Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3605-3613.doi: 10.12307/2025.638
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of 1,8-cineole on inflammatory response in a rat model of experimental periodontitis
He Li1, 2, Ren Lu1, 2, Jiang Xiaoxi1, 2, Liu Xuqian1, 2, Li Chunhui1, 2
- 1Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Institute of Stomatology, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-21Accepted:2024-07-20Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-02 -
Contact:Liu Xuqian, MD, Associate professor, Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Institute of Stomatology, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:He Li, Master candidate, Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Institute of Stomatology, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China Corresponding author: Li Chunhui, MS, Associate professor, Department of Periodontics & Oral Mucosal Diseases, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Institute of Stomatology, The Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the State Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Prevention and Treatment Open Project, No. SKLOD2024OF04 (to LXQ); Sichuan Province Medical Scientific Research Project Plan, No. S23043 (to LXQ); the Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project of Luzhou City, No. 2023RCX171 (to LXQ); the “RYTIME Foundation” Scientific Research and Cultivation Program of the Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, No. 2022RT07 (to HL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Li, , Ren Lu, , Jiang Xiaoxi, , Liu Xuqian, , Li Chunhui, . Effects of 1,8-cineole on inflammatory response in a rat model of experimental periodontitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3605-3613.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

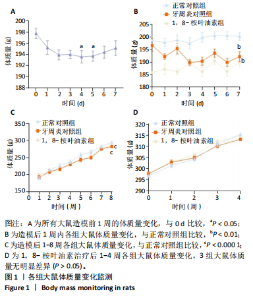
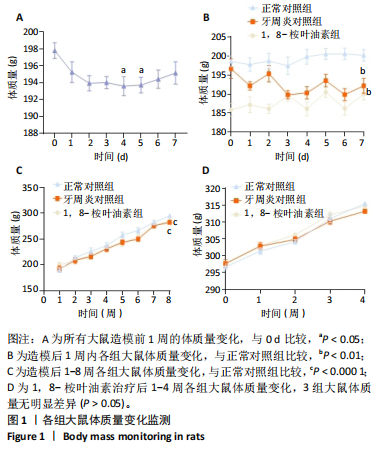
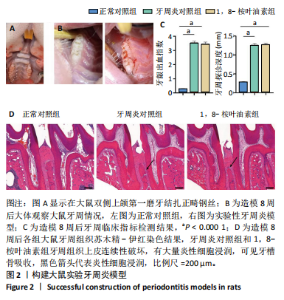
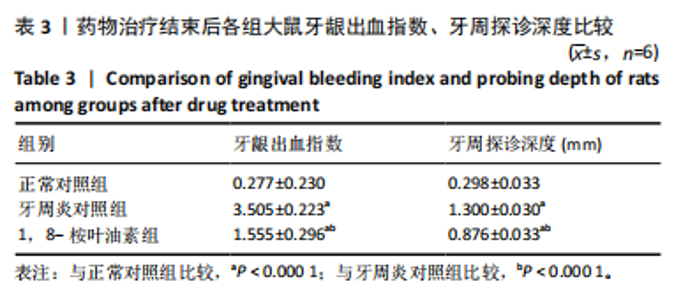
2.1 实验动物数量分析 除去验证造模成功的12只大鼠,剩余的18只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组大鼠体质量变化 造模前大鼠体质量出现波动,相比于第0天,第4,5天的体质量减少(P < 0.05),见图1A,可能由于大鼠的个体适应性差异导致。正常对照组大鼠精神良好,毛发具有光泽,生长正常,摄食饮水正常。牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠在造模1-3 d内出现过活动减少、精神萎靡、毛发杂乱、摄食饮水减少的情况,体质量有所下降,7 d后逐渐恢复正常摄食饮水,活动增多,体质量慢慢回升,但仍低于于正常对照组(P < 0.01),见图1B,表明造模对大鼠进食存在影响。造模1-8周内,各组大鼠体质量逐渐增加,至第8周时牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠体质量仍低于正常对照组(P < 0.000 1),见图1C。药物治疗期间,各组大鼠体质量进一步增加,3组大鼠体质量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图1D,表明牙周袋内局部给予1,8-桉叶油素治疗对大鼠生长没有显著影响。 2.3 大鼠实验性牙周炎模型建立情况 利用结扎法构建实验性牙周炎大鼠动物模型,见图2A。大体观察各组大鼠双侧上颌第一磨牙牙周组织情况,正常对照组牙龈组织颜色正常,龈缘菲薄紧贴于牙面,质地致密而坚韧;牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组牙龈充血水肿,质地松软,龈缘肥厚,见图2B。 牙周临床指标检测结果显示,正常对照组无深牙周袋和探诊出血;相较于正常对照组,牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠牙龈出血指数、牙周探诊深度增加(P < 0.000 1),见表2和图2C。"
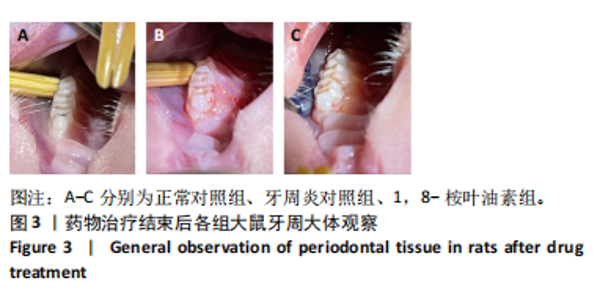
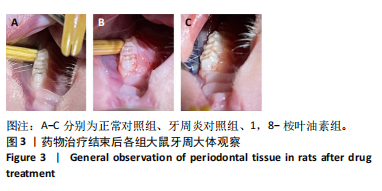
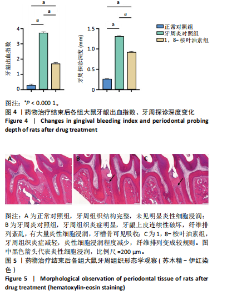
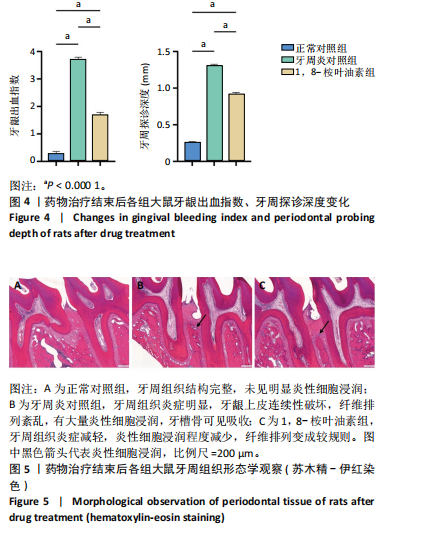
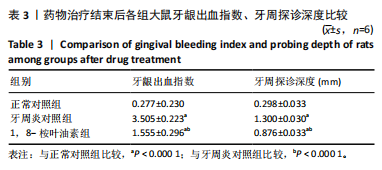
苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,正常对照组大鼠牙周组织结构完整,未见明显炎性细胞浸润;牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠牙周组织上皮连续性破坏,有大量炎性细胞浸润,可见牙槽骨吸收,见图2D。以上结果表明成功构建大鼠实验性牙周炎模型。 2.4 药物治疗结束后各组大鼠牙周临床指标检查结果 药物治疗结束后大体观察可见:正常对照组大鼠牙龈无明显异常,无牙龈红肿;牙周炎对照组和1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠牙龈有红肿现象,其中1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠牙龈红肿情况较牙周炎对照组减轻,见图3。 