Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6092-6098.doi: 10.12307/2026.344
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of influencing factors and risk prediction model for spasticity severity in stroke patients with hemiplegia
Cao Xinyan1, Leng Xiaoxuan1, Gao Shiai1, Chen Jinhui1, Liu Xihua2
- 1School of Rehabilitation, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250011, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-08-14Online:2026-08-18Published:2026-01-05 -
Contact:Liu Xihua, PhD, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250011, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Cao Xinyan, MS candidate, School of Rehabilitation, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81802239 (to LXH); Shandong Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science & Technology Project (General Project), No. M-2023142 (to LXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Xinyan, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Analysis of influencing factors and risk prediction model for spasticity severity in stroke patients with hemiplegia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6092-6098.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
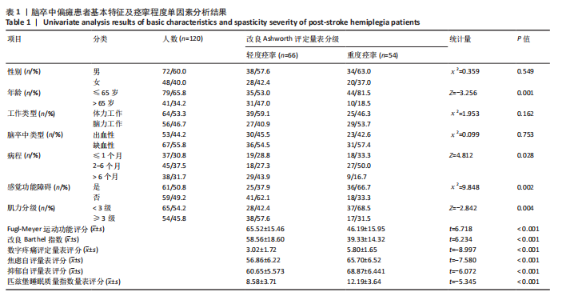
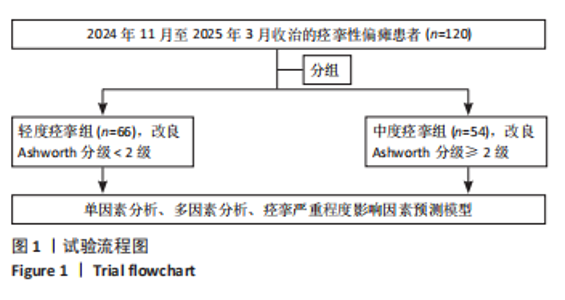
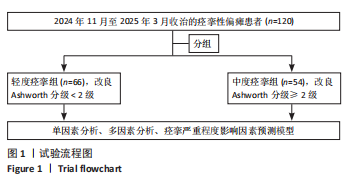
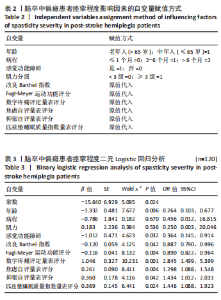
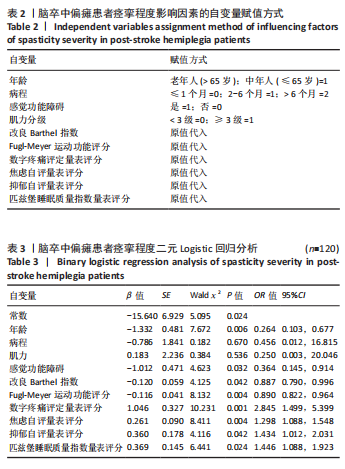
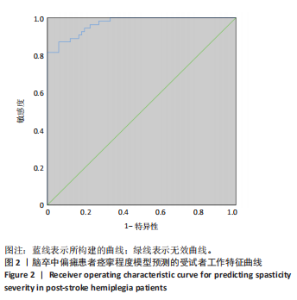
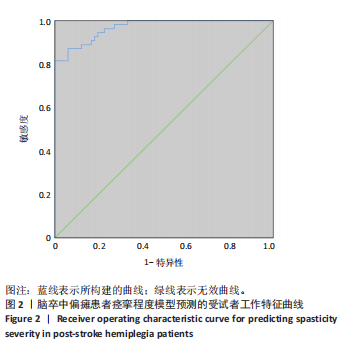
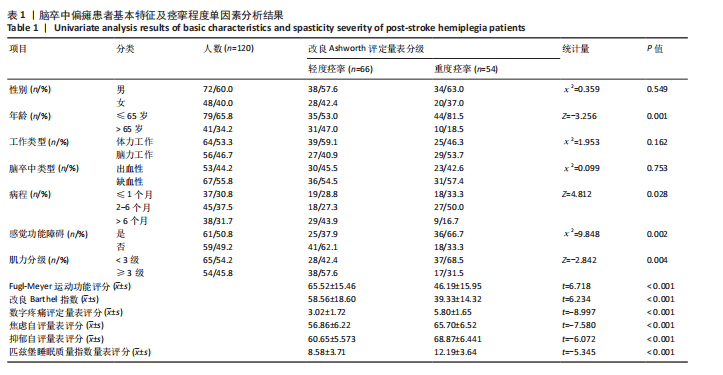
2.3 研究对象基本特征 共收集120例脑卒中后痉挛患者资料,其中男72例占60%,女48例占40%;65岁及以下患者79例占65.8%,65岁以上患者41例占34.2%;体力工作者64例占53.3%,脑力工作者56例占46.7%;出血型脑卒中53例占44.2%,缺血性脑卒中67例占55.8%;病程≤1个月的患者37例占30.8%,2-6个月的患者45例占37.5%,> 6个月的患者38例占31.7%;存在感觉障碍的患者61例占50.8%,见表1。 2.4 偏瘫患者痉挛严重程度单因素分析结果 单因素分析结果显示,不同痉挛程度组间在性别、工作类型、脑卒中类型方面差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);而两组在年龄、病程、是否存在感觉障碍、肌力分级、Fugl-Meyer运动功能评分、改良Barthel指数、疼痛等级、焦虑与抑郁情绪、睡眠质量方面差异有显著意义(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.5 偏瘫患者痉挛严重程度多因素分析结果 以痉挛严重程度作为因变量,以单因素分析结果中P < 0.05的影响因素(年龄、病程、感觉功能障碍、肌力分级、改良Barthel指数、Fugl-Meyer运动功能评分、疼痛分级、焦虑、抑郁评分、睡眠质量评分)作为自变量进行二元Logistic回归分析,赋值方式见表2。回归分析结果显示年龄、感觉功能障碍、改良Barthel指数、Fugl-Meyer运动功能评分是脑卒中偏瘫患者痉挛程度的保护因素,疼痛等级、焦虑抑郁情绪和睡眠质量是脑卒中偏瘫患者痉挛程度的危险因素,结果见表3。 2.6 偏瘫患者痉挛严重程度影响因素预测模型 根据Logistic回归分析结果构建脑卒中偏瘫患者痉挛程度影响因素的预测模型:Logit(P)=-15.640-1.332×年龄-0.786×病程+0.183×肌力-1.012×感觉功能障碍-0.120×改良Barthel指数-0.116×Fugl-Meyer运动功能评分+1.046×疼痛等级+0.261×焦虑评分+0.360×抑郁评分+0.369×睡眠质量。以预测概率值为检验变量,痉挛严重程度为状态变量,预测模型受试者工作特征曲线下面积为0.969[95%CI(0.944,0.994)],说明模型预测能力较好,模型最大约登指数为0.809,灵敏度为0.870,特异度为0.939,受试者工作特征曲线见图2。"
| [1] CHEN B, YANG T, LIAO Z, et al. Pathophysiology and Management Strategies for Post-Stroke Spasticity: An Update Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26(1):406. [2] 姜帅,肖娟,刘泽键,等.高频重复经颅磁刺激联合功能性电刺激对脑卒中患者下肢痉挛及激活后抑制的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2024,39(11):1638-1643. [3] ZENG H, CHEN J, GUO Y, et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Spasticity After Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol. 2021;11:616097. [4] 吕阳婷,殷艺雯.肌筋膜松解术治疗脑卒中后上肢痉挛性瘫痪的效果[J].