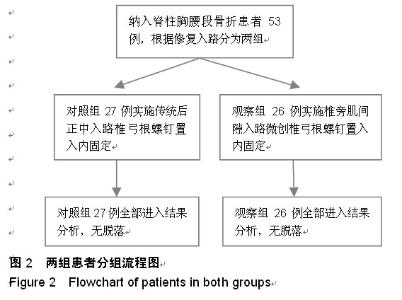
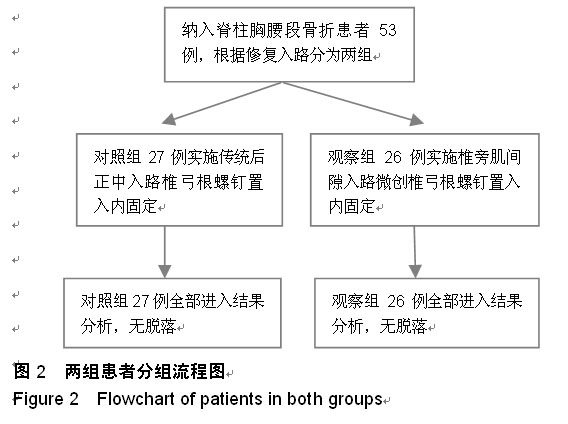
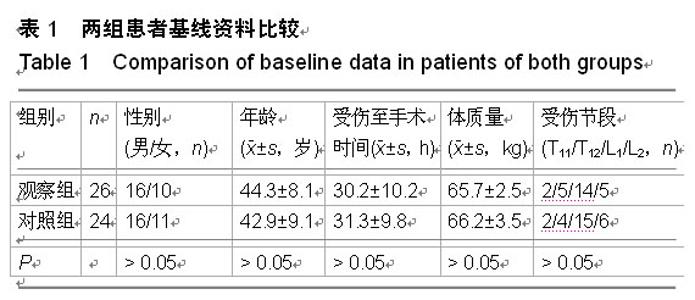
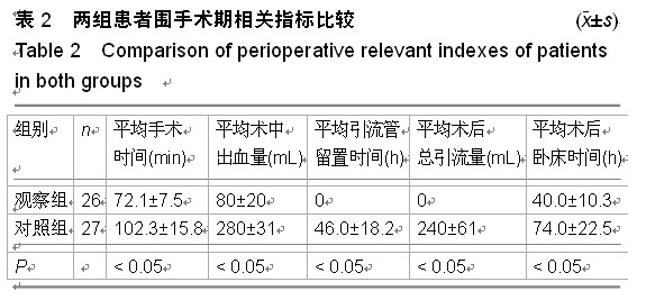
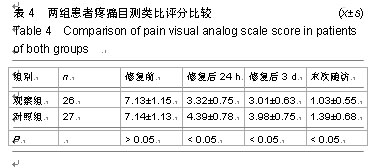
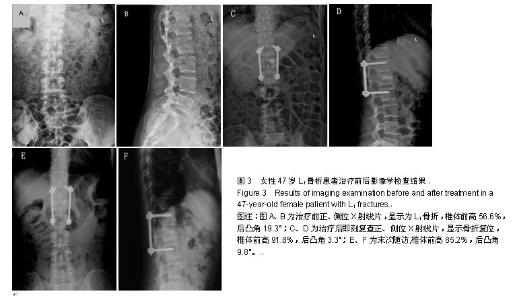
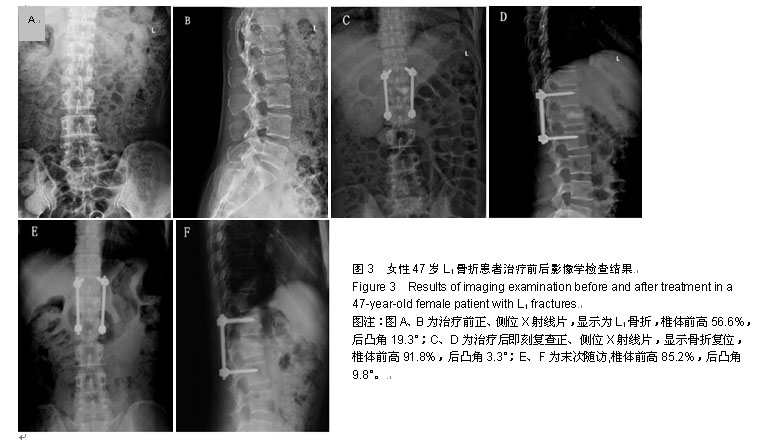
| [1] 焦伟,于海洋,崔西龙,等.后正中小切口非融合技术治疗胸腰段脊柱骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(2):144-145,148.
[2] Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H .Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. A histologic and enzymaticanalysis. Spine.1996;21(8):941-944.
[3] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al. The paraspinal sacrospinalis- splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1968;50: 919-926.
[4] 戴胡明,方诗元,夏睿,等.传统入路与椎旁肌间隙入路置入椎弓根螺钉治疗胸腰段骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2339-2345.
[5] 王毓幸,陈新军.最长肌多裂肌间隙入路治疗胸腰段骨折[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(6):1008-1009.
[6] 刘侃,吴闻文,郭继东,等.经Wiltse肌间隙入路内固定结合椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎骨折的早期疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2013,6(4):349-354.
[7] 焦伟,于海洋,梁成民,等.经椎旁肌间隙入路微创小切口在胸腰段骨折术后内固定取出术中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(2): 168-170.
[8] 水小龙,徐华梓,池永龙,等.微创技术在不同类型胸腰段骨折中的应用[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1086-1090.
[9] 徐海栋,赵建宁,刘刚,等.椎旁肌间隙入路伤椎置钉技术治疗胸腰段骨折近期疗效观察[J].医学研究生学报,2015,28(1):45-48.
