Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 1013-1020.doi: 10.12307/2025.291
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanisms of ligament flavum hypertrophy: analysis based on methylation sequencing and transcriptome integration
He Yang1, Tang Buyuan1, Lu Changhuai2
- 1Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China; 2No. 2 Spinal Ward, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Changde, Changde 415000, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-12Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-02-18Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Lu Changhuai, MD, Chief physician, No. 2 Spinal Ward, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Changde, Changde 415000, Hunan Province, China -
About author:He Yang, Master candidate, Physician, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (General Program), No. 2021JJ30049 (to LCH); Postgraduate Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province, No. 2022CX201 (to HY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Yang, Tang Buyuan, Lu Changhuai. Molecular mechanisms of ligament flavum hypertrophy: analysis based on methylation sequencing and transcriptome integration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1013-1020.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
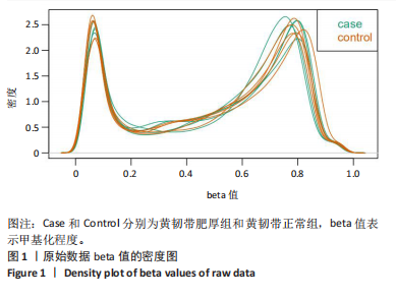
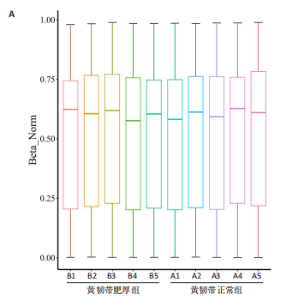
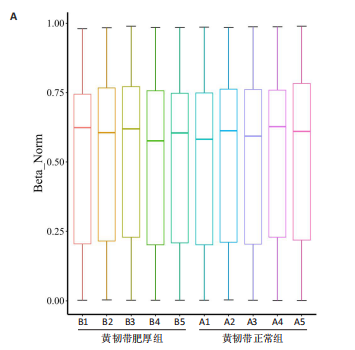
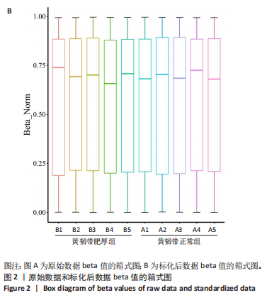
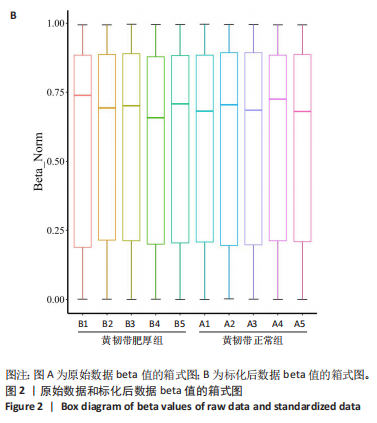
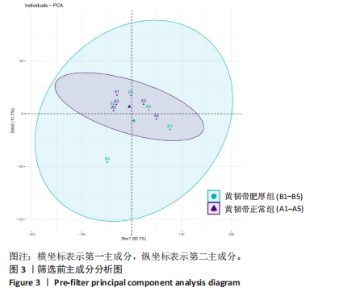
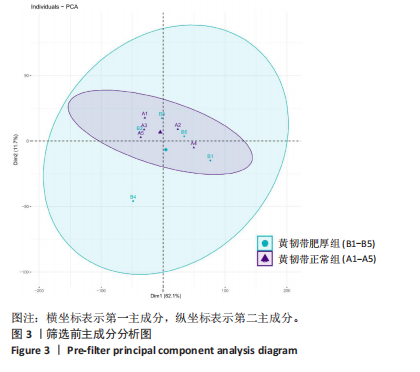
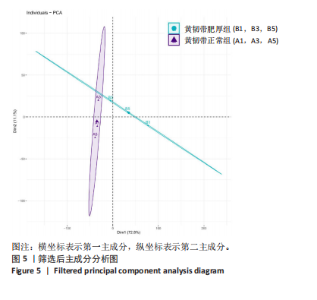
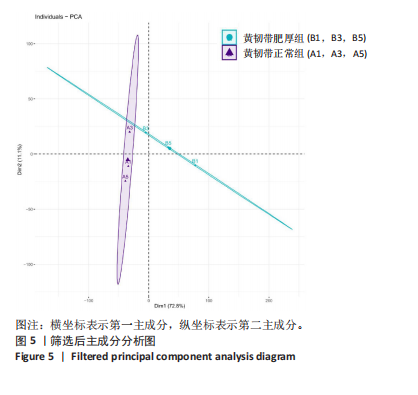
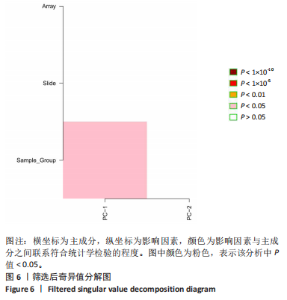
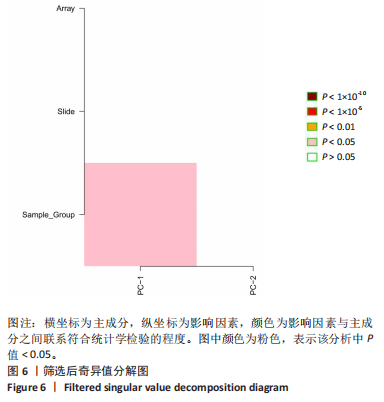
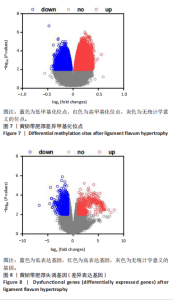
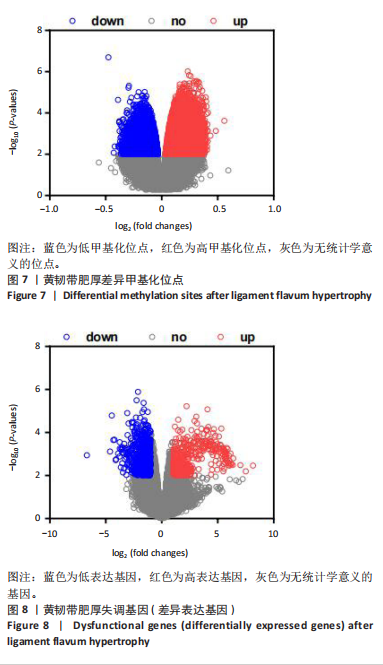
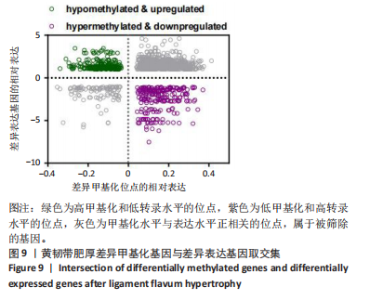
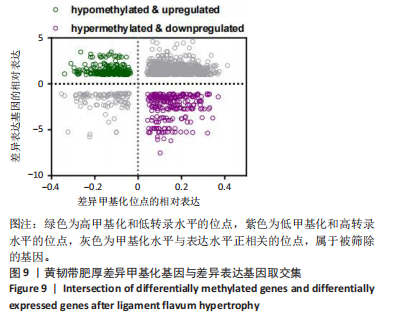
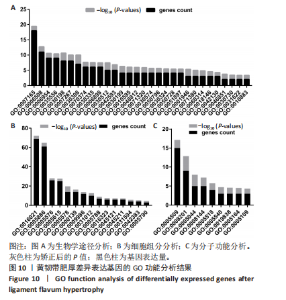
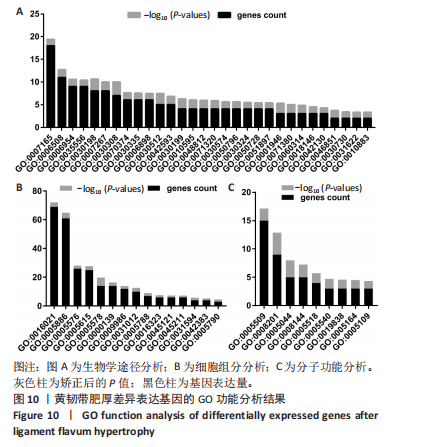
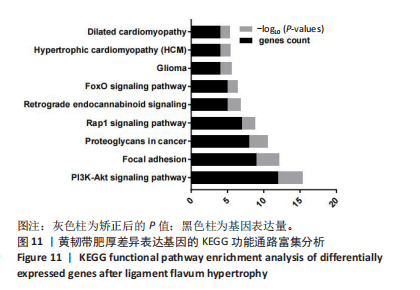
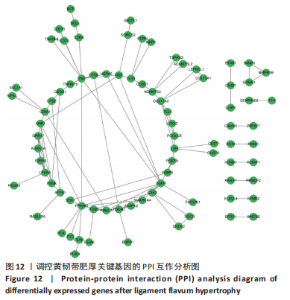
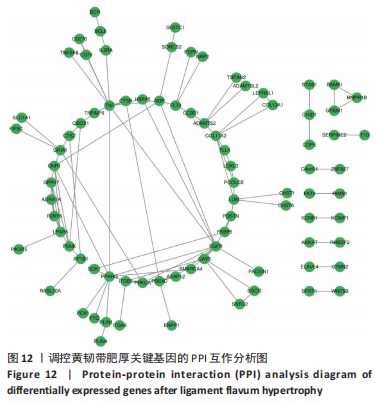
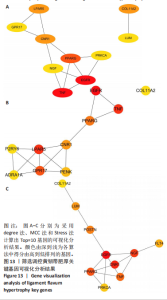
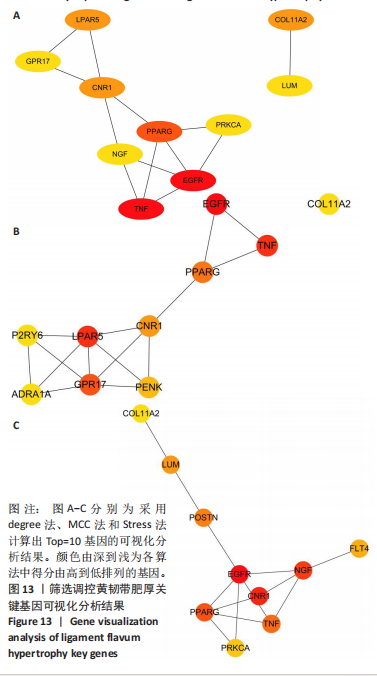
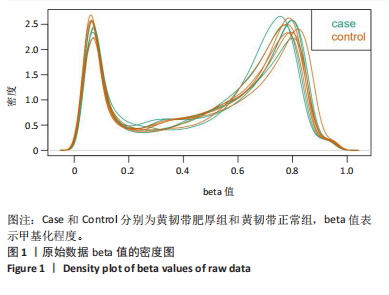
