Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3458-3473.doi: 10.12307/2026.324
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification of diagnostic biomarkers related to osteoporosis exosomes and preliminary drug screening
Liang Zhou1, 2, Pan Chengzhen2, Chen Feng3, Zhang Chi3, Yang Bo2, Wei Zongbo2, Meng Jianhua2, Zhou Zhu1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Yulin Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Orthopedic Hospital, Yulin 537000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Accepted:2025-07-07Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Zhang Chi, MD, Attending physician, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liang Zhou, Doctoral candidate, Associate chief physician, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Yulin Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Orthopedic Hospital, Yulin 537000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Science Fund Project), No. 82405434 (to ZC); Guangxi Young Qihuang Scholars Training Project, No. GXQH202421 (to LZ); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (General Program), No. 2025GXNSFAA069451 (to LZ); Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Traditional Chinese Medicine Self-raised Fund Research Project, No. GXZYK20230695 (to LZ); Guangxi University Young and Middle-aged Teachers' Scientific Research Basic Ability Improvement Project, No. 2024KY0295 (to ZC); Guangxi Graduate Education Innovation Program Project, No. YCBXJ2023034 (to LZ); Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Prevention and Treatment of Bone Injury Key Research Room (Cultivation), No. [2023]9 (to LZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Zhou, Pan Chengzhen, Chen Feng, Zhang Chi, Yang Bo, Wei Zongbo, Meng Jianhua, Zhou Zhu. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers related to osteoporosis exosomes and preliminary drug screening[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3458-3473.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
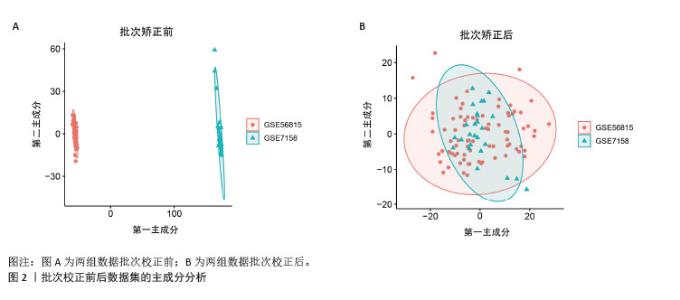
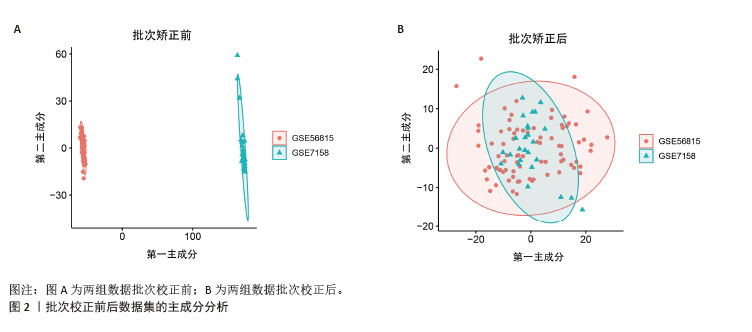