[10] 尹利强,聂新富,秦海江,等.肌间隙入路结合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(5):448-449,450.
[11] 戴胡明,方诗元,夏睿,等.椎旁肌间隙入路和传统入路在治疗胸腰段骨折对椎旁肌损伤的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013, 21(14):1379-1383.
[12] 孙树发,孙海燕,张引锋,等.30例椎旁肌间隙入路治疗胸腰段骨折临床体会[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(4):317-319.
[13] 吴剑飞,谢德胜,龚进红,等.Wiltse肌间隙入路治疗57例胸腰段无神经损伤症状的单节段椎体骨折[J].临床军医杂志,2012,40(4): 867-868.
[14] 张亚军,方礼明,张军,等.经椎旁肌间隙短节段椎弓根钉固定治疗伴后方韧带复合体损伤的胸腰段骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(12):1049-1053.
[15] 曾显代.经椎旁肌间隙入路微创小切口在胸腰段骨折术后内固定取出术中的应用价值[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2014,22(7): 58-58,59.
[16] 辛荣超,白永鑫.胸腰椎骨折经Wiltse肌间隙入路与传统入路的临床对比研究[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2014,46(8):897-900.
[17] 杨再丰,郑满红,胡军,等.后正中入路与肌间隙入路治疗脊柱胸腰段骨折的比较研究[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(11):287-288.
[18] 靳江波.浅谈用肌间隙入路经椎间孔开窗术治疗胸腰椎退变性椎管狭窄性疾病的临床疗效[J].当代医药论丛,2014,12(3): 140-141.
[19] 梁军阳,谢斌,许传勇,等.经肌间隙入路、自制器械经椎弓根椎体内植骨、伤椎置钉微创治疗胸腰段椎体骨折[J].中国医学创新, 2013,10(22):1-3,4.
[20] 章其益,管四炎.小切口椎旁肌间隙入路、短节段椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰段骨折的临床研究[J].健康研究,2014,34(3): 277-279.
[21] 那孟奇.Wiltse肌间隙入路与传统后正中入路在治疗胸腰段骨折的比较研究[J].右江民族医学院学报,2011,33(2):145-147.
[22] 徐光辉,徐东潭.经肌间隙入路单节段椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰段骨折[J].中国综合临床,2014,30(12):1327-1329.
[23] 吐尔洪江•吐尔迪,伍政疆.经肌间隙入路与正中常规切口入路植椎弓根钉治疗胸腰段骨折比较研究[J].中国保健营养(中旬刊), 2013,23(8):157-157.
[24] 陶玉平,王永祥,王静成,等.经椎旁肌间隙入路微创小切口在胸腰椎骨折手术的应用[J].江苏医药,2012,38(10):1204-1206.
[25] 李文生,陈永峰.椎旁肌间隙入路在治疗胸腰段骨折中的应用[J].医学信息,2014,27(17):140-140.
[26] 郭志辉,霍三顺.经椎旁肌间隙入路和后正中入路治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效比较[J].中国伤残医学,2014,22(4):58-59.
[27] 张毅,钟德君.肌间隙入路结合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段骨折34例分析[J].医学信息,2014,27(33):366-366.
[28] 冯明星,肖杰,龙浩,等.胸腰段骨折伴后方韧带复合体损伤经肌间隙固定疗效分析[J].创伤外科杂志,2015,27(1):67-67.
[29] 周鑫,吴永铁,范华华,等.伤椎植骨结合伤椎置钉治疗胸腰段骨折的临床观察[J].重庆医学,2013,42(5):544-546.
[30] 尹若峰,刘艳,赵建武,等.超声检查评估对轻微胸腰段骨折患者脊柱后方韧带复合体的意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(11): 2309-2311.
[31] 吕游,张大明,李瑞,等.三种胸腰段骨折分类法的可信度和可重复性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(7):566-568.
[32] 朱宗波,康建平,吴韬韬,等.A型胸腰段骨折椎体邻近椎间盘在磁共振T2加权像上的影像学特点[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(11):900-904.
[33] 李想,洪毅,张军卫,等.侧入路微创椎间融合结合后路短节段固定治疗胸腰段骨折的初步临床疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014, 24(5):400-406.
[34] 张锋,张文志,段丽群,等.Wiltse入路与传统后正中入路治疗胸腰段骨折疗效比较[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013,34(2):136-138.
[35] 严清理,张本其,桂春生,等.传统后正中入路与 Wiltse 入路治疗胸腰段骨折的比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014,12(4):231-234.
[36] Talebian S, Hosseini M, Bagheri H, et al. Trunk muscle fatigue in subjects with a history of low back pain and a group of healthy controls measured by similarily index. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011;24:17-22.
[37] Kawaguchi Y, Yabuki S, Styf J, et al. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery. Topographic evaluation of intramuscular pressure and blood flow in the porcine back muscle during surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21: 2683-2688.
[38] 卢荣,陈建,赵存赛,等.肌电图评价不同手术入路治疗脊柱胸腰段骨折对椎旁肌功能的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2014,36(8): 876-878, 882.
[39] 黄伟,尹毅,单辉强,等.短节段椎旁入路经伤椎椎弓根钉治疗胸腰段骨折疗效分析[J].实用临床医药杂志,2012,16(19): 134-135, 138.
[40] 戴胡明,夏睿,杨家赵,等.椎旁肌间隙入路和传统后正中入路在治疗胸腰段骨折对比研究[C].//安徽省医学会骨科学第十三次学术会议论文集,2012:254-257.
[41] Jiang XZ, Tian W, Liu B, et al. Comparison of a paraspinal approach with a percutaneous approach in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with posterior ligamentous complex injury: a prospective randomized controlled trial.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(4):1343-1356.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|