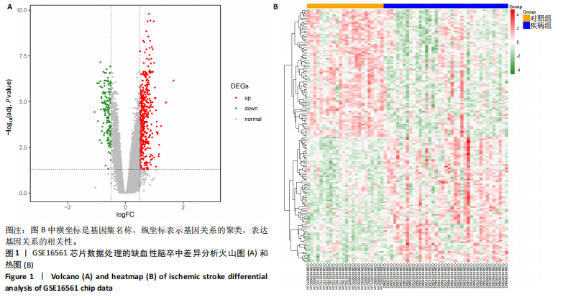
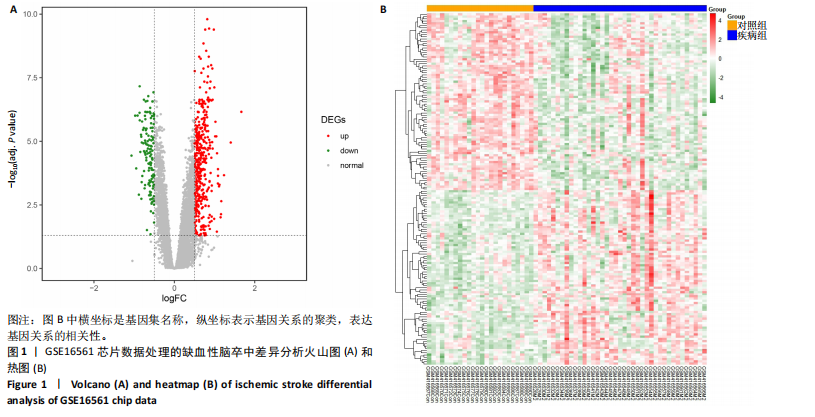
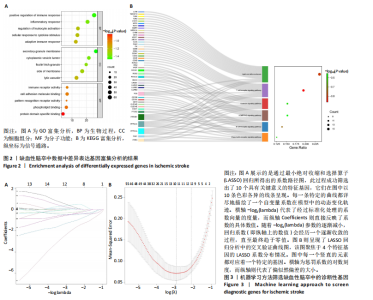
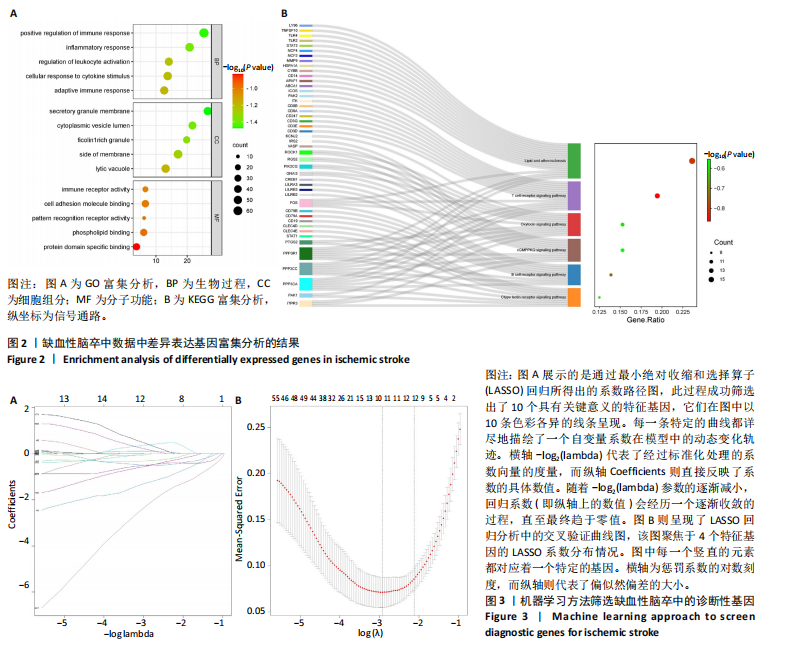
[1] TERRILL AL. Mental Health Issues Poststroke: Underrecognized and Undertreated. Stroke. 2023;54(6):1528-1530.
[2] 唐春花,郭露,李琼,等. 2022年全球卒中数据报告解读[J].诊断学理论与实践,2023,22(3):238-246.
[3] KAHLSON MA, DIXON SJ. Copper-induced cell death. Science. 2022; 375(6586):1231-1232.
