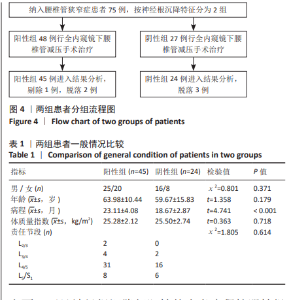
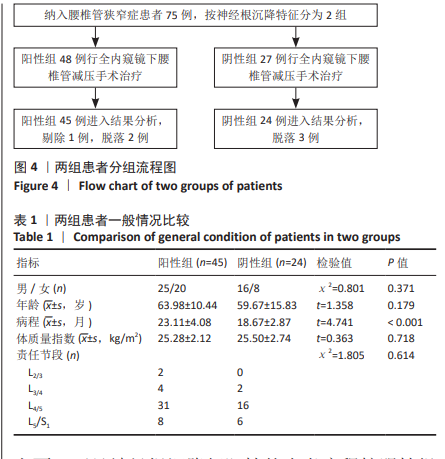
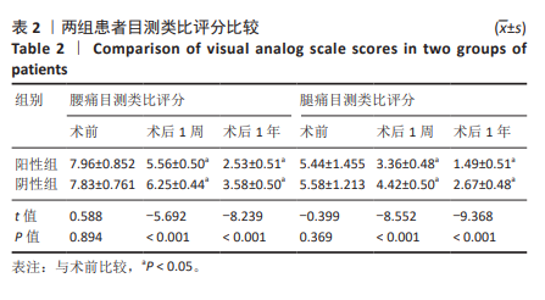
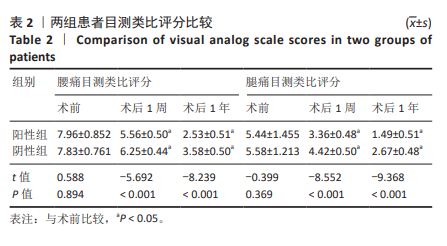
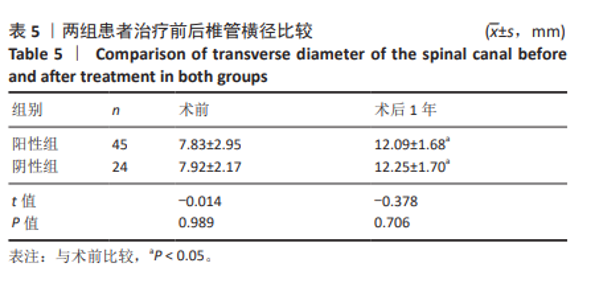
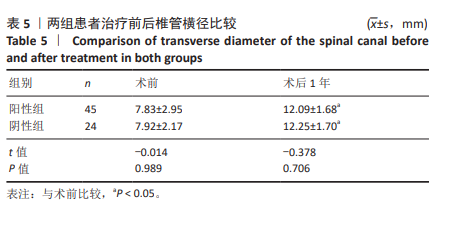
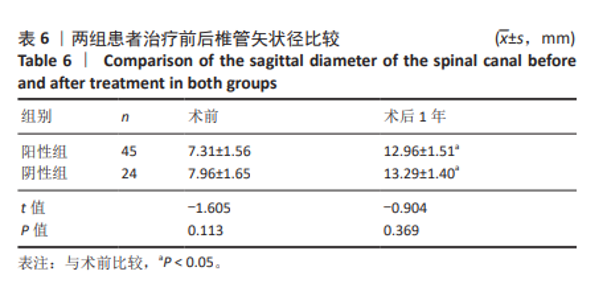
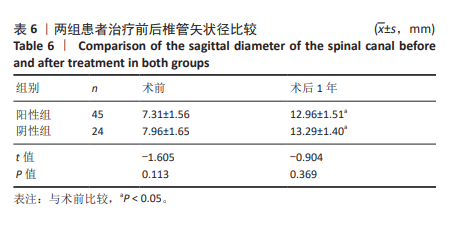
[1] BAGLEY C, MACALLISTER M, DOSSELMAN L, et al. Current concepts and recent advances in understanding and managing lumbar spine stenosis. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-137.
[2] BARZ T, MELLOH M, STAUB LP, et al. Nerve root sedimentation sign: evaluation of a new radiological sign in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 2010;35(8):892-897.