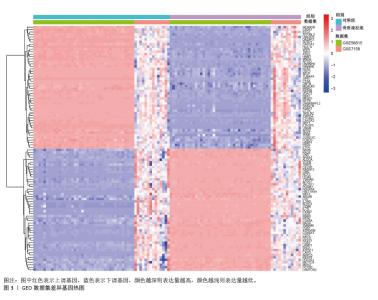
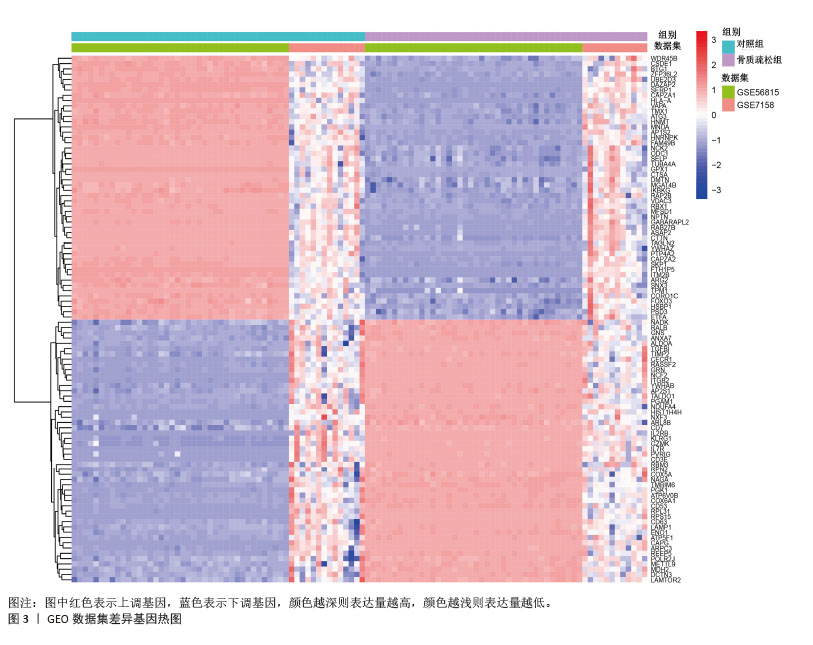
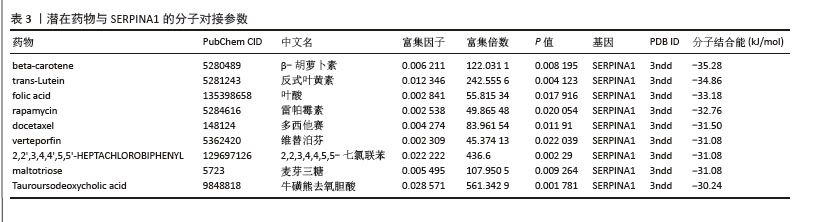
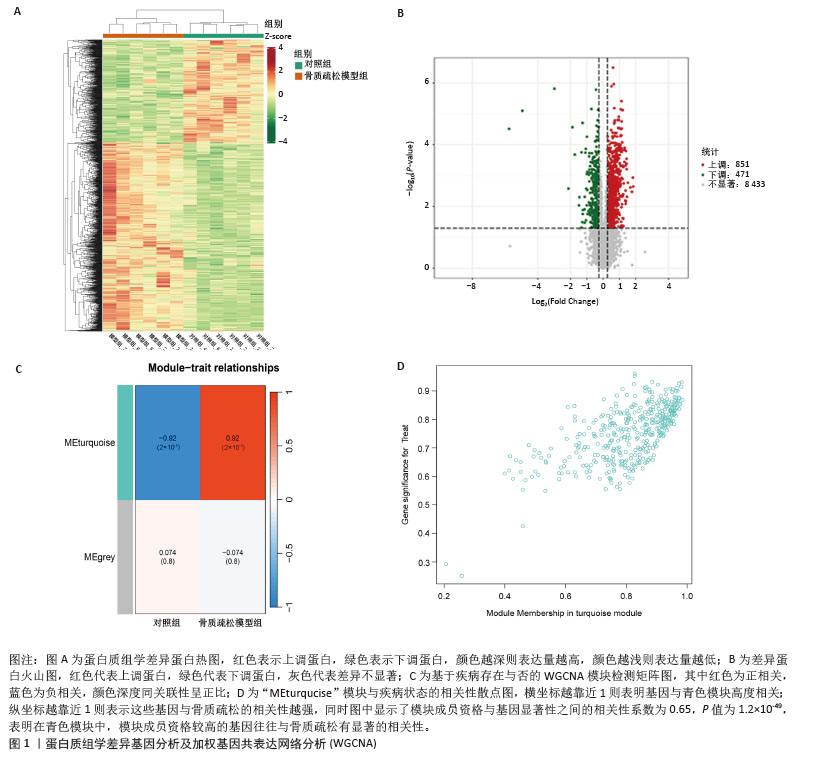
2.1 蛋白质组学联合WGCNA分析筛选差异蛋白 首先,采用4D-DIA蛋白质组学技术对骨质疏松模型组与假手术组大鼠股骨组织进行蛋白质表达谱分析,采用FC > 1.2或FC < 0.833且P < 0.05作为差异蛋白筛选标准,最终在模型组与假手术组之间检测到1 322个差异蛋白,包括851个上调蛋白和471个下调蛋白(图1A,B)。为了进一步了解这些差异蛋白之间的相互作用和共表达模式,采用WGCNA分析构建蛋白共表达网络,结果显示,“MEturquoise”(P=1.2×10-49)模块的P值< 0.05,表明该模块与骨质疏松有密切联系,其包含了402个基因作为蛋白质组学的核心基因(图1C,D)。"
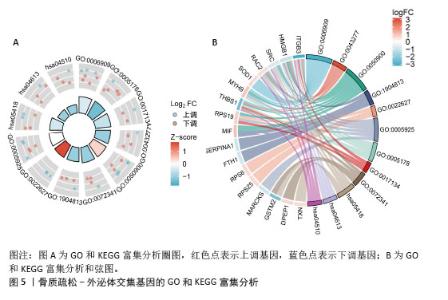
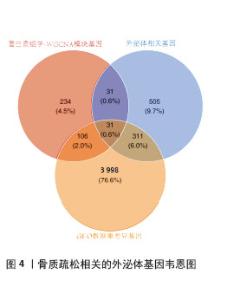
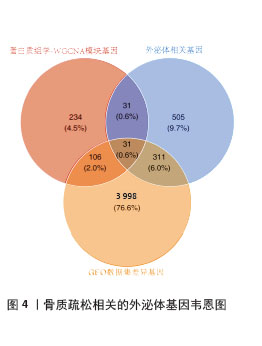
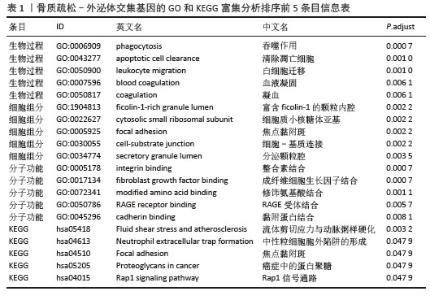
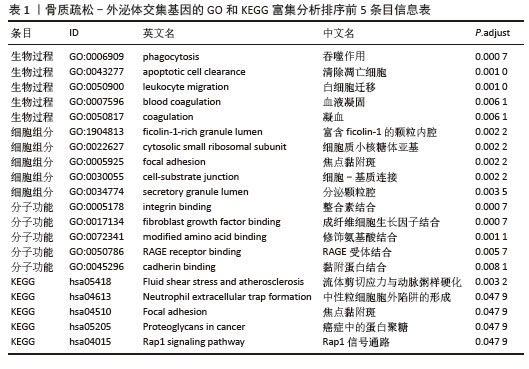
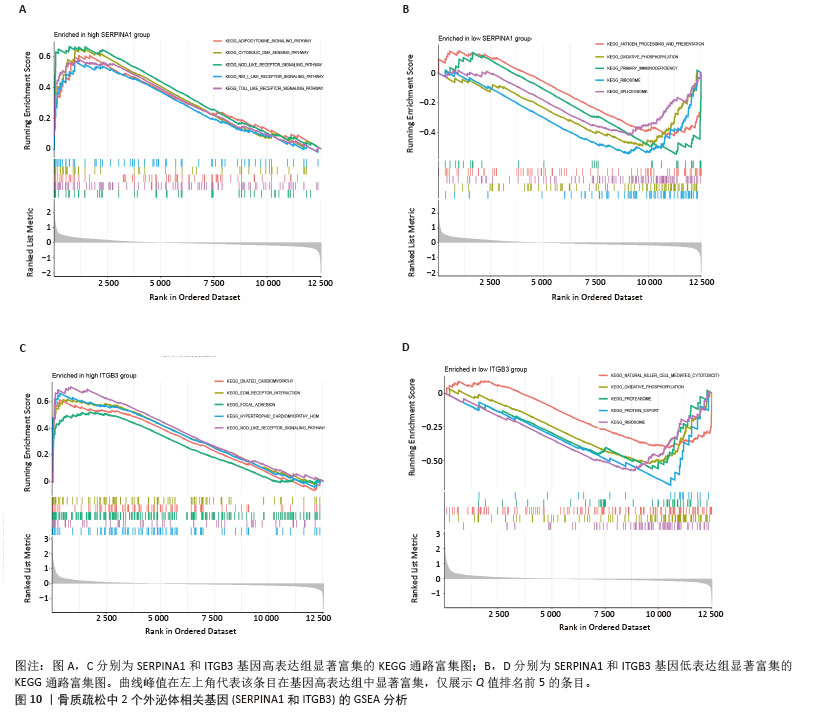
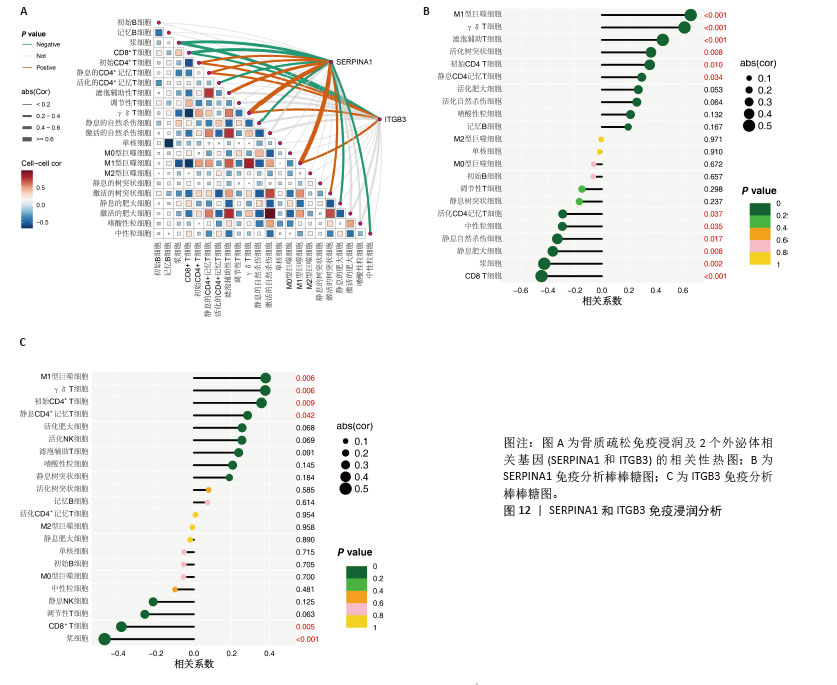
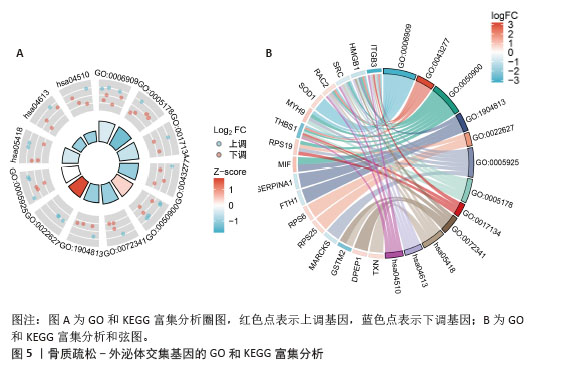
2.4 骨质疏松-外泌体相关基因富集分析 通过对31个骨质疏松-外泌体相关基因进行GO和KEGG富集分析,以校正后P值< 0.05为筛选条件,共得到生物过程条目211条,细胞组分条目32条,分子功能条目25条,KEGG通路6条。对显著性排名前5的条目进行可视化,GO富集分析生物过程主要集中于吞噬作用、清除凋亡细胞、白细胞迁移、血液凝固、凝血;细胞组分主要集中于富含ficolin-1的颗粒内腔、细胞质小核糖体亚基、病灶黏附、细胞-基质连接、分泌颗粒腔;分子功能主要集中于整合素结合、成纤维细胞生长因子结合、修饰氨基酸结合、RAGE受体结合、黏附蛋白结合。KEGG富集分析主要与流体剪切应力与动脉粥样硬化、中性粒细胞胞外陷阱的形成、焦点黏附斑、癌症中的蛋白聚糖、Rap1 信号通路等通路有关,见表1,图5A,B。"
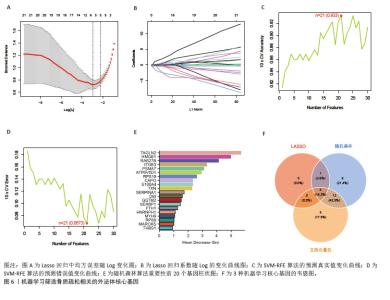
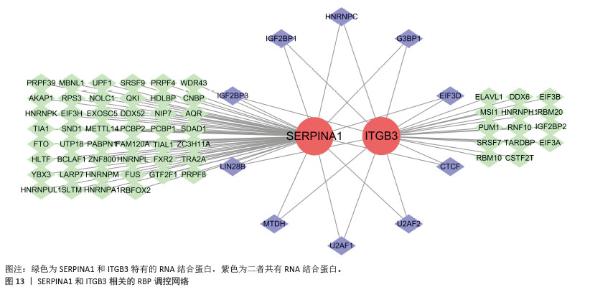
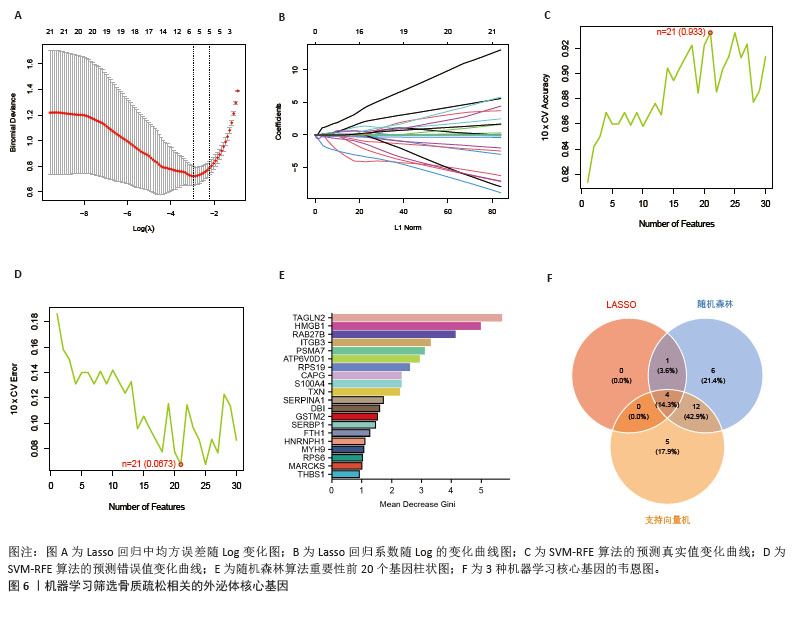
2.5 骨质疏松-外泌体相关核心基因的鉴定 鉴于骨质疏松和健康之间的明显差异,评估外泌体相关基因的诊断潜力。通过3种机器学习算法(LASSO、支持向量机和随机森林算法)在GEO表达数据集中筛选有意义的关键基因,以区分骨质疏松。在LASSO算法中,采用1 000次迭代的10倍交叉验证方法,当横坐标正则化参数增大偏差减小到4时,纵坐标表示的模型二项偏差最小,模型拟合度最高。最终从31个外泌体相关基因中选择了5个基因(图6A,B)。 同时,在支持向量机算法中,当基因数量为21时,模型的预测准确率达到最高(准确率为0.933),而此时模型的误差最小(误差为0.067 3),表明21个基因是该支持向量机模型的最佳特征数量,筛选出的21个基因为外泌体相关基因(图6C,D)。使用随机森林树算法来确定外泌体相关基因的基因重要性,确定了20个重要性> 2的基因(图6E)。最后,结合了3种机器学习算法的结果,其中4个基因被确定为核心基因(ATP6V0D1、ITGB3、SERPINA1和TAGLN2) (图6F)。"
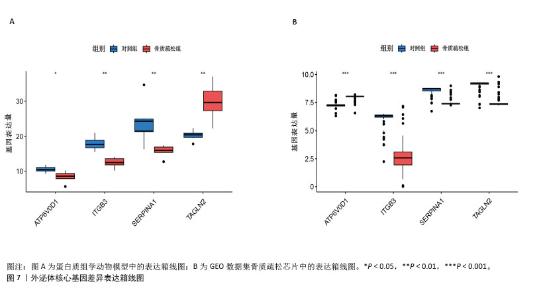
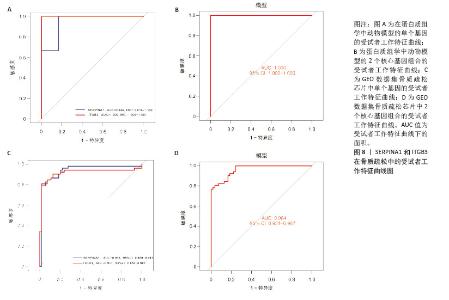
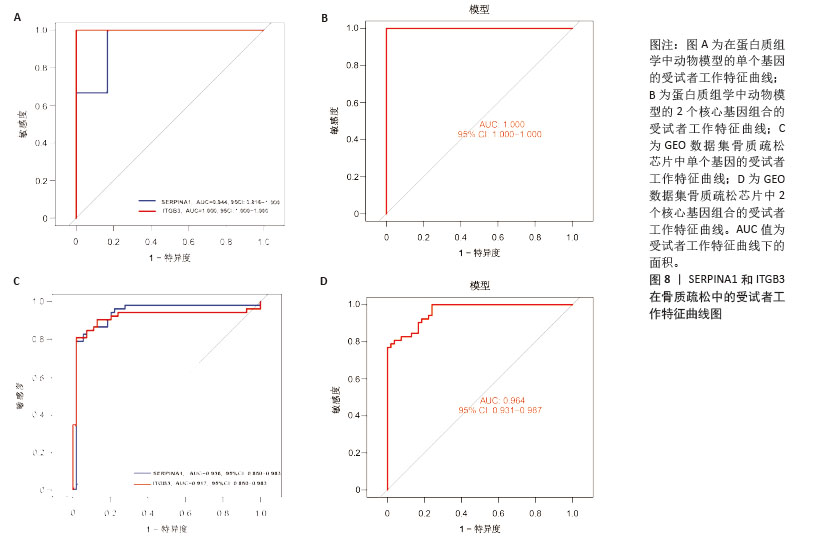
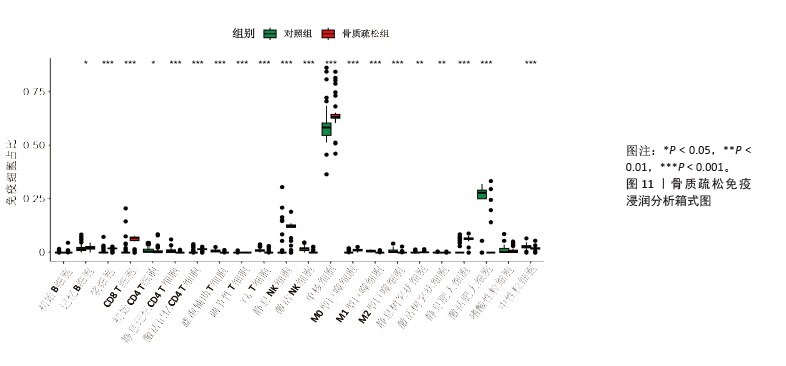
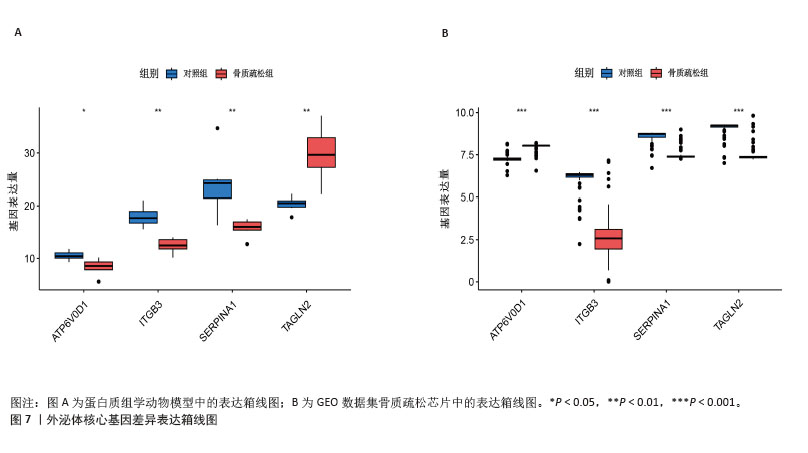