[4] REN X, PAN C, PAN Z, et al. Knowledge mapping of copper-induced cell death: A bibliometric study from 2012 to 2022. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(45):e31133.
[5] XUE Q, KANG R, KLIONSKY DJ, et al. Copper metabolism in cell death and autophagy. Autophagy. 2023;19(8):2175-2195.
[6] CHANG W, LI P. Copper and Diabetes: Current Research and Prospect.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023;67(23):e2300468.
[7] YANG S, LI Y, ZHOU L, et al. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in atherosclerosis: metabolism, mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1):25.
[8] CHEN L, MIN J, WANG F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):378.
[9] 卓桂锋,陈炜,朱健敏,等. 血管性痴呆铜死亡关键差异基因的生物信息学分析及防治中药筛选[J]. 中草药,2023,54(21):7120-7129.
[10] HE YJ, CONG L, LIANG SL, et al. Discovery and validation of Ferroptosis-related molecular patterns and immune characteristics in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:1056312.
[11] FAN J, CHEN M, CAO S, et al. Identification of a ferroptosis-related gene pair biomarker with immune infiltration landscapes in ischemic stroke:a bioinformatics-based comprehensive study. BMC Genomics. 2022;23(1):59.
[12] 王咪,马书杰,刘杨,等.缺血性脑卒中铁死亡特征基因NFE2L2的鉴定与验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(7):1466-1474.
[13] XING L, WANG Z, HAO Z, et al. Cuproptosis in stroke: focusing on pathogenesis and treatment. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024;17:1349123.
[14] LAI MC, WANG D, LIN ZX, et al. Small Molecule Copper and Its Relative Metabolites in Serum of Cerebral Ischemic Stroke Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25(1):214-219.
[15] JIANG Y, WANG LP, DONG XH, et al. Trace Amounts of Copper in Drinking Water Aggravate Cerebral Ischemic Injury via Impairing Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21(8):677-680.
[16] SHI L, SUN Z, SU W, et al. Treg cell-derived osteopontin promotes microglia-mediated white matter repair after ischemic stroke. Immunity. 2021;54(7):1527-1542.
[17] ZHANG X, LEI B, YUAN Y, et al. Brain control of humoral immune responses amenable to behavioural modulation. Nature. 2020; 581(7807):204-208.
[18] JIN WN, SHI SX, LI Z, et al. Depletion of microglia exacerbates postischemic inflammation and brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(6):2224-2236.
[19] 董一蕾,李珺媛,张业昊,等. 缺血性脑卒中免疫炎症机制及中医药干预研究进展[J].世界中医药,2024,19(2):291-297.
[20] JIANG M, YIN P, BAI X, et al. Proinflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Genes in Stroke Pathogenesis. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(34):4220-4233.
[21] SCHALLER B. Prospects for the future: the role of free radicals in the treatment of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005;38(4):411-425.
[22] XU XH, SHAH PK, FAURE E, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 is expressed by macrophages in murine and human lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques and upregulated by oxidized LDL. Circulation. 2001;104(25):3103-3108.
[23] MA W, YANG Y, XIE T, et al. Treatment of Ischemic Stroke With Wenyang Huayu Formula: Network Pharmacology Analysis and Experimental Validation. Natural Product Communications. 2023;18(2): 1934578X-2211473X.
[24] YAMAMOTO S, MATSUI A, OHYAGI M, et al. In Vitro Generation of Brain Regulatory T Cells by Co-culturing With Astrocytes. Front Immunol. 2022;13:960036.
[25] SHICHITA T, SUGIYAMA Y, OOBOSHI H, et al. Pivotal role of cerebral interleukin-17-producing gammadeltaT cells in the delayed phase of ischemic brain injury. Nat Med. 2009;15(8):946-950.
[26] RAYASAM A, KIJAK JA, KISSEL L, et al. CXCL13 expressed on inflamed cerebral blood vessels recruit IL-21 producing T(FH) cells to damage neurons following stroke. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):125.
[27] KHAN S. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Clinical Medicine. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(25):2398.
[28] CHOI B, ZHENG W. Copper transport to the brain by the blood-brain barrier and blood-CSF barrier. Brain Res. 2009;1248:14-21.
[29] TALUKDER M, BI SS, JIN HT, et al. Cadmium induced cerebral toxicity via modulating MTF1-MTs regulatory axis. Environ Pollut. 2021;285: 117083. |