Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2920-2932.doi: 10.12307/2026.074
Previous Articles Next Articles
Global research status, trends and hotspots of anxiety/depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Wang Jiaying, Xu Chun, Mayila · Abudukelimu
- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2025-03-06Accepted:2025-05-11Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-10 -
Contact:Mayila Abudukelimu, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Jiaying, MS candidate, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 62266041 (to XC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jiaying, Xu Chun, Mayila · Abudukelimu. Global research status, trends and hotspots of anxiety/depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2920-2932.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
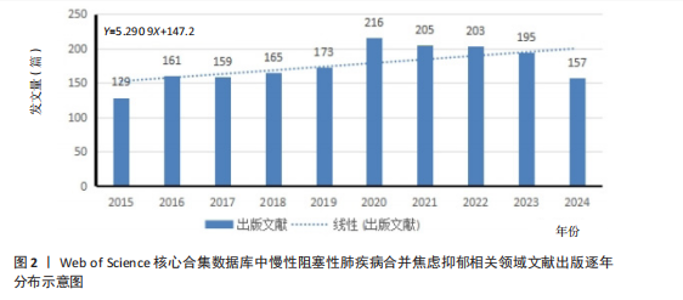
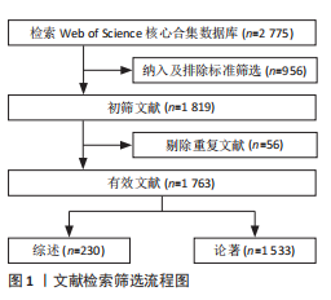
2.2 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域年度全球发文趋势分析 发文趋势往往是专业领域发展趋势和前沿热点的缩影,文章统计了2015-2024年该领域相关发文量并分析其发文趋势。近10年慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域共发表文献 1 763篇,平均每年发表176.3篇。从年发文量来看,2015年发文量最少(129篇),2020年发文量最多(216篇)。如图2所示,2015-2020年发文量稳步上升,表明这一时期慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁逐渐受到各国越来越多的关注,并且该领域进入快速发展阶段;2020-2021年发文量短暂下降;2021-2023年文献发文量整体趋于平缓,没有明显变化,但文献数量高于平均水平,表明全球对于慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁的重视程度仍较高;2024年的数据尚未完全统计,但截至数据收集日期,已收集相关文献157篇,年底发文量有望超过176篇。对发文量的分布进行线性拟合,趋势线为Y=5.290 9X+147.2,近10年"
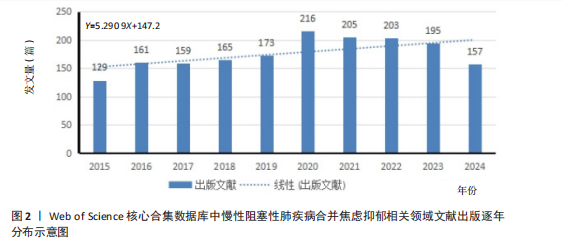
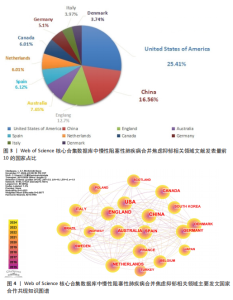
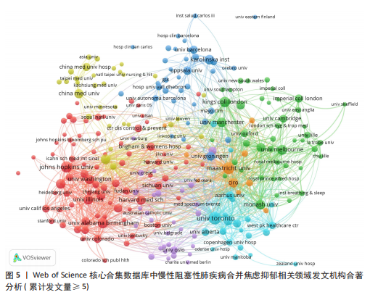
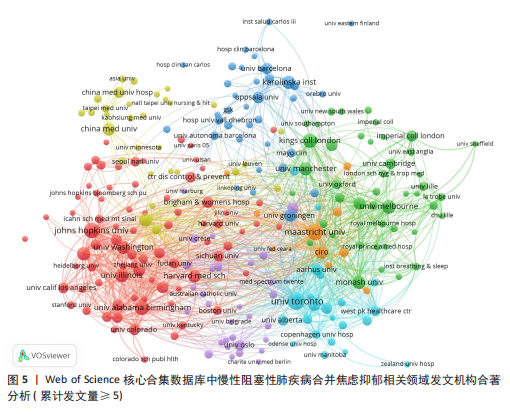
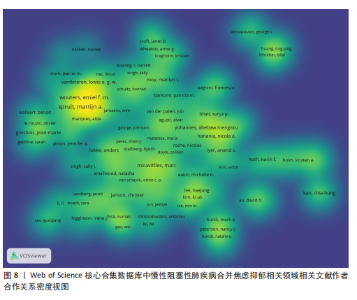
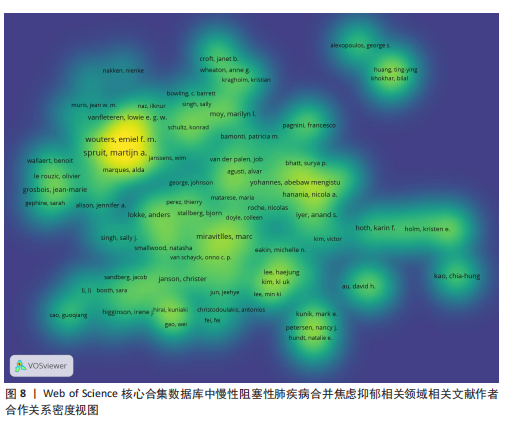
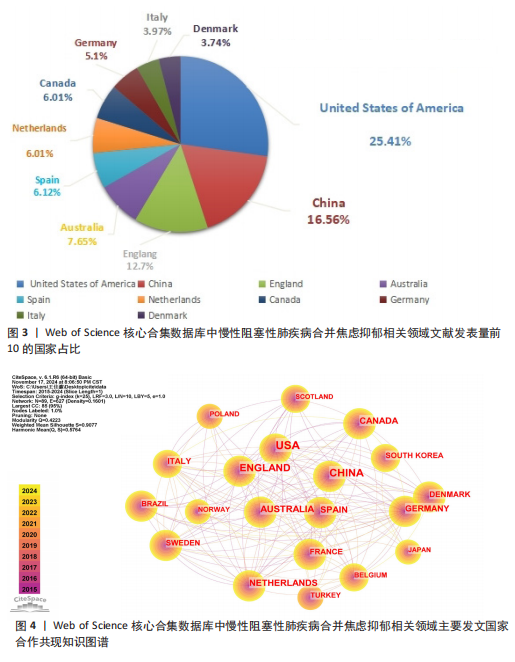
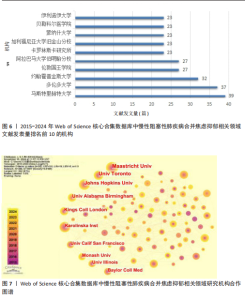
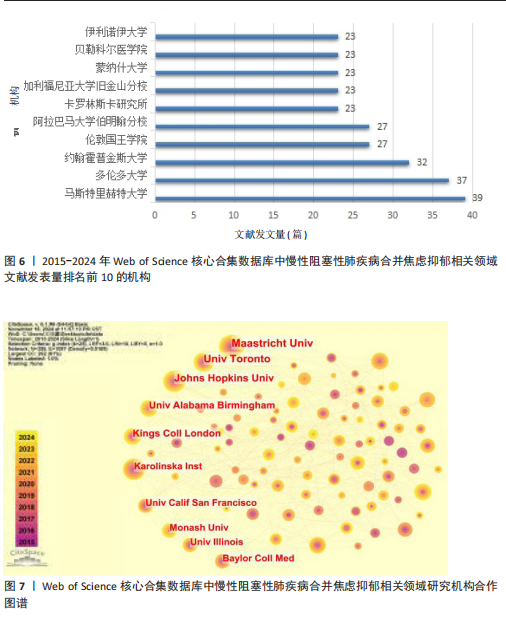
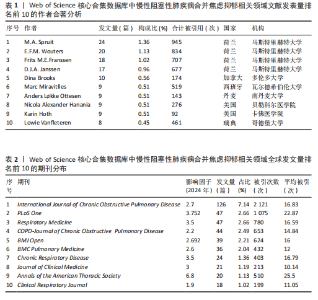
发文量在趋势线周围上下波动,2023年回落趋势线上,说明慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关研究量总体呈现稳定上升趋势且未来发文量仍可能继续增加。 2.3 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域发文国家分布 一个国家在某领域研究的活跃程度与该国国家的发文量紧密相关。根据检索结果,共有83个国家发表相关文章。文献数量前10的国家如图3所示,这些国家文献发表量占总数的93.3%,美国(占比25.41%)与中国(占比16.56%)是发文最多的2个国家,在全球发文占比明显高于其他国家,表明两国针对慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁的研究更为系统和深入,处于领先地位。从国家合作网络图中(图4)可以发现,美国作为文献产出最大国与中国、英国、澳大利亚、西班牙等主要发文国家均有所合作;澳大利亚在国际领域十分活跃,与多个国家展开交流合作;总体而言,形成了以美国、中国、英国、澳大利亚、西班牙为核心的研究网络,各国家之间的合作较为密切。 2.4 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域研究机构分布及合作网络分析 根据机构的研究产出情况,2015-2024 年,全球共有3 106个研究机构参与了慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁的研究,发文主力研究机构为各科研院所及大学,但累计发文量5篇以上(含5篇)的仅有253家机构(图5),约占总数的8.1%,说明该领域大多数机构的研究缺乏连续性。