Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5116-5126.doi: 10.12307/2025.734
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis
Wang Zhifeng1, Yang Jiao2, Xi Yujiang1, Xu Shuangfeng1, Shi Ting1, Lan Junfeng1, Hao Zhihui1, He Pengfen1, Yang Aiming3, Pan Pan2, #br# Wang Jian1#br#
- 1The First Clinical Medical College of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 3Yunnan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650021, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-08Accepted:2024-10-22Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-01-24 -
Contact:Wang Jian, MD, Associate professor, The First Clinical Medical College of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China Co-corresponding author: Pan Pan, MD, Lecturer, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Wang Zhifeng, Master candidate, The First Clinical Medical College of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:General Project of Applied Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province, No. 202201AT070214 (to WJ); Joint Special Funds for Applied Basic Research in Traditional Chinese Medicine of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Nos. 202001AZ070001-020 and 202301AZ070001-016 (to WJ); Two-type Talents Project of Yunnan Province, No. 202205AD160024 (to WJ); Scientific Research Fund Project of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education, Nos. 2024Y398 (to WZF) and 2024Y391 (to HPF); Department of Science and Technology of Yunnan Province - Basic Research Program, No. 202201AU070176 (to PP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhifeng, Yang Jiao, Xi Yujiang, Xu Shuangfeng, Shi Ting, Lan Junfeng, Hao Zhihui, He Pengfen, Yang Aiming, Pan Pan, Wang Jian. Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
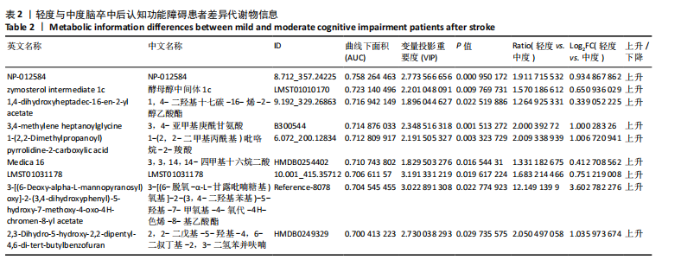
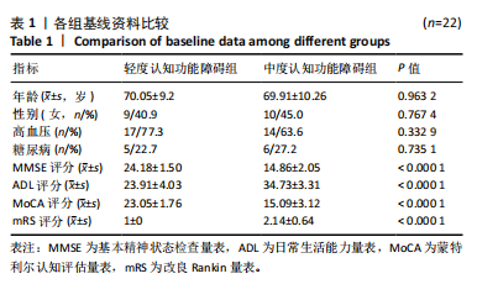
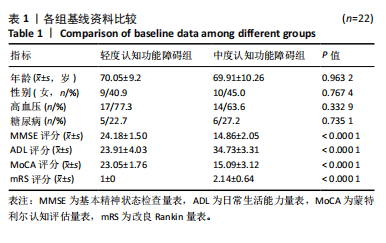
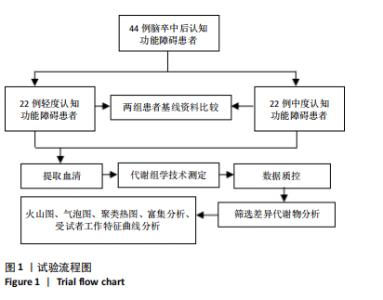
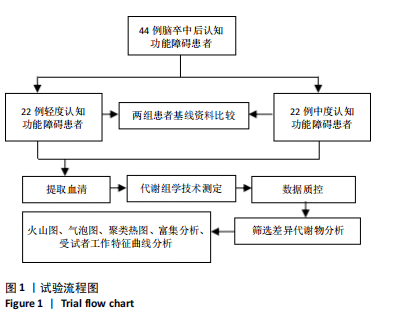
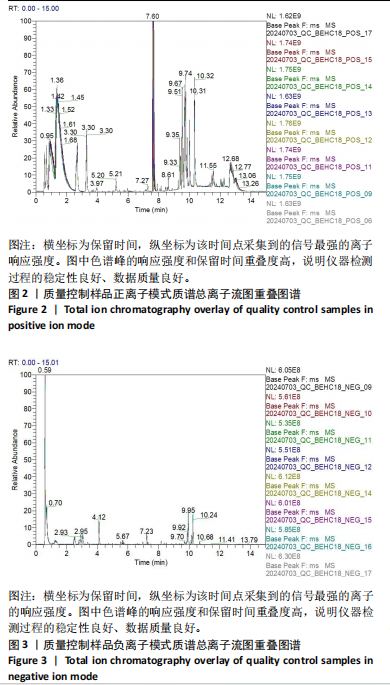
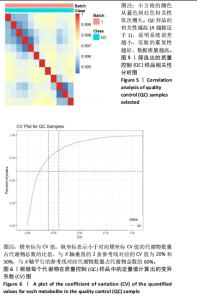
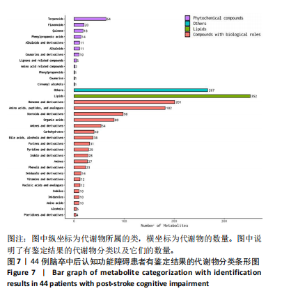
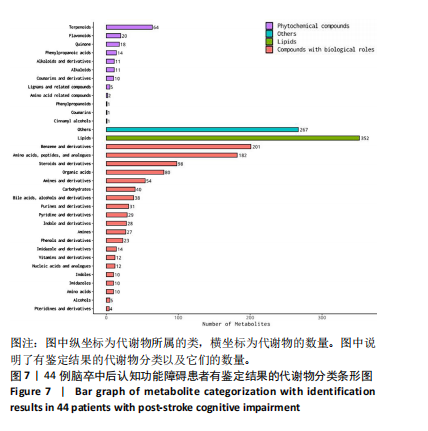
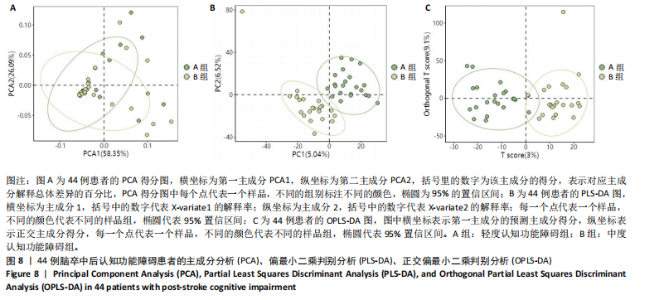
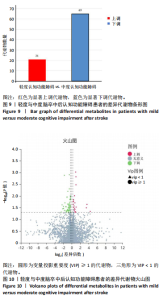
2.4 基峰色谱图 基峰色谱图是一种通过连续记录每个时间点上检测到的最高离子强度而生成的图谱。高度的色谱峰重叠性是对仪器稳定性及数据质量优良性的一种直观验证,见图2,3。 2.5 质量控制与质量保证 通过对数据总表(包含质量控制样品在内)中所有样品的定量值进行主成分分析(principle component analysis,PCA),可以从多维数据空间中提取出主要特征,进而观察各组样品与质量控制样品在主成分分析图上的总体分布情况。质量控制样品在主成分分析图中的紧密聚集是实验稳定性和数据可靠性的有力证明,见图4。 2.6 质量控制样品相关性分析 在数据总表中,特别筛选出质量控制样品的数据集,并基于这些质量控制样品的定量值,采用Spearman相关系数进行统计分析。Spearman相关系数(R值)的高低直接反映了质量控制样品间数据的相关性强弱。当R值越趋近于1时,意味着质量控制样品之间的相关性越强,见图5。 2.7 变异系数分析 在数据总表中筛选出质量控制样品后,针对每个代谢物在质量控制样品中的定量值,计算了变异系数(coefficientof variation,CV),当变异系数值小于或等于30%时,认为该代谢物的定量结果重复性良好,适合用于后续的数据分析,见图6。 2.8 代谢物分类以及代谢通路分类 有鉴定结果的代谢物,按照Final Class对代谢物的数量进行统计,其次按照其参与的KEGG代谢通路的大类(Super Pathway)对代谢物的数量进行统计(如果代谢物是脂质,那么按照Sub Pathway对代谢物的数量进行统计),见图7。 2.9 差异代谢物多变量分析 为了分析两组样品之间的差异及分布情况,构建了主成分分析的模型。通过观察两组样品在主成分分析图上的位置及分布形态,可以直观评估它们之间的分离趋势,椭圆代表95%置信区间,见图8A。偏最小二乘判别分析(PLS-DA)是一种监督模型分析方法。对两组生物样品进行偏最小二乘判别分析,探索并量化代谢物表达水平与样品所属类别之间的复杂关系,椭圆代表95%置信区间,见图8B。