2.6 外泌体核心基因差异表达水平及受试者工作特征曲线验证 外泌体核心基因的差异表达箱式图显示ITGB3、SERPINA1的表达差异在动物模型、GEO数据集骨质疏松芯片中一致,两者皆在骨质疏松中下调,可能为骨质疏松外泌体相关的诊断基因(图7A,B)。 在动物模型中,SERPINA1和ITGB3的曲线下面积分别为0.944和1.000,曲线下面积 > 0.9说明基因有很高的诊断效能(图8A)。同时,两个基因组合在动物模型中的诊断效能极高(曲线下面积为1.000,95%置信区间为1.000-1.000),表明在模型中能够区分骨质疏松组和假手术组,敏感性和特异性均达到最佳水平(图8B)。在GEO数据集骨质疏松芯片中进一步说明SERPINA1和ITGB3具有极高的诊断效能,曲线下面积分别为0.936和0.917(图8C)。而这两个基因组合在GEO数据构建的模型中有较高的诊断效能,曲线下面积为0.964,95%置信区间为0.931-0.987(图8D)。 综上,SERPINA1和ITGB3联合对于预测外泌体介导的骨质疏松患者患病与否有较高的诊断准确性。"
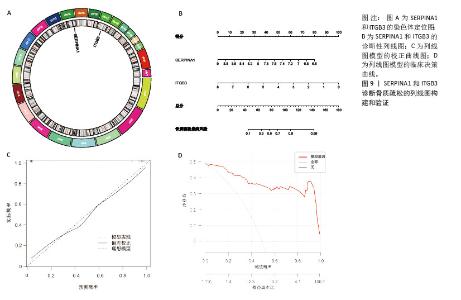
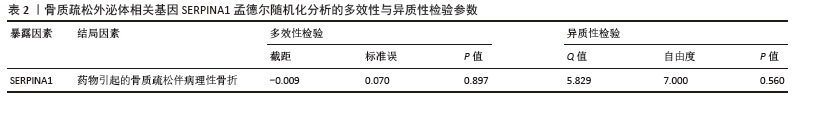
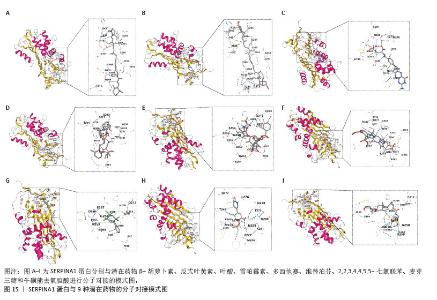
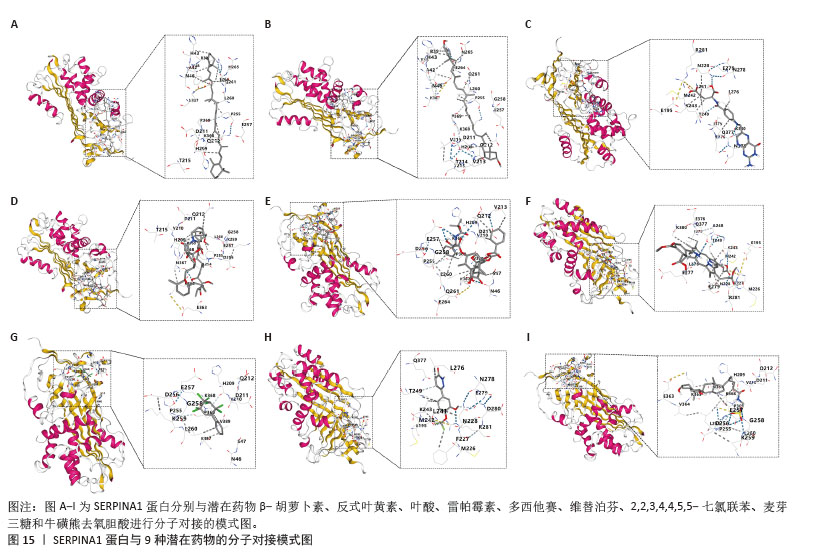
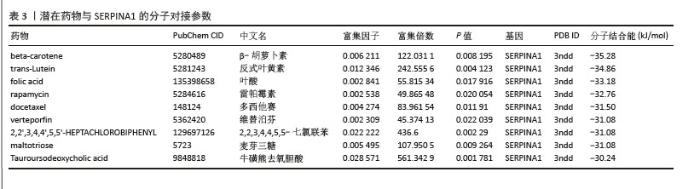
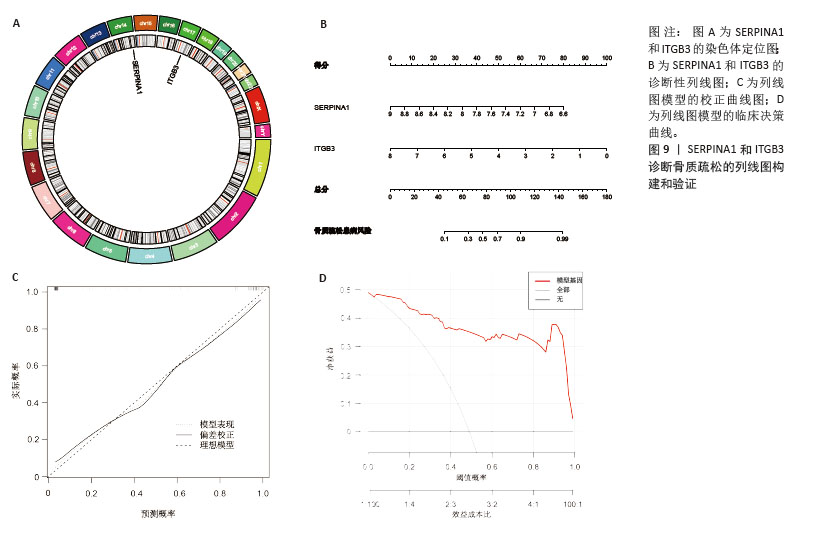
2.7 外泌体核心基因列线图构建和验证 染色体定位图显示ITGB3位于17号染色体上,SERPINA1位于14号染色体上(图9A)。在二分类逻辑回归分析模式下,对2个外泌体核心基因进行列线图模型构建,列出各个基因的分数区间,用来评估基因表达水平在不同分数下的风险贡献,并通过相加每个基因的分数计算出总分,通过总分评估相对应的风险概率。总分越高,患骨质疏松的风险越大(图9B)。同时基于Bootstrap方法,重复1 000次,进行模型校正曲线绘制(图9C),以进行内部验证,结果发现校正曲线与理想曲线贴合度高,证明模型的构建精度良好。进一步构建临床决策曲线(图9D),发现预测模型曲线与所有样本患病曲线之间离散度较高,表明模型具有一定的临床效用。"
| [1] ZHENG XQ, XU L, HUANG J, et al. Incidence and cost of vertebral fracture in urban China: a 5-year population-based cohort study. Int J Surg. 2023;109(7):1910-1918. [2] ZHU K, LIU K, HUANG J, et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection as a risk factor for osteoporosis: a case-control study. Parasit Vectors. 2022;15(1):151. [3] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, HOU W, et al. Reversing the imbalance in bone homeostasis via sustained release of SIRT-1 agonist to promote bone healing under osteoporotic condition. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:429-443. [4] ZHANG J, XIA L, ZHANG X, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for vertebral fracture risk in osteoporosis patients. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(8):3242-3260. [5] PISANI P, RENNA MD, CONVERSANO F, et al. Major osteoporotic fragility fractures: Risk factor updates and societal impact. World J Orthop. 