图6所示排名前10的机构文献贡献情况如下:马斯特里赫特大学(荷兰)贡献了39篇论文;多伦多大学(加拿大)贡献了37篇论文;约翰霍普金斯大学(美国)贡献了32篇论文;伦敦国王学院(英国)和阿拉巴马大学伯明翰分校(美国)贡献了27篇论文;卡罗林斯卡研究所(瑞典)、加利福尼亚大学旧金山分校(美国)、蒙纳什大学(澳大利亚)、贝勒科尔医学院(美国)和伊利诺伊大学(美国)则各贡献了23篇论文。美国研究机构在前10名中的数量占半数,这凸显了美国在该领域的研究活动十分活跃。研究机构合作图谱分析可以反映各机构之间的合作关系及发表论文情况(图7),可以看出,在全球进行独立研究的机构相对较少,各大研究机构间的联系密切,实现了该领域的知识共享和合作交流,有助于推动慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关研究领域的进展。其中多伦多大学、约翰霍普金斯大学、伦敦国王学院、伊利诺伊大学等研究机构不仅文献产出量大而且对外交流频繁。 2.5 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域作者分布及合作情况分析 Web of Science 核心合集数据库纳入文献涵盖9 616位作者,其中发文量排在前10的作者分别为M.A. Spruit(24篇)、E.F.M. Wouters(20篇)、Frits M.E. Franssen(18篇)、D.J.A. Janssen (17篇)、Dina Brooks(10篇)、Marc Miravitlles(9篇)、Nicola Alexander Hanania(9篇)、Karin Hoth(9篇)、"
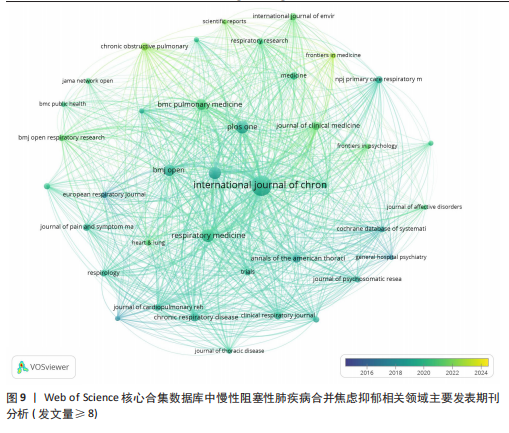
Anders L?kke Ottesen(9篇)、Lowie Vanfleteren(8篇),见表1,这些学者为促进慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁领域的研究发挥了很重要的作用,值得注意的是,马斯特里赫特大学的4位研究者在该领域有关研究中表现出色,占据了前4位的榜单。采用普赖斯定律进行核心作者认定,根据M=0.749Mmax 1/2(Mmax为最高产作者的发文量)计算可得,核心作者最低发文量M≈4,符合该条件的作者人数为201人(占比2.09%),表明该领域研究尚未形成稳定的核心作者群。将符合要求的核心作者生成作者合作关系密度视图(图8),可见全球形成了多个联系较为紧密的研究团队,发文量最多且合作最为紧密的是以M.A. Spruit-E.F.M. Wouters为核心的团队,但仍可见部分节点分布松散,表明研究者集群尚未达到一定规模,团队间存在交流与合作缺乏的情况。 2.6 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域文献来源期刊分析 关于与慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关研究的论文涉及623种期刊,其中主要发表期刊如下:《International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》 发文量最多(126篇),其次是《Respiratory Medicine》(47篇)、《PLoS One》(47篇)、《COPD-Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》(44篇)、《BMJ Open》(39篇)等,排名前10的期刊发文量占总发文量的23.93%,平均影响因子为3.26(表2)。在排名前10的期刊中,《International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》为发文量和被引次数方面的双第一。按照发文数量,选取发文量≥8篇的期刊进行可视化分析(图9),节点代表不同期刊,节点大小取决于发文量,用圆圈表示,节点颜色对应年份,颜色越浅表明该期刊刊登内容越接近于当前该领域所探讨的最新热点问题。被引次数是评价期刊对某研究领域的学术影响程度的客观指标,反映了其在科学交流中的作用和地位。被引频次排名前3位的期刊分"
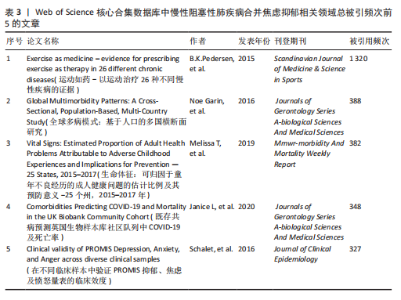
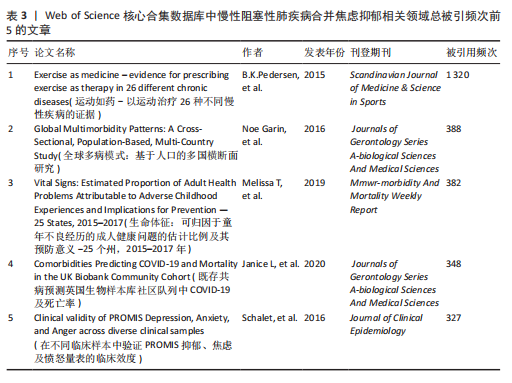
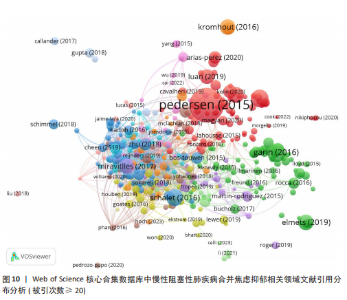
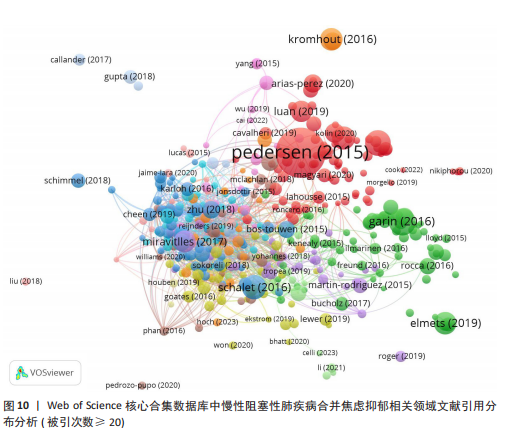
别是《International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》《PLoS One》和《Respiratory Medicine》;平均被引排名前3位的期刊是《Annals of the American Thoracic Society》《PLoS One》和《International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease》,说明上述期刊在慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁领域中影响力及成果较突出,学者可参考上述期刊发文快速把握该领域的热点问题并为该领域的研究开辟新的方向。 2.7 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域文献共被引分析 一定时期内被多次引用的文献,说明研究者们对文章的研究主题是高度关注的,因此可从中识别焦点话题。此次研究列出了被引文献排名前5位的文献,见表3。就出版时间而言,60%的高被引论文为2017年前的文献,2017年后出版的高被引论文仅占40%。