Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (28): 4472-4477.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.28.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
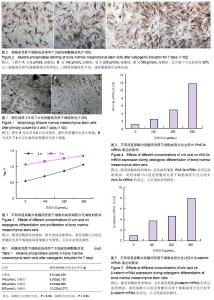
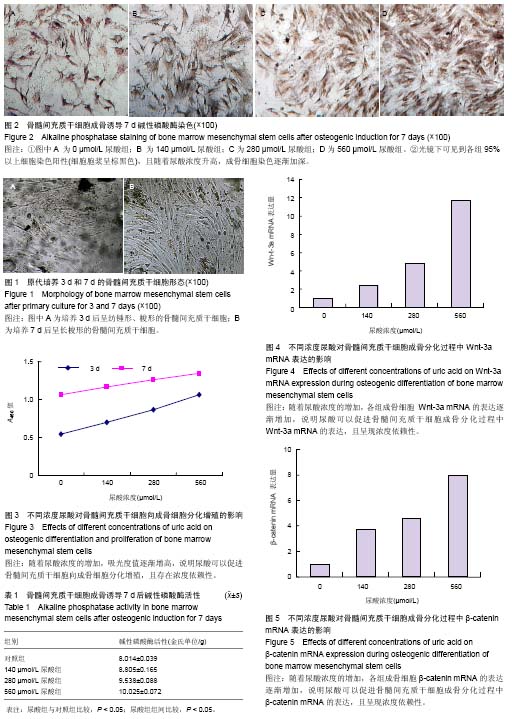
Uric acid effect on Wnt signaling pathways during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Xiao-li, Xu Li-li, Yang Nai-long
- Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2015-07-02Published:2015-07-02 -
Contact:Yang Nai-long, Master, Chief physician, Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yang Nai-long, Master, Chief physician, Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xiao-li, Xu Li-li, Yang Nai-long. Uric acid effect on Wnt signaling pathways during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(28): 4472-4477.
share this article
| [1] Sohni A, Verfaillie CM. Mesenchymal stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:130763. [2] Kim EJ, Kim N, Cho SG. The potential use of mesenchymal stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45:e2. [3] Sharma RR, Pollock K, Hubel A, et al. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells: a review of clinical applications and manufacturing practices. Transfusion. 2014;54(5):1418-1437. [4] Beane OS, Darling EM. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation of stem cells for cartilage regeneration. Ann Biomed Eng. 2012;40(10):2079-2097. [5] Matsumoto T, Kuroda R, Mifune Y, et al. Circulating endothelial/skeletal progenitor cells for bone regeneration and healing. Bone. 2008;43(3):434-439. [6] 彭俊琼,袁伟杰.肾脏尿酸转运体对调节尿酸的影响及尿酸在氧化应激中的双重作用[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2011,27(11):862-864. [7] Ames BN, Cathcart R, Schwiers E, et al. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981;78(11):6858-6862. [8] Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004; 20:781-810. [9] Macsai CE, Foster BK, Xian CJ. Roles of Wnt signalling in bone growth, remodelling, skeletal disorders and fracture repair. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215(3):578-587. [10] Liu G, Vijayakumar S, Grumolato L, et al. Canonical Wnts function as potent regulators of osteogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biol. 2009;185(1):67-75. [11] Augello A, De Bari C. The regulation of differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2010;21(10): 1226-1238. [12] Chen Y, Alman BA. Wnt pathway, an essential role in bone regeneration. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(3):353-362. [13] Bultink IE, Vis M, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, et al. Inflammatory rheumatic disorders and bone. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012;14(3):224-230. [14] Krause U, Gregory CA. Potential of modulating Wnt signaling pathway toward the development of bone anabolic agent. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2012;5(2):164-173. [15] MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009; 17(1):9-26. [16] Cadigan KM, Liu YI. Wnt signaling: complexity at the surface. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 3):395-402. [17] 许兵,刘慧,许应星,等.成骨细胞中经典Wnt/β-catenin通路研究进展[J].生命科学, 2011, 23(5):477-481. [18] 张山山,杨乃龙,徐丽丽,等.尿酸对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中Cbfα1/Runx2表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(4): 363-366. [19] 杨乃龙,朱晓琳,张冬.不同浓度尿酸对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志,2012,6(17):5145-5148. [20] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊治指南(2011年)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1): 2-17. [21] 罗树君,曾荣,胡资兵.骨质疏松症的药物治疗进展[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(18):14-15. [22] Nuttall ME, Gimble JM. Controlling the balance between osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis and the consequent therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4(3): 290-294. [23] Clabaut A, Delplace S, Chauveau C, et al. Human osteoblasts derived from mesenchymal stem cells express adipogenic markers upon coculture with bone marrow adipocytes. Differentiation. 2010;80(1):40-45. [24] Angers S, Moon RT. Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(7):468-477. [25] Geng X, Xiao L, Lin GF, et al. Lef/Tcf-dependent Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during Xenopus axis specification. FEBS Lett. 2003;547(1-3):1-6. [26] Lee PN, Pang K, Matus DQ, et al. A WNT of things to come: evolution of Wnt signaling and polarity in cnidarians. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006;17(2):157-167. [27] Zhou H, Mak W, Zheng Y, et al. Osteoblasts directly control lineage commitment of mesenchymal progenitor cells through Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(4):1936-1945. [28] Liu B,Tang J,Li SY,et al.Involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway and cell apoptosis in the rat hippocampus following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(1): 70-75. [29] Jullien N, Maudinet A, Leloutre B, et al. Downregulation of ErbB3 by Wnt3a contributes to wnt-induced osteoblast differentiation in mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012; 113(6):2047-2056. [30] Tokuda H, Adachi S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, et al. Enhancement of basic fibroblast growth factor-stimulated VEGF synthesis by Wnt3a in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2011;27(6):859-864. [31] Li HX, Luo X, Liu RX, et al. Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;291(1-2):116-124. [32] Krishnan V, Bryant HU, Macdougald OA. Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5):1202-1209. [33] Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, et al. Essential role of beta-catenin in postnatal bone acquisition. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(22):21162-21168. [34] Mbalaviele G, Sheikh S, Stains JP, et al. Beta-catenin and BMP-2 synergize to promote osteoblast differentiation and new bone formation. J Cell Biochem. 2005;94(2):403-418. [35] Deschaseaux F, Sensébé L, Heymann D. Mechanisms of bone repair and regeneration. Trends Mol Med. 2009;15(9): 417-429. |
| [1] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [4] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [5] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [6] | Chen Lei, Zheng Rui, Jie Yongsheng, Qi Hui, Sun Lei, Shu Xiong. In vitro evaluation of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction combined with osteochondral integrated scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3487-3492. |
| [7] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [8] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [9] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [10] | Li Congcong, Yao Nan, Huang Dane, Song Min, Peng Sha, Li Anan, Lu Chao, Liu Wengang. Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2976-2981. |
| [11] | Gao Yuanhui, Xiang Yang, Cao Hui, Wang Shunlan, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang, Huang Denggao. Comparison of biological characteristics of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in Wuzhishan inbreed miniature pigs aged two different months [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2988-2993. |
| [12] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [13] | Dai Min, Wang Shuai, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Yu Limei, Hu Xiaohua, Yi Jie, Yao Li, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of hypoxic preconditioned human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3004-3008. |
| [14] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||