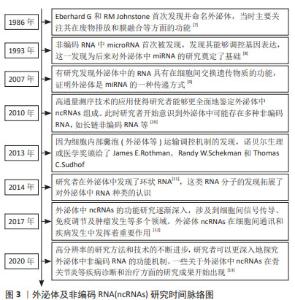
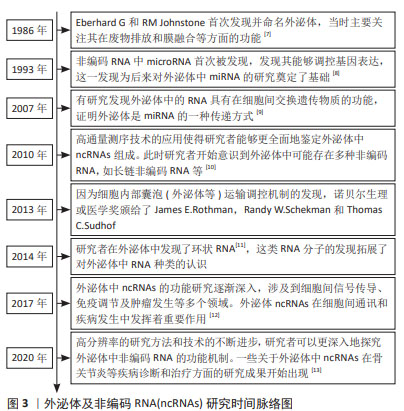
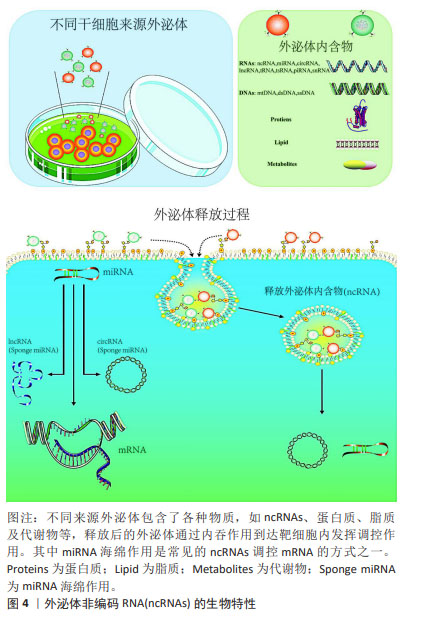
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2784-2792.doi: 10.12307/2025.033
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and clinical application progress of exosome-derived non-coding RNA in microenvironment of osteoarthritis
Li Zhichao1, 2, Yang Zhenguo2, Wang Lei2, Wang Wenbo2, Xue Jingcai2, Liu Wenbin2, Cao Hui1
- 1Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 2Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-14Accepted:2024-02-24Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-12 -
Contact:Cao Hui, Master, Professor, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Li Zhichao, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82374620 (to CH); Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2021MH298 (to WL); Shandong Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2022QH105 (to LZC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhichao, Yang Zhenguo, Wang Lei, Wang Wenbo, Xue Jingcai, Liu Wenbin, Cao Hui. Role and clinical application progress of exosome-derived non-coding RNA in microenvironment of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2784-2792.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
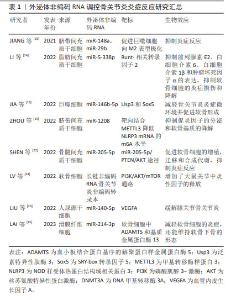
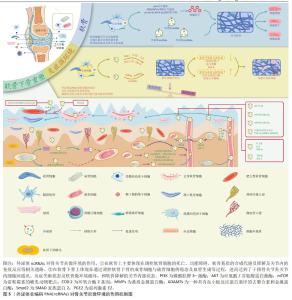
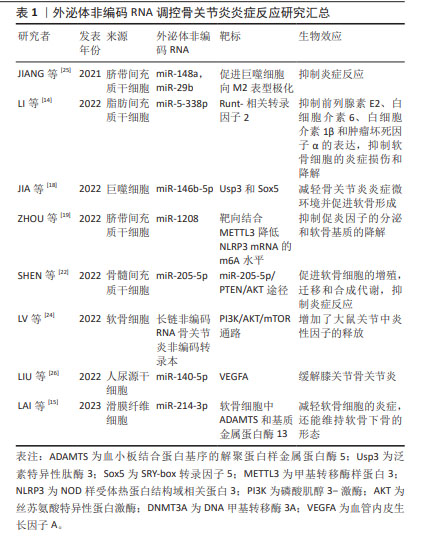
调节炎症因子和炎症小体的表达或激活:外泌体ncRNAs可以通过影响细胞内特定基因的表达来调节炎症因子的产生。它们可以作为信使RNA,通过外泌体传递到其他细胞,从而影响目标细胞中的基因表达,进而调节炎症因子的合成和分泌。LI等[14]发现脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体通过转移miR-5-338p可靶向Runt-相关转录因子2促进软骨细胞增殖,抑制前列腺素E2、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达。LAI等[15]对滑膜成纤维细胞来源的外泌体miRNA分析发现,miR-214-3p外泌体可降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达。这些外泌体ncRNAs均是通过调控炎症因子的表达以抑制软骨细胞的炎症损伤,甚至是维持软骨下骨的形态。此外,外泌体ncRNAs在骨关节炎的发生发展过程中还可激活炎性小体。炎症小体是一种细胞内多聚体结构,它参与调控细胞内的炎症反应,外泌体ncRNAs可通过调节炎性小体激活相关通路中基因或蛋白的表达干预其激活[16]。研究表明,骨关节炎患者软骨细胞的外泌体miR-449a-5p能诱导细胞系细胞中炎症小体的激活,且能加速骨关节炎小鼠模型中的软骨侵蚀[17]。 而炎症小体的激活还是细胞焦亡过程中的重要环节,而细胞焦亡又可引起炎性因子的释放,加重了关节内的炎症反应,形成恶性循环。由于炎症因子和炎症小体在骨关节炎发病机制中的重要作用,可作为其上游调控因子的ncRNAs在骨关节炎的微环境中的传递很可能是骨关节炎软骨细胞死亡及基质退变程序的启动者。 免疫细胞调节:外泌体ncRNAs可通过影响免疫细胞的活性来调节炎症反应。例如,它们可以在调节巨噬细胞等免疫细胞的功能方面发挥作用,从而影响免疫反应的强度和性质。研究表明,下调M1型巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体miR-146b-5p可靶向Usp3和Sox5,在体外和体内减轻骨关节炎炎症微环境并促进软骨形成[18]。ZHOU等[19]发现人脐带间充质干细胞来源的外泌体miR-6通过与METTL3相互作用降低巨噬细胞NLRP3的m6A,抑制促炎因子的分泌和软骨细胞外基质的降解,来缓解小鼠膝关节骨关节炎。类似的还有外泌体miR-486-5p可通过调节巨噬细胞极化缓解软骨细胞凋亡[20]。而外泌体ncRNAs通过其他免疫细胞(如淋巴细胞和中性粒细胞等)干预骨关节炎内环境的研究中,目前研究多体现在可减轻其参与的炎性反应,具体机制尚不清晰[21]。由此可见,现阶段伴随着免疫调节在机体病变中作用的研究不断深入,外泌体ncRNAs可靶向免疫系统调控骨关节炎的炎症反应。随后的研究中外泌体ncRNAs可与不同免疫细胞的免疫激活相关联进一步研究。 调节信号通路:外泌体ncRNAs可以影响细胞内的多种信号通路,它们可以通过抑制或促进这些通路的活性来影响软骨细胞对炎症刺激的反应。缺氧预处理骨髓间充质干细胞的外泌体通过miR-205-5p/PTEN/AKT途径有效促进软骨细胞的增殖、迁移和合成代谢,并抑制关节内炎症反应[22]。在软骨细胞间的相互作用研究中,发现软骨细胞分泌的外泌体在骨关节炎中还可以起到调控骨关节炎病理过程及细胞间通讯的作用[23]。研究表明,受损软骨细胞的外泌体lncRNA,可靶向激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路,降低了关节内炎症反应,增加了大鼠关节退变的发展[24]。在关节的退变过程中,大量的信号通路逐渐被阐明,外泌体ncRNAs作为其上游的调控因子,发挥承上启下的作用。因此,外泌体ncRNAs很可能是“外泌体-信号通路-炎症反应/软骨细胞程序性死亡/非程序性死亡等”中的关键环节,相关的信号通路还有待进一步扩展。其中,外泌体ncRNAs通过多靶点、多机制调控关节内炎症反应,而炎症反应在骨关节炎的发展过程中几乎贯穿整个病理过程,这提示研究者们调控外泌体ncRNAs的表达及转运可有效抑制骨关节炎的炎症反应[14-15,18-19,22,24-26],见表1。"