排名前5的文章引用次数均超过了300次,被引用次数最多的文献是2015年发表在《Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports》杂志上的“Exercise as medicine – evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases”,该文章发表以来总被引用了1 320次,其次是Noe Garin等在2016发表在《Journals of Gerontology Series A-biological Sciences And Medical Sciences》杂志上的文章“Global Multimorbidity Patterns: A Cross-Sectional, Population-Based, Multi-Country Study”和Melissa T等在《Mmwr-morbidity And Mortality Weekly Report》上发表的文章“Vital Signs: Estimated Proportion of Adult Health Problems Attributable to Adverse Childhood Experiences and Implications for Prevention — 25 States, 2015–2017”,这些高被引文献推动了各阶段慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁有关研究的发展。图10对被引次数超过20次的466篇文献进行可视化分析,线条表示节点之间的联系,节点的颜色不同代表其属于的聚类不同,节点的大小由文献的被引次"

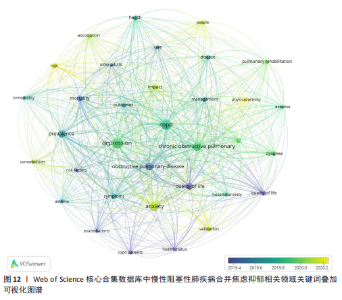
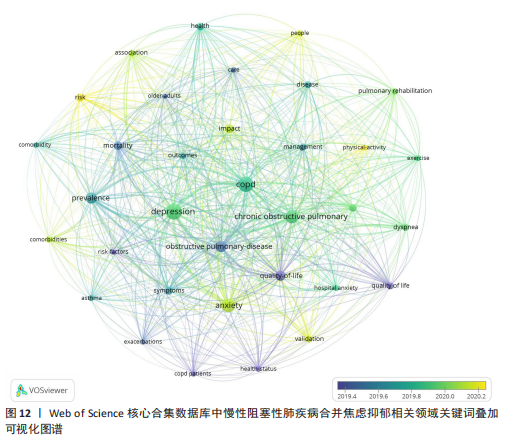
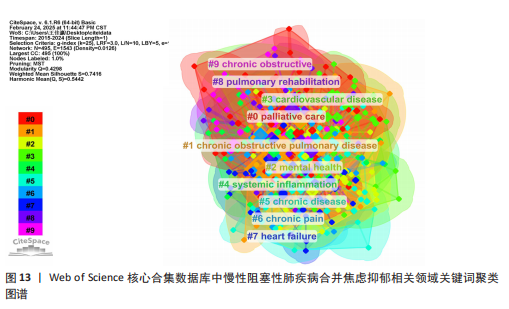
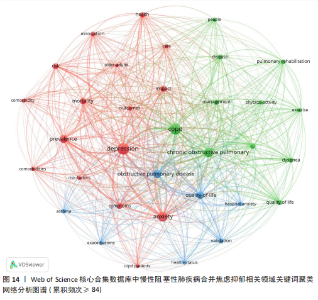
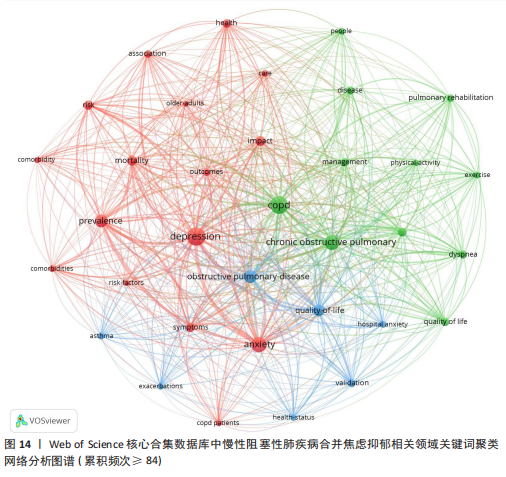
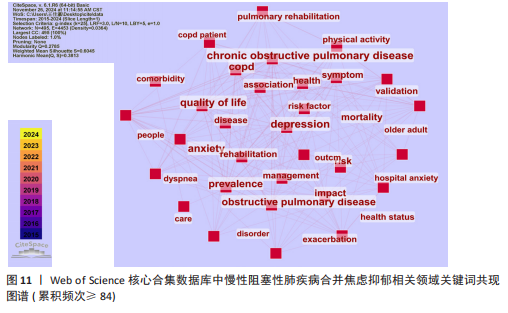
数所决定,节点的越大意味着此文献在该研究领域的学术影响力和关注度更高。 2.8 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁相关领域研究热点分析 关键词能反映学科领域的主旨和核心研究主题,通过对关键词进行可视化分析,可发现当前领域的研究方向与学科关注热点。 2.8.1 关键词共现 关键词是对论文主题的高度概括和凝练,通过词频分析得出的高频关键词可揭示该研究领域的研究热点。出现频次是衡量关键词重要性的重要指标,出现频次越多,该关键词的影响力越高。根据Donohue提出的高频及低频词界分公式进行计算,其中,T代表高低频次的界定阈值,I代表词频为1的关键词数量。此次研究纳入的1 763篇文献中词频为1(I=1)的关键词共3 471个,将其带入公式可得出界定阈值T≈83.82,取整数为84,则前34个关键词为与慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁研究领域的高频关键词。排除与检索策略相关的主题词,出现频次最多的是quality-of-life。通过CiteSpace对这34个累积频次≥84次的关键词进行共线分析(图11),每个关键词用方块表示,方块的大小代表关键词的出现次数,方块越大表示关键词在该研究领域中出现的频率越高,也意味着该关键词在研究领域中的影响力越大。VOSviewer图谱中不同颜色在图中可代表着不同的年份信息,通过颜色变化可以直观地观察到关键词在不同年份的出现情况和研究趋势,见图12,关键词节点颜色越黄,表明该关键词近期研究越多,图中physical-activity、validation、risk关键词颜色偏黄,意味着近段时间学者们对这些关键词的相关研究关注度较高。 2.8.2 关键词聚类 聚类是一种将数据集分成多个类或组的过程,使得同一类内的数据点相似度较高,而不同类间的数据点相似度较低。通过分析关键词聚类图,可以识别出某一领域内的研究热点和前沿趋势。聚类模块值(Q)和平均轮廓值(S)是评价聚类合理性和有效性的重要指标,一般认为Q > 0.3表示聚类结构显著,S > 0.5表示聚类合理,S > 0.7表示聚类令人信服。在关键词共现图谱基础上,采用 LLR(Loglikelihood-ratio)检验算法对关键词进行聚类分析(图13),其中Q=0.429 8(Q > 0.3)、S=0.741 6(S > 0.7),表明聚类结果合理有效。关键词聚类有图谱叠加,表明各个聚类相互间联系紧密。排名前10的聚类分别是#0(姑息治疗)、#1(慢性阻塞性肺疾病)、#2(心理健康)、#3(心血管疾病)、#4(全身炎症反应)、#5(慢性"
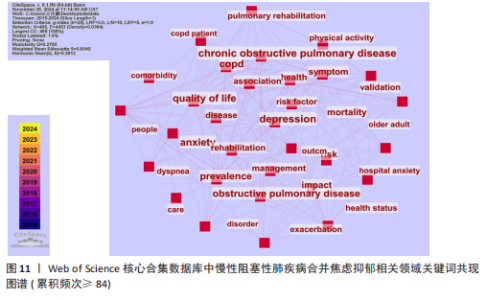
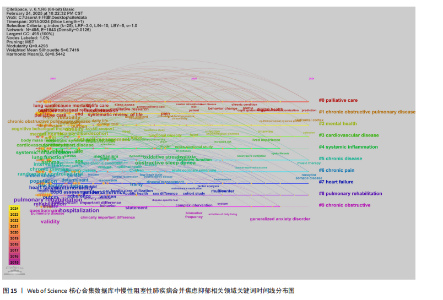
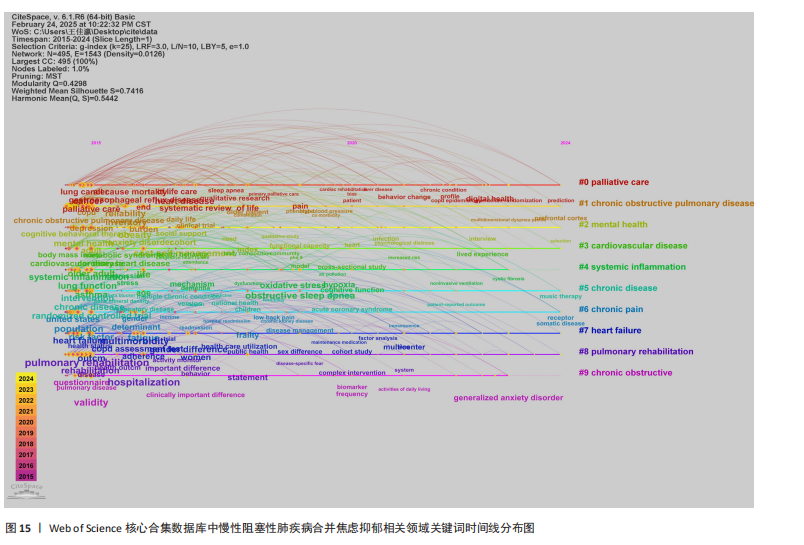
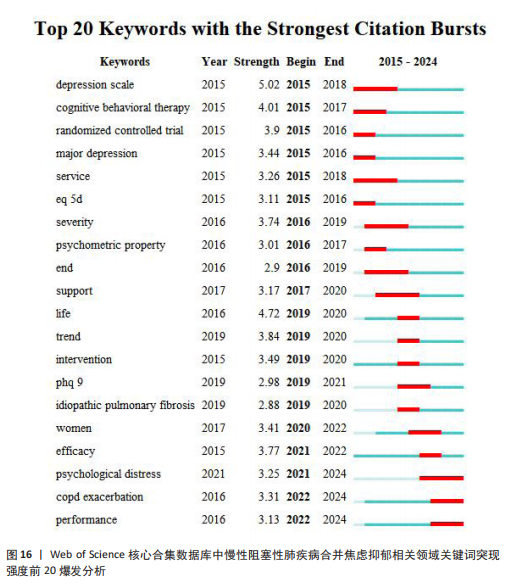
病)、#6(慢性疼痛)、#7(心力衰竭)、#8(肺康复)、#9(慢性阻塞性),聚类编号越小,表明该聚类下的文献研究规模越大、研究热度越高。其中,病例对照研究(聚类#5)为相关研究方法,#1(慢性阻塞性肺疾病)、#2(心理健康)、#3(心血管疾病)、#5(慢性病)、#6(慢性疼痛)、#7(心力衰竭)为临床危险因素,#4(全身炎症反应)主要为相关机制,#0(姑息治疗)、#8(肺康复)集中在临床治疗方式。采用VOS viewer将34个高频关键词进行聚类分析,形成了3个具有代表性的聚类图谱(图14),最核心的聚类为红色部分,主要包括相关的症状、临床表现、并发症、死亡率等方面;绿色部分包括运动、肺康复等相关管理及治疗措施;蓝色部分是关于该领域人群的生活质量、健康状况、病情恶化等相关内容。 2.8.3 关键词时间线 时间线图是引入时间维度,通过节点和连线直观地展示关键词之间的关联性和相互影响。