药物治疗结束后牙周临床指标检查结果显示,与正常对照组相比较,牙周炎对照组大鼠牙龈出血指数、牙周探诊深度增加(P < 0.000 1);与牙周炎对照组比较,1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠牙龈出血指数、牙周探诊深度减少(P < 0.000 1),见表3,图4。"
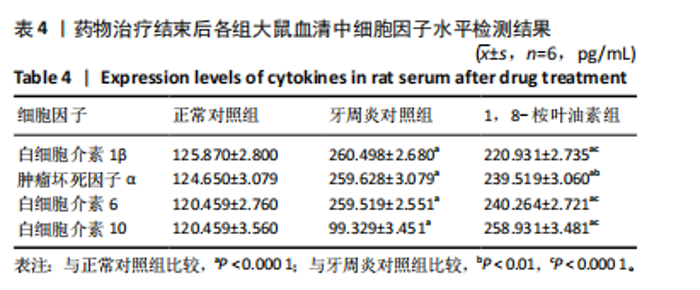
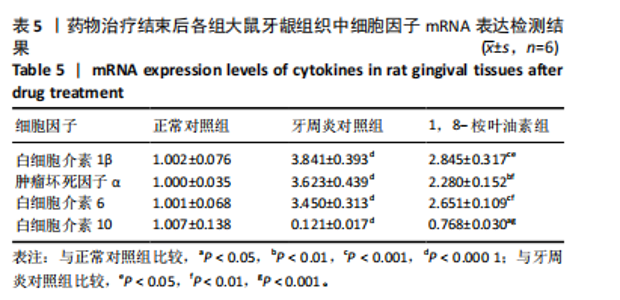
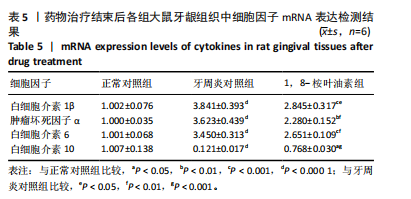
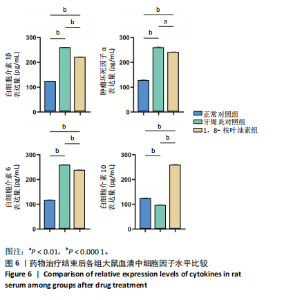
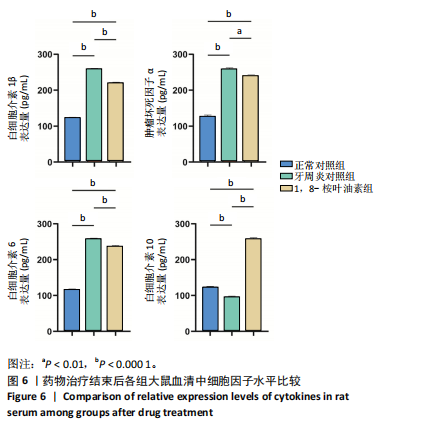
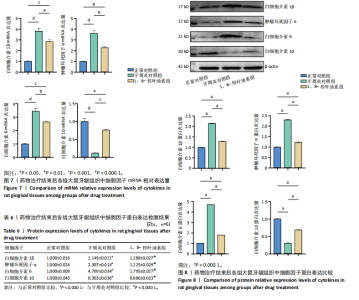
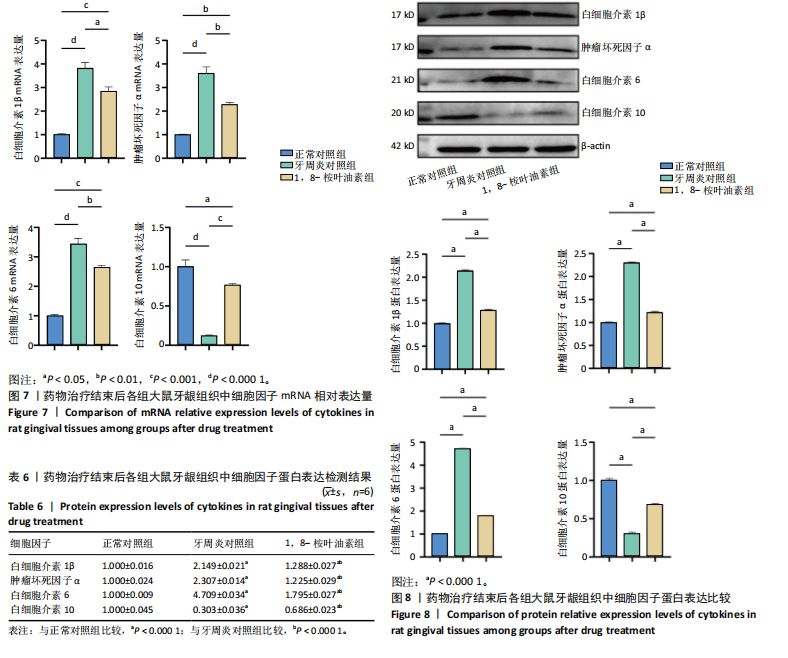
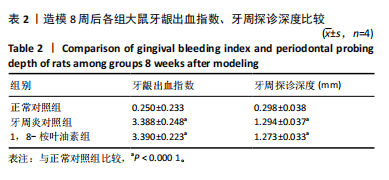
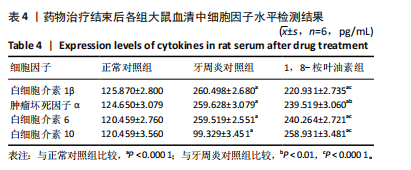
2.5 药物治疗结束后各组大鼠牙周组织学评估结果 大鼠牙周组织苏木精-伊红染色显示,正常对照组牙周组织结构完整,未见明显炎性细胞浸润;牙周炎对照组牙周组织炎症明显,牙龈上皮连续性破坏,纤维排列紊乱,有大量炎性细胞浸润,牙槽骨可见吸收;与牙周炎对照组比较,1,8-桉叶油素组牙周组织炎症减轻,炎性细胞浸润程度减少,纤维排列变成较规则,见图5。 2.6 药物治疗结束后各组大鼠血清中细胞因子水平检测结果 牙周炎对照组大鼠血清中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平均高于正常对照组(P < 0.000 1),白细胞介素10水平低于正常对照组(P < 0.000 1);1,8-桉叶油素组大鼠血清中白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平均低于牙周炎对照组(P < 0.01,P < 0.000 1),白细胞介素10水平高于牙周炎对照组(P < 0.000 1),见表4,图6。"
| [1] LEI F, LI M, LIN T, et al. Treatment of inflammatory bone loss in periodontitis by stem cell-derived exosomes. Acta Biomater. 2022;141: 333-343. [2] QIAO X, TANG J, DOU L, et al. Dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes regulate anti-inflammatory and osteogenesis in periodontal ligament stem cells and promote the repair of experimental periodontitis in rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4683-4703. [3] EKE P I, BORGNAKKE WS, GENCO RJ. Recent epidemiologic trends in periodontitis in the USA. Periodontol 2000. 