Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5735-5742.doi: 10.12307/2025.823
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of application of variable angle screws in posterolateral tibial plateau fractures
Hu Zhenghui1, Zhang Wen2, Heng Hongquan3, Ren Weizhi1, Wu Chenying1, Gu Zenghui1, Peng Jian1, Li Liubing1, Xu Wei1
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopedic Surgery, Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Center for Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Army Medical University, Chongqing 400000, China
-
Received:2024-06-15Accepted:2024-08-12Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-03 -
Contact:Xu Wei, MD, Chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Co-corresponding author: Li Liubing, MD, Chief physician, Department of Joint Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Hu Zhenghui, MS, Department of Joint Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Zhang Wen, MS, Senior experimenter, Institute of Orthopedic Surgery, Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China Heng Hongquan, Physician, MS, Center for Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Army Medical University, Chongqing 400000, China Hu Zhenghui, Zhang Wen, and Heng Hongquan contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Suzhou Talent Program, No. 2020092 (to LLB); Suzhou Key Discipline, No. SZXK202104; Clinical New Technology Development Project of Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, No. 23ZL009 (to XW); Provincial and Ministry Joint Construction of State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Radiation Protection Open Project, No. GZK1202215 (to LLB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Zhenghui, Zhang Wen, Heng Hongquan, Ren Weizhi, Wu Chenying, Gu Zenghui, Peng Jian, Li Liubing, Xu Wei. Finite element analysis of application of variable angle screws in posterolateral tibial plateau fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5735-5742.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
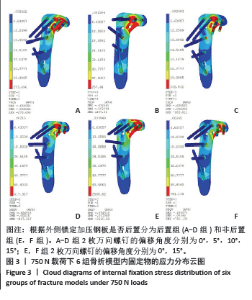
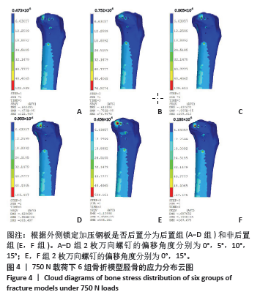
2.1 不同载荷条件下内固定物的von Mises应力云图 250-750 N的轴向载荷下,随着施加载荷增加,内固定物的最大von Mises应力随之增加,且趋势相似。750 N下最大von Mises应力情况:B组(后置+偏移5°) < C组(后置+偏移10°) < A组(后置+非偏移) < D组(后置+偏移15°) < F组(非后置+偏移15°) < E组(非后置+非偏移)。A-D组中随着施加载荷增加,应力集中点在钢板与钢板后2枚螺钉结合处和钢板拐角处,且随着偏移角度增加,钢板于螺钉结合处应力由倒数第一二枚螺钉逐渐转移至倒数第二三枚螺钉。而E,F组钢板未进行后置,E组螺钉未进行偏移,应力于钢板拐角处和钢板与后2枚螺钉结合处产生大量集中;F组对后2枚螺钉进行了偏移,应力集中点和E组位置相似,但区域明显缩小和分散。750 N下内固定物的von Mises应力云图见图3。"
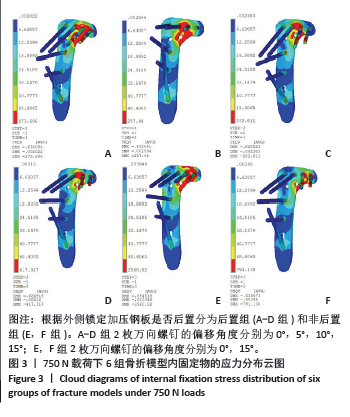
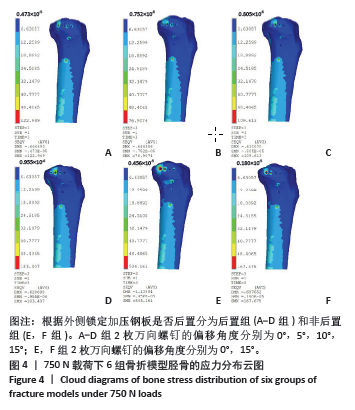
2.2 不同载荷条件下胫骨的von Mises应力云图 随着压缩负荷增加,最大von Mises应力亦增加,趋势相似。750 N载荷下胫骨模型中最大von Mises应力呈现以下趋势:B组(后置+偏移5°) < C组(后置+偏移10°) < A组(后置+非偏移) < F组(非后置+偏移15°) < D组(后置+偏移15°) < E组(非后置+非偏移)。后置组(A-D组)胫骨模型可见与内固定模型相似的应力集中趋势,随着角度偏移增加,胫骨模型应力集中点由倒数第1个钉孔过渡到第2枚钉孔周围。非后置组(E,F组)胫骨模型应力主要集中在最后一枚钉孔周围,角度偏移后应力进一步降低。750 N下胫骨的von Mises应力云图见图4。"
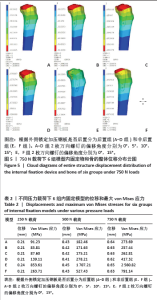
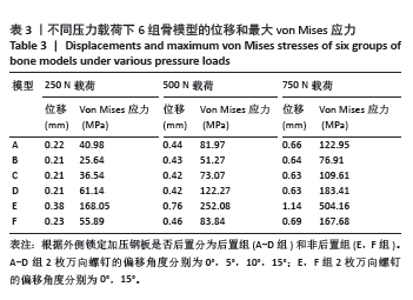
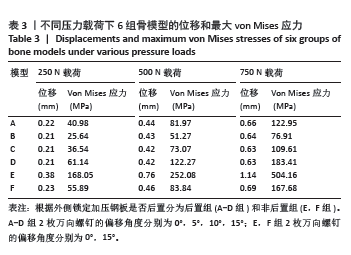
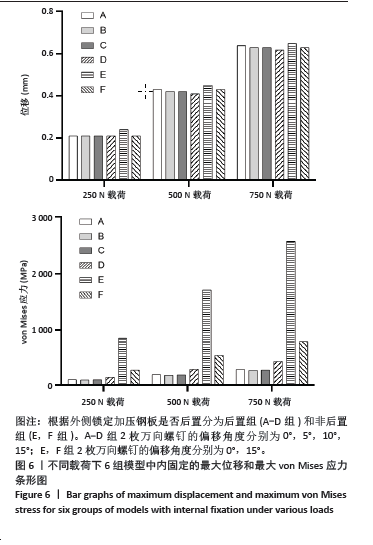
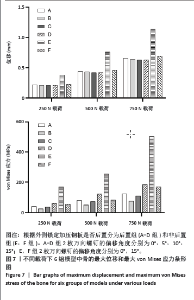
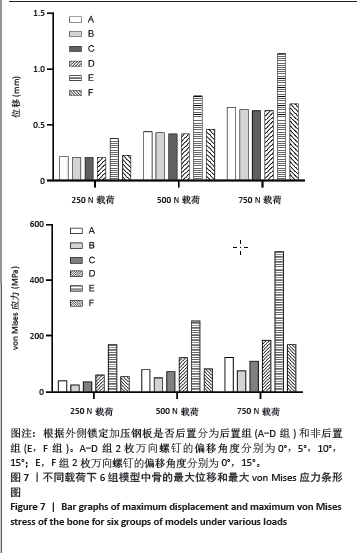
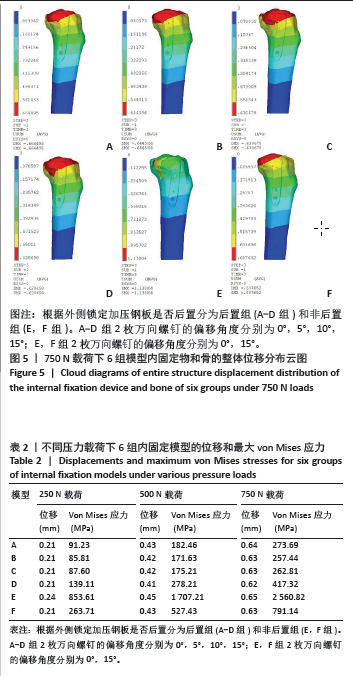
