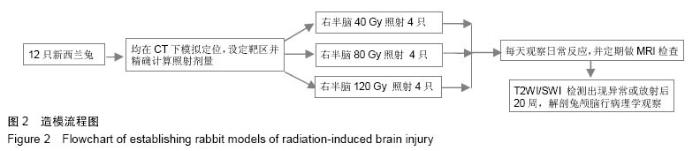
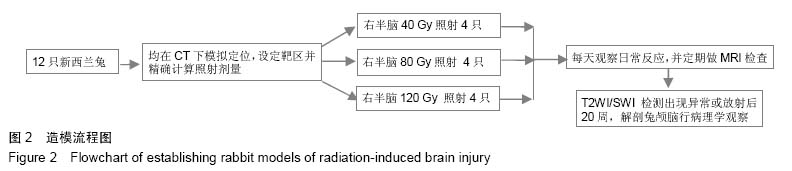
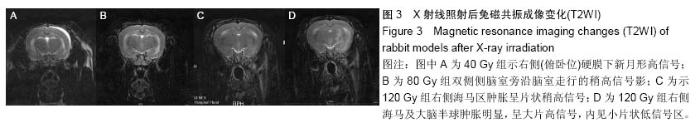
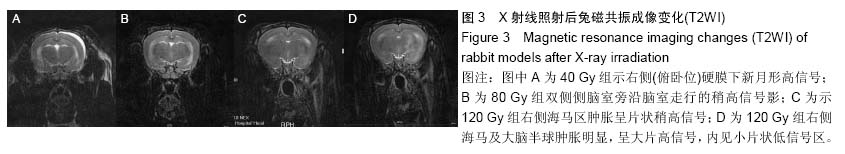
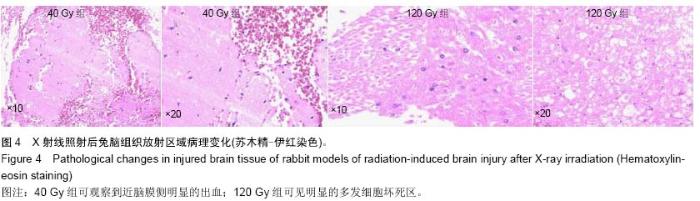
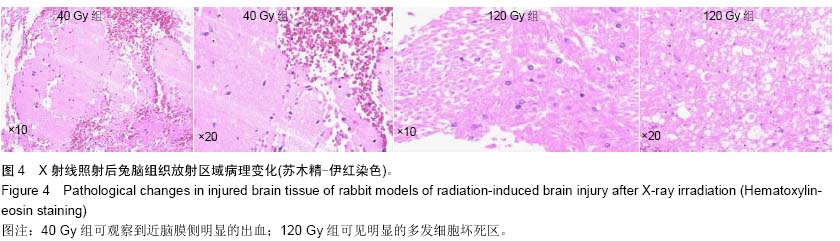
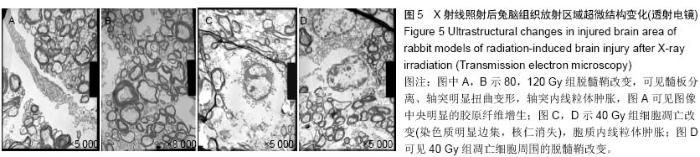
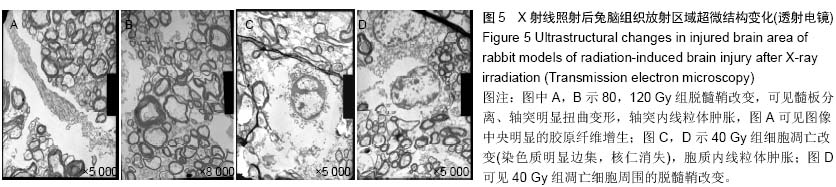
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4299-4303.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction of rabbit models of radiation-induced brain injury and selection of magnetic resonance parameters
Lang Xiao-yan1, Shao Guo-liang2, Sun Jing-jing2, Shi Lei2, Fan Lin-yin2
- 1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China;
2Department of Radiology, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou 310022, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-30Published:2015-06-30 -
About author:Lang Xiao-yan, Master, Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lang Xiao-yan, Shao Guo-liang, Sun Jing-jing, Shi Lei, Fan Lin-yin. Construction of rabbit models of radiation-induced brain injury and selection of magnetic resonance parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4299-4303.