2016;7(3):171-181. [6] ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes reveals the functional contribution of N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase to Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(10):2998-3012. [7] LIU J, WANG B, CHEN H, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomes influence osteoblast differentiation in osteoporosis progression via the lncRNA AW011738/ miR-24-2-5p/ TREM1 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;178:117231. [8] HE Y, CHEN Y. The Potential of Exosomes for Osteoporosis Treatment: A Review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:979-989. [9] QIU M, ZHAI S, FU Q, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-150-3p Promotes Osteoblast Proliferation and Differentiation in Osteoporosis. Hum Gene Ther. 2021; 32(13-14):717-729. [10] WANG L, TIAN W, WANG S, et al. Serum proteomics identifies biomarkers for predicting non-survivors in elderly COVID-19 patients. J Proteomics. 2025;311:105356. [11] CAO B, LI M, LI X, et al. Innovative biomarkers TCN2 and LY6E can significantly inhibit respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):854. [12] QIU X, YANG Z, ZHANG C, et al. Integration of eQTL and multi-omics comprehensive analysis of triacylglycerol synthase 1 (TGS1) as a prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker across pan-cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;284(Pt 1):137862. [13] JI J, WU S, BAO X, et al. Mediating oxidative stress through the Palbociclib/miR-141-3p/STAT4 axis in osteoporosis: a bioinformatics and experimental validation study. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):19560. [14] 梁周,张驰,潘成镇,等.基于肠道菌群和广泛靶向代谢组学的山柰酚抗骨质疏松的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(20):4190-4204. [15] PAN C, ZHANG C, LIN Z, et al. Disulfidptosis-related Protein RPN1 may be a Novel Anti-osteoporosis Target of Kaempferol. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(11):1611-1628. [16] WÁNG YXJ, CHAN WP, YU W, et al. Quantitative CT lumbar spine BMD cutpoint value for classifying osteoporosis among older Chinese men can be the same as that of older Chinese women, both much lower than the value for Caucasians. Skeletal Radiol. 2025;54(2):193-198. [17] HUANG X, LI S, LU W, et al. Metformin activates Wnt/β-catenin for the treatment of diabetic osteoporosis. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):189. [18] ZHANG Y, BAI J, XIAO B, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes promote osteoporosis alleviation via M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Med. 2024;30(1):220. [19] YAO C, SUN J, LUO W, et al. Down-expression of miR-494-3p in senescent osteocyte-derived exosomes inhibits osteogenesis and accelerates age-related bone loss via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Bone Joint Res. 2024;13(2):52-65. [20] BEHERA J, TYAGI N. Exosomes: mediators of bone diseases, protection, and therapeutics potential. Oncoscience. 2018;5(5-6): 181-195. [21] LIU J, SUN Z, YOU Y, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-486-5p influences the differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(18):9499-9520. [22] HAN M, LIU Y, CAO Y, et al. The Imbalance of Homeostasis in Neutrophil Extracellular Traps is Associated with Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024;12(12):1009-1019. [23] YANG W, WANG Y, MO K, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals multiple immune cell subpopulations promote the formation of abnormal bone microenvironment in osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):29493. [24] YANG P, LIU X, LYU J, et al. Down-regulation of TAGLN2 associated with the development of preeclampsia by effecting the Rap1 signaling pathway. Placenta. 2025;159: 20-31. [25] HU L, XIE X, XUE H, et al. MiR-1224-5p modulates osteogenesis by coordinating osteoblast/osteoclast differentiation via the Rap1 signaling target ADCY2. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(7):961-972. [26] HAN J, WAN M, MA Z, et al. Prediction of Targets of Curculigoside A in Osteoporosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5235-5250. [27] ZINTZARAS E, DOXANI C, KOUFAKIS T, et al. Synopsis and meta-analysis of genetic association studies in osteoporosis for the focal adhesion family genes: the CUMAGAS-OSTEOporosis information system. BMC Med. 2011;9:9. [28] BAGI CM, ROBERTS GW, ANDRESEN CJ. Dual focal adhesion kinase/Pyk2 inhibitor has positive effects on bone tumors: implications for bone metastases. Cancer. 