正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)作为一种增强的统计方法,用来构建代谢物表达量与样品类别之间的精确关系模型。在正交偏最小二乘判别分析模型构建完成后,利用变量投影重要度(VIP)这一指标来评估各代谢物在区分不同样品类别中的贡献度。变量投影重要度值越高,表示该代谢物对分类判别的贡献越大,说明其在模型中的重要性越高,椭圆代表95%置信区间,见图8C。 2.10 差异代谢物单变量分析 综合运用了单变量统计分析与多变量统计分析手段,旨在精准识别两个生物组别间的差异代谢物。首先,通过主成分分析与偏最小二乘判别分析,初步揭示了两组样本在整体代谢谱上的差异性。随后,为了进一步细化差异代谢物,采用了正交偏最小二乘判别分析,结合变量投影重要度值、差异倍数变化以及P值显著性水平进行综合评估。具体筛选标准为:变量投影重要度值≥1,差异倍数≥1.2或者≤0.83,P值< 0.05。通过这一系列严格筛选,成功筛选出86种具有显著差异的代谢物,其中21种表现为上调,65种表现为下调,见图9。这些发现以火山图的形式直观展示,图中横轴代表经log2转换的差异倍数值,纵轴则为-log10转换后的q值,颜色与形状编码分别指示了代谢物的表达变化方向和变量投影重要度值大小,见图10。 为进一步验证这些差异代谢物的生物学意义及诊断潜力,采用了受试者工作特征曲线分析,结果显示,在所筛选出的86种代谢物中,有9种代谢物的曲线下面积值超过了0.7,这说明这9种代谢物可能作为轻、中度脑卒"
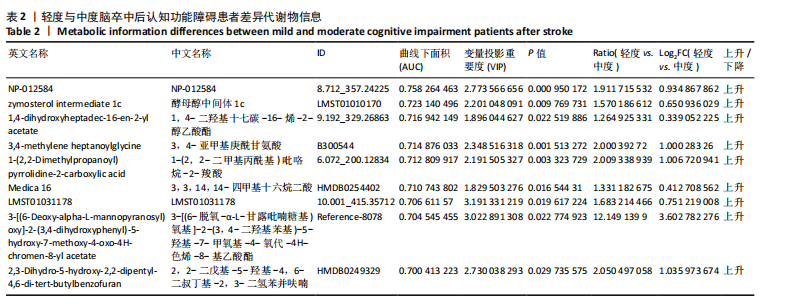
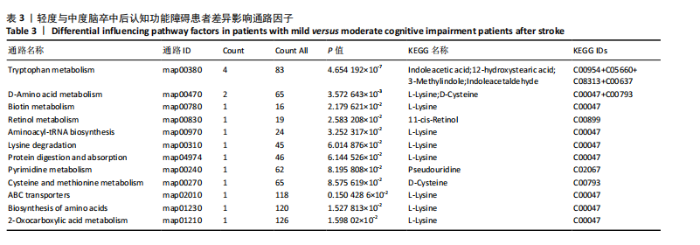
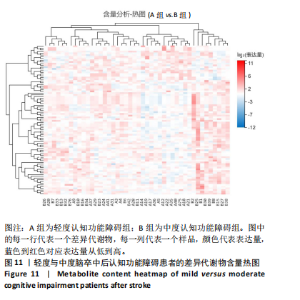
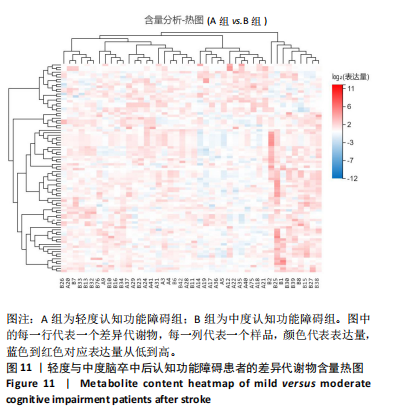
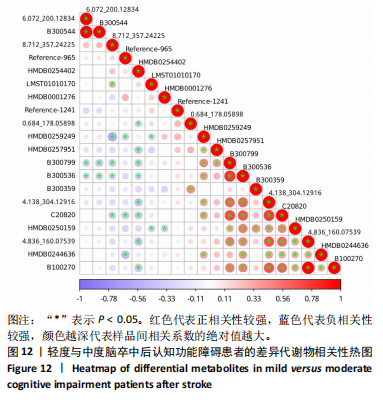
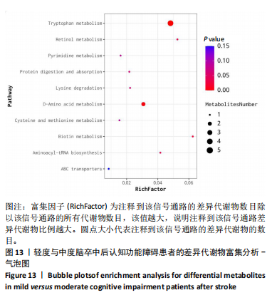
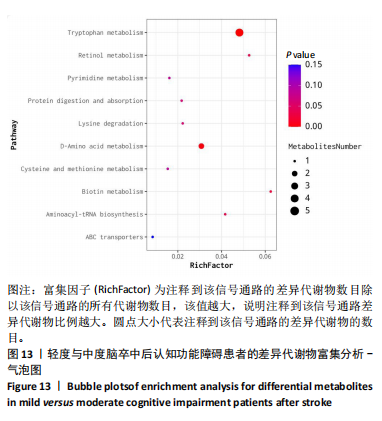
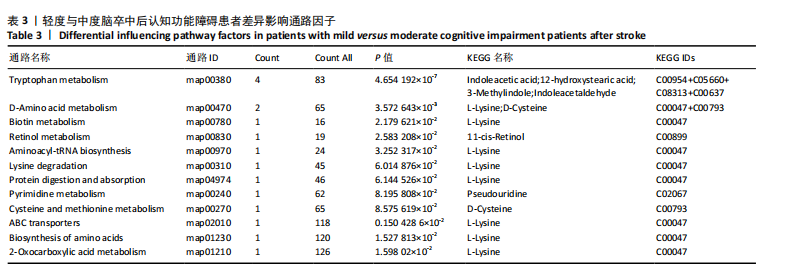
中后认知功能障碍疾病进展的关键潜在生物标志物,对于疾病的早期诊断、病情监测及预后评估具有重要价值,见表2。 2.11 差异代谢物含量分析 热图的可视化结果清晰地揭示了86种差异代谢物在两组样本间的显著区分度及组内样本间的高度相似性。该热图通过层次聚类(Hierarchical Cluster)算法,结合数据预处理步骤中的log2转换与z-score标准化(zero-mean normalization),有效地呈现了代谢物表达水平的分布模式。图中每一行对应一个特定的差异代谢物,而每一列则代表一个独立的样品;颜色编码直观反映了代谢物表达量的变化,从冷色调的蓝色(表示低表达)渐变至暖色调的红色(表示高表达),见图11。 2.12 差异代谢物相关性分析 该分析通过计算所有代谢物对之间的Spearman相关系数来实现,这是一种非参数统计方法,特别适用于评估变量间的单调关系,无需假设数据服从正态分布。在生成的相关性矩阵中,红色色调的深浅反映了代谢物间正相关性的强度,即颜色越深表示两种代谢物的变化趋势越趋于一致;相反,蓝色色调则表示代谢物间存在较强的负相关性,颜色越深则变化趋势越相反,见图12。 2.13 差异代谢物通路分析 设定P值< 0.05作为判断标准,以此筛选出差异代谢物显著富集的代谢通路。