Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (19): 4052-4062.doi: 10.12307/2025.061
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiawei Xiaoyao San exerts anti-liver cancer effects via exosomal miRNA pathway
Liu Xiaoming1, Cheng Jinlai1, Li Rushuang1, Li Niuniu2, Qin Qiuyun2, Xia Meng1, Yao Chun2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-01-10Accepted:2024-04-18Online:2025-07-08Published:2024-09-13 -
Contact:Xia Meng, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Co-corresponding author: Yao Chun, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Xiaoming, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2021GXNSFAA220128 (to XM); Guangxi Key Research and Development Project, No. AB23026137 (to XM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Xiaoming, Cheng Jinlai, Li Rushuang, Li Niuniu, Qin Qiuyun, Xia Meng, Yao Chun. Jiawei Xiaoyao San exerts anti-liver cancer effects via exosomal miRNA pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(19): 4052-4062.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
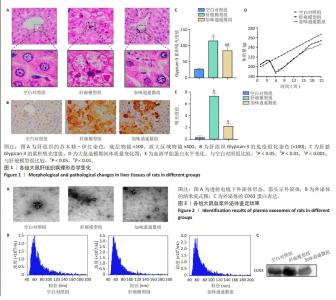
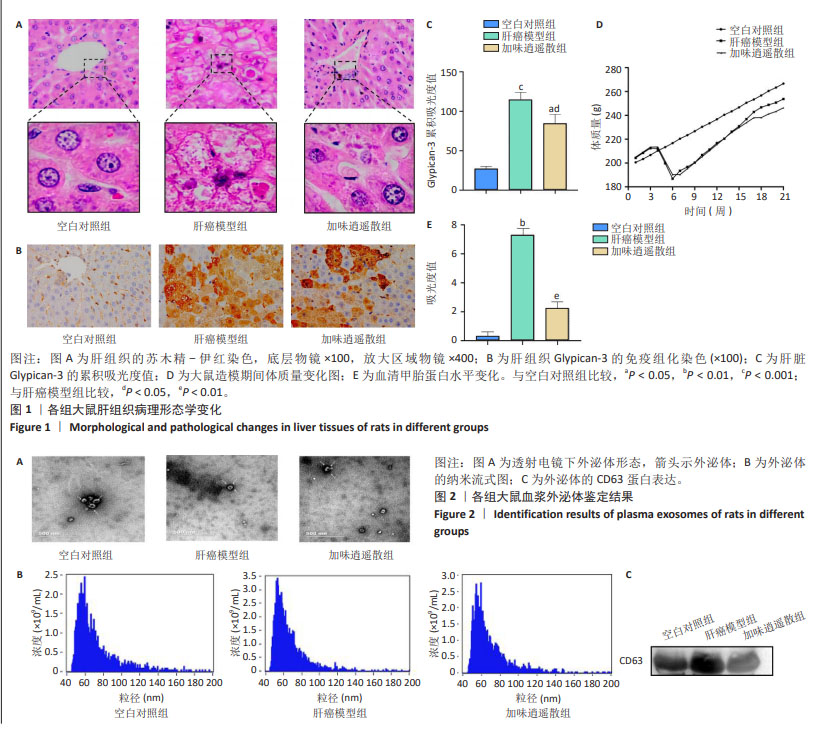
2.1 实验动物数量分析 参与此次实验的SD大鼠共有31只,在20周,1只肝癌模型组大鼠因肝腹水死亡,23只大鼠造模成功,肝癌模型组11只、加味逍遥散组12只与空白对照组7只进入结果分析。 2.2 加味逍遥散对肝癌模型大鼠的抗肝癌作用 苏木精-伊红染色显示,空白对照组大鼠的肝细胞结构完整,胞质内颗粒清晰可见,且肝小叶中央静脉周围的肝细胞呈放射状排列;肝癌模型组肝细胞成团块状结节,伴有炎性细胞浸润;加味逍遥散治疗后肝小叶损伤且炎性细胞浸润等情况改善,见图1A。免疫组化结果显示,与空白对照组相比,肝癌模型组呈现出大量黄棕色,Glypican-3的累积吸光度值显著上升,提示Glypican-3的表达明显升高,加味逍遥散组Glypican-3的累积吸光度值有所降低,见图1B,C。 大鼠体质量监测结果显示,空白对照组大鼠体质量持续稳定增长,模型组、加味逍遥散组大鼠总体体质量增长较缓,在造模期第4周由于毒性反应以及失血等影响,导致体质量有所下降。但模型组和加味逍遥散组间体质量没有显著统计学差异,见图1D。血清甲胎蛋白检测结果显示,空白对照组大鼠血清甲胎蛋白水平最低,肝癌模型组大鼠血清甲胎蛋白水平显著升高,加味逍遥散组治疗后甲胎蛋白水平有所降低,见图1E。 2.3 血浆外泌体表征 透射电子显微镜观察显示,分离出的物质为杯状或圆形囊泡,见图2A。纳米流式报告分析显示,外泌体颗粒大小的中心值均在60-70 nm,其中空白对照组为1.18×1011 particles/mL,加味逍遥散组为9.99×109 particles/mL,肝癌模型组为8.87×1010 particles/mL,见图2B。Western blot检测显示肝癌模型组CD63的表达水平增加,加味逍遥散组CD63的表达水平被抑制,见图2C。以上3种检测方法结果提示从空白对照组、肝癌模型组以及加味逍遥散组提取到的样本被鉴定为外泌体。"
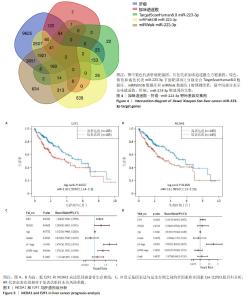
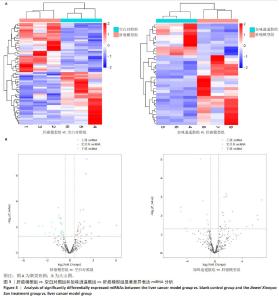
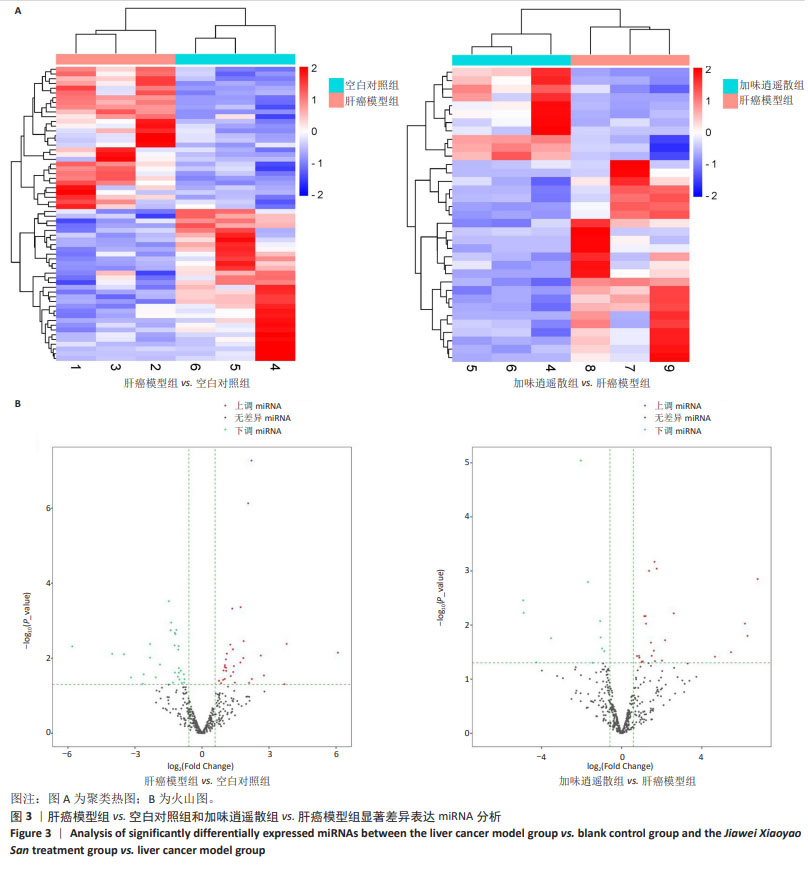
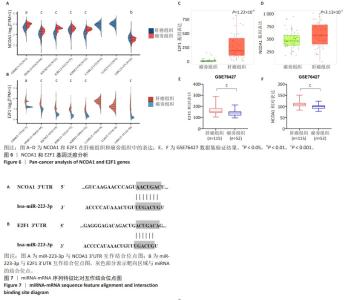
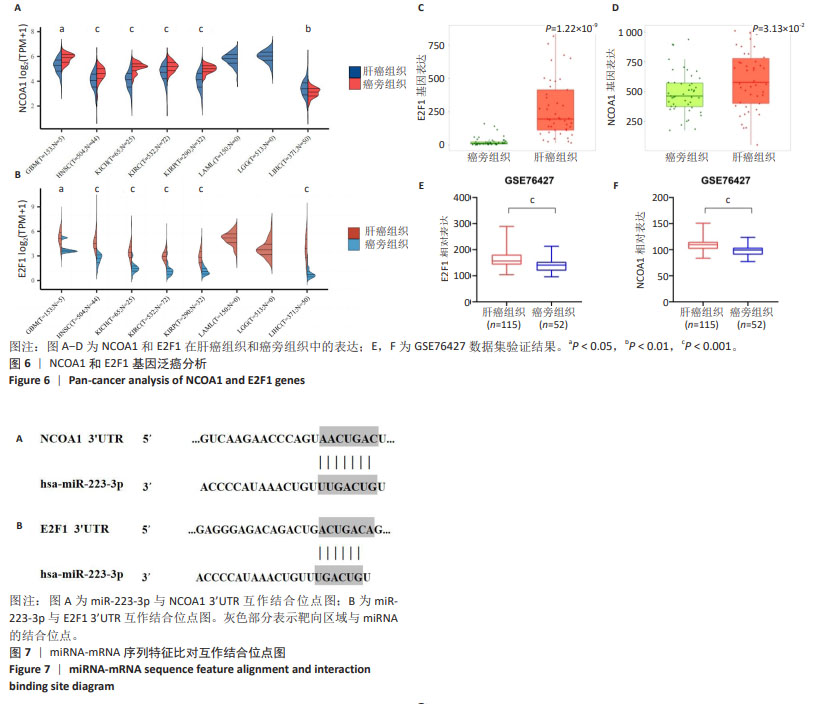
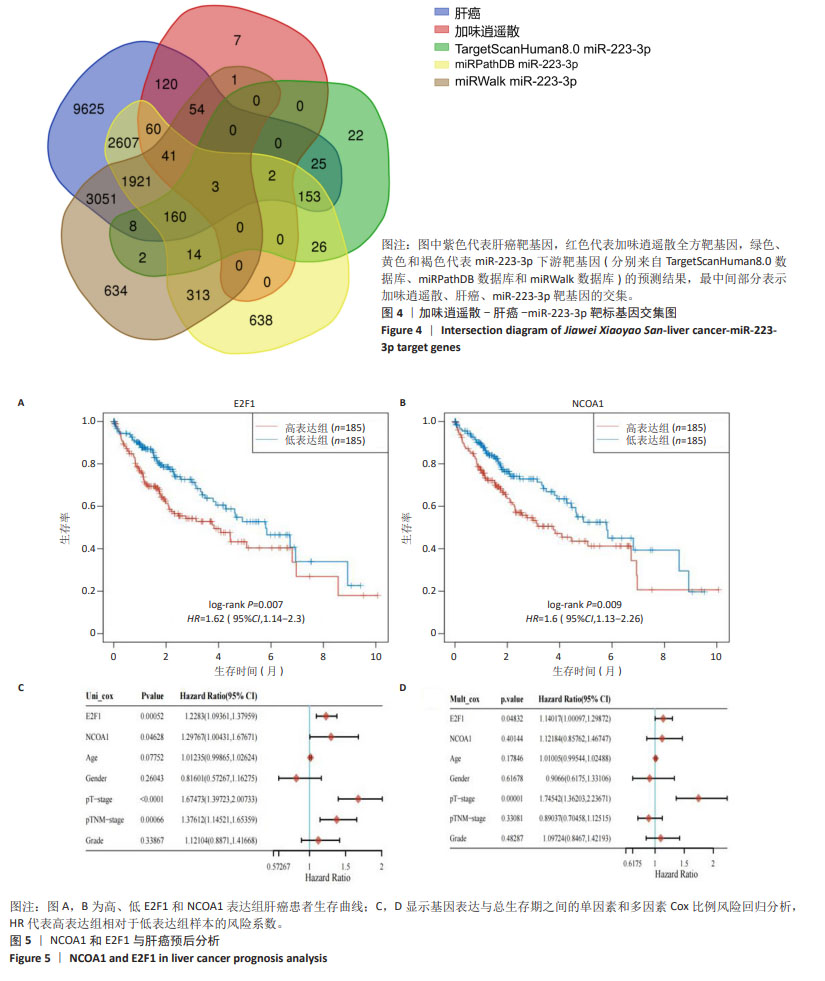
