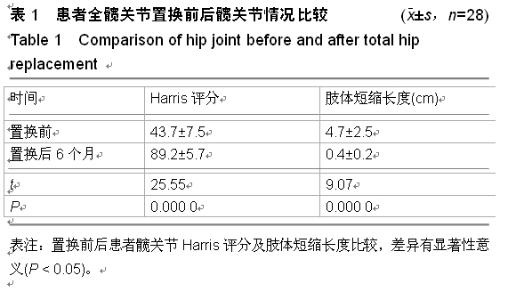
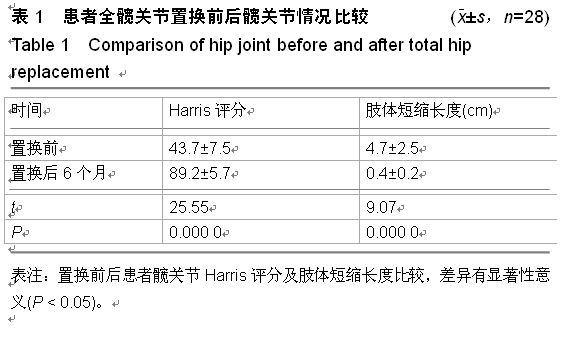
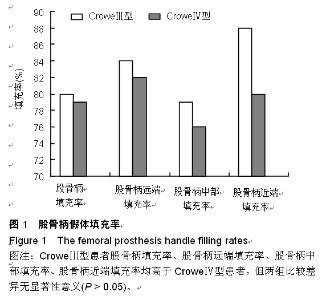
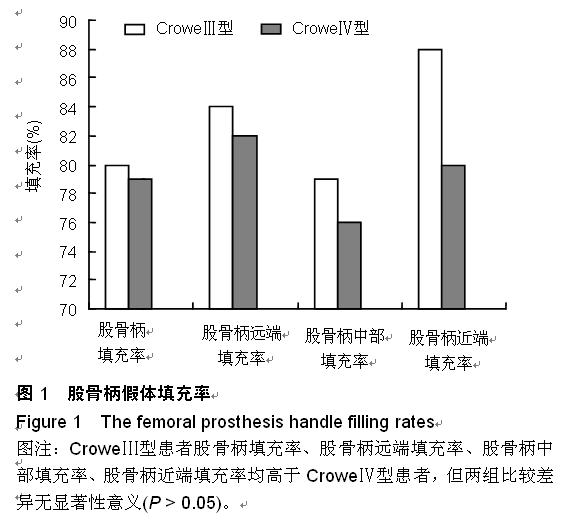
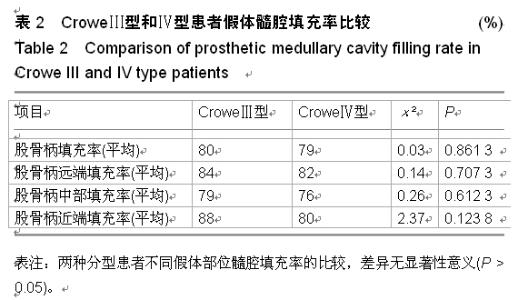
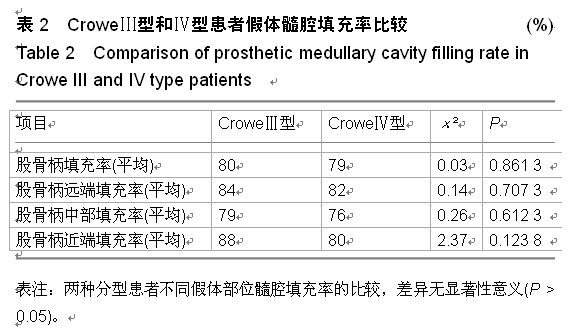
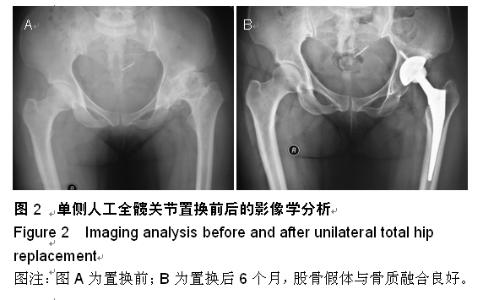
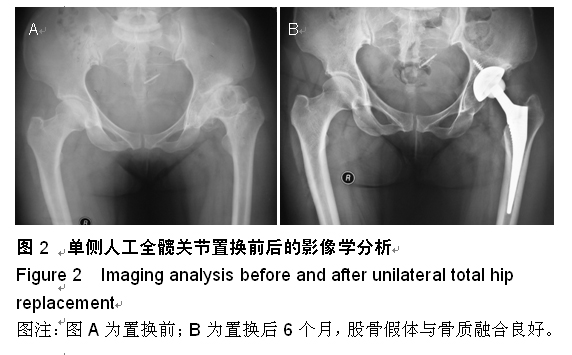
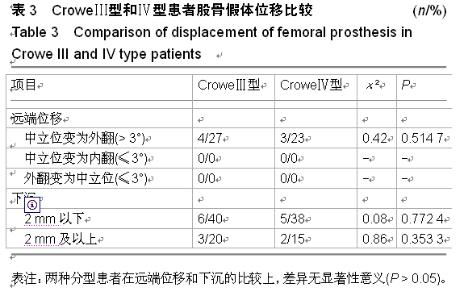
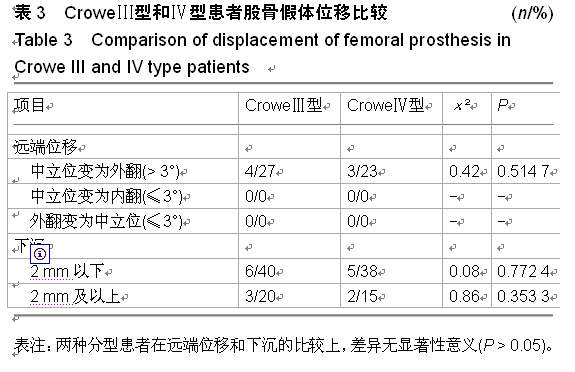
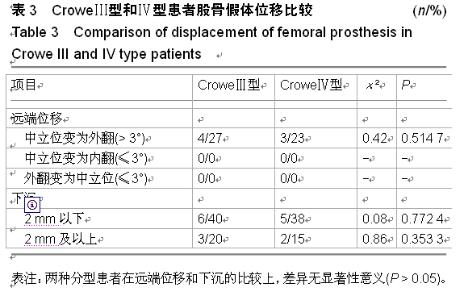
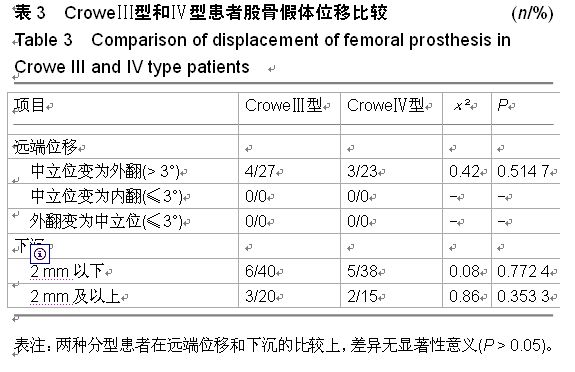
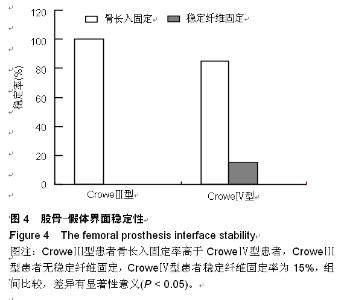
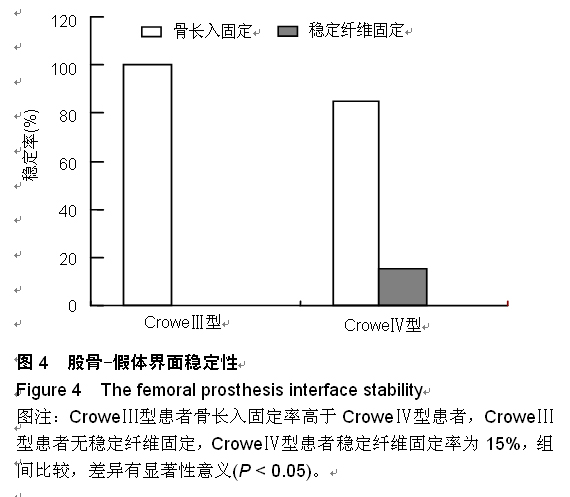
| [1] 顾建明,杜辉,邵宏翊,等.股骨转子下截骨的全髋关节置换治疗高脱位髋臼发育不良[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(48): 8331-8336.
[2] 张功林,甄平,陈克明,等.加强后侧软组织修复技术预防全髋关节置换术后脱位[J].国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(1):36-38.
[3] 白志刚,牛东生,禹全恩,等.全髋关节置换术治疗重度成人髋臼发育不良并骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2011, 26(4):337-338.
[4] 刘云,肖增明,廖世杰,等.微创切口和传统切口全髋关节置换临床疗效的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(22): 4044- 4048.
[5] 李国威,董明岩,张海飞,等.全髋关节置换与双极人工股骨头置换治疗老年股骨颈骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22):4061-4064.
[6] 及松洁,周一新.髋关节置换后不稳定的相关研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(13):2505-2510.
[7] 廖亮,赵劲民,苏伟,等.计算机导航技术辅助全髋关节置换的系统分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(9):1599-1602.
[8] 周军杰,曹成福,庞金辉,等.立体影像学分析对组配式全髋关节置换术后股骨假体迁移的早期评估[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(9): 881-887.
[9] 刘燚,严建军,崔志明,等.人工全髋置换联合髋臼造盖治疗先天性髋关节脱位[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(30):5434-5439.