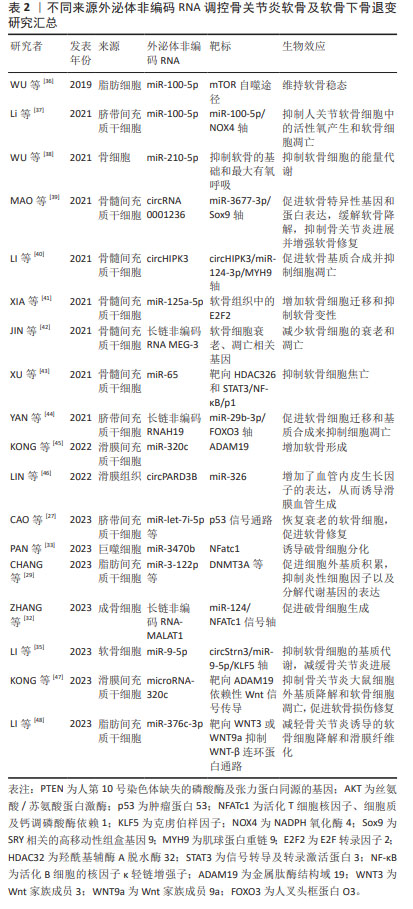
2.1.2 外泌体ncRNAs调控软骨退化 关节软骨主要由软骨细胞和细胞外基质组成,软骨细胞作为软骨组织的独特细胞,调节细胞外基质的合成与代谢。 首先,外泌体中的ncRNAs可影响软骨细胞的功能和生存,从而减缓软骨的退变。在抑制软骨细胞衰老方面,ncRNAs就可以通过调控p53相关通路恢复衰老的软骨细胞。如CAO等[27]发现脐带间充质干细胞外泌体中的miRNAs(miR-let-7i-5p等)可靶向软骨细胞p53信号通路,促进软骨修复。此外,MENG等[28]发现脂肪干细胞的外泌体中miR-429通过靶向FEZ2促进软骨细胞自噬,来改善软骨损伤。除了自噬,软骨细胞的凋亡、焦亡、铁死亡等均与外泌体ncRNAs有密切的联系。 其次,外泌体ncRNAs还可通过调控基因表达或与细胞外基质相互作用,影响软骨细胞的凋亡和变性。例如,CHANG等[29]发现来自缺氧的脂肪干细胞外泌体中的miRNAs (miR-3-122p等)可促进骨关节炎样炎症关节软骨细胞的软骨基质(聚集蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原)的表达,并能抑制骨关节炎样炎症关节软骨细胞中的炎性细胞因子(CEBPβ,环氧化酶2,白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α)以及分解代谢基因(基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMT5)的表达。 最后,外泌体ncRNAs调节细胞外基质的代谢在维持软骨细胞的功能方面也起着重要作用。ZHANG等[30]使用去细胞化细胞外基质为间充质干细胞的扩增提供了最佳的微环境,此环境中的外泌体可通过上调miR-3473b靶向PTEN,激活PTEN/AKT信号通路,促进软骨基质迁徙、改善合成代谢和抑制软骨细胞凋亡来缓解骨关节炎。 2.1.3 外泌体ncRNAs调控软骨下骨重塑 软骨下骨是构成关节结构和功能的基本单位之一。随着软骨基质的磨损,软骨下骨所承受的压力随之增加,破骨细胞与成骨细胞的平衡受到干扰,随之出现软骨下骨的吸收与重塑[31]。外泌体中ncRNAs可与骨细胞相互作用,调控骨髓基质中的骨细胞分化和功能,从而影响骨吸收重塑的过程。已有研究表明,成骨细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA-MALAT1通过靶向骨髓来源巨噬细胞中的miR-124/NFATc1信号轴促进破骨细胞生成[32]。PAN等[33]证明成骨细胞和成熟破骨细胞捕获巨噬细胞来源的外泌体,外泌体miR-3470b靶向TAB3/NF-κB信号通路增加NFatc1的表达来诱导破骨细胞分化。同时,他们还证明了富含miR-3470b的工程外泌体有助于抑制骨的溶解。而软骨下骨来源的外泌体ncRNAs又会对软骨细胞及软骨基质起到调控作用,其转运途径可能是通过微裂缝或者血管到达软骨的[34],这也是外泌体ncRNAs在关节内各细胞间发挥通讯作用的一种体现。 2.1.4 外泌体ncRNAs调控细胞间通讯 外泌体中ncRNAs可以作为细胞间的信使,传递信息并调节相邻和远离病变区域细胞的行为,这种细胞间通讯可能在骨关节炎的发病机制中发挥关键作用。LI等[35]探索了拉伸应变刺激软骨细胞分泌外泌体miR-9-5p,它通过靶向克虏伯样因子5抑制成骨细胞的分化,通过circStrn3/miR-9-5p/KLF5轴抑制软骨细胞的基质代谢,减缓骨关节炎进展。而来自髌下脂肪垫中细胞产生大量外泌体,其中miR-100-5p水平在microRNA中最高,并通过抑制mTOR自噬途径维持软骨稳态[36]。值得注意的是,除了关节内部或者附近的组织产生干预骨关节炎的外泌体ncRNAs,远离关节组织产生的外泌体ncRNAs也与关节内细胞产生细胞间通讯作用。如人尿源干细胞来源的外泌体miR-140-5p通过下调大鼠模型中的血管内皮生长因子A来缓解膝骨关节炎,来自人脐带间充质干细胞的外泌体通过miR-100-5p/NOX4轴抑制人关节软骨细胞中的活化氧产生和软骨细胞凋亡[26,37]。这些都是外泌体ncRNAs调控细胞间通讯的具体研究,这可能与外泌体进入血液循环参与全身细胞代谢功能调节有关,这也是其对诊治骨关节炎甚至全身疾病具有巨大研究价值的体现[27,29,32-33,35-48],详见表2。文章对外泌体ncRNAs对骨关节炎微环境的作用机制进行了初步归纳,见图5。"

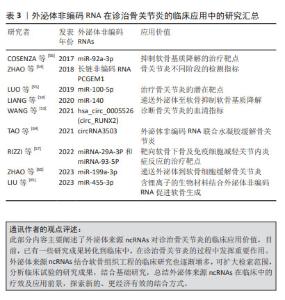
2.2 外泌体ncRNAs对诊治骨关节炎的临床应用价值 将外泌体来源ncRNAs应用到治疗方法中,作为一种无细胞方法已成为治疗骨和关节相关肌肉骨骼疾病的最有前途策略之一[49]。因为它们具有增强循环稳定性、生物相容性、低免疫原性及毒性等特征[50]。 2.2.1 外泌体ncRNAs作为生物标志物 在以往研究中,骨关节炎的标志性诊断标准仍以MRI等影像学为主[51],尚缺少可以明确诊断的标志物。外泌体中的ncRNAs可以作为骨关节炎的生物标志物,帮助早期诊断和监测疾病进展与预后,它们的表达水平可能与疾病的严重程度和炎症状态相关[52]。WANG等[53]发现RUNX2 衍生的hsa_circ_0005526 (circ_RUNX2)在骨关节炎血清中显著高表达,circ_RUNX2可能通过与软骨基质受体相互作用途径参与骨关节炎的发展,并可成为骨关节炎的潜在临床指标。此外,关节滑液中的ncRNA也可以作为关节病变及分期的指标,如外泌体lncRNA PCGEM1在骨关节炎患者中也高表达,并且在骨关节炎的不同阶段存在差异[54]。在之后的研究中,骨关节炎的标志性ncRNAs还可以与骨关节炎的等级、病理变化相关联。 