2.1 甲基化位点原始数据质控及处理 2.1.1 过滤以及标化甲基化数据 使用BMIQ(Beta Mlxture Quantile dilation)方法对检测后得到的甲基化位点进行beta值的标准化处理,用beta值的密度图来看图上是否有异常样本(图1),用箱式图(图2)来验证数据标化的情况。结果显示,样本都正常,标化后样本数据整齐。 2.1.2 甲基化数据主成分分析与奇异值分解 通过降维度以及奇异值分解来看数据集中变异情况以及它的重要组成部分的来源(图3,4),可以看出如果用全部样本,黄韧带肥厚组与黄韧带正常组之间距离不大,而且它们的主要差异并非来源于组别。为了得到差异来源于组别,选取了比较集中在一起的样本B1,B3,B5以及A1,A3,A5,再做主成分分析和奇异值分解(图5,6),可以看出当只选取B1,B3,B5与A1,A3,A5样本时,组别距离大,差异来源主要是组别差异。 2.2 甲基化测序结果 使用P < 0.01筛选出47 756个差异的探针位点,其中高甲基化位点37 173个,低甲基化位点10 583个。使用火山图展示差异结果,见图7。 2.3 转录组整合分析结果 筛选阈值为P < 0.01和|logFC |> 1。一共找到720个差异表达基因,其中463个上调基因,257个下调基因。使用火山图展示差异结果,见图8。 2.4 差异甲基化基因与差异表达基因四象分析及富集通路分析 两者之间重叠的基因有383个,其中192个基因的mRNA表达水平与其甲基化水平负相关,见图9。针对重叠基因中呈负相关的192个基因进行GO、KEGG功能通路富集分析,筛选条件为P < 0.05。GO功能分析结果表明,GO的分子功能(molecular function,MF)富集到10个条目,细胞组分(cellular component,CC)富集到15个条目,生物学途径(biological process,BP)富集到30个条目,见图10。KEGG通路富集分析结果表明,192个基因主要富集到PI3K-Akt信号通路、Rap1信号通路、Focal adhesion信号通路、FoxO 信号通路等9条通路,见图11。 2.5 PPI互作分析 筛选调控黄韧带肥厚的关键基因。通过Strings数据库进行PPI互作网络分析,将degree≥ 2的基因导入 Cystocape进行可视化,见图12。进一步采用degree法、Stress法和MCC法计算出Top=10的基因并可视化分析,其中有5个重叠基因(PPARG、EGFR、CNR1、TNF和COL11A2 ),这5个基因可能是调控黄韧带肥厚的关键基因,见图13。"
| [1] KATZ JN, ZIMMERMAN ZE, MASS H, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(17):1688-1699. [2] BYVALTSEV VA, KALININ AA, HERNANDEZ PA, et al. Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of Spinal Stenosis Formation: Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):13479. [3] KWON WK, HAM CH, CHOI H, et al. Elucidating the effect of mechanical stretch stress on the mechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Development of a novel in vitro multi-torsional stretch loading device. PLoS One. 2022;17(10):e0275239. [4] HAYASHI F, MORIMOTO M, HIGASHINO K, et al. Myofibroblasts are increased in the dorsal layer of the hypertrophic ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine J. 2022;22(4):697-704. [5] KIM J, KWON WK, CHO H, et al. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy significantly contributes to the severity of neurogenic intermittent claudication in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(36):e30171. [6] MEHROTRA A, SINGH K, KANJILAL S, et al. Expanding the Horizons of Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Experience of the Destandau Technique for the Treatment of Multiple Spinal Diseases. World Neurosurg. 2024;181:e970-e977. [7] BURILE G, JAWADE S, SETH N. The Scope of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation in Compressive Myelopathy Managed by Spinal Fusion: A Case Report. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e48290. [8] KURZ E, SCHENK P, BRAKOPP F, et al. Muscle activity and rehabilitation in spinal stenosis (MARSS) after conservative therapy and surgical decompression with or without fusion: Protocol for a partially randomized patient preference trial on rehabilitation timing. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024;38:101273. [9] SOBAŃSKI D, STASZKIEWICZ R, STACHURA M, et al. Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management of Lower Back Pain Associated with Spinal Stenosis: A Narrative Review. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e939237. [10] WANG S, QU Y, FANG X, et al. Decorin: a potential therapeutic candidate for ligamentum flavum hypertrophy by antagonizing TGF-β1. Exp Mol Med. 2023;55(7):1413-1423. [11] SUN C, ZHANG H, WANG X, et al. Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways, cellular mechanisms, and future directions. FASEB J. 2020;34(8):9854-9868. [12] WU L, MUNAKOMI S, CRUZ R. Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2024. [13] ZHAO R, DONG J, LIU C, et al. Thrombospondin-1 promotes mechanical stress-mediated ligamentum flavum hypertrophy through the TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Matrix Biol. 2024;127:8-22. [14] WEISKIRCHEN R, WEISKIRCHEN S, TACKE F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:2-15. [15] LIN Z, ZHOU P, VON GISE A, et al. Pi3kcb links Hippo-YAP and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival. Circ Res. 2015;116(1):35-45. [16] ARCERI L, NGUYEN TK, GIBSON S, et al. Cannabinoid Signaling in Kidney Disease. Cells. 2023;12(10):1419. [17] GOLOSOVA D, LEVCHENKO V, KRAVTSOVA O, et al. Acute and long-term effects of cannabinoids on hypertension and kidney injury. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):6080. [18] TAHAMTAN A, SAMIEIPOOR Y, NAYERI FS, et al. Effects of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in respiratory syncytial virus infection in human subjects and mice. Virulence. 2018;9(1):217-230. [19] GHALLAB A, SEDDEK A. PPARG as therapeutic target for antifibrotic therapy. EXCLI J. 2020;19:227-229. [20] LU C, LIU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Proliferation effect of ligamentum flavum cells induced by transforming growth factor β 1 and its effect on connective tissue growth factor. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(7):883-888. [21] SABBAH DA, HAJJO R, SWEIDAN K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(10):815-834. [22] NEEDHAM SR, ZANETTI-DOMINGUES LC, HIRSCH M, et al. Structure-function relationships and supramolecular organization of the EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) on the cell surface. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42(1):114-119. [23] KIM BJ, HUR JW, PARK JS, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human ligamentum flavum cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):428-435. [24] WEBSTER JD, VUCIC D. The Balance of TNF Mediated Pathways Regulates Inflammatory Cell Death Signaling in Healthy and Diseased Tissues. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:365. [25] SUN C, WANG Z, TIAN JW, et al. Leptin-induced inflammation by activating IL-6 expression contributes to the fibrosis and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(2):BSR20171214. [26] PARNELL J, MARTIN N, DEDEK A, et al. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Expression and Localization in the Dorsal Horn of Male and Female Rat and Human Spinal Cord. Can J Pain. 2023;7(2):2264895. [27] 薛翠华,高振军,李秋萍,等.塞来昔布对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎血清TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-6及IL-8水平的影响[J].江苏大学学报(医学版), 2009,19(6):496-498,504. [28] GOPAL D, HO AL, SHAH A, et al. Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;760:114-133. [29] CALDEIRA J, SANTA C, OSÓRIO H, et al. Matrisome Profiling During Intervertebral Disc Development And Ageing. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11629. [30] XIE G, LIANG C, YU H, et al. Association between polymorphisms of collagen genes and susceptibility to intervertebral disc degeneration: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):616. [31] SOPHIA FOX AJ, BEDI A, RODEO SA. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2009; 1(6):461-468. [32] YOSHIDA M, SHIMA K, TANIGUCHI Y, et al. Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Pathogenesis and morphologic and immunohistochemical observation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992; 17(11):1353-1360. |
| [1] | Guo Song, Li Xinhua, Yan Meijun, Liu Yanbin, Liu Zhong, Li Kewei, Liu Pengcheng, Zhang Beiting, Fu Qiang. Comparison of decompression effects between spine endoscopy hybrid technique and uniportal endoscopic surgery in treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with bilateral symptom [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 517-523. |
| [2] | Fang Zhao, Qiao Pan, Xu Tiantong. Correlation between sagittal alignment and clinical symptom improvement after lumbar fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3778-3782. |
| [3] | Liu Jiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Ding Yiwei, Jiang Qiang, Li Tusheng, Huang Jie, Yang Guangnan, Ding Yu. Finite element analysis of interspinous fixation-assisted endoscopic interbody fusion in treatment of severe lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3789-3795. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinghe, Dou Yongfeng, Xu Shidong, Xing Jianqiang, Liu Dong, Tian Lin, Dai Guohua. Effect of finite element simulation of bilateral lumbar spinal canal decompression under single-channel splintered endoscope on lumbar biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1849-1854. |