实用医学杂志,2024,40(23):3379-3383. [5] PINHO S, CAMÕES-BARBOSA A, HATIA M, et al. Shoulder Spasticity Treatment With Botulinum Toxin: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Survey of Clinical Practices. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e48493. [6] LI S, FRANCISCO GE, RYMER WZ. A New Definition of Poststroke Spasticity and the Interference of Spasticity With Motor Recovery From Acute to Chronic Stages. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021;35(7):601-610. [7] 胡延超,李瑞青,郝文雪,等.γ-氨基丁酸能系统在脑卒中后痉挛状态中的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(4):994-997. [8] LIU J, ZHAO G, NIU Y, et al. Effect of electro-acupuncture therapy on limb spasm and excitability of motor neurons in stroke rats. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021;50(3):361-368. [9] ZHOU Z, WANG S, ZHANG J. Progress on acupuncture in relieving stroke induced limb spasticity by regulating neuroplasticity-related signals. World J Acupunct Moxibustion. 2023;33(2):65-71. [10] 黄赛娥,卓丽萍,黄丹霞,等.偏瘫肌痉挛影响因素临床研究[J].亚太传统医药,2015,11(21):80-83. [11] 中华医学会神经病学分会 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J].中华神经科杂志,2019,52(9):710-715. [12] 中风的诊断依据、证候分类、疗效评定:中华人民共和国中医药行业标准《中医内科病证诊断疗效标准》(ZY/T001.1-94)[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2016,18(10):16. [13] 何紫艳,唐晓晓,田亚星,等.指部徒手感觉刺激前后脑卒中偏瘫患者手指屈、伸肌张力及超声剪切波弹性成像的变化[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(2):204-211. [14] MESEGUER-HENAREJOS AB, SÁNCHEZ-MECA J, LÓPEZ-PINA JA, et al. Inter- and intra-rater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2018; 54(4):576-590. [15] VIANA RB, DE OLIVEIRA VN, DANKEL SJ, et al. The effects of exergames on muscle strength: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(8):1592-1611. [16] WANG YC, CHANG PF, CHEN YM, et al. Comparison of responsiveness of the Barthel Index and modified Barthel Index in patients with stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;45(6):1097-1102. [17] LIAO LY, WANG PY, ZHU Y, et al. Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with extracorporeal shockwave therapy for poststroke spasticity: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2025;15(1):e086300. [18] SINGER B, GARCIA-VEGA J. The Fugl-Meyer Upper Extremity Scale. J Physiother. 2017;63(1):53. [19] WIESNER K, SCHWARZ A, MEYA L, et al. Interrater reliability of the Fugl-Meyer Motor assessment in stroke patients: a quality management project within the ESTREL study. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1335375. [20] FARRAR JT, YOUNG JP JR, LAMOREAUX L, et al. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain. 2001;94(2):149-158. [21] 万丽,赵晴,陈军,等.疼痛评估量表应用的中国专家共识(2020版)[J].中华疼痛学杂志,2020,16(3):177-187. [22] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会睡眠障碍学组,中华医学会神经病学分会神经心理与行为神经病学学组.中国成人失眠伴抑郁焦虑诊治专家共识[J].中华神经科杂志,2020, 53(8):564-574. [23] 王存利,王红霞.社区围绝经期女性主观认知下降现状及影响因素分析[J].护理学杂志,2025,40(1):79-83. [24] 刘贤臣,唐茂芹,胡蕾,等.匹兹堡睡眠质量指数的信度和效度研究[J].中华精神科杂志,1996,29(2):103-107. [25] OPHEIM A, DANIELSSON A, ALT MURPHY M, et al. Early prediction of long-term upper limb spasticity after stroke: part of the SALGOT study. Neurology. 