Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5662-5672.doi: 10.12307/2025.740
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis
Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong
- Research Center of Exercise Capacity Assessment and Promotion, School of Physical Education, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-14Accepted:2024-11-04Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-28 -
Contact:Shi Jipeng, PhD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Research Center of Exercise Capacity Assessment and Promotion, School of Physical Education, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Zhu Tianrui, Master’s candidate, Research Center of Exercise Capacity Assessment and Promotion, School of Physical Education, Northeast Normal University, Changchun 130024, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:National Social Science Foundation of China, No. 22BTY075 (to XHQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Tianrui, Shi Jipeng, Sun Jiahe, Wang Luyi, Zhang Chen, Xu Hongqi, Quan Helong. Effectiveness of different exercise regimens to reduce fall risks in older adults: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5662-5672.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

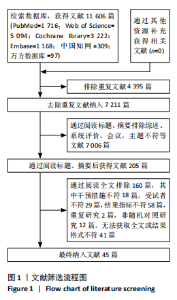
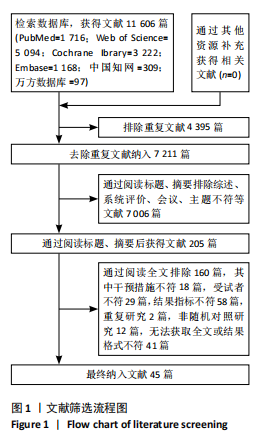
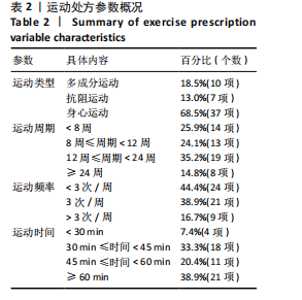
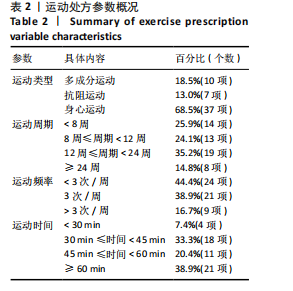
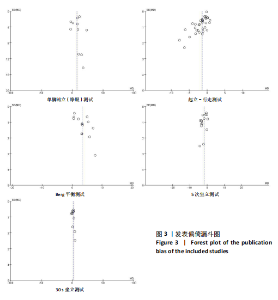
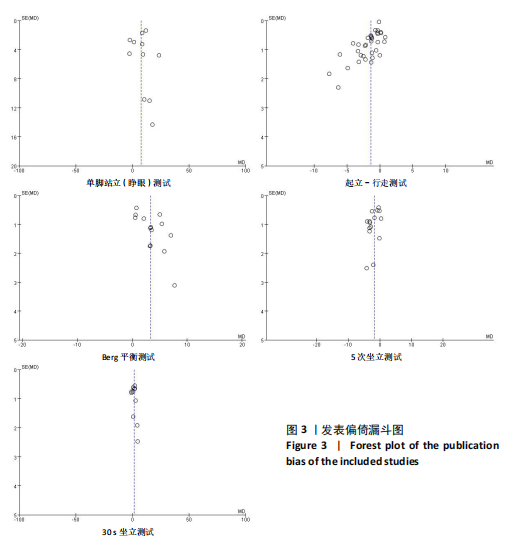
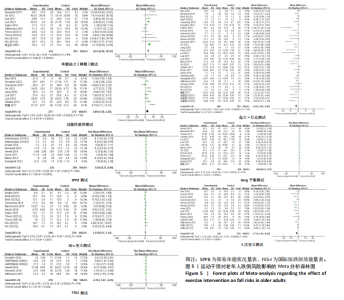
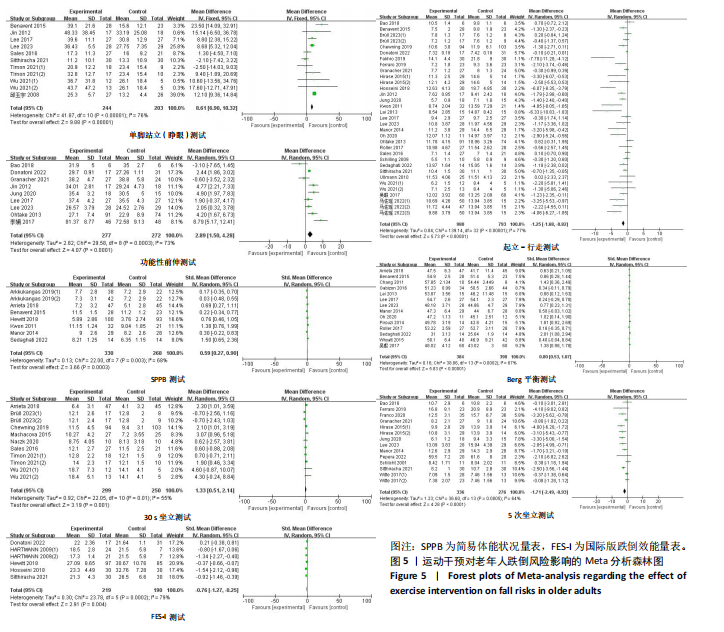
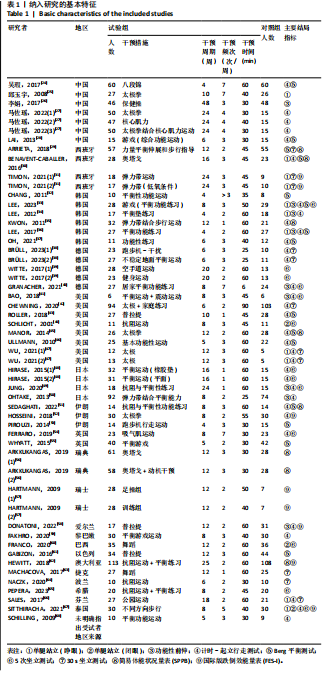
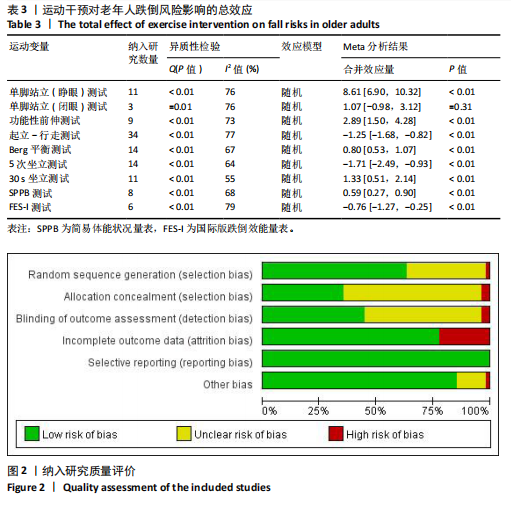
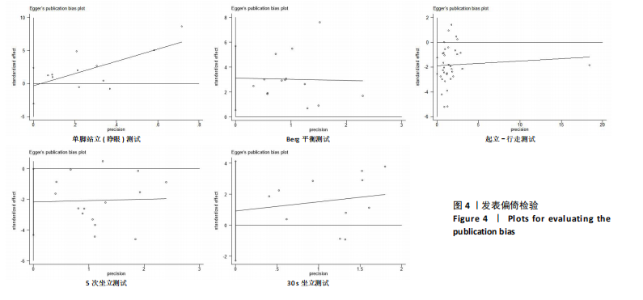
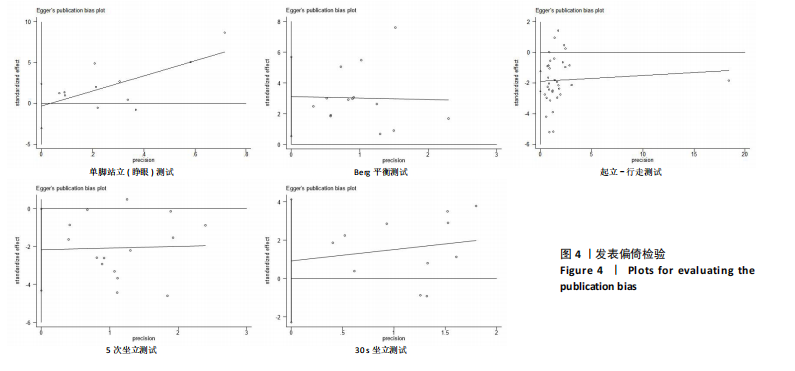
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 经过筛选,共纳入45篇文献[24-68],其中包含54项研究,即1篇文献中若包含多种研究方法,则每种研究方法算作1项研究。54项研究共包含3 074名受试者(试验组1 717名,对照组1 362名),多为社区群体,纳入群体年龄多为60-75岁,由于部分研究并没有报告性别比例,因此无法对总体性别比例进行计算,通过已知数据发现男女比例接近1∶2。由于干预方案无法对受试者进行隐藏,仅有部分研究采用盲法,因此没有列出(表1)。 根据先前研究,将干预方式划分为身心运动、有氧运动、抗阻运动和多成分运动[69-72]。由于以步行为主的运动仅有3项研究[38,53,67],其中2项干预方式对受试者认知能力存在一定影响,总体运动强度较低,因此3项研究归为身心运动组。身心运动以中国传统武术或平衡性功能练习为主,共有37项(68.5%)研究;抗阻运动多以弹力带锻炼为主,共7项(13.0%)研究;多成分运动主要以奥塔戈运动为主,共10项(18.5%)研究。