此次研究通过展现近10年各个研究热点的时间跨度以及不同研究主题之间的影响和联系,进一步展示与慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁在不同年份的研究热点变化和未来研究趋势,见图15所示。除了聚类4、聚类9,其他聚类的持续时间都延续至今。距离现在最近时间轴上的关键词主要包括prediction(预测)、prefrontal cortex(前额皮质)、music therapy(音乐疗法)、receptor(受体)、somatic disease(躯体疾病)。通过整体分析可以发现,最新的研究主题除传统聚焦于焦虑和(或)抑郁对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者带来的不良影响及发生机制外,逐渐开始致力于寻找如何早期发现、早期识别的筛查方法。 2.8.4 关键词突现 关键词突现是指在短时间内某个关键词频次显著增加,可以表明此段时间关注度较高的研究,据此可判断研究领域的热点和趋势转向。关键词突现强度前20 位汇总如图16所示,近10年的发展过程中,突现强度前20位的突现词大致可分为研究方法、病情评估、临床表现和治疗手段4类,“抑郁量表”是突现强度值最大的文献关键词,由2015年持续至2018年;“心理压力”是最近一次突现的关键词,出现在2021年并持续至今,突现强度为3.25。"
| [1] CHRISTENSON SA, SMITH BM, BAFADHEL M, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2022;399(10342):2227-2242. [2] LI HY, GAO TY, FANG W, et al. Global, regional and national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease over a 30-year period: Estimates from the 1990 to 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. Respirology. 2023;28(1):29-36. [3] GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2100-2132. [4] AGUSTÍ A, CELLI BR, CRINER GJ, et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 Report: GOLD Executive Summary. Eur Respir J. 2023;61(4):2300239. [5] SAMPAIO MS, VIEIRA WA, BERNARDINO ÍM, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as a risk factor for suicide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med. 2019;151:11-18. [6] BENZO R, HOULT J, MCEVOY C, et al. Promoting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Wellness through Remote Monitoring and Health Coaching: A Clinical Trial. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022; 19(11):1808-1817. [7] HUANG J, BIAN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. The Impact of Depression and Anxiety on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Acute Exacerbations: A prospective cohort study. J Affect Disord. 2021;281:147-152. [8] 裴文婧,李萍,汪若文,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者焦虑抑郁现况及其影响因素[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2024,23(7):457-464. [9] NINKOV A, FRANK JR, MAGGIO LA. Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. 2022;11(3):173-176. [10] LONG Y, ZHAO S, TANG X, et al. Research status and prospect of purification technology of sulfur-containing odor gas. J Environ Sci (China). 2025;149:301-313. [11] SUN SW, QI C, XIONG XZ. Challenges of COPD Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pathogens. 2022;11(12): 1484. [12] LAM GY, WEN C, RONKSLEY PE, et al. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Healthcare Use, Exacerbations, and Mortality: A Population Study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2024;21(9):1281-1288. [13] ALSALLAKH MA, SIVAKUMARAN S, KENNEDY S, et al. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the incidence and mortality of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: national interrupted time series analyses for Scotland and Wales. BMC Med. 2021;19(1):124. [14] POUCINEAU J, KHLAT M, LAPIDUS N, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on COPD Patient Mortality: A Nationwide Study in France. Int J Public Health. 2024; 69:1606617. [15] STOUSTRUP AL, JANSSEN DJA, NAKKEN N, et al. Association of inadequate social support and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - A cross-sectional study. Respir Med. 2024; 226:107625. [16] VAN HERCK M, ANTONS J, VERCOULEN JH, et al. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Reduces Subjective Fatigue in COPD: A Responder Analysis. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(8):1264. [17] SMID DE, FRANSSEN FM, HOUBEN-WILKE S, et al. Responsiveness and MCID Estimates for CAT, CCQ, and HADS in Patients With COPD Undergoing Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A Prospective Analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(1):53-58. [18] HOUBEN CHM, SPRUIT MA, LUYTEN H, et al. Cluster-randomised trial of a nurse-led advance care planning session in patients with COPD and their loved ones. Thorax. 2019;74(4):328-336. [19] MESQUITA R, FRANSSEN FM, HOUBEN-WILKE S, et al. What is the impact of impaired left ventricular ejection fraction in COPD after adjusting for confounders? Int J Cardiol. 2016;225: 365-370. [20] MARTÍNEZ-GESTOSO S, GARCÍA-SANZ MT, CARREIRA JM, et al. Impact of anxiety and depression on the prognosis of copd exacerbations. BMC Pulm Med. 2022; 22(1):169. [21] WRZECIONO A, CZECH O, BUCHTA K, et al. Assessment of Stress, Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Patients with COPD during In-Hospital Pulmonary Rehabilitation: An Observational Cohort Study. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(3):197. [22] 李兴洋,孙婉琪,尹孟洁,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者睡眠质量和焦虑抑郁情况及其影响因素:一项多中心横断面研究[J].中国全科医学,2024,27(20):2437-2444. [23] HUANG K, HUANG K, XU J, et al. Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in China: Results from the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] Study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:3387-3396. [24] HAN YY, YAN Q, CHEN W, et al. Child maltreatment, anxiety and depression, and asthma among British adults in the UK Biobank. Eur Respir J. 2022;60(4): 2103160. [25] LONG J, OUYANG Y, DUAN H, et al. Multiple Factor Analysis of Depression and/or Anxiety in Patients with Acute