为了进一步聚焦关键通路,特别关注了P值最小的前10条代谢通路,并通过绘制气泡图的方式直观展示这些通路的信息。在气泡图中,X轴所代表的富集因子(Rich Factor)是一个关键指标,它计算的是注释到某一特定代谢通路的差异代谢物数量与该通路总代谢物数量的比值。富集因子值越高,意味着该通路中差异代谢物的比例越大,从而可能在生物过程中扮演更为重要的角色。此外,气泡图中的圆点大小用来直观显示注释到该通路的差异代谢物数量,圆点越大,说明涉及的差异代谢物越多,进一步强调了该通路在整体代谢网络中的活跃度和重要性,见图13。通过非靶向代谢组学分析,识别出了12条关键代谢通路,这些通路因差异代谢物的显著扰动而显得尤为突出,这12条通路在轻、中度脑卒中后认知功能障碍的疾病进程中扮演着重要角色,其受扰动程度与疾病干预下机体代谢波动的强度紧密相关,因此它们被视为潜在的病理机制通路,对探讨脑卒中后认知功能障碍疾病进展具有深远意义。这些通路包括:色氨酸代谢(Tryptophan metabolism)、D-氨基酸代谢(D-Amino acid metabolism)、生物素代谢(Biotin metabolism)、视黄醇代谢(Retinol metabolism)、氨酰-tRNA生物合成(Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis)、赖氨酸降解(Lysine degradation)、蛋白质的消化和吸收(Protein digestion and absorption)、嘧啶代谢(Pyrimidine metabolism)、半胱氨酸和甲硫氨酸代谢(Cysteine and methionine metabolism)、ABC转运蛋白(ABC transporters)、氨基酸的生物合成(Biosynthesis of amino acids)、2-氧代羧酸代谢(2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism),见表3。"
| [1] 吴永亚,边红.脑卒中后认知功能障碍研究进展[J].神经病学与神经康复学杂志,2020,16(1):34-40. [2] HUANG YY, CHEN SD, LENG XY, et al. Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Management. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022; 86(3):983-999. [3] CHI X, FAN X, FU G, et al. Research trends and hotspots of post-stroke cognitive impairment: a bibliometric analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1184830. [4] AI Y, LIU Y, YIN M, et al. Interactions between tDCS treatment and COMT Val158Met in poststroke cognitive impairment. Clin Neurophysiol. 