2.2.2 外泌体ncRNAs作为治疗靶点 由于外泌体中的ncRNAs可以作为骨关节炎的标志性调节因子,并且参与调控骨关节炎相关的分子通路,它也成为了潜在的治疗靶点。目前一些研究正在探讨使用RNA或药物来干预这些ncRNAs的表达,以减轻关节炎症和疼痛。当然,外泌体可以作为潜在的药物递送载体,将治疗性ncRNA或药物传递到关节炎病灶,进而提高治疗效果和减少不良反应。这其中有通过miR-100-5p/mTOR通路抑制关节内炎症的外泌体miRNA-100-5P[55];有诱导软骨细胞标志物(Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖)表达,同时抑制基质金属蛋白酶13分解代谢的外泌体miR-92a-3p[56],也有靶向软骨下骨及免疫细胞减轻关节内炎症反应的外泌体miRNA-29A-3P和miRNA-93-5P[57]。因此,更多的研究应聚焦于提高来自自身可减轻关节内炎症的外泌体ncRNAs含量,或者减少有促炎作用或者参与促炎机制的外泌体ncRNAs的释放。 2.2.3 外泌体ncRNAs的递送 由于外泌体通过软骨致密的非血管细胞外基质具有优异的组织渗透能力,其作为新的药物递送系统的研究不断出现[58]。不少学者使用外泌体搭载ncRNAs有效缓解骨关节炎进展,目前研究较多的是通过外泌体将miRNAs递送到关节内部。LIANG等[59]通过将软骨细胞亲和肽(CAP)与外泌体表面的溶酶体相关膜糖蛋白2b蛋白融合,获得了可以有效封装miR-140的CAP外泌体,其通过致密的中软骨将miR-140递送到深层软骨区域,有效抑制软骨降解蛋白酶,并缓解大鼠模型中的骨关节炎进展。最近,ZHAO等[60]使用临床上通过吸脂手术获得的人类皮下脂肪设计了间充质干细胞来源的外泌体,实现miR-199a-3p靶向递送到软骨细胞中,在体内骨关节炎动物模型中发挥了优异的治疗效果。目前,关节内外泌体的递送方法在不断研究中,更优质更合适的支架或生物材料被需要以有效递送外泌体[61]。 2.2.4 外泌体ncRNAs与软骨组织工程 软骨组织工程是一种利用细胞、生物材料和生长因子等手段来修复或再生受损软骨的技术。在此过程中,研究人员使用软骨细胞结合支架材料和生长因子,以促进细胞的黏附、增殖和分化。外泌体ncRNAs在这个过程中可以通过调控基因表达、促进细胞间通讯,提高软骨组织工程的效果[62]。之前的研究已经探索了注射天然生物材料或合成材料产生的聚合物来包封天然细胞或生长因子来修复骨软骨,仍存在一定的局限性[63]。现阶段,更稳定、更有效的组织工程材料被应用到软骨组织的修复过程中,联合外泌体ncRNAs的研究有了更多新的进展。 TAO等[64]发现将外泌体与circRNA3503联合使用,联合可注射热敏水凝胶,可作为一种有效预防骨关节炎的靶向治疗剂。而LIU等[65]在体内体外实验中使用含锂离子的生物材料结合外泌体可促进软骨生成,其机制在于上调的外泌体miR-455-3p抑制组蛋白去乙酰化酶2并增强软骨细胞中的组蛋白H3乙酰化,该研究可能为含锂生物材料促进软骨生成的内在机制提供新的可能性。此外,3D打印生产的仿生水凝胶支架可促进人脂肪间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体在体外的附着、扩散、迁移和增殖,联合ncRNAs可以促进软骨和成骨分化,这可能是基于生物活性外泌体的持续释放形成的[66]。文章总结了外泌体ncRNAs在诊治骨关节炎的临床应用进展[53-60,64-65],详见表3。"

| [1] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59. [2] LI Y, XIE W, XIAO W, et al. Progress in osteoarthritis research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):41. [3] HERRMANN K, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759. [4] PI YN, XIA BR, JIN MZ, et al. Exosomes: powerful weapon for cancer nano-immunoengineering. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;186:114487. [5] ALI SA, PEFFERS MJ, ORMSETH MJ, et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021; 17(11):692-705. [6] TU C, HE J, CHEN R, LI Z. The emerging role of exosomal non-coding rnas in musculoskeletal diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(42): 4523-4535. [7] JEPPESEN DK, ZHANG Q, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(8): 667-681. [8] MATSUI M, COREY DR. Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):167-179. [9] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [10] HOSSEINI K, RANJBAR M, PIRPOUR TAZEHKAND A, et al. Evaluation of exosomal non-coding RNAs in cancer using high-throughput sequencing. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):30. [11] HE AT, LIU J, LI F, et al. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: current strategies and challenges. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):185. [12] KRYLOVA SV, FENG D. The machinery of exosomes: biogenesis, release, and uptake. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1337. [13] ZHANG Z, ZHAO S, SUN Z, et al. Enhancement of the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoarthritis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):75. [14] LI C, LI W, PU G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-338-3p-modified adipose stem cells inhibited inflammation injury of chondrocytes via targeting RUNX2 in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):567. [15] LAI C, LIAO B, PENG S, et al. Synovial fibroblast-miR-214-3p-derived exosomes inhibit inflammation and degeneration of cartilage tissues of osteoarthritis rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023;478(3):637-649. [16] HEGDE M, KUMAR A, GIRISA S, et al. Exosomal noncoding RNA-mediated spatiotemporal regulation of lipid metabolism: implications in immune evasion and chronic inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;73:114-134. [17] NOONIN C, THONGBOONKERD V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics. 2021;11(9): 4436-4451. [18] JIA H, DUAN L, YU P, et al. Digoxin ameliorates joint inflammatory microenvironment by downregulating synovial macrophage M1-like-polarization and its-derived exosomal miR-146b-5p/Usp3&Sox5 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109135. [19] ZHOU H, SHEN X, YAN C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis of the knee in mice model by interacting with METTL3 to reduce m6A of NLRP3 in macrophage. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):322. [20] WANG Y, FAN A, LU L, et al. Exosome modification to better alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced chondrocyte apoptosis and osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;206:115343. [21] HUANG L, DONG G, PENG J, et al. The role of exosomes and their enhancement strategies in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Hum Cell. 2023;36(6):1887-1900. [22] SHEN K, DUAN A, CHENG J, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells laden in a silk hydrogel promote cartilage regeneration via the miR-205-5p/PTEN/AKT pathway. Acta Biomater. 2022;143:173-188. [23] FAN Y, LI Z, HE Y. Exosomes in the pathogenesis, progression, and treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(3):99. [24] LV G, WANG B, LI L, et al. Exosomes from dysfunctional chondrocytes affect osteoarthritis in sprague-dawley rats through FTO-dependent regulation of PIK3R5 mRNA stability. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(9): 652-668. [25] JIANG S, TIAN G,YANG Z, et al. Enhancement of acellular cartilage matrix scaffold by Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to promote osteochondral regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2711-2728. [26] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. [27] CAO H, CHEN M, CUI X, et al. Cell-free osteoarthritis treatment with sustained-release of chondrocyte-targeting exosomes from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to rejuvenate aging chondrocytes. ACS Nano. 2023;17(14):13358-13376. [28] MENG C, NA Y, HAN C, et al. Exosomal miR-429 derived from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorated chondral injury in osteoarthritis via autophagy by targeting FEZ2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;120: 110315. [29] CHANG LH, WU SC, CHEN CH, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxia-cultured human adipose stem cells alleviate articular chondrocyte inflammaging and post-traumatic osteoarthritis progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13414. [30] ZHANG Y, QI G, YAN Y, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with decellularized extracellular matrix enhance the alleviation of osteoarthritis through miR-3473b/phosphatase and tensin homolog axis. J Gene Med. 2023;25(8):e3510. [31] WU Y, LI J, ZENG Y, et al. Exosomes rewire the cartilage microenvironment in osteoarthritis: from intercellular communication to therapeutic strategies. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):40. [32] ZHANG C, PAN L, ZHANG H, et al. Osteoblasts-derived exosomal lncRNA-MALAT1 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting the miR-124/NFATc1 signaling axis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:781-795. [33] PAN B, ZHANG Z, WU X, et al. Macrophage-derived exosomes modulate wear particle-induced osteolysis via miR-3470b targeting TAB3/NF-κB signaling. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:181-193. [34] LIU J, WU X, LU J, et al. Exosomal transfer of osteoclast-derived miRNAs to chondrocytes contributes to osteoarthritis progression. Nat Aging. 2021;1(4):368-384. [35] LI B, DING T, CHEN H, et al. CircStrn3 targeting microRNA-9-5p is involved in the regulation of cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2023;12(1):33-45. [36] WU J, KUANG L, CHEN C, et al. miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2019;206:87-100. [37] LI X, WANG Y, CAI Z, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ROS production and cell apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes via the miR-100-5p/NOX4 axis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(10):2096-2106. [38] WU X, CRAWFORD R, XIAO Y, et al. Osteoarthritic subchondral bone release exosomes that promote cartilage degeneration. Cells. 