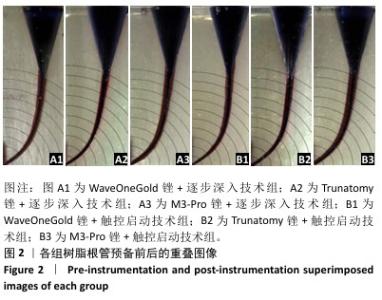
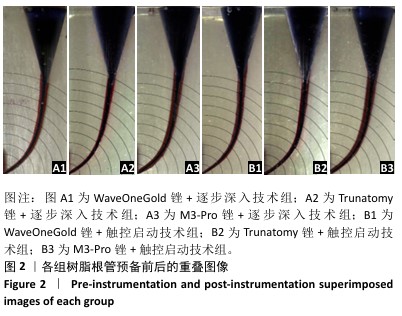
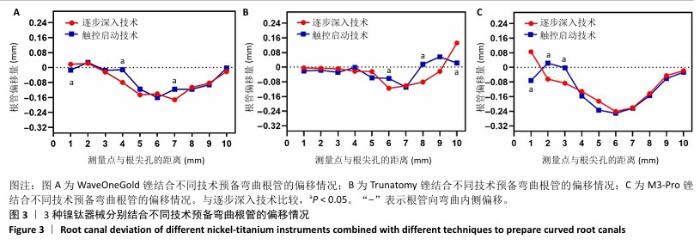
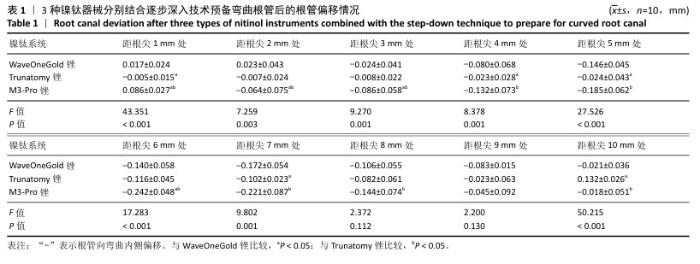
[1] KINJRAWI L, ABDO A, ALNOUR A, et al. Post-endodontic pain in curved canals prepared with different rotary instrumentation techniques: A randomized controlled trial. Dent Med Probl. 2024;61(2):191-196.
[2] TANTIWANICHPUN B, KULVITIT S. Efficiency and complications in root canal retreatment using nickel titanium rotary file with continuous rotation, reciprocating, or adaptive motion in curved root canals: a laboratory investigation. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):871.
[3] DABLANCA-BLANCO AB, CASTELO-BAZ P, MIGUENS-VILA R, et al. Endodontic Rotary Files, What Should an Endodontist Know? Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(6):719.
[4] AGRAWAL PR, CHANDAK M, NIKHADE PP, et al. Revolutionizing endodontics: Advancements in nickel-titanium instrument surfaces. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024;27(2):126-133.
[5] CHANIOTIS A, ORDINOLA-ZAPATA R. Present status and future directions: Management of curved and calcified root canals. Int Endod J. 2022;55 Suppl 3:656-684.
[6] 樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012.
[7] CLAUDER T. Present status and future directions - Managing perforations. Int Endod J. 2022;55 Suppl 4:872-891.
[8] TERAUCHI Y, ALI WT, ABIELHASSAN MM. Present status and future directions: Removal of fractured instruments. Int Endod J. 2022;55 Suppl 3:685-709.
[9] 李婷婷,姜葳,潘悦萍.两种机用镍钛器械在模拟弯曲根管内的成形能力比较[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(4):246-249.
[10] KYAW M S, EBIHARA A, IINO Y, et al. Effect of preset torque setting on torque/force generation, shaping ability and surface changes of nickel titanium rotary instrument in different root canal curvature locations: An ex vivo study. Dent Mater J. 2024;43(3):329-337.
[11] KIM H, JEON SJ, SEO MS. Comparison of the canal transportation of ProTaper GOLD, WaveOne GOLD, and TruNatomy in simulated double-curved canals. BMC Oral Health. 2021;21(1):533.
[12] ZHANG Y, LIU J, GU Y, et al. Analysis of second mesiobuccal root canal instrumentation in maxillary first molars with three nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a micro-computed tomographic study. Odontology. 2021;109(2):496-505.
[13] ZANZA A, REDA R, TESTARELLI L. Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments: Mechanical and Metallurgical Characteristics. Clin Pract. 2022;12(1): 94-96.