2024;158:43-55. [5] ZHANG L, ZHOU L, YE Q, et al. Impact of transcranial direct current stimulation combined with motor-cognitive intervention on post-stroke cognitive impairment. Neurol Sci. 2024;45(4):1581-1588. [6] LIN C, TIAN Q, GUO S, et al. Metabolomics for Clinical Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Target Identification. Molecules. 2024; 29(10):2198. [7] CHIKH K, TONON D, TRIGLIA T, et al. Early Metabolic Disruption and Predictive Biomarkers of Delayed-Cerebral Ischemia in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Proteome Res. 2024;23(1):316-328. [8] LU H, XIE T, WEI S, et al. Metabolome and transcriptome integration reveals cerebral cortical metabolic profiles in rats with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024;16:1424312. [9] WANG M, WEI T, YU C, et al. Integrative Metabolomics and Whole Transcriptome Sequencing Reveal Role for TREM2 in Metabolism Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(7):4188-4202. [10] LIU Y, LI H, WANG X, et al. Anti-Alzheimers molecular mechanism of icariin: insights from gut microbiota, metabolomics, and network pharmacology. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):277. [11] ZHU H, WU Z, YU Y, et al. Integrated non-targeted metabolomics and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanisms of berberine in the long-term treatment of PTZ-induced epilepsy. Life Sci. 2024; 336:122347. [12] LIAN X, LIU Z, LIU S, et al. Alterations in serum metabolomics during the first seizure and after effective control of epilepsy. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):19180. [13] 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组.中国急性缺血性卒中诊治指南2023[J].中华神经科杂志,2024, 57(6):523-559.