2021;10(2):251. [39] MAO G, XU Y, LONG D, et al. Exosome-transported circRNA_0001236 enhances chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via the miR-3677-3p/Sox9 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):389. [40] LI S, LIU J, LIU S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9 axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):194. [41] XIA Q, WANG Q, LIN F, et al. miR-125a-5p-abundant exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress chondrocyte degeneration via targeting E2F2 in traumatic osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):11225-11238. [42] JIN Y, XU M, ZHU H, et al. Therapeutic effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(19):9281-9294. [43] XU H, XU B. BMSC-derived exosomes ameliorate osteoarthritis by inhibiting pyroptosis of cartilage via delivering miR-326 targeting HDAC3 and STAT1//NF-κB p65 to chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9972805. [44] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e255. [45] KONG R, GAO J, ZHANG J, et al. Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-320c enhances chondrogenesis by targeting ADAM19. Future Med Chem. 2022;14(2):81-96. [46] LIN Z, MA Y, ZHU X, et al. Potential predictive and therapeutic applications of small extracellular vesicles-derived circPARD3B in osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:968776. [47] KONG R, ZHANG J, JI L, et al. Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-320c facilitates cartilage damage repair by targeting ADAM19-dependent Wnt signalling in osteoarthritis rats. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(2):915-926. [48] LI F, XU Z, XIE Z, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate osteoarthritis by transporting microRNA-376c-3p and targeting the WNT-beta-catenin signaling axis. Apoptosis. 2023; 28(3-4):362-378. [49] ZOU J, YANG W, CUI W, et al. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive materials in tendon-bone healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):14. [50] GARCIA-MARTIN R, WANG G, BRANDAO BB, et al. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature. 2022;601(7893):446-451. [51] KIJOWSKI R, DEMEHRI S, ROEMER F, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(3):285-295. [52] CHEN A, CHEN Y, RONG X, et al. The application of exosomes in the early diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1154135. [53] WANG C, LI N,LIU Q, et al. The role of circRNA derived from RUNX2 in the serum of osteoarthritis and its clinical value. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(7):e23858. [54] ZHAO Y, XU J. Synovial fluid-derived exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as biomarker for the different stages of osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(12):2865-2872. [55] LUO P, JIANG C, JI P, et al. Exosomes of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an anti-inflammatory agent in temporomandibular joint chondrocytes via miR-100-5p/mTOR. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):216. [56] COSENZA S, RUI M, TOUPET K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16214. [57] RIZZI L, TURATI M, BRESCIANI E, et al. Characterization of microRNA levels in synovial fluid from knee osteoarthritis and anterior cruciate ligament tears. Biomedicines. 