2020;82(1):257-267. [4] ZHAO Y, QUAN Y, LEI T, et al. The role of inflammasome NLPR3 in the development and therapy of periodontitis. Int J Med Sci. 2022; 19(10):1603-1614. [5] SHARAF S, HIJAZI K. Modulatory mechanisms of pathogenicity in porphyromonas gingivalis and other periodontal pathobionts. Microorganisms. 2022;11(1):15. [6] EBERSOLE JL, KIRAKODU SS, NEUMANN E, et al. Oral microbiome and gingival tissue apoptosis and autophagy transcriptomics. Front Immunol. 2020;11:585414. [7] SONG WJ, LIU MM, SHANG LL, et al. Galectin-3 inhibition alleviated LPS-induced periodontal inflammation in gingival fibroblasts and experimental periodontitis mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 2024;138(12):725-739. [8] LEONOV GE, VARAEVA YR, LIVABTSOVA EN, et al. The complicated relationship of short-chain fatty acids and oral microbiome: a narrative review. Biomedicines. 2023;11(10):2749. [9] WANG X. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and their extracellular vesicles modulate Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in ligature-induced periodontitis. Iran J Immunol. 2023;20(4):446-455. [10] USUI M, ONIZUKA S, SATO T, et al. Mechanism of alveolar bone destruction in periodontitis-periodontal bacteria and inflammation. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021;57:201-208. [11] SIRISEREEPHAP K, MAEKAWA T, TAMURA H, et al. Osteoimmunology in periodontitis: local proteins and compounds to alleviate periodontitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5540. [12] SCHENKEIN HA, PAPAPANOU PN, GENCO R, et al. Mechanisms underlying the association between periodontitis and atherosclerotic disease. Periodontol 2000. 2020;83(1):90-106. [13] HAJISHENGALLIS G, CHAVAKIS T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(7):426-440.