运动周期4-48周不等,其中运动周期为12-24周的方案占比最高,为 35.2%(19项);每周运动频率小于3次占比最高,为44.4%(25项);每次运动时间≥30 min,但不超过45 min占比最高,为33.3%(18项)(表2)。 2.3 纳入文献的质量 在纳入的54项研究中,共有32项研究采用了随机分配方法并进行了说明。由于试验方案的特点,对试验人员和研究对象采用盲法存在一定困难,共24项采用了单盲或双盲的方案,12项研究明确说明分配方案采用隐蔽性处理。54项研究数据均报告完整,并对部分失访原因进行说明。研究方法学上整体质量较高(图2)。 2.4 发表偏倚检验 在运动干预对老年人单腿站立(睁眼)、单腿站立(闭眼)、功能性前伸测试、起立-行走测试、Berg平衡测试、5次坐立测试、30 s坐立测试、SPPB测试、FES-I测试干预效果的分析中,分别对纳入10项研究以上的干预分组做漏斗图分析,漏斗图显示两侧基本左右对称分布在漏斗图顶部,形成倒置漏斗形(图3)。 对包含10项研究以上的干预分组进行Begg检验和Egger检验,单腿站立(睁眼)、Berg平衡测试、5次坐立测试、30 s坐立测试Egger检验均提示不存在发表偏倚(P > 0.05)(图4)。在起立-行走测试纳入研究中,Begg检验(P=0.011)和Egger检验结果(P < 0.01)均提示存在偏倚,进行剪补法后发现结果没有发生逆转,较为稳健。 2.5 Meta分析结果 2.5.1 运动干预对老年人跌倒风险影响的Meta分析 运动干预对老年人跌倒风险的影响主要通过单脚站立(睁眼)、单脚站立(闭眼)、功能性前伸、起立-行走测试、Berg平衡量表、"
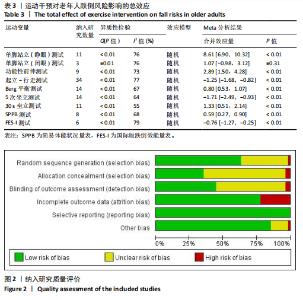
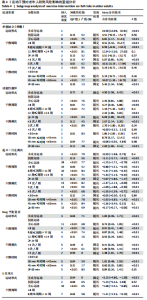
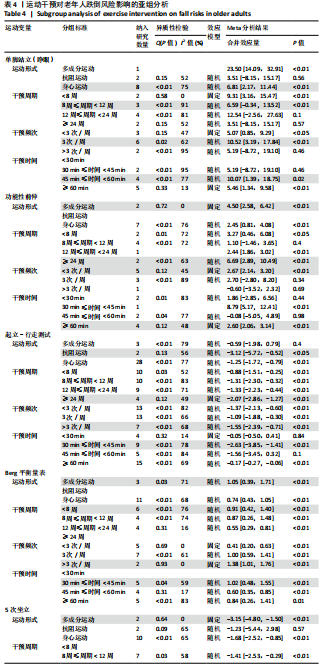
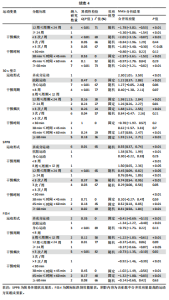
5次坐立、30 s坐立、SPPB测试和FES-I测试共9项干预结果进行比较分析。上述各项测试分别纳入11项、3项、9项、34项、14项、15项、11项、10项和6项研究,均存在一定异质性,采用随机效应模型得到合并后总效应量(表3)。除单脚站立(闭眼)合并效应量结果无统计学意义(P=0.31)外,各项测试合并效应量均具有统计学意义,表明运动干预能够有效降低老年人跌倒风险(图5)。 2.5.2 运动干预对老年人跌倒风险影响的亚组Meta分析 为探究平衡能力(睁眼单脚站立、功能性前伸、起立-行走测试、Berg平衡量表测试)、下肢肌力(30 s坐立测试、5次坐立测试、SPPB测试)、心理效能(国际版跌倒效能量表)干预结果异质性的来源,分别进行敏感性分析和亚组分析发现,无法通过剔除个别研究而使异质性明显降低。因此,为进一步探究潜在异质性来源,对潜在的调节变量进行亚组分析,确定各亚组合并效应量。亚组分析结果表明不同运动方案组成要素对老年人跌倒风险筛查指标影响效果不同(表4)。 在此研究中,通过对单脚站立(睁眼)测试运动周期各亚组所纳入研究逐一剔除发现,剔除效应量为负值的SITTHIRACHA等[67]和TIMON 等(1)[31]以及效应量较小的SALES等[66],均可分别使其所在亚组异质性大幅度降低,合并效应量具有统计学意义,结果显示干预总周期12周以上但不超过24周合并效应量最高,MD=21.06,95%CI(12.84,29.28),这"
与过往研究结果基本一致。单脚站立(闭眼)纳入文献较少,并未进行亚组分析。在功能性前伸测试合并结果中多成分运动的合并效应量高于仅采用身心运动的合并效应量,仅采用身心运动的亚组中6项研究异质性较高,BAO等[41]和GRANACHER等[40]2项研究甚至在运动干预后出现老年人功能性前伸成绩下降的结果,主要原因可能是由于测试的天花板效应以及运动强度较低,2项研究试验组对象的功能性前伸测试成绩在干预前均接近该亚组内最高水平,2项研究的干预方案也均是基于家庭环境中进行。在FES-I测试合并结果中DONATONI DA SILVA等[58]研究导致了身心运动亚组结果异质性高,且结果不具有统计学意义。运动评估的学习效果和霍索恩效应可能是引起异质性的主要原因[73],将其剔除后,SMD=-1.22,95%CI(-1.83,-0.61),结果具有统计学意义。"
| [1] FEDER G, CRYER C, DONOVAN S, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of falls in people over 65. The Guidelines’ Development Group. BMJ. 2000;321(7267): 1007-1011. [2] WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Falls. [2024-01-22]. https: //www. Who.int /news-room/factsheets/detail /falls. [3] KANNUS P, SIEVÄNEN H, PALVANEN M, et al. Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people. Lancet. 2005; 366(9500):1885-1893. [4] STEVENS JA, CORSO PS, FINKELSTEIN EA, et al. The costs of fatal and non-fatal falls among older adults. Inj Prev. 2006;12(5): 290-295. [5] KWAN MM, CLOSE JC, WONG AK, et al. Falls incidence, risk factors, and consequences in Chinese older people: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(3):536-543. [6] DELBAERE K, CLOSE JC, HEIM J, et al. A multifactorial approach to understanding fall risk in older people. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58(9):1679-1685. [7] SHERRINGTON C, MICHALEFF ZA, FAIRHALL N, et al. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2017; 51(24):1750-1758. [8] SHERRINGTON C, TIEDEMANN A, FAIRHALL N, et al. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: an updated meta-analysis and best practice recommendations. N S W Public Health Bull. 2011;22(3-4):78-83. [9] HOPEWELL S, COPSEY B, NICOLSON P, et al. Multifactorial interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 41 trials and almost 20 000 participants. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(22):1340-1350. [10] 郭静霞,陈亮,余启超,等.运动对预防老年人跌倒效果的网状Meta分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2021,27(5):563-573. [11] 胡慧秀,赵雅洁,孙超.老年人失能预防运动干预临床实践指南(2023版)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(22):2695-2710+2714. [12] 祝莉,王正珍,朱为模.健康中国视域中的运动处方库构建[J].体育科学,2020, 40(1):4-15. [13] MONTERO-ODASSO M, VAN DER VELDE N, MARTIN FC, et al. World guidelines for falls prevention and management for older adults: a global initiative. Age Ageing. 2022;51(9):afac205. [14] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. [15] SPRINGER BA, MARIN R, CYHAN T, et al. Normative values for the unipedal stance test with eyes open and closed. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2007;30(1):8-15. [16] DUNCAN PW, WEINER DK, CHANDLER J, et al. Functional reach: a new clinical measure of balance. J Gerontol. 