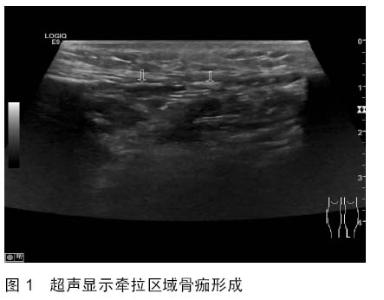
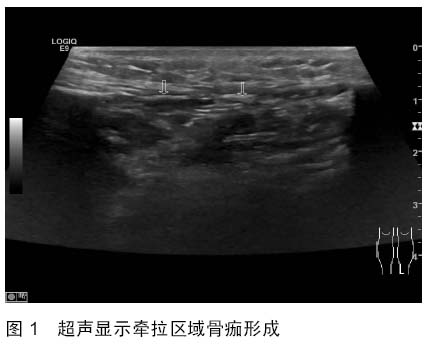
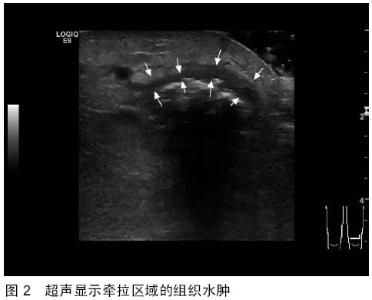
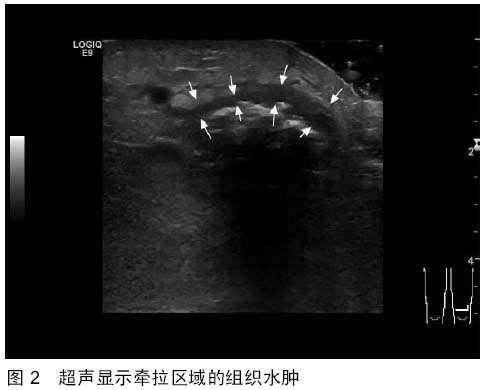
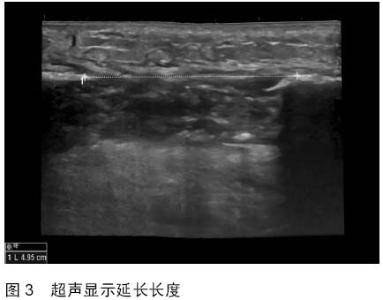
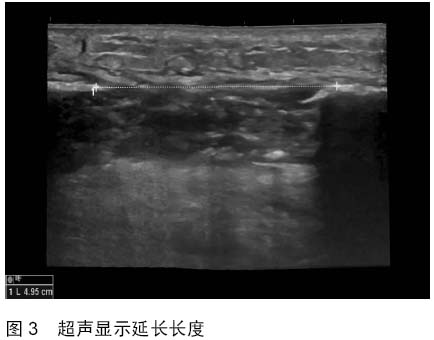
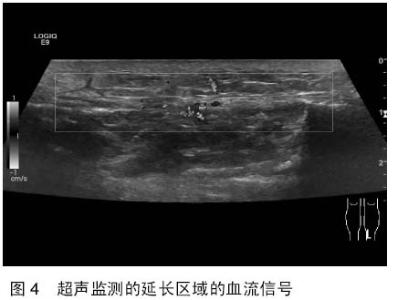
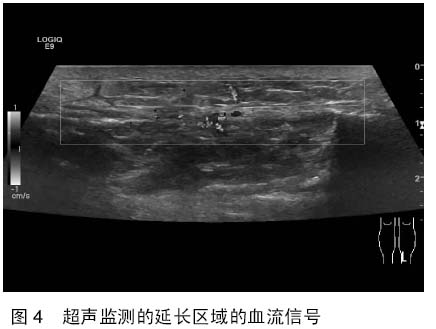
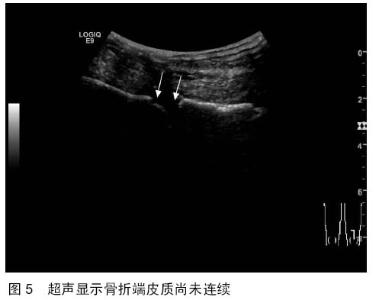
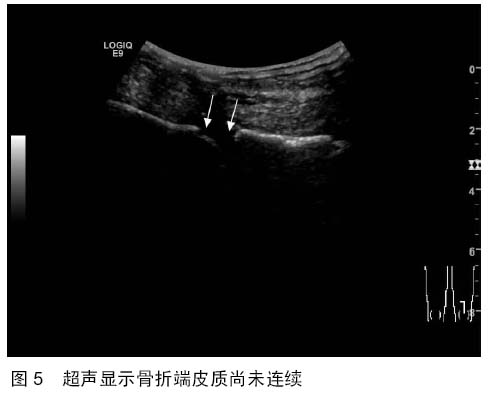
| [1] 秦泗河,葛建忠,郭保逢.“牵拉成骨”与“牵拉组织再生” 技术的来源与汉语表述[J].中华外科杂志, 2012, 50(5): 461-461.