[14] 汪凯,董强.卒中后认知障碍管理专家共识2021[J].中国卒中杂志, 2021,16(4):376-389. [15] PATHMASIRI W, RUSHING BR, MCRITCHIE S, et al. Untargeted metabolomics reveal signatures of a healthy lifestyle. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):13630. [16] ZHANG A, PAN C, WU M, et al. Causal association between plasma metabolites and neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2024;134:111067. [17] QIANG YX, YOU J, HE XY, et al. Plasma metabolic profiles predict future dementia and dementia subtypes: a prospective analysis of 274,160 participants. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024;16(1):16. [18] KIJPAISALRATANA N, AMENT Z, PATKI A, et al. Plasma Metabolites and Life’s Simple 7 in REGARDS. Stroke. 2024;55(5):1191-1199. [19] DAVIDSON M, RASHIDI N, NURGALI K, et al. The Role of Tryptophan Metabolites in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17): 9968. [20] XIE L, WU Q, LI K, et al. Tryptophan Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease with the Involvement of Microglia and Astrocyte Crosstalk and Gut-Brain Axis. Aging Dis. 2024;15(5):2168-2190. [21] CORREIA AS, VALE N. Tryptophan Metabolism in Depression: A Narrative Review with a Focus on Serotonin and Kynurenine Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8493. [22] 杨沛勋,范小雪,刘忞璇,等.淫羊藿总黄酮胶囊对脑卒中后认知障碍大鼠的作用[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(8):2262-2272. [23] MA J, WANG R, CHEN Y, et al. 5-HT attenuates chronic stress-induced cognitive impairment in mice through intestinal flora disruption. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):23. [24] RUDZKI L, OSTROWSKA L, PAWLAK D, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum 299v decreases kynurenine concentration and improves cognitive functions in patients with major depression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019;100:213-222. [25] VINTS WAJ, GÖKÇE E, ŠEIKINAITĖ J, et al. Resistance training’s impact on blood biomarkers and cognitive function in older adults with low and high risk of mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2024;21(1):9. [26] LIU Z, DAI X, ZHANG H, et al. Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):855. [27] PORRAS-DOMINGUEZ J, LOTHIER J, LIMAMI AM, et al. d-amino acids metabolism reflects the evolutionary origin of higher plants and their adaptation to the environment. Plant Cell Environ. 2024;47(5): 1503-1512. [28] KIMURA R, TSUJIMURA H, TSUCHIYA M, et al. Development of a cognitive function marker based on D-amino acid proportions using new chiral tandem LC-MS/MS systems. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):804. [29] LIN CH, LANE HY. Blood D-Amino Acid Oxidase Levels Increased With Cognitive Decline Among People With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Two-Year Prospective Study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022; 25(8):660-665. [30] YAP SH, LEE CS, ZULKIFLI ND, et al. D-Amino acids differentially trigger an inflammatory environment in vitro. Amino Acids. 2024;56(1):6. [31] DAWSON MI. The importance of vitamin A in nutrition. Curr Pharm Des. 2000;6(3):311-325. [32] REAY WR, KILTSCHEWSKIJ DJ, DI BIASE MA, et al. Genetic influences on circulating retinol and its relationship to human health. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):1490. [33] JAKUBCZYK K, DEC K, KAŁDUŃSKA J, et al. Reactive oxygen species- sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020; 48(284):124-127. [34] KLAMT F, DAL-PIZZOL F, BERNARD EA, et al. Enhanced UV-mediated free radical generation; DNA and mitochondrial damage caused by retinol supplementation. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2003;2(8):856-860. [35] GONZÁLEZ RP, DE LA CRUZ-GÓNGORA V, RODRÍGUEZ AS. Serum retinol levels are associated with cognitive function among community-dwelling older Mexican adults. Nutr Neurosci. 2022;25(9):1881-1888. [36] SAARI JC. Vitamin A and Vision. Subcell Biochem. 2016;81:231-259. [37] SHARMA K. Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(2):1479-1487. [38] POLCZ ME, BARBUL A. The Role of Vitamin A in Wound Healing. Nutr Clin Pract. 