2.3 不同载荷条件下内固定和整体位移云图 3种载荷下6组内固定模型位移差别不明显,随着轴向载荷的增加,内固定模型最大压缩位移相应增加。750 N压缩载荷下6组内固定模型位移趋势如下:D组(后置+偏移15°) < B组(后置+偏移5°)=C组(后置+偏移10°)=F组(非后置+偏移15°) < A组(后置+非偏移) < E组(非后置+非偏移)。6组内固定位移峰值集中在横臂远端以及倒数后3枚螺钉钉孔周围。而于750 N压缩载荷下6组骨的整体位移云图中趋势如下:C组(后置+偏移10°)=D组(后置+偏移15°) < B组(后置+偏移5°) < A组(后置+非偏移) < F组(非后置+偏移15°) < E组(非后置+非偏移)。云图中可见整个外侧平台均为位移峰值集中部分,由近端向远端位移峰值逐渐下降。750 N下内固定物和骨整体位移云图见图5。表2,3及图6,7详细展示了内固定和骨的位移及最大von Mises应力结果。"
| [1] ZHANG C, BAI H, MA T, et al. Biomechanics and finite element analysis of a novel plate designed for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures via the anterolateral approach. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):20114. [2] XIANG G, ZHI-JUN P, QIANG Z, et al. Morphological characteristics of posterolateral articular fragments in tibial plateau fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(10):e1256-e1261. [3] ZHANG BB, WANG BH, MEI J, et al. Biomechanical study of a new rim plate fixation strategy for two kinds of posterolateral depression patterns of tibial plateau fractures: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):840. [4] LU Y, XU Y, REN C, et al. A feasibility study of robot-assisted percutaneous reduction and fixation technique for treating posterolateral depression tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2023; 13(1):22026. [5] HU Z, REN W, PENG J, et al. Biomechanics and finite element analysis comparing posterior T-plates with LCP for fixation of posterolateral tibial plate fractures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1286993. [6] LI J, ALI KA, XIA C, et al. Anterolateral approach for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Acta Orthop Belg. 2023;89(2):354-361. [7] HU S, CHEN S, CHANG S, et al. Treatment of Isolated Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fracture with a Horizontal Belt Plate through the Anterolateral Supra-Fibular-Head Approach. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:4186712. [8] MAO W, CHEN G, ZHU Y, et al. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures involving the posterolateral column using the extended anterolateral approach. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(38):e27316. [9] LU Y, BAI H, WANG Q, et al. The study of biomechanics and finite element analysis on a novel plate for tibial plateau fractures via anterolateral supra-fibular-head approach. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):13516. [10] HU Z, REN W, ZHANG W, et al. Potential problem and solution of lateral plate postposition for the posterolateral tibial plateau fracture. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):984. [11] LIU ZD, LI XF, QIAN L, et al. Lever reduction using polyaxial screw and rod fixation system for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: technique and clinical outcome. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:29. [12] HUANG L, XIONG C, GUO Z, et al. Comparison of monoplanar and polyaxial screw fixation systems in percutaneous intermediate fixation for thoracolumbar fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):172. [13] ELERIAN S, SINGH T, N AJ, et al. Early Results of a Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate for Distal Radius Fractures: A Bi-centre Study. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18321. [14] VLČEK M, PECH J, MUSIL V, et al. [Conservative and Surgical Treatment for Distal Ulna Fractures Associated with Distal Radius Fractures]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015;82(6):412-417. [15] 程晓东, 魏小飞, 俞宇,等.