为进一步探索加味逍遥散对肝癌大鼠外泌体miRNA异常表达的影响,对肝癌模型组vs.空白对照组上调而加味逍遥散组vs.肝癌模型组下调的促癌miRNA,以及肝癌模型组vs.空白对照组下调同时加味逍遥散组vs.肝癌模型组上调的抑癌miRNA进行交叉对比,目的是寻找肝癌模型组 vs. 空白对照组和加味逍遥散组 vs. 肝癌模型组间共同调节的miRNA。结果共获得6个显著表达的miRNA: miR-23b-5p、miR-146b-3p、miR-672-3p、miR-147、miR-674-3p、miR-223-3p (P < 0.05,log2FC >1或< -1.45)。 2.5 加味逍遥散-肝癌-miR-223-3p下游靶蛋白预测 加味逍遥散、肝癌和miR-223-3p三者交集靶基因3个,分别是:NCOA1、E2F1、RASA1,见图4。 2.6 交集靶基因的生物信息学分析 从近5年生存率来看,与高表达组相比,低表达NCOA1和E2F1组总生存率更高,见图5A,B,提示在肝癌中高表达的NCOA1和E2F1预后较差(HR > 1,P < 0.05)。RASA1的生存分析无统计学意义。Cox比例风险回归分析显示:E2F1与肝癌预后显著相关(P < 0.05),TNM分期可能成为治疗肝癌的一个独立预后因素,见图5C,D。泛癌分析显示,NCOA1和E2F1在多种癌症中高表达;与癌旁组织相比,NCOA1和E2F1在肝癌组织中均显著高表达(P < 0.01),见图6A-D。基于GEO数据库115例肝癌组织和52例癌旁组织的GSE76427数据集验证NCOA1和E2F1在肝癌中的表达趋势与上述结果保持一致(P < 0.05),见图6E,F。通过 miRNA 和靶基因 mRNA 序列特征比对,结果显示E2F1和NCOA1基因的mRNA 3’UTR均与miR-223-3p存在互作结合位点,见图7A,B。已有研究表明E2F1在肝癌中高表达。双荧光素酶报告基因检测miR-223-3p靶向负调控E2F1,即在非酒精性脂肪肝病中上调miR-223-3p可以抑制E2F1的表达[16]。"
| [1] FOERSTER F, GAIRING SJ, ILYAS SI, et al. Emerging immunotherapy for HCC: A guide for hepatologists. Hepatology. 2022;75(6):1604-1626. [2] ANWANWAN D, SINGH SK, SINGH S, et al. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1873(1):188314. [3] MAKI H, HASEGAWA K. Advances in the surgical treatment of liver cancer. Biosci Trends. 2022;16(3):178-188. [4] RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J Hepatol. 2022;77(6): 1598-1606. [5] LIU J, REN L, LI S, et al. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(9):2783-2797. [6] XIE QH, ZHENG JQ, DING JY, et al. Exosome-Mediated Immunosuppression in Tumor Microenvironments. Cells. 2022; 11(12):1946. [7] 任展志,麻瑶瑶,石玉群,等.不同来源外泌体在肝癌诊断与治疗中的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2023,31(12):2340-2346. [8] NASERI Z, OSKUEE RK, JAAFARI MR, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-142-3p inhibitor reduces tumorigenicity of breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 7727-7747. [9] REZAEI R, BAGHAEI K, AMANI D, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-375-3p mimic regulate epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colon cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021;269: 119035. [10] LIN Q, ZHOU CR, BAI MJ, et al. Exosome-mediated miRNA delivery promotes liver cancer EMT and metastasis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(3): 