[14] AHMAD MZ, SADAF D, MERDAD KA, et al. Calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medication for postoperative pain during primary root canal therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2022;22(1):101680.
[15] JOHNSEN GF, HAUGEN HJ, NOGUEIRA LP, et al. Assessment of the Root Canal Similarity in Contralateral Mandibular Incisors. Int Dent J. 2023;73(1):71-78.
[16] CHANIOTIS A, FILIPPATOS C. Root canal treatment of a dilacerated mandibular premolar using a novel instrumentation approach. A case report. Int Endod J. 2017;50(2):202-211.
[17] REDDY BN, MURUGESAN S, BASHEER SN, et al. Comparison of Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel TruNatomy Files with Conventional Endodontic Files: An In Vitro SEM Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021; 22(11):1243-1249.
[18] EREN I, SEZER B. Comparison of the Effects of WaveOne Gold, TruNatomy, and Conventional Hand Files on Remaining Dentin Volume in the Coronal Part of the Root and Preparation Efficiency in Mandibular Molars. J Endod. 2023;49(8):1027-1034.
[19] PEREZ MM, GONZALEZ SJ, OLIVIERI JG, et al. Micro-computed Tomographic Assessment and Comparative Study of the Shaping Ability of 6 Nickel-Titanium Files: An In Vitro Study. J Endod. 2021;47(5): 812-819.
[20] MUSTAFA R, AL OT, AL-NASRAWI S, et al. Evaluating In Vitro Performance of Novel Nickel-Titanium Rotary System (TruNatomy) Based on Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time from Severely Curved Canals. J Endod. 2021;47(6):976-981.
[21] ELKHOLY M, NAWAR NN, HA WN, et al. Impact of Canal Taper and Access Cavity Design on the Life Span of an Endodontically Treated Mandibular Molar: A Finite Element Analysis. J Endod. 2021;47(9): 1472-1480.
[22] SOUSA VC, ALENCAR A, BUENO MR, et al. Evaluation in the danger zone of mandibular molars after root canal preparation using novel CBCT software. Braz Oral Res. 2022;36:e038.
[23] SELVARAJ H, KRITHIKADATTA J, VENKATA TK. Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis of Deformation of TruNatomy File Systems: An Ex-vivo Study. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e44183.
[24] MORALES M, SANCHEZ J, ELMSMARI F, et al. Microcomputed tomographic evaluation of 6 NiTi files on the pericervical dentin and the smallest dentin thickness zones in mesial root canals of mandibular molars: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(3):166.
[25] RIBEIRO G, MARTIN V, RODRIGUES C, et al. Comparative Evaluation of the Canal Shaping Ability, Pericervical Dentin Preservation, and Smear Layer Removal of TruNatomy, WaveOne Gold, and ProTaper Ultimate-An Ex Vivo Study in Human Teeth. J Endod. 2023;49(12):1733-1738.
[26] MARTINS J, SILVA E, MARQUES D, et al. Design, metallurgical features, mechanical performance and canal preparation of six reciprocating instruments. Int Endod J. 2021;54(9):1623-1637.
[27] SILVA E, PENA-BENGOA F, AJUZ NC, et al. Multimethod analysis of large- and low-tapered single file reciprocating instruments: Design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and irrigation flow. Int Endod J. 2024;57(5):601-616.
[28] ARIAS A, PETERS OA. Present status and future directions: Canal shaping. Int Endod J. 2022;55 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):637-655.
[29] SHYMA P, MATHEW J, GEORGE L, et al. Comparative evaluation of pericervical dentin preservation and fracture resistance of root canal-treated teeth with rotary endodontic file systems of different types of taper - An in vitro study. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2023;26(4):429-433.
[30] SHETTY B, SINGH R, PATIL V, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Single Rotary File System and Sequential Multi-file Rotary Systems on Time for Biomechanical Preparation and Obturation Quality in Single-visit Pulpectomy Protocol: A Double-blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023;16(Suppl 3):247-252.
[31] PEDULLA E, PLOTINO G, GRANDE NM, et al. Shaping ability of two nickel-titanium instruments activated by continuous rotation or adaptive motion: a micro-computed tomography study. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(8):2227-2233.
[32] URGUPLUOGLU SN, AKINCI L, SIMSEK N. Micro-computed tomography analysis of shaping ability of nickel-titanium instruments activated by continuous rotation or adaptive motion. Aust Endod J. 2024;50(2): 334-340.
[33] ELASHIRY MM, SABER SE, ELASHRY SH. Comparison of Shaping Ability of Different Single-File Systems Using Microcomputed Tomography. Eur J Dent. 2020;14(1):70-76.