经皮相邻椎体单平面螺钉联合伤椎万向螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2023,38(1):53-55. [16] 朱梁豫, 李兴华, 王爱国.闭口万向螺钉骶髂固定系统联合脊柱内固定系统治疗不稳定型骶骨骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(3): 345-347. [17] NOURBAKHSH A, HIRSCHFELD AG, DHULIPALA S, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Fixed- versus Variable-Angle Locking Screws for Distal Humerus Comminuted Fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3): 302-308. [18] 卢永辉, 董伟强, 白波.老年人多节段腰椎管狭窄症应用椎弓根钉系统治疗的特点[J].中国老年学杂志,2004,24(9):824-825. [19] HAMANDI F, SIMON G, LAUGHLIN R, et al. Biomechanical Behavior of a Variable Angle Locked Tibiotalocalcaneal Construct. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(1):27. [20] KACZMAREK J, BARTKOWIAK T, PACZOS P, et al. What Is the Cost of Off-Axis Insertion of Locking Screws? A Biomechanical Comparison of a 3.5 mm Fixed-Angle and 3.5 mm Variable-Angle Stainless Steel Locking Plate Systems. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2022;35(5):339-346. [21] TIDWELL JE, ROUSH EP, ONDECK CL, et al. The biomechanical cost of variable angle locking screws. Injury. 2016;47(8):1624-1630. [22] SUN H, HE QF, ZHANG BB, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of different fixation strategies for posterolateral fragments in tibial plateau fractures and introduction of the ‘magic screw’. Knee. 2018;25(3): 417-426. [23] KUMAR VK, PRASAD K, SANSGIRI T, et al. Self-Drilling Versus Self-Tapping Screws: A 3D Finite Element Analysis. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2021;14(1):4-10. [24] REN W, ZHANG W, JIANG S, et al. The Study of Biomechanics and Clinical Anatomy on a Novel Plate Designed for Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures via Anterolateral Approach. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:818610. [25] ZHAO K, SHAN C, LUXIMON Y. Contributions of individual muscle forces to hip, knee, and ankle contact forces during the stance phase of running: a model-based study. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2022; 10(1):11. [26] ZHANG BB, HU H, ZHAN S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of “Barrel hoop plate” technique for the posterolateral fragments of tibial plateau fractures with different displacement tendency. Injury. 2020; 51(11):2465-2473. [27] 林旺,王盈盈,郭卫中,等.胫骨平台后外侧柱骨折扩大外侧入路内固定增强力学稳定性及膝关节功能[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24):3826-3831. [28] CARRERA I, GELBER PE, CHARY G, et al. Fixation of a split fracture of the lateral tibial plateau with a locking screw plate instead of cannulated screws would allow early weight bearing: a computational exploration. Int Orthop. 2016;40(10):2163-2169. [29] LOBENHOFFER P, GERICH T, BERTRAM T, et al. [Particular posteromedial and posterolateral approaches for the treatment of tibial head fractures]. Unfallchirurg. 1997;100(12):957-967. [30] FROSCH KH, BALCAREK P, WALDE T, et al. A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):515-520. [31] SOLOMON LB, STEVENSON AW, BAIRD RP, et al. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures: technique, results, and rationale. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8):505-514. [32] YOON YC, SIM JA, KIM DH, et al. Combined lateral femoral epicondylar osteotomy and a submeniscal approach for the treatment of a tibial plateau fracture involving the posterolateral quadrant. Injury. 