2019;34(5):695-700. [39] KUNZLER A, RIBEIRO CT, GASPAROTTO J, et al. The effects of retinol oral supplementation in 6-hydroxydopamine dopaminergic denervation model in Wistar rats. Neurochem Int. 2019;125:25-34. [40] KATOH T, SUGA H. Flexizyme-catalyzed synthesis of 3’-aminoacyl-NH-tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(9):e54. [41] HAYES JM, O’HARA DM, DAVEY GP. Metabolic Labeling of Primary Neurons Using Carbohydrate Click Chemistry. Methods Mol Biol. 2022; 2370:315-322. [42] PALEY EL, SMELYANSKI L, MALINOVSKII V, et al. Mapping and molecular characterization of novel monoclonal antibodies to conformational epitopes on NH2 and COOH termini of mammalian tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase reveal link of the epitopes to aggregation and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Immunol. 2007;44(4):541-557. [43] LIU X. ABC Family Transporters. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1141:13-100. [44] CAMPION D, CHARBONNIER C, NICOLAS G. SORL1 genetic variants and Alzheimer disease risk: a literature review and meta-analysis of sequencing data. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(2):173-186. [45] PURIS E, AURIOLA S, KORHONEN P, et al. Systemic Inflammation Induced Changes in Protein Expression of ABC Transporters and Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor Subunit 1 in the Cerebral Cortex of Familial Alzheimer`s Disease Mouse Model. J Pharm Sci. 2021;110(12): 3953-3962. [46] PÁCHA J, BALOUNOVÁ K, SOTÁK M. Circadian regulation of transporter expression and implications for drug disposition. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021;17(4):425-439. [47] LIU M, ZHOU K, LI H, et al. Potential of serum metabolites for diagnosing post-stroke cognitive impairment. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(12):3287-3296. [48] KOTLĘGA D, PEDA B, DROZD A, et al. Prostaglandin E2, 9S-, 13S-HODE and resolvin D1 are strongly associated with the post-stroke cognitive impairment. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021;156:106576. [49] KOTLĘGA D, PEDA B, PALMA J, et al. Free Fatty Acids Are Associated with the Cognitive Functions in Stroke Survivors. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(12):6500. [50] SANDVIG HV, AAM S, ALME KN, et al. Neopterin, kynurenine metabolites, and indexes related to vitamin B6 are associated with post-stroke cognitive impairment: The Nor-COAST study. Brain Behav Immun. 2024;118:167-177. [51] LONG Y, ZHAO Z, XIE W, et al. Kallistatin leads to cognition impairment via downregulating glutamine synthetase. Pharmacol Res. 2024;202: 107145. |
| [1] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [4] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [5] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [6] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [7] |
Zhou Rulin, Hu Yuanzheng, Wang Zongqing, Zhou Guoping, Zhang Baochao, Xu Qian, Bai Fanghui.
Exploration of biomarkers for moyamoya disease and analysis of traditional Chinese medicine targets#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6927-6938.
|
| [8] | Hao Maochen, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Liu Kexin, Meng Lingting, Wang Xingru, Wang Jianzhong. Bioinformatics screening of key genes for endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5632-5641. |
| [9] | Wang Lei, Wang Baiyan, Zhou Chunguang, Ren Xiaoyun, Dai Yueyou, Feng Shuying. Role of different cell-derived exosomal miRNAs in progression, diagnosis, and prognosis of gastric cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5434-5442. |
| [10] | Wu Ao, Yu Peng, Teng Jiawen, Kong Peng, Bian Sishan. Analysis of oxidative stress-related genes and immune infiltration in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 302-311. |
| [11] | Zhu Kai, Liu Wanxin, Luo Haobing, Feng Shengyi, Wang Qiugen. Association between plasma proteins and osteoporosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets: information analysis based on the UK Biobank database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3948-3960. |
| [12] | Li Zhichao, Yang Zhenguo, Wang Lei, Wang Wenbo, Xue Jingcai, Liu Wenbin, Cao Hui. Role and clinical application progress of exosome-derived non-coding RNA in microenvironment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2784-2792. |
| [13] | Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen. Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(在线): 1-6. |
| [14] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [15] | Lu Guangqi, Cui Ying, Li Jing, Yu Zhangjingze, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie, Zhuang Minghui. Feasibility of constructing a diagnostic classification model for cervical instability by magnetic resonance imaging radiomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5370-5374. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||