1990;45(6): M192-M197. [17] PODSIADLO D, RICHARDSON S. The timed “Up & Go”: a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(2):142-148. [18] PARK SH, LEE YS. The Diagnostic Accuracy of the Berg Balance Scale in Predicting Falls. West J Nurs Res. 2017;39(11):1502-1525. [19] CSUKA M, MCCARTY DJ. Simple method for measurement of lower extremity muscle strength. Am J Med. 1985;78(1):77-81. [20] JONES CJ, RIKLI RE, BEAM WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70(2):113-119. [21] GURALNIK JM, SIMONSICK EM, FERRUCCI L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol. 1994;49(2): M85-M94. [22] YARDLEY L, BEYER N, HAUER K, et al. Development and initial validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I). Age Ageing. 2005;34(6):614-619. [23] Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial [2024-01-22]. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-08. [24] 吴瑕,薛武更,方静,等.八段锦锻炼干预社区老年人跌倒风险60例[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2017,15(3):106-109. [25] 邱玉宇,崔焱.太极拳锻炼对防止老年人跌倒作用机制的研究[J].护理研究, 2008,22(6):490-491. [26] 李娟,赵庆华,邓洪波,等.护养中心老年人防跌倒保健操训练的效果[J].护理学杂志,2017,32(11):67-69. [27] 马佐瑶,马海滨,杨小燕,等.核心肌力联合太极拳运动对老年人步行能力及跌倒风险的影响[J].宁夏医学杂志,2022, 44(3):237-240. [28] LAI CH, PENG CW, CHEN YL, et al. Effects of interactive video-game based system exercise on the balance of the elderly. Gait Posture. 2013;37(4):511-515. [29] ARRIETA H, REZOLA-PARDO C, ZARRAZQUIN I, et al. A multicomponent exercise program improves physical function in long-term nursing home residents: A randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol. 2018;103:94-100. [30] BENAVENT-CABALLER V, ROSADO-CALATAYUD P, SEGURA-ORTÍ E, et al. The effectiveness of a video-supported group-based Otago exercise programme on physical performance in community-dwelling older adults: a preliminary study. Physiotherapy. 2016;102(3):280-286. [31] TIMON R, CAMACHO-CARDEÑOSA M, GONZÁLEZ-CUSTODIO A, et al. Effect of hypoxic conditioning on functional fitness, balance and fear of falling in healthy older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021;18(1):25. [32] CHANG M, HUANG YH, JUNG H. The Effectiveness of the Exercise Education Programme on Fall Prevention of the Community-dwelling Elderly: A Preliminary Study. Hong Kong J Occup Ther. 2011;21(2): 56-63. [33] LEE K. Home-Based Exergame Program to Improve Physical Function, Fall Efficacy, Depression and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(8):1109. [34] LEE KJ, KIM SH, SONG CH. Balance Exercise Program Using Training Mats Improves the Postural Balance of Elderly Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Korean Phys Soc. 2012; 24(3): 223-228. [35] KWON MS. Effects of a fall prevention program on physical fitness and psychological functions in community dwelling elders. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(2):165-174. [36] LEE K, LEE YW. Efficacy of ankle control balance training on postural balance and gait ability in community-dwelling older adults: a single-blinded, randomized clinical trial. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(9):1590-1595. [37] OH DS, CHOI JD. Effects of Motor Imagery Training on Balance and Gait in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(2):650. [38] BRÜLL L, HEZEL N, ARAMPATZIS A, et al. Comparing the Effects of Two Perturbation-Based Balance Training Paradigms in Fall-Prone Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gerontology. 2023;69(7):910-922. [39] WITTE K, EMMERMACHER P, PLISKE G. Improvement of Balance and General Physical Fitness in Older Adults by Karate: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Complement Med Res. 2017;24(6):390-393. [40] GRANACHER U, MUEHLBAUER T, GÖSTEMEYER G, et al. The performance of balance exercises during daily tooth brushing is not sufficient to improve balance and muscle strength in healthy older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):257. [41] BAO T, CARENDER WJ, KINNAIRD C, et al. Effects of long-term balance training with vibrotactile sensory augmentation among community-dwelling healthy older adults: a randomized preliminary study. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2018;15(1):5. [42] CHEWNING B, HALLISY KM, MAHONEY JE, et al. Disseminating Tai Chi in the Community: Promoting Home Practice and Improving Balance. Gerontologist. 2020;60(4):765-775. [43] ROLLER M, KACHINGWE A, BELING J, et al. Pilates Reformer exercises for fall risk reduction in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2018; 22(4):983-998. [44] SCHLICHT J, CAMAIONE DN, OWEN SV. Effect of intense strength training on standing balance, walking speed, and sit-to-stand performance in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(5):M281-286. [45] MANOR B, LOUGH M, GAGNON MM, et al. Functional benefits of tai chi training in senior housing facilities. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(8):1484-1489. [46] ULLMANN G, WILLIAMS HG, HUSSEY J, et al. Effects of Feldenkrais exercises on balance, mobility, balance confidence, and gait performance in community-dwelling adults age 65 and older. J Altern Complement Med. 2010;16(1):97-105. [47] WU Y, SENK C, COLL P, et al. A comparison of two Tai Chi interventions tailored for different health outcomes. Complement Ther Med. 2021;59:102731. [48] HIRASE T, INOKUCHI S, MATSUSAKA N, et al. Effects of a balance training program using a foam rubber pad in community-based older adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2015;38(2):62-70. [49] JUNG H, MIKI Y, TANAKA R, et al. The Effects of a Multicomponent Lower Extremity Training Technique on Physical Function in Healthy Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420935702. [50] OHTAKE M, MORIKAGI Y, SUZUKI I, et al. Effects of exercise on the prevention of conditions leading to the need for long-term care. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013;25(1):49-57. [51] SEDAGHATI P, GOUDARZIAN M, AHMADABADI S, et al. The impact of a multicomponent-functional training with postural correction on functional balance in the elderly with a history of falling. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):23. [52] HOSSEINI L, KARGOZAR E, SHARIFI F, et al. Tai Chi Chuan can improve balance and reduce fear of falling in community dwelling older adults: a randomized control trial. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018;14(6):1024-1031. [53] PIROUZI S, MOTEALLEH AR, FALLAHZADEH F, et al. Effectiveness of treadmill training on balance control in elderly people: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Iran J Med Sci. 2014;39(6):565-570. [54] FERRARO FV, GAVIN JP, WAINWRIGHT T, et al. The effects of 8 weeks of inspiratory muscle training on the balance of healthy older adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Physiol Rep. 2019;7(9):e14076. [55] WHYATT C, MERRIMAN NA, YOUNG WR, et al. A Wii Bit of Fun: A Novel Platform to Deliver Effective Balance Training to Older Adults. Games Health J. 2015;4(6):423-433.