2008;112(10):2313-2321. [29] LOPES HB, FREITAS GP, ELIAS CN, et al. Participation of integrin β3 in osteoblast differentiation induced by titanium with nano or microtopography. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(6):1303-1313. [30] YAMADA S, YOSHIZAWA Y, KAWAKUBO A, et al. Early gene and protein expression associated with osteoblast differentiation in response to fish collagen peptides powder. Dent Mater J. 2013;32(2):233-240. [31] ZOU Z, LIU R, WANG Y, et al. IL1RN promotes osteoblastic differentiation via interacting with ITGB3 in osteoporosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(3):294-303. [32] YU D, LI Z, CAO J, et al. microRNA-25-3p suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in patients with osteoporosis by targeting ITGB3. Acta Histochem. 2022; 124(6):151926. [33] MURUGANANDAN S, DRANSE HJ, ROURKE JL, et al. Chemerin neutralization blocks hematopoietic stem cell osteoclastogenesis. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10):2172-2182. [34] QIU Z, LI L, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin specifically disrupts osteoclast activation via blocking integrin-β3 Pyk2/Src/Cbl signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:55-69. [35] LI L, SONG X, CHEN G, et al. Plasma exosomal protein PLG and SERPINA1 in colorectal cancer diagnosis and coagulation abnormalities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(11):8507-8519. [36] MASLAKOVA AA, GOLYSHEV SA, POTASHNIKOVA DM, et al. SERPINA1 long transcripts produce non-secretory alpha1-antitrypsin isoform: In vitro translation in living cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023; 241:124433. [37] AKBAR MA, LU Y, ELSHIKHA AS, et al. Transplantation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (ATMSC) Expressing Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Reduces Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Osteoporosis Mice. Hum Gene Ther. 2017;28(2): 179-189. [38] CAO JJ, GREGOIRE BR, SUN L, et al. Alpha-1 antitrypsin reduces ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1240:E31-35. [39] BABUTA M, MOREL C, DE CARVALHO RIBEIRO M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps activate hepatic stellate cells and monocytes via NLRP3 sensing in alcohol-induced acceleration of MASH fibrosis. Gut. 2024;73(11):1854-1869. [40] LI Y, ZHU X, ZHANG M, et al. Heatstroke-induced hepatocyte exosomes promote liver injury by activating the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway in mice. PeerJ. 2019;7:e8216. [41] YU T, XIONG Y, LUU S, et al. The shared KEGG pathways between icariin-targeted genes and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(9):8191-8201. [42] ZHAI X, YAN Z, ZHAO J, et al. Muscone Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss and Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κb Ligand-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Suppressing TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:348. [43] EBRAHIMI T, RUST M, KAISER SN, et al. α1-antitrypsin mitigates NLRP3-inflammasome activation in amyloid β1-42-stimulated murine astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):282. [44] KE K, SUL OJ, CHUNG SW, et al. Lack of NOD2 attenuates ovariectomy-induced bone loss via inhibition of osteoclasts. J Endocrinol. 2017;235(2):85-96. [45] SUN D, LU J, TIAN H, et al. The impact of POSTN on tumor cell behavior and the tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;145:113713. [46] QIU P, LIU L, FANG J, et al. Identification of Pharmacological Autophagy Regulators of Active Ulcerative Colitis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:769718. [47] CLARK D, BRAZINA S, YANG F, et al. Age-related changes to macrophages are detrimental to fracture healing in mice. Aging Cell. 2020;19(3):e13112. [48] XU Y, YAN H, ZHANG X, et al. Roles of Altered Macrophages and Cytokines: Implications for Pathological Mechanisms of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:876269. [49] GENIN M, CLEMENT F, FATTACCIOLI A, et al. M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:577. [50] MARTÍNEZ FAJARDO C, MOROTE L, MORENO-GIMÉNEZ E, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles from Arbutus unedo L. mitigate LPS-induced inflammation via JAK-STAT inactivation. Food Funct. 