2015;46(2):422-426. [33] CARLSON DA. Posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(2):73-78. [34] CHANG SM, ZHENG HP, LI HF, et al. Treatment of isolated posterior coronal fracture of the lateral tibial plateau through posterolateral approach for direct exposure and buttress plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(7):955-962. [35] 程邦君,毛冯缘,黄燕峰,等.胫骨外侧锁定接骨板联合前侧拉力螺钉或后外侧支撑接骨板治疗Schatzker Ⅱ型胫骨平台骨折合并后外侧骨折的临床研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(11): 1021-1027. [36] 蒋靓君,郑强,冯刚,等.扩展前外侧入路治疗伴后外侧骨块的胫骨平台骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(19):1161-1169. [37] HOEKSTRA H, VANHEES J, VAN DEN BERG J, et al. Extended lateral column tibial plateau fractures. How do we do it? Injury. 2018;49(10): 1878-1885. [38] 郭亮,徐广,夏欣,等.腓骨头上入路锁定加压钢板治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2023,26(3):425-428. [39] YAN Z, ZOU C, KENMEGNE GR, et al. Newly designed plate for the treatment of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):201. [40] ANDONOV Y. Lateral tibial plateau fractures with posterior comminution. Can a rim plate offer sufficient support? Acta Orthop Belg. 2023;89(2):275-279. [41] KÄÄB MJ, FRENK A, SCHMELING A, et al. Locked internal fixator: sensitivity of screw/plate stability to the correct insertion angle of the screw. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(8):483-487. |
| [1] | Zhou Daobin, Wang Kehao, Xie Yang, Ning Rende. Biomechanical characteristics of volar locking plate only versus combined dorsal mini-plate fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal ulnar fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [2] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [3] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [4] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [5] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [6] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [7] | Yan Xiangning, Chen Lei, Chen Yonghuan, Wang Chao, Li Xiaosheng. Influence of different depths and loads on knee joint mechanics and peripheral muscle force characteristics during squatting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2236-2247. |
| [8] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [9] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [10] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [11] | Wu Hongxu, Liu Xuanyu, Wang Taoyu, Wang Shiyao, Cheng Jingyi, Zhang Mingwen, Zhang Yinxia, Liu Zhihua, Wang Xiaojie. Finite element simulation of scoliosis with muscle unit introduction: verification of correction effect under bidirectional load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2172-2181. |
| [12] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [13] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [14] | Zhong Caihong, Xiao Xiaoge, Li Ming, Lin Jianhong, Hong Jing. Biomechanical mechanism of sports-related patellar tendinitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1417-1423. |
| [15] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Mechanical effect of mechanical wear of abutment screws on the Morse taper connection implant system: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1375-1383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||