[56] ARKKUKANGAS M, SÖDERLUND A, ERIKSSON S, et al. Fall Preventive Exercise With or Without Behavior Change Support for Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial With Short-Term Follow-up. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019; 42(1):9-17. [57] HARTMANN A, MURER K, DE BIE RA, et al. The effect of a foot gymnastic exercise programme on gait performance in older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil. 2009;31(25):2101-2110. [58] DONATONI DA SILVA L, SHIEL A, MCINTOSH C. Effects of Pilates on the risk of falls, gait, balance and functional mobility in healthy older adults: A randomised controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2022;30:30-41. [59] FAKHRO MA, HADCHITI R, AWAD B. Effects of Nintendo Wii fit game training on balance among Lebanese older adults. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(11):2271-2278. [60] FRANCO MR, SHERRINGTON C, TIEDEMANN A, et al. Effect of Senior Dance (DanSE) on Fall Risk Factors in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys Ther. 2020;100(4):600-608. [61] GABIZON H, PRESS Y, VOLKOV I, et al. The Effects of Pilates Training on Balance Control and Self-Reported Health Status in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Aging Phys Act. 2016;24(3):376-383. [62] HEWITT J, GOODALL S, CLEMSON L, et al. Progressive Resistance and Balance Training for Falls Prevention in Long-Term Residential Aged Care: A Cluster Randomized Trial of the Sunbeam Program. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2018;19(4):361-369. [63] MACHACOVA K, VANKOVA H, VOLICER L, et al. Dance as Prevention of Late Life Functional Decline Among Nursing Home Residents. J Appl Gerontol. 2017; 36(12):1453-1470. [64] NACZK M, MARSZALEK S, NACZK A. Inertial Training Improves Strength, Balance, and Gait Speed in Elderly Nursing Home Residents. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:177-184. [65] PEPERA G, KRINTA K, MPEA C, et al. Randomized Controlled Trial of Group Exercise Intervention for Fall Risk Factors Reduction in Nursing Home Residents. Can J Aging. 2023;42(2):328-336. [66] SALES M, POLMAN R, HILL KD, et al. A Novel Exercise Initiative for Seniors to Improve Balance and Physical Function. J Aging Health. 2017;29(8):1424-1443. [67] SITTHIRACHA P, EUNGPINICHPONG W, CHATCHAWAN U. Effect of Progressive Step Marching Exercise on Balance Ability in the Elderly: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3146. [68] SCHILLING BK, FALVO MJ, KARLAGE RE, et al. Effects of unstable surface training on measures of balance in older adults. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(4):1211-1216. [69] MILLER KJ, GONÇALVES-BRADLEY DC, AREEROB P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of three exercise types to treat clinical depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;58:100999. [70] HUANG X, ZHAO X, LI B, et al. Comparative efficacy of various exercise interventions on cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2022;11(2):212-223. [71] PIERCY KL, TROIANO RP, BALLARD RM, et al. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. JAMA. 2018;320(19):2020-2028. [72] SHERRINGTON C, FAIRHALL NJ, WALLBANK GK, et al. Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;1(1): CD012424. [73] MCCARNEY R, WARNER J, ILIFFE S, et al. The Hawthorne Effect: a randomised, controlled trial. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007;7:30. [74] 王志灼,谷莉,周谋望.中国老年人跌倒风险因素识别及评估工具应用的研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2021,36(11): 1440-1444. [75] 陈洪萍,杨小丽,张菁,等.2018年内江市社区老年人跌倒情况及其危险因素分析[J].预防医学情报杂志,2020,36(2): 224-228. [76] HUANG Y, LIU X. Improvement of balance control ability and flexibility in the elderly Tai Chi Chuan (TCC) practitioners: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015;60(2):233-238. [77] CLEMSON L, FIATARONE SINGH MA, BUNDY A, et al. Integration of balance and strength training into daily life activity to reduce rate of falls in older people (the LiFE study): randomised parallel trial. BMJ. 2012;345:e4547. [78] CLEGG A, BARBER S, YOUNG J, et al. The Home-based Older People’s Exercise (HOPE) trial: a pilot randomised controlled trial of a home-based exercise intervention for older people with frailty. Age Ageing. 2014; 43(5):687-695. [79] LESINSKI M, HORTOBÁGYI T, MUEHLBAUER T, et al. Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45(12): 1721-1738. [80] RIVA D, MAMO C, FANÌ M, et al. Single stance stability and proprioceptive control in older adults living at home: gender and age differences. J Aging Res. 2013;2013:561695. [81] LIMA CA, RICCI NA, NOGUEIRA EC, et al. The Berg Balance Scale as a clinical screening tool to predict fall risk in older adults: a systematic review. Physiotherapy. 