[34] ELIASZ W, KUBIAK K, PONCYLJUSZ W, et al. Root Canal Transportation after Root Canal Preparation with ProTaper Next, WaveOne Gold, and Twisted Files. J Clin Med. 2020;9(11):3661.
[35] KASUGA Y, KIMURA S, MAKI K, et al. Phase transformation and mechanical properties of heat-treated nickel-titanium rotary endodontic instruments at room and body temperatures. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):825.
[36] VINODHINI V, BAIG MM, ATTUR K, et al. Compare the Centering Ability, Canal Transportation and Root Canal Area Increase of XP Endoshaper, Hyflex CM and K3 XF File System by using Cone Beam: An Original Research. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024;16(Suppl 1):S380-S382.
[37] SUBRAMANIAN A, BALASUBRAMANIAN R, JAYAKUMAR S, et al. Evaluation of Canal-centering Ability and Apical Transportation of Hyflex-EDM, OneShape, WaveOne Gold, and Reciproc Files: An Ex Vivo Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2023;24(10):802-808.
[38] YU D, GUO L, GAO J, et al. Evaluation of apical extrusion of debris and centering ability in different nickel-titanium files during curved root canal preparation. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):395.
[39] CHINCHIYANONT P, YANPISET K, BANOMYONG D, et al. Shaping ability of non-adaptive and adaptive core nickel-titanium single-file systems with supplementary file in ribbon-shaped canals analysed by micro-computed tomography. Aust Endod J. 2023;49(1):38-47.
[40] NASSAR S, SHETTY HK, NAIR P, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Endodontically Treated Bicuspids Instrumented With Hand Files, TruNatomy, ProTaper Next, ProTaper Gold, and WaveOne - An In vitro Study. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2022;14(Suppl 1):S600-S604.
[41] ROSHDY NN, HASSAN R. Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals. BDJ Open. 2022;8(1):13.
[42] CAI C, CHEN X, LI Y, et al. Advances in the Role of Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigant in Chemical Preparation of Root Canal Treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2023;2023:8858283.
[43] AZIZI MS, SHIRVANI A, AZIZI MH, et al. Evaluation of irrigant extrusion following the use of different root canal irrigation techniques: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust Endod J. 2023;49(2): 396-417.
[44] SUSILA AV, SAI S, SHARMA N, et al. Can natural irrigants replace sodium hypochlorite? A systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(5): 1831-1849.
[45] THAKUR VS, KANKAR PK, PAREY A, et al. Numerical analysis of WaveOne Gold and 2Shape endodontic files during root canal treatment. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2022;236(3):329-340.
[46] KARACA SA, EKICI MA. Evaluation of shaping ability, apical transportation and centering ratio of T-Endo Must, WaveOne Gold, and Trunatomy in resin blocks. PeerJ. 2024;12:e18088.
[47] DONG X, XU X. Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(3):354.
[48] ESTRELA C, CINTRA L, DUARTE M, et al. Mechanism of action of Bioactive Endodontic Materials. Braz Dent J. 2023;34(1):1-11.
[49] WANG X, XIAO Y, SONG W, et al. Clinical application of calcium silicate-based bioceramics in endodontics. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):853.
[50] LIANG ZH, ZHANG Y. Comparison of the ability of four different kinds of nickel-titanium instruments to prepare simulated resin to simulate curved root canal forming. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2024;33(1): 54-58.
[51] NAZARIMOGHADAM K, DARYAEIAN M, RAMAZANI N. An in vitro comparison of root canal transportation by reciproc file with and without glide path. J Dent (Tehran). 2014;11(5):554-559.
[52] SILVA E, LIMA CO, BARBOSA A, et al. The Impact of TruNatomy and ProTaper Gold Instruments on the Preservation of the Periradicular Dentin and on the Enlargement of the Apical Canal of Mandibular Molars. J Endod. 2022;48(5):650-658.
[53] DE-DEUS G, RODRIGUES EA, LEE JK, et al. Root groove depth and inter-orifice canal distance as anatomical predictive factors for danger zone in the mesial root of mandibular first molars. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(6):3641-3649.
[54] LIANG Y, YUE L. Evolution and development: engine-driven endodontic rotary nickel-titanium instruments. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):12.
[55] ELIASZ W, CZARNECKA B, SURDACKA A. Apical Extrusion of Debris during Root Canal Preparation with ProTaper Next, WaveOne Gold and Twisted Files. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(21):6254. |