-374. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||