[14] SHOLAPURKAR A, SHARMA D, GLASS B, et al. Professionally delivered local antimicrobials in the treatment of patients with periodontitis-a narrative review. Dent J (Basel). 2020;9(1):2. [15] WU Q, DENG T, CHENG J, et al. Constructing interfacial charge transfer channels and electric field in violet phosphorus-based van der Waals heterojunction for phototherapy of periodontitis. ACS nano. 2024; 18(18):11988-12009. [16] FAKHERAN O, KHADEMI A, BAGHERNIYA M, et al. The effects of nutraceuticals and bioactive natural compounds on chronic periodontitis: a clinical review. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1328:59-80. [17] 李莎莎,王卫峰,李凡,等.中药治疗牙周炎的研究进展[J].西北药学杂志,2020,35(2):313-317. [18] MACKENZIE C, GOERKE T, BUECKING M, et al. Determination of orally administered 1,8-Cineol in nasal polyp tissues from chronic rhinosinusitis patients using gas chromatography: mass spectrometry. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):3605. [19] TAN X, XU R, LI AP, et al. Antioxidant and anti-Alzheimer’s disease activities of 1,8-cineole and its cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175:116784. [20] VAZQUEZ NM, MORENO S, GALVAN EM. Exposure of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms to 1,8-cineole leads to bacterial cell death and biomass disruption. Biofilm. 2022;4:100085. [21] LI L, HE M, FANG C, et al. Preparation, characterization, ex vivo transdermal properties and skin irritation evaluation of 1,8-cineole nanoemulsion gel. Int J Pharm. 2022;624:121982. [22] MOHAMMED HA, MOHAMMED SAA, KHAN O, et al. Topical eucalyptol ointment accelerates wound healing and exerts antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory effects in rats’ skin burn model. J Oleo Sci. 2022; 71(12):1777-1788. [23] CAI ZM, PENG JQ, CHEN Y, et al. 1,8-Cineole: a review of source, biological activities, and application. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2021;23(10): 938-954. [24] 任潞,杨心仪,李适廷,等.1,8-桉叶油素对三种牙周致病菌的抑菌作用研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2023,39(3):131-134. [25] XU G, GUO J, SUN C. Eucalyptol ameliorates early brain injury after subarachnoid haemorrhage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in a rat model. Pharm Biol. 2021;59(1):114-120. [26] YIN C, LIU B, WANG P, et al. Eucalyptol alleviates inflammation and pain responses in a mouse model of gout arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(9):2042-2057. [27] AN F, BAI Y, XUAN X, et al. 1,8-Cineole ameliorates advanced glycation end products-induced Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in vitro and in vivo. Molecules. 2022;27(12):3913. [28] JUERGEN LJ, WORTH H, JUERGENS UR. New perspectives for mucolytic, anti-inflammatory and adjunctive therapy with 1,8-Cineole in COPD and Asthma: review on the new therapeutic approach. Adv Ther. 2020;37(5):1737-1753. [29] 陈晨,陈栋,陆珂,等.基于OPG/RANKL途径青蒿琥酯对牙周炎大鼠牙槽骨吸收的影响及抑炎作用研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2022,38(4):434-438. [30] AYDINYURT HS, SANCAK T, TASKIN C, et al. Effects of injectable platelet-rich fibrin in experimental periodontitis in rats. Odontology. 2021;109(2):422-432. [31] MURAD H. Effect of eucalyptol on matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its tissue inhibitor in hypertensive rats. Bioinformation. 2023;19(5):562-564. [32] 杨心仪,任潞,李适廷,等.1,8-桉叶油素对常见致龋菌的抗菌作用研究[J].北京口腔医学,2023,31(6):396-399. [33] XIA BY, LI Y, DING X, et al. Effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α on liver injury induced by periodontitis in rats. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021;39(5):518-523. [34] BASTOS VPD, GOMES AS, Lima FJB, et al. Inhaled 1,8-cineole reduces inflammatory parameters in airways of ovalbumin-challenged Guinea pigs. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;108(1):34-39. [35] VENKATARAMAN B, ALMARZOOQI S, RAJ V, et al. Molecular docking identifies 1,8-Cineole (eucalyptol) as a novel PPARγ agonist that alleviates colon inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6160. [36] LIMA PR, DE MELO TS, CARVALHO KM MB, et al. 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol) ameliorates cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis via modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress and NF-κB activity in mice. Life Sci. 2013; 92(24-26):1195-1201. [37] JIANG F, WU G, LI W, et al. Preparation and protective effects of 1,8-cineole-loaded self-microemulsifying drug delivery system on lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial injury in mice. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019;127:14-23. [38] KUTLU Z, GULABOGLU M, HALICI Z, et al. Biochemical research of the effects of essential oil obtained from the fruit of myrtus communis L. on cell damage associated with lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in a human umbilical cord vein endothelial cell. Biochem Genet. 2021;59(1):315-334. [39] STRUPPEK J, SCHNABEL RB, WALTHER C, et al. Periodontitis, dental plaque, and atrial fibrillation in the Hamburg city health study. PloS One. 2021;16(11):e0259652. [40] SOLA G, LO GIUDICE A, POLIZZI A, et al. Identification of the different salivary interleukin-6 profiles in patients with periodontitis: a cross-sectional study. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;122:104997. [41] WANG T, WANG ZB, JIANG CM, et al. Oroxylin A inhibits inflammatory cytokines in periodontitis via HO‑1. Mol Med Rep. 2024;30(1):126. [42] SCHETT G, DAYER M, MANGER B. Interleukin-1 function and role in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(1):14-24. [43] CARDOSO EM, REIS C, MANZANARES-CESPEDES MC. Chronic periodontitis, inflammatory cytokines, and interrelationship with other chronic diseases. Postgrad Med. 2018;130(1):98-104. [44] BARNEA TV, SAVA A, GENTIMIR C, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of TNFA and IL-1A and generalized aggressive periodontitis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2015;56(2):459-464. [45] KUO PJ, FU E, LIN CY, et al. Ameliorative effect of hesperidin on ligation-induced periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol. 2019;90(3):271-280. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [3] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [4] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [5] | Zhao Zengbo, Li Chenxi, Dou Chenlei, Ma Na, Zhou Guanjun. Anti-inflammatory and osteogenic effects of chitosan/sodium glycerophosphate/sodium alginate/leonurine hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [6] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [7] | Li Chen, Liu Ye, Ni Xindi, Zhang Yuang. Simulation analysis of real-time continuous stiffness in muscle fibers and tendons of the triceps surae during multi-joint movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7529-7536. |
| [8] | Yang Bo, Pan Xinfang, Chang Liuhui, Ni Yong. Correlation of echocardiographic parameters with disability at 3 months after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7544-7551. |
| [9] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [10] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [11] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [12] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [13] | Li Zhongzheng, Chen Zhenghao, Tang Ziyou, Lou Kaiyang, Zhang Rui, Liu Qi, Zhao Na, Yang Kun. Effects of scaffold materials combined with biological factors on biological characteristics of dental follicle cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7405-7414. |
| [14] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [15] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||