| [5] | Wang Jianye, Liu Xin, Tian Lin, Sun Ning, Li Yuefei, Bi Jingwei, Liu Changzhen, Sun Zhaozhong . Measuring the position relation between nerve tissue and bony structure in lumbar spinal canal decompression area by constructing a three-dimensional model of the lumbar spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 539-546. |
| [6] | Wang Mengshu, Zhang Yu, Zheng Zhouhang, Chen Long, You Dongchun, Guo Weifeng, Hu Fei, Chen Huan, Liu Xingming, Wu Ronghai, Zhang Yin. Differential protein expression analysis of hypertrophic and normal ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis with Qi deficiency and blood stasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5589-5595. |
| [7] | An Hepeng, Liu Zhenteng, Li Lixin, Xu Yafang, Fan Guofeng. Effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neuronal activity, pain, and related cytokines in rats with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4120-4125. |
| [8] | Xiao Shipeng, Guo Chen, Li Shichun, Li Qinliang, Xu Yong, Xu Shuai. Analysis and reconstruction of sagittal lumbo-pelvic parameters in the elderly with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2903-2909. |
| [9] | Zhang Hanshuo, Ding Yu, Jiang Qiang, Lu Zhengcao, Lian Shilin, Li Tusheng. Biomechanical stability and finite element analysis of endoscopic LOVE decompression technique and endoscopic unilateral laminotomy for bilateral decompression technique for lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 1981-1986. |
| [10] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [11] | Tian Yang, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Ma Fei, Zhong Dejun. Consistency and repeatability of CT and MRI in measurement of spinal canal area in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3882-3887. |
| [12] | Wang Jing, Xu Shuai, Liu Haiying. Hidden blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5307-5314. |
| [13] | Zhang Chunlin, Shang Lijie, Yan Xu, Cao Zhengming, Shao Chenglong, Feng Yang. Mid-long-term effect of only placed expandable interbody fusion cage in the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with vertebral instability using micro-endoscopic discectomy system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 335-341. |
| [14] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yu, Jiang Qiang, Cui Hongpeng, Lu Zhengcao. A finite element model of full endoscope lumbar fenestration and biomechanical characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4291-4296. |
| [15] | He Da, Zhao Jingwei, Liu Bo, Tian Wei. Comparison of limited fusion and full curve fusion for mild lumbar degenerative scoliosis with stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5811-5817. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||