2022;10(11):2909. [58] PIFFOUX M, VOLATRON J, CHERUKULA K, et al. Engineering and loading therapeutic extracellular vesicles for clinical translation: a data reporting frame for comparability. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;178: 113972. [59] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36938-36947. [60] ZHAO S, XIU G, WANG J, et al. Engineering exosomes derived from subcutaneous fat MSCs specially promote cartilage repair as miR-199a-3p delivery vehicles in Osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):341. [61] FOO JB, LOOI QH, HOW CW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and microRNAs in cartilage regeneration: biogenesis, efficacy, miRNA enrichment and delivery. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(11):1093. [62] KWON DG, KIM MK, JEON YS, et al. State of the art: the immunomodulatory role of MSCs for osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1618. [63] FAN WJ, LIU D, PAN LY, et al. Exosomes in osteoarthritis: updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:949690. [64] TAO SC, HUANG JY, GAO Y, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in combination with sleep-related circRNA3503: a targeted therapeutic agent with injectable thermosensitive hydrogel to prevent osteoarthritis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4455-4469. [65] LIU L, YU F, CHEN L, et al. Lithium-containing biomaterials stimulate cartilage repair through bone marrow stromal cells-derived exosomal miR-455-3p and histone H3 acetylation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023; 12(11):e2202390. [66] LI Q, YU H, ZHAO F, et al. 3D Printing of microenvironment-specific bioinspired and exosome-reinforced hydrogel scaffolds for efficient cartilage and subchondral bone regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(26):e2303650. |
| [1] | Ma Chi, Wang Ning, Chen Yong, Wei Zhihan, Liu Fengji, Piao Chengzhe. Application of 3D-printing patient-specific instruments combined with customized locking plate in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [7] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [8] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [9] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [10] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [11] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [12] | Wang Peiguang, Zhang Xiaowen, Mai Meisi, Li Luqian, Huang Hao. Generalized equation estimation of the therapeutic effect of floating needle therapy combined with acupoint embedding on different stages of human knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [13] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [14] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [15] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||