2015;85(10):873-880. [26] URBAN PP, WOLF T, UEBELE M, et al. Occurence and clinical predictors of spasticity after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2010;41(9):2016-2020. [27] WELMER AK, WIDÉN HOLMQVIST L, SOMMERFELD DK. Location and severity of spasticity in the first 1-2 weeks and at 3 and 18 months after stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(5):720-725. [28] LIAO LY, XU PD, FANG XQ, et al. Prevalence and clinical predictors of spasticity after intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2906. [29] CHUNG SG, VAN REY EM, BAI Z, et al. Aging-related neuromuscular changes characterized by tendon reflex system properties. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(2):318-327. [30] JONES R, RATNAKUMAR N, AKBAŞ K, et al. Delayed center of mass feedback in elderly humans leads to greater muscle co-contraction and altered balance strategy under perturbed balance: A predictive musculoskeletal simulation study. PLoS One. 2024;19(5):e0296548. [31] WISSEL J, SCHELOSKY LD, SCOTT J, et al. Early development of spasticity following stroke: a prospective, observational trial. J Neurol. 2010;257(7):1067-1072. [32] 孟凡刚,许天奇,季玉陈,等.小脑齿状核脑深部电刺激术对脑卒中后运动功能的改善作用[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2024, 24(7):507-509. [33] YE Q, WANG X, LI T, et al. Clinical efficacy of NIBS in enhancing neuroplasticity for stroke recovery. J Neurosci Methods. 2025;417: 110399. [34] LUO J, FENG Y, HONG Z, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes neural stem cell proliferation after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1772-1780. [35] HOH JE, SEMRAU JA. The Role of Sensory Impairments on Recovery and Rehabilitation After Stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025;25(1):22. [36] TSAO CW, ADAY AW, ALMARZOOQ ZI, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145(8):e153-e639. [37] ZHAO H, ZHANG T, ZHANG H, et al. Exercise-with-melatonin therapy improves sleep disorder and motor dysfunction in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(6):1336-1343. [38] MOHANDAS P, ALOMARI Z, ARTI F, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Identification of Predictors Associated With Insomnia or Sleep Disturbance in Post-stroke Patients. Cureus. 2024;16(3):e56578. [39] HWANG HS, KIM H. Factors Affecting the Quality of Sleep and Social Participation of Stroke Patients. Brain Sci. 2023;13(7):1068. [40] ALI M, TIBBLE H, BRADY MC, et al. Prevalence, Trajectory, and Predictors of Poststroke Pain: Retrospective Analysis of Pooled Clinical Trial Data Set. Stroke. 2023;54(12):3107-3116. [41] PLECASH AR, CHEBINI A, IP A, et al. Updates in the Treatment of Post-Stroke Pain. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(11):86. [42] TREISTER AK, HATCH MN, CRAMER SC, et al. Demystifying Poststroke Pain: From Etiology to Treatment. PM R. 2017;9(1):63-75. [43] 李佳祺,赵彤,杨琨,等.脑卒中患者恢复期症状负担及其影响因素调查[J].护理学杂志,2021,36(14):1-3. |
| [1] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Yu Zifu, Cao Xinyan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Balance function and its influencing factors in patients with post-stroke hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4611-4617. |