1080-1095. [11] PAN JH, ZHOU H, ZHAO XX, et al. Role of exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential in diagnosis and antitumour treatments (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):1809-1816. [12] KALLURI R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1208-1215. [13] WU Z, ZENG Q, CAO K, et al. Exosomes: small vesicles with big roles in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(37):60687-60697. [14] 温小雨,孙玉浩,李卓娴,等.加味逍遥散治疗肝癌并发抑郁症模型大鼠的网络药理学及蛋白质组学分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(32):5132-5142. [15] 黄继汉,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9):1069-1072. [16] NIU Q, WANG T, WANG Z, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-secreted extracellular vesicles alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via delivering miR-223-3p. Adipocyte. 2022;11(1):572-587. [17] VILLANUEVA A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(15): 1450-1462. [18] 程荣菲,武哲丽.原发性肝癌虚、郁、痰、瘀、毒病机探讨[J].山东中医杂志,2014,33(10):804-806. [19] AN S, ZHANG D, ZHANG Y, et al. GPC3-targeted immunoPET imaging of hepatocellular carcinomas. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49(8): 2682-2692. [20] ZHOU F, SHANG W, YU X, et al. Glypican-3: A promising biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Med Res Rev. 2018;38(2):741-767. [21] NISHIDA T, KATAOKA H. Glypican 3-Targeted Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(9):1339. [22] LIU Z, PU Y, BAO Y, et al. Investigation of Potential Molecular Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of AFP-Negative HCC. Int J Gen Med. 2021; 14:4369-4380. [23] LUO P, WU S, YU Y, et al. Current Status and Perspective Biomarkers in AFP Negative HCC: Towards Screening for and Diagnosing Hepatocellular Carcinoma at an Earlier Stage. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020;26(2):599-603. [24] 李瑞生.肝郁脾虚因素对二乙基亚硝胺诱发大鼠实验性肝癌影响的研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2002. [25] 周文斌,郑越,尚佳,等.二乙基亚硝胺诱导肝细胞癌模型鼠肠道微生态研究[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2022,51(4):438-453. [26] WANG YJ, XU HY, HUO XH, et al. Multi-stress accelerated liver cancer progression in rats treated with diethylnitrosamine. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(14):1762-1764. [27] KRISHNAN GS, RAJAGOPAL V, ANTONY JOSEPH SR, et al. In vitro, In silico and In vivo Antitumor Activity of Crude Methanolic Extract of Tetilla dactyloidea (Carter, 1869) on DEN Induced HCC in a Rat Model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:795-807. [28] CHEN T, DAI X, DAI J, et al. AFP promotes HCC progression by suppressing the HuR-mediated Fas/FADD apoptotic pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):822. [29] GUPTA C, VIKRAM A, TRIPATHI DN,et al. Antioxidant and antimutagenic effect of quercetin against DEN induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Phytother Res. 2010;24(1):119-128. [30] FU Y, URBAN DJ, NANI RR, et al. Glypican-3-Specific Antibody Drug Conjugates Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology. 2019; 70(2):563-576. [31] DENZER K, KLEIJMEER MJ, HEIJNEN HF, et al. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 Pt 19:3365-3374. [32] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [33] CORREIA DE SOUSA M, GJORGJIEVA M, DOLICKA D, et al. Deciphering miRNAs’ Action through miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6249. [34] NIU X, WEI N, PENG L, et al. miR-34a-5p plays an inhibitory role in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating target gene VEGFA. Malays J Pathol. 2022;44(1):39-52. [35] BASHIR AO, EL-MESERY ME, ANWER R, et al. Thymoquinone potentiates miR-16 and miR-375 expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 2020;254:117794. [36] KRIVOSOVA M, ADAMCAKOVA J, KAADT E, et al. The VEGF protein levels, miR-101-3p, and miR-122-5p are dysregulated in plasma from adolescents with major depression. J Affect Disord. 2023;334:60-68. [37] LI S, CHEN Z, ZHOU R, et al. Hsa_circ_0048674 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and natural killer cell exhaustion depending on the regulation of miR-223-3p/PDL1. Histol Histopathol. 2022;37(12): 1185-1199. [38] HANEKLAUS M, GERLIC M, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, et al. Cutting edge: miR-223 and EBV miR-BART15 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β production. J Immunol. 