2024; 15(22):11280-11290. [51] CHEN X, BAI Z, LI J. The Mantle Exosome and MicroRNAs of Hyriopsis cumingii Involved in Nacre Color Formation. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2019;21(5):634-642. [52] GAO SS, ZHAO Y. The effects of β-carotene on osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int. 2023;34(4):627-639. [53] KAN B, GUO D, YUAN B, et al. Dietary carotenoid intake and osteoporosis: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005-2018. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;17(1):2. |
| [1] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [2] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [3] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [4] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [5] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [6] | Han Teng, Ma Hong, Yang Ruoyi, Luo Yi, Li Chao. Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived exosomal delivery of angiopoietin-2 is involved in tumor angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1755-1767. |
| [7] | Huang Jiawen, Pan Zhiyi, Xue Wenjun, Lian Yuanpei, Xu Jianda. Plant-derived vesicles and malignant tumor therapy: cross-species communication and modulation of host cell responses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1828-1838. |
| [8] | Wang Baiyan, Yang Shu, Wang Yiming, Wu Mengqing, Xiao Yu, Guo Zixuan, Zhang Boyi, Feng Shuying. Exosome-delivered CRISPR/Cas system enables gene editing in target cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1839-1849. |
| [9] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [10] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [11] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [12] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [13] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [14] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [15] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||