Exacerbation Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1449-1464. [26] STROLLO HC, NOURAIE SM, HOTH KF, et al. Association of Systemic Inflammation with Depressive Symptoms in Individuals with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:2515-2522. [27] LONG J, XU P, CHEN J, et al. Inflammation and comorbidities of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The cytokines put on a mask! Cytokine. 2023;172:156404. [28] HILLAS G, PERLIKOS F, TSILIGIANNI I, et al. Managing comorbidities in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:95-109. [29] ATLANTIS E, FAHEY P, COCHRANE B, et al. Bidirectional associations between clinically relevant depression or anxiety and COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2013;144(3):766-777. [30] ZHANG F, ZHONG R, LI S, et al. Acute Hypoxia Induced an Imbalanced M1/M2 Activation of Microglia through NF-κB Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice and Wild-Type Littermates. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:282. [31] COLONNA M, BUTOVSKY O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:441-468. [32] TANIGUCHI A, TSUGE M, MIYAHARA N, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidative Defense in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(10):1537. [33] MASOUDI M, GOODARZI M, RAHMANI MA, et al. Vitamin C improved anxiety and depression like behavior induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in adolescent rats by influencing on oxidative stress balance, neurotransmitter systems, and inflammatory response. Nutr Neurosci. 2024:1-10. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2024.2389499. [34] LI Z, CHEN K, SHAO Q, et al. Nanoparticulate MgH2 ameliorates anxiety/depression-like behaviors in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis by regulating microglial polarization and oxidative stress. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):16. [35] PINTANA H, SAENGMEARNUPARP T, APAIJAI N, et al. Chronic Exposure with 5‐Alpha Reductase Inhibitor Ameliorates Anxiety and Depression‐like Behaviors By Reducing Systemic Oxidative Stress in D‐galactose‐Induced Aging Male Rats. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(S13):doi:10.1002/alz.074018 [36] BORROTO-ESCUELA DO, AMBROGINI P, CHRUŚCICKA B, et al. The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1927. [37] MARGOLIS KG, CRYAN JF, MAYER EA. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5): 1486-1501. [38] BHATT S, DEVADOSS T, MANJULA SN, et al. 5-HT3 receptor antagonism a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of depression and other disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1545-1559. [39] ZAILANI H, SATYANARAYANAN SK, LIAO WC, et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Comorbid Mood Disorders in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Review. J Clin Med. 2023;12(7):2653. [40] YE J, LI P, LIU P, et al. Serum Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Metabolic Pathways Related to AECOPD Complicated with Anxiety and Depression. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024;19:2135-2151. [41] TANG T, LI Z, LU X, et al. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for anxiety or depression among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease between 2018 and 2020. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):2181-2190. [42] CHOI JS, KWAK SH, SON NH, et al. Sex differences in risk factors for depressive symptoms in patients with COPD: The 2014 and 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21(1):180. [43] CHEN X, GUO Y, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2024;21(3):288-306. [44] SOHANPAL R, PINNOCK H, STEED L, et al. Tailored, psychological intervention for anxiety or depression in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), TANDEM (Tailored intervention for ANxiety and DEpression Management in COPD): protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 202;21(1):18. [45] TAYLOR SJC, SOHANPAL R, STEED L, et al. Tailored psychological intervention for anxiety or depression in COPD (TANDEM): a randomised controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300432. [46] SOHANPAL R, MAMMOLITI KM, BARRADELL A, et al. Patient perspectives on the Tailored intervention for Anxiety and Depression Management in COPD (TANDEM): a qualitative evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024;24(1):960. [47] WAN X, HUANG H, LIANG D, et al. Effect of remote mindfulness-based interventions on symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12(2): e055369. [48] GIUSTI EM, PAPAZIAN B, MANNA C, et al. The Effects of an Acceptance and Commitment-Informed Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation Program for Chronic Airway Diseases on Health Status and Psychological Symptoms. Front Psychol. 2022;12:818659. [49] 何金泉,卢梦琴,刘聪聪,等.桂枝龙骨牡蛎汤联合重复经颅磁刺激在慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁症中的应用[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2025,43(7):204-207. [50] 方盛,张海峰,颜平康.俞募配穴中药贴敷治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病伴焦虑抑郁的临床研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2024,51(5):159-163. [51] WANG X, REN H, REN J, et al. Machine learning-enabled risk prediction of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with unbalanced data. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;230:107340. [52] XUE M, JIA S, CHEN L, et al. CT-based COPD identification using multiple instance learning with two-stage attention. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;230: 107356. [53] ZHU Z, ZHAO S, LI J, et al. Development and application of a deep learning-based comprehensive early diagnostic model for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2024;25(1):167. [54] KUMAR S, BHAGAT V, SAHU P, et al. A novel multimodal framework for early diagnosis and classification of COPD based on CT scan images and multivariate pulmonary respiratory diseases. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024;243:107911. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Xu Chang, Jiang Mingzhu, Liu Xin, Yan Weijun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant anchorage combined with torque auxiliary arch to lower anterior teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1971-1978. |
| [4] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [5] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [6] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [7] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [8] | Li Kanglin, Jiang Yongdong, Wu Yufeng. Visualization analysis of piriformis syndrome: research trends and hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2886-2895. |
| [9] | Song Andong, , Fu Huiling, , Yuan Bo, Li Guohua, Jia Xusheng, Jia Menghui . Dodder intervenes with chronic stress depression in a mouse model: changes in NLRP3 inflammasome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2440-2448. |
| [10] | Liu Tongyan, Li Yuan, Sun Wei, Yao Bing, Fang Shanshan, Zhou Lingyun. Current status and hotspot analysis of experimental research on electroacupuncture intervention for peripheral nerve regeneration: electroacupuncture parameters, acupuncture effects and molecular mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2608-2617. |
| [11] | Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen. Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2618-2628. |
| [12] | Jiao Jingya, Zhang Yeting. Analysis of thematic evolution pathways in the field of physical activity and neurogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2653-2661. |
| [13] | Zhao Qianwei, Sun Guangyuan . Intestinal organoids: a bibliometric analysis of the latest trends in tissue/organ biology, disease modeling, and clinical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 238-247. |
| [14] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [15] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||