share this article
| [1] 韩蓝,任庆兰.放射性脑损伤及放射保护剂的研究进展[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(7):77-79. [2] 郎晓燕,邵国良.放射性脑病的早期影像学特征与诊断[J].医学影像学杂志,2012,22(3):490-493. [3] 石磊,邵国良.磁共振成像早期诊断放射性脑损伤的研究现状[J].中国药物与临床,2010,10(1):73-74. [4] 袁文佳,涂彧,崔凤梅.放射性脑损伤的发病机制及治疗[J].国际放射医学核医学杂志,2008,32(4):250-254. [5] 钟静,姜恩海.放射性脑损伤发病机制及免疫系统改变的研究[J].国际放射医学核医学杂志,2006,30(5):301-304. [6] 沈海林,纪芳,秦颂兵,等.大鼠全脑照射后早期放射性脑损伤的磁共振波谱与病理对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2005,24(9): 818-823. [7] 肖颂华,段朝晖,沈庆煜,等.VEGF转基因神经干细胞移植对大鼠急性放射性脑损伤后脑组织中NSE表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(8):1559-1563. [8] Rabinov JD, Brisman JL, Cole AJ, et al. MRI changes in the rat hippocampus following proton radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2004;82(4):156-164. [9] Chan KC, Khong PL, Cheung MM, et al. MRI of late microstructural and metabolic alterations in radiation-induced brain injuries. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29(5): 1013-1020. [10] Liu Y, Xiao S, Liu J, et al. An Experimental Study of Acute Radiation-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in a Young Rat Model. AJNR. 2010;31:383-387. [11] 廉春容.60Co-γ射线全脑照射对血脑屏障通透性的改变和侧脑室室管膜下区神经发生的影响[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2010. [12] 段琼玉.左卡尼汀对大鼠急性放射性脑损伤后脑组织Caspase-3和Bcl-2表达的影响[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2012. [13] 刘运林,张谦,肖颂华,等.全脑照射对迟发性脑损伤大鼠学习记忆能力和海马突触结构的影响,2010,19(10):879-881. [14] Caceres LG, Aon Bertolino L, Saraceno GE, et al. Hippocampal-related memory deficits and histological damage induced by neonatal ionizing radiation exposure. Role of oxidative status. 2010;1312:67-78. [15] 马辰莺,徐晓婷,涂彧,等.VEGF mRNA及蛋白在大鼠放射性脑损伤模型中的动态变化[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2014,34(6): 405-410. [16] 孙晨,王凡,王鹏,等.大鼠放射性脑损伤磁共振成像的初步研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2013,17(3):449-452. [17] 宋琼,夏黎明,王承缘,等.超急性期放射性脑损伤的MRS和DTI研究[J].放射学实践,2007,22(7):687-690. [18] 陈旺生,李建军.鼻咽癌放射性脑损伤的MR扩散张量成像研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2010,29(6):747-750. [19] 石磊,郎晓燕,孙晶晶,等.鼻咽癌放疗后放射性脑病早期阶段磁共振成像及磁敏感加权成像表现及其临床意义[J].国药物与临床, 2013,10(1):1256-1258. [20] 石磊,郎晓燕,孙晶晶,等.鼻咽癌放疗后放射性脑病早期阶段MRI及SWI表现[A].2013年浙江省放射学学术年会论文集[C].2013年. [21] 陈旺生,李建军,洪澜,等.鼻咽癌放射性脑损伤迟发反应期的磁共振波谱研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2011,30(4):481-484. [22] 张海博,梁海亁,涂悦,等.放射性脑损伤的研究现状[J].山东医药, 2014, (26):95-97. [23] 李响.放射性脑损伤的MRS、PWI动物实验研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2013. [24] 李建鹏.早期放射性脑损伤动物模型建立、磁共振波谱(1H-MRS)分析与病理对照研究[D].广东:中山大学,2010. [25] 刘家斌.依达拉奉对急性期放射性脑损伤保护作用实验研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2010. [26] 阮林,韦力,廉春蓉,等.全脑照射后血脑屏障改变对放射性脑损伤的影响[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2011,37(10):591-595. [27] 李卉,耿志君,刘学文,等.兔早期放射性脑损伤:1H-MRS与病理对照研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2012,28(12):2117-2121. [28] Buatti JM, Friedman WA, Theele DP, et al. The lazaroid U74389G protects normal brain from stereotactic radiosurgery-induced radiation injury. Int JRadiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996;34(3):591. [29] Miot E, Hoffschir D, Alapetite C, et al. Experimental MR Study of Cerebral Radiation Injury: Quantitative T2 Changes Over Time and Histopathologic Correlation. AJNR. 1995;16:79-85. [30] 官键,陈龙华,李志勇,等.放射性脑损伤实验兔模型的建立[J].肿瘤防治研究,2007,34(7):477-547. [31] 邢诒刚,唐亚梅,孙颖,等.急性放射性脑损伤鼠模型的建立[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2003,23(4):269-270. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||