[2] 李刚,秦泗河.牵拉成骨技术的基础研究进展与带给骨科的启示[J].中华外科杂志, 2005, 43: 540-543.
[3] Aronson J, Shin HD. Imaging techniques for bone regenerate analysis during distraction osteogenesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003;23(4):550-560.
[4] Luk HK, Lai YM, Qin L, et al. Computed Radiographic and Ultrasonic Evaluation of Bone Regeneration During Tibial Distraction Osteogenesis in Rabbits. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38(10):1744-1758.
[5] Hughes CW, Williams RW, Bradley M, et al. Ultrasound monitoring of distraction osteogenesis.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2003;41: 256-258.
[6] Chen T, Lai RF, Zhou ZY, et al. Application of ultrasonic inspection in monitoring dynamic healing of mandibular fracture in rabbit model. Asian Pac J Trop Med.2012;5(5): 406-409.
[7] Poposka A, Atanasov N, Dzoleva-Tolevska R. Use of ultrasonography in evaluation of new bone formation in patients treated by the method of Ilizarov. Prilozi. 2012;33(1): 199-208.
[8] Young JW, Kostrubiak IS, Resnik CS, et al. Sonographic evaluation of bone production at the distraction site in Ilizarov limb-lengthening procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990; 154(1):125-128.
[9] Higashihori KM, Baba Y, Tetsumura A, et al.Ultrasonographic assessment of new bone formation in maxillary distraction osteogenesis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(8):1750-1753.
[10] 吴贽,赖仁发,刘湘宁等, 超声显像对兔下颌骨体部骨折愈合过程的监测[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(48):9489-9492.
[11] 秦泗河. Ilizarov技术概述[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26: 642-645.
[12] Nocini PF, Albanese M, Wangerin K, et al. Distraction osteogenesis of the mandible: evaluation of callus distraction by B-scan ultrasonography. J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2002; 30(5):286-291.
[13] Sumer AP, Ozer M, Sumer M, et al.Ultrasonography in the Evaluation of Midpalatal Suture in Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion. J Craniofac Surg.2012;23(5):1375-1377.
[14] Liantis P, Mavrogenis AF, Stavropoulos NA, et al. Risk factors for and complications of distraction osteogenesis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(5):693-698
[15] Babatunde OM, Fragomen AT, Rozbruch SR. Noninvasive quantitative assessment of bone healing after distraction osteogenesis. HSS J. 2010;6(1):71-78.
[16] Selim H, Elbargothy N, Nabil Y, et al. Evaluation of distracted mandibular bone using computed tomography scan and ultrasonography: technical note. Evaluation. 2009;38. 274-280.
[17] Ilizarov GA. The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues: Part I. The influence of stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1989; (238): 249-281.
[18] Weinberg ER, Tunik MG, Tsung JW. Accuracy of clinician-performed point-of-care ultrasound for the diagnosis of fractures in children and young adults. Injury. 2010; 41: 862-868.
[19] Augat P, Morgan EF, Lujan TJ, et al. Imaging techniques for the assessment of fracture repair. Injury.2014;45: S16-S22.
[20] Hughes CW, Williams RW, Bradley M, et al. Ultrasound monitoring of distraction osteogenesis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;41: 256-258.
[21] Liantis P, Mavrogenis AF, Stavropoulos NA, et al. Risk factors for and complications of distraction osteogenesis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2014;24(5):693-698.
[22] 姚志兰,贲丽媛,姚志娟,等.骨延长术后骨痂愈合过程的多普勒超声监测[J].中国超声医学杂志,1997,13:45-46.
[23] 师红立. X线和彩色多普勒超声检查在肢体延长中的应用价值[D]. 天津医科大学,2009.
[24] Issar Y, Sahoo NK, Sinha R, et al. Comparative evaluation of the mandibular distraction zone using ultrasonography and conventional radiography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 43(5):587-594. |