2012;189(8):3795-3799. [39] 戚欣,王会子,陈旭东,等.miR-223-3p通过靶向RAC1调控肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞的增殖和凋亡[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志, 2020,27(6):664-670. [40] PRATEDRAT P, CHUAYPEN N, NIMSAMER P, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic roles of circulating miRNA-223-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2020;15(4):e0232211. [41] ZHANG R, ZHANG LJ, YANG ML, et al. Potential role of microRNA‑223‑3p in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive study based on data mining and bioinformatics. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17(2):2211-2228. [42] WONG VC, WONG MI, LAM CT, et al. Hallmark microRNA signature in liquid biopsy identifies hepatocellular carcinoma and differentiates it from liver metastasis. J Cancer. 2021;12(15):4585-4594. [43] FANG Z, LIN M, LI C, et al. A comprehensive review of the roles of E2F1 in colon cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(3):757-768. [44] CHUN JN, CHO M, PARK S, et al. The conflicting role of E2F1 in prostate cancer: A matter of cell context or interpretational flexibility? Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020;1873(1):188336. [45] FOUAD S, HAUTON D, D’ANGIOLELLA V. E2F1: Cause and Consequence of DNA Replication Stress. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;7:599332. [46] SHELDON LA. Inhibition of E2F1 activity and cell cycle progression by arsenic via retinoblastoma protein. Cell Cycle. 2017;16(21):2058-2072. [47] ENGELMANN D, PÜTZER BM. Translating DNA damage into cancer cell death-A roadmap for E2F1 apoptotic signalling and opportunities for new drug combinations to overcome chemoresistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2010;13(4-5):119-131. [48] BISWAS AK, JOHNSON DG. Transcriptional and nontranscriptional functions of E2F1 in response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 2012; 72(1):13-17. [49] ZHANG Y, HAO X, HAN G, et al. E2F1-mediated GINS2 transcriptional activation promotes tumor progression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12(4): 1707-1726. [50] QIAO L, ZHANG Q, SUN Z, et al. The E2F1/USP11 positive feedback loop promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and inhibits autophagy by activating