| [2] | Chen Jinhui, Yu Zifu, Gao Shiai, Cao Xinyan, Leng Xiaoxuan, Liu Xihua. Effects of central and peripheral rehabilitation therapies on upper extremity function and activities of daily living in stroke patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4457-4471. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Gu Dongyang, Zhu Zihao, Li Qiujie, Wan Xianglin. Relationship between spatio-temporal gait characteristics and fall risk in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4038-4044. |
| [4] | Gao Zan, Liu Yixuan, Zhang Lichen, Hou Bing, Tang Yalei, Li Shumei, Che Pengcheng, Dou Na. Network meta-analysis of robot-assisted gait training interventions on lower limb motor function in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4219-4228. |
| [5] | Ma Shanxin, Zheng Jianling, Cheng Jian, Lin Xi, Li Qiuyuan, Wang Li, Zeng Yangkang, Song Luping. Early intelligent active assistance in walking for hemiplegic patients under suspension protection: #br# a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3075-3082. |
| [6] | Cheng Le, Zhu Caifeng, Zhou Bingyuan, Gao Dahong, Cui Xiaoya, Li Jing, Wang Xuewei, Yang Gaoshang, Chen Xiyang. Mechanisms of stroke therapy targeting inflammatory cytokines: a big data analysis based on the IEU Open GWAS [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3198-3216. |
| [7] | Li Jie, Zhao Xiaofeng, Zeng Qi, Zhou Runtian, Chen Rong, Hu Xijian, Zhao Bin. Influencing factors of spine deformity progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and construction of a joint prediction model and nomogram [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2727-2735. |
| [8] | Xing Cong . Fatigue induction protocols for the lumbar extensor muscles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2515-2524. |
| [9] | Zhu Chuanxi, Qiu Long, Li Lingxu, Ji Guangcheng. Chinese herbal prescription combined with head acupuncture exercise therapy improves limb spasticity in rats with ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7571-7577. |
| [10] | Ding Kai, Yao Yujing, Li Zhipeng, Wang Lei, Gu Changyuan, Shu Hao, Sun Luning. Arthroscopic long head of the biceps tendon transposition for augmented repair of massive rotator cuff tear [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5675-5680. |
| [11] | Zhi Liang, Wang Yulong, Zhang Qingfang, Hong Yaqing, Ke Meihua, Liu Quanquan, Long Jianjun. Propulsion deficits in hemiplegic gait of stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5709-5715. |
| [12] | Liu Shiwen, Liu Quanfeng, Yang Zhibo, Duan Changqiu, Zhang Baoying, Tan Yue, Ai Changshan, Jiang Huiqiang, Feng Xugang, Kong Nianhua. Rhythmic auditory stimulation for non-acute dyskinesia in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5583-5588. |
| [13] | Jin Naying, Wu Jiabao, Li Yuyue, Li Yingjie, Zhou Li, Li Zongheng, Zhang Yong. Gait analysis for hemiplegic patients with cerebral infarction based on RSSCAN gait system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3609-3615. |
| [14] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [15] | Liu Yubo, Zhang Huizeng, Zhang Tongrun, Sui Gengyi, Ma Nan, Cheng Xu, Gao Xupeng, Xu Jing, Wang Chaoliang. Correlation analysis between the morphological changes of ankle acupoints and the ankle function after ankle fracture surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 440-445. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||