[3] 汤润民,谭利贤,杜小康,等.神经根沉降征在腰椎管狭窄症诊断中的预测价值[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2024,38(5):550-555.
[4] PIECHOTA M, KRÓL R, ELIAS DA, et al. The nerve root sedimentation sign in diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Radiol. 2019;60(5): 634-642.
[5] HUA W, WANG B, KE W, et al. Comparison of lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy bilateral decompression and minimally invasive surgery transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for one-level lumbar spinal stenosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):785.
[6] MO Z, ZHANG R, CHANG M, et al. Exercise therapy versus surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pak J Med Sci. 2018;34(4):879-885.
[7] SHAH M, KOLB B, YILMAZ E, et al. Comparison of lumbar laminectomy alone,lumbar laminectomy and fusion,stand-alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion,and stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis:a review of the literature. Cureus. 2019;11(9):e5691.
[8] 徐峰,李涛,胡昊,等.椎间孔镜I See技术治疗腰椎管狭窄合并腰椎间盘突出症:附10例患者[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(3): 260-265.
[9] LEE JC, KIM Y, SOH JW, et al. Risk factors of adjacent segment disease requiring surgery after lumbar spinal fusion:comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(5):E339-E345.
[10] WU MH, WU PC, LEE CY, et al. Outcome analysis of lumbar endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression in patients with degenerative lumbar central canal stenosis. Spine J. 2021;21(1): 122-133.
[11] FAN N, SONG H, ZANG L, et al. Clinical outcomes of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic decompression for the treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis in elderly individuals: a matched comparison study. Int Orthop. 2024 Dec;48(12):3197-3205.
[12] ZHANG F, YE D, ZHANG W, et al. Efficacy of lumbar decompression under large-channel spinal endoscope in elderly patients with segmental lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024; 19(1):16.
[13] CHEN X, QIN R, HAO J, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic decompression via transforaminal approach for lumbar lateral recess stenosis in geriatric patients. Int Orthop. 2019;43(5):1263-1269.
[14] CHEN J, WANG J, WANG B, et al. Post-surgical functional recovery,lumbar lordosis, and range of motion associated with MR-detectable redundant nerve roots in lumbar spinal stenosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;140(1):79-84.
[15] HUET T, COHEN-SOLAL M, LAREDO JD, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis and disc alterations affect the upper lumbar spine in adults with achondroplasia. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):4699.
[16] 冯强, 周誉.脊柱测量尺和Spinal Mouse脊柱测量仪测量胸椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角的信度和效度[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017, 36(2):150-155.
[17] WANG C, CHANG H, GAO X, et al. Risk factors of degenerative lumbar scoliosis in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(38):e17177.
[18] 刁树娟,王斌,杨滨.马尾神经根沉降征对腰椎管狭窄患者的应用价值[J].影像研究与医学应用,2022,6(12):135-137.
[19] WANG G, PENG Z, LI J, et al. Diagnostic performance of the nerve root sedimentation sign in lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroradiology. 2019;61(10):1111-1121.
[20] PATEL K, SON SM, ZHANG Q, et al. An Investigation Into the Relationship Between the Sedimentation Sign and Lumbar Disc Herniation in Upright Magnetic Resonance Images. Global Spine J. 2024;14(7):2088-2094.
[21] 李敏红,余林,李志铭,等.MRI检查神经根沉降征诊断LSS患者的价值及其危险因素分析[J].影像科学与光化学,2022,40(1):53-58.
[22] 邓罗义,宁旭,杨华,等.神经根沉降征在非手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症中的疗效预测价值[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(5): 449-452.
[23] DENG L, YANG H, LIU M, et al. The role of positive nerve root sedimentation sign in the treatment of patients undergoing lumbar disc herniation. Br J Neurosurg. 2024;38(3):556-561.
[24] 姜杰,徐丽彪,熊丹婷,等.神经根沉降征对腰椎管狭窄症患者行Endo-ULBD手术治疗效果的评定价值[J].哈尔滨医药,2024,44(4): 69-71.
[25] BARZ T, STAUB LP, MELLOH M, et al. Clinical validity of the nerve root sedimentation sign in patients with suspected lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2014;14(4):667-674. |