2018;104(4):383-394. [82] FYFE JJ, HAMILTON DL, DALY RM. Minimal-Dose Resistance Training for Improving Muscle Mass, Strength, and Function: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Practical Considerations. Sports Med. 2022;52(3):463-479. [83] GRANACHER U, ZAHNER L, GOLLHOFER A. Strength, power, and postural control in seniors: Considerations for functional adaptations and for fall prevention. Eur J Sport Sci. 2008;8(6):325-340. [84] KIRKENDALL DT, GARRETT WE JR. The effects of aging and training on skeletal muscle. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26(4):598-602. [85] LIU TW, NG GYF, CHUNG RCK, et al. Cognitive behavioural therapy for fear of falling and balance among older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2018;47(4):520-527. [86] KRUISBRINK M, CRUTZEN R, KEMPEN GIJM, et al. Disentangling interventions to reduce fear of falling in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention components. Disabil Rehabil. 2022;44(21):6247-6257. [87] FREIBERGER E, HÄBERLE L, SPIRDUSO WW, et al. Long-term effects of three multicomponent exercise interventions on physical performance and fall-related psychological outcomes in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012; 60(3):437-446. [88] FRÄNDIN K, GRÖNSTEDT H, HELBOSTAD JL, et al. Long-Term Effects of Individually Tailored Physical Training and Activity on Physical Function, Well-Being and Cognition in Scandinavian Nursing Home Residents: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gerontology. 2016;62(6):571-580. |
| [1] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [2] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [3] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [4] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| [5] | Wang Juan, Wang Guanglan, Zuo Huiwu. Efficacy of exercise therapy in the treatment of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients: #br# a network meta-analysis #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1714-1726. |
| [6] | Zheng Huakun, Yin Mingyue, Liu Qian. Effects of interval and continuous training on the quality of life in physically inactive adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1727-1740. |
| [7] |
Liang Xiaoxiao, Zheng Jiejiao, Duan Linru, Chen Xi, Zhang Tingyu.
Characterization of postural stability in elderly patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1208-1213.
|
| [8] | Wu Yihan, Liu Zhongqiang, Wei Qiaoye, Liu Mingdong, Chen Keyi, Li Zhigang. Effect of balance training with different visual conditions on proprioception in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1050-1057. |
| [9] | Wen Zixing, Xu Xin, Zhu Shengqun. Correlations between gastrocnemius morphology parameters and physical activity capacity in elderly females under high-frequency ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1058-1063. |
| [10] | Li Zhe, Li Ping, Zhang Chao, Guo Guangling. A network meta-analysis of efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of premature ovarian failure animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7898-7908. |
| [11] | Wang Kaigang, Hao Dongsheng, Ma Pei, Zhou Shuo, Li Ruimin. Comparison of efficacy of different biological scaffolds for pulp regeneration therapy in immature permanent teeth: a Bayesian network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7447-7460. |
| [12] | Wang He, Yu Shaohong, . Meta-analysis of transcranial direct current stimulation in improving lower limb motor dysfunction in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6556-6565. |
| [13] | Wang Jianlei, He Peiliang, Sun Yongjian. A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous glucocorticoids before lower limb joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 599-607. |
| [14] | Li Jia, Liu Qianru, Xing Mengnan, Chen Bo, Jiao Wei, Meng Zhaoxiang. A network meta-analysis on therapeutic effect of different types of exercise on knee osteoarthritis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 609-616. |
| [15] | Zhou Yanjie, Cao Chunfeng, Zhang Zhongzu, Niu Xiong, Wang Xin, Yang Zaihai, Zhou Liang, Li Bo. Meta-analysis of anterior cervical decompression and fusion ROI-CTM self-locking system in treatment of degenerative cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 617-627. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||