[10] Cho SM, Han HS, Park JW, et al. Multifunctional Composite Coating as a Wear-Resistant Layer for the Bearing in Total Hip Joint Replacement. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013 5(2):395-403.
[11] 李浩,王义生,张桐,等.全髋置换术治疗先天性髋关节脱位的早期疗效观察[J].中国实用医刊,2013,40(11):62-64.
[12] 张道俭,朱天岳,柴卫兵,等.全髋关节置换术中解剖柄股骨假体周围骨折的影像学分析[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(9):690-692.
[13] 彭阳,杨柳,陈光兴,等.Crowe Ⅲ及Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术中髋臼骨缺损的重建[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(1): 25-29.
[14] 丛锐军,符培亮,吴宇黎,等.下肢重建方式对Crowe Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术后疗效的影响[J].中华骨科杂志, 2013,33(3):214-219.
[15] 杨述华,许伟华,叶树楠,等.髋臼重建及股骨转子下短缩截骨全髋关节置换治疗Crowe Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良[J].中华骨科杂志, 2013,33(9):888-894.
[16] 王勇,司刚,蒋建农,等.髋臼假体角度与全髋关节置换术后脱位的关系[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(12):1119-1121.
[17] 高磊,瞿玉兴,潘留美,等.成人先天性髋关节脱位全髋关节置换术后早期功能康复15例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2012,12(1): 190-191.
[18] 张江涛,尚延春,吴富源,等.髋关节假体置换中股骨头直径及髋臼前倾角的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(30):5427-5433.
[19] 刘志刚,陈经勇,陈如见,等.减小髋臼杯外展角预防偏瘫患者全髋关节置换后的假体脱位[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4): 630-633.
[20] Ruther C, Ewald H, Mittelmeier W, et al.A Novel Sensor Concept for Optimization of Loosening Diagnostics in Total Hip Replacement. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(10):104503.
[21] 孙敏,尹良军,俞玮,等.髂骨定位针技术对全髋关节置换患者术后康复的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(2):173-175.
[22] 陈为民,黄建明,康一凡,等.全髋置换两种不同手术入路髋臼假体前倾角的比较分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(4): 332-333.
[23] 詹远平.前外侧入路与后外侧入路在全髋关节置换中的疗效分析[J].中国社区医师(医学专业),2013,15(9):106-107.
[24] 何斌,成伟男,王云华,等.前、后外侧入路对髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓及脱位的影响[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013, 12(2): 54-56.
[25] 刘金钊,姜宁,高鹏,等.全髋关节置换关节囊修复对预后功能的影响[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014,15(6):414-418.
[26] 高红兵.全髋关节置换术治疗成人发育性髋关节脱位临床观察[J].中国农村卫生,2012,8(2):133-134.
[27] 方红亮.不同手术方式在全髋关节置换术中的应用效果观察[J].河南医学研究,2014,23(10):104-105.
[28] 吴长沙,李恩贤,李让贤,等.分析初次全髋关节置换术后髋关节的疼痛原因[J].中国伤残医学,2014,11(17):41-42.
[29] 邓信昌.全髋关节置换术治疗先天性髋关节脱位并股骨头缺血性无菌性坏死临床观察[J].中国基层医药,2014,30(23): 3543- 3544,3545.
[30] 赵勇,刘克贵,孙涛,等.人工全髋关节置换术中经皮多针刺技术松解内收肌的疗效观察[J].中华医学杂志,2014,28(45): 3567- 3570.
[31] Alidousti H, Taylor M, Bressloff NW, et al. Do Capsular Pressure and Implant Motion Interact to Cause High Pressure in the Periprosthetic Bone in Total Hip Replacement. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(12):121001.
[32] 李虎,林剑浩.人工髋关节翻修术中股骨干前侧皮质开窗术的临床应用研究[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(5):398-401.
[33] 何文野,陈云苏,张先龙,等.先天性髋关节发育不良Ⅳ型全髋关节置换术的肢体平衡[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(11):965-970.
[34] 郑鸿,何冰,谭宏昌,等.不同手术入路髋臼假体放置角度差异对疗效的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(8):734-736.
[35] 赵东风,刘欣伟,岳勇,等.全髋关节置换术治疗成人先天性髋关节发育不良伴股骨头坏死中期随访疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2):132-133.
[36] 许杰,马若凡,李登,等.髋臼发育不良髋关节置换前髋臼侧的三维测量[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(43):7507-7513.
[37] 钱宏.人工全髋关节置换术对成人先天性髋脱位的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2012,8(33):421-422.
[38] 李慧武,朱振安,毛远青,等.非截骨全髋关节置换术治疗单侧CroweⅣ型髋关节发育不良[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,24(12): 1205-1211.
[39] 雷鹏飞,胡懿郃,蔡碰德,等.大转子截骨非骨水泥全髋置换治疗成人髋关节发育不良[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44): 8191-8195.
[40] 王洪源.成人先天性髋脱位的人工全髋关节置换术[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(6):98-99. |