ERK/mTOR pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021;514:63-78. [51] CHEN M, ZHAO Z, WU L, et al. E2F1/CKS2/PTEN signaling axis regulates malignant phenotypes in pediatric retinoblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(9):784. [52] ZELENKO Z, AGHAJANOVA L, IRWIN JC, et al. Nuclear receptor, coregulator signaling, and chromatin remodeling pathways suggest involvement of the epigenome in the steroid hormone response of endometrium and abnormalities in endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2012;19(2):152-162. [53] REUTRAKUL S, SADOW PM, PANNAIN S, et al. Search for abnormalities of nuclear corepressors, coactivators, and a coregulator in families with resistance to thyroid hormone without mutations in thyroid hormone receptor beta or alpha genes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000; 85(10):3609-3617. [54] QIN L, WU YL, TONEFF MJ, et al. NCOA1 Directly Targets M-CSF1 Expression to Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(13):3477-3488. [55] PENG Q, HUA Y, XU H, et al. The NCOA1-CBP-NF-κB transcriptional complex induces inflammation response and triggers endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction. Exp Cell Res. 2022;415(2):113114. |
| [1] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [6] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [7] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [8] | Weng Zongqin, Zhao Hailong. Mechanism of exosomal miRNA involved in tumor chemotherapy resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1504-1511. |
| [9] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [10] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [11] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [12] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Huang Jing, Shang Wenya, Yang Yike, Liu Huiyao. Action mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miRNAs in improving spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7827-7838. |
| [14] | Zhou Yang, Liu Kexin, Wang Deli, Sun Zhang. Regenerative effects of engineered extracellular vesicles on repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
| [15] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||