Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (13): 2793-2801.doi: 10.12307/2025.058
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in promoting wound healing
Long Chenyan1, 2, Cheng Biao3, Tian Ju2
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Burns, Plastic Surgery, and Aesthetic Medicine, People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City, Guangdong Medical University, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Southern Theater Command, Guangzhou 510030, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-26Accepted:2024-04-14Online:2025-05-08Published:2024-09-12 -
Contact:Tian Ju, PhD, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Burns, Plastic Surgery, and Aesthetic Medicine, People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City, Guangdong Medical University, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Cheng Biao, PhD, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery, General Hospital of Southern Theater Command, Guangzhou 510030, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Long Chenyan, Master candidate, Physician, First Clinical Medical College of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Burns, Plastic Surgery, and Aesthetic Medicine, People’s Hospital of Zhongshan City, Guangdong Medical University, Zhongshan 528400, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82172223, 82372531 (to CB); Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20241357 (to TJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Long Chenyan, Cheng Biao, Tian Ju. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in promoting wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2793-2801.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
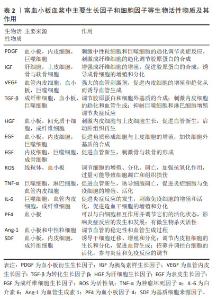
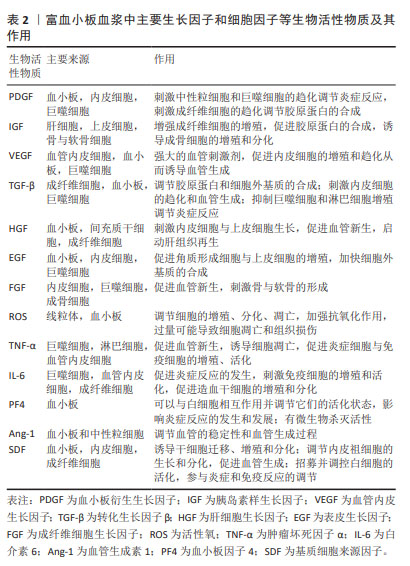
富血小板血浆促进创面愈合是一个备受关注的研究领域,经历了从初步发现到深入机制研究的漫长历程,不断为临床治疗提供理论支持和实验基础[6-8],见表1。虽然已知富血小板血浆富含多种生长因子,但对这些生长因子在创面愈合过程中具体作用机制的理解仍然不够深入,需要进一步研究这些生长因子如何影响细胞增殖、血管生成、基质合成和免疫调节等愈合过程中的关键步骤。富血小板血浆在创面愈合中如何调控细胞信号通路,以及与愈合相关细胞因子的交互作用还需要深入研究。富血小板血浆如何影响创面愈合中的基质合成和修复过程,以及对于不同类型的组织损伤,其作用是否存在差异性等问题需要进一步探讨。富血小板血浆对创面愈合中炎症反应和免疫调节的作用机制仍不十分清楚,需要深入研究其对免疫细胞的影响以及在愈合过程中的调控作用。富血小板血浆在创面愈合的不同阶段发挥的作用也需深入研究。通过解决上述问题,可以更好地理解富血小板血浆在创面愈合中的作用机制,为其在临床治疗中的应用提供更加可靠的科学依据。"
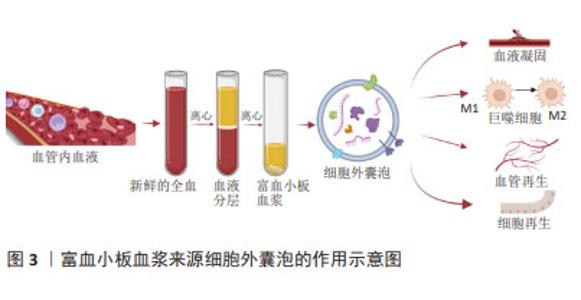
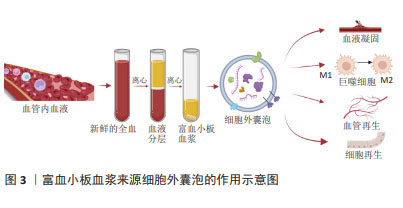
在富血小板血浆疗法中,细胞外囊泡可能扮演着重要角色,通过传递其携带的生长因子等物质,影响受体细胞的生物学行为,这些囊泡可以在细胞间传递信号,调节细胞增殖、分化,并参与组织再生过程[8,16-23]。研究表明,细胞外囊泡比富血小板血浆活化后释放的细胞因子和生长因子浓度更高[8,16]。受刺激活化的血小板分泌血小板衍生细胞外囊泡,根据直径的不同可分为微泡或微颗粒和外泌体[17-18]。血小板来源细胞外囊泡中含有许多促进凝血的因子和分子,能够促进血栓的形成,加速止血过程[24];通过激活内皮细胞和诱导内皮细胞增殖,从而促进新血管的形成[25];可能通过携带一系列生物活性分子(例如蛋白质、RNA等)来调控受体细胞的信号传导通路,从而影响细胞的增殖、分化和迁移[26-27];通过调节免疫细胞的活化状态和介导炎症反应来参与组织再生过程[8]。这些细胞外囊泡可能通过携带特定的基质蛋白或分子,影响细胞外基质的合成和降解,从而影响组织再生的微环境。总之,血小板来源细胞外囊泡可能通过多种机制参与和促进组织再生,对于维持组织结构和功能的恢复具有重要作用,见图3。未来血小板细胞外囊泡可能成为再生医学中替代富血小板血浆的无细胞疗法[28]。"
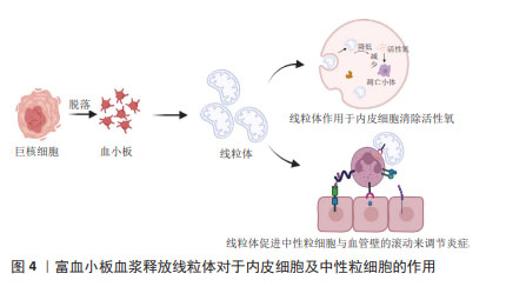
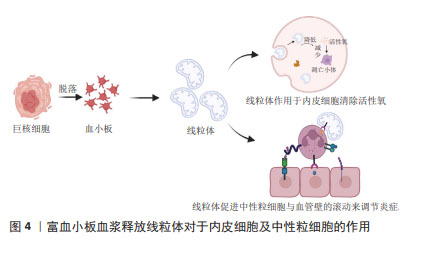
由于富血小板血浆含有多种生物活性成分,不同的个体及不同制备方法、保存方法、激活方法等多种体内外因素都会对富血小板血浆生物活性成分的种类和浓度产生重要的影响[29-30]。另外,富血小板血浆治疗过程面临着疗效不稳定、生长因子半衰期短以及突然释放等诸多不足,这些都限制了其治疗效果。由于水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性、免疫原性低、安全性好等优点,人们利用水凝胶作为传递载体,包封各种活性成分,消除异物反应,提高疗效。由于具有潜在的生物学功能,载有富血小板血浆水凝胶被广泛用于增强组织再生和作为药物传递的功能性载体[31-34]。未来的研究重点可以放在进一步探索富血小板血浆中不同生长因子和细胞因子的作用机制,以及它们之间的相互作用,有助于更全面地理解富血小板血浆在创面愈合中的作用方式。研究如何更好地提取和保留富血小板血浆中的生长因子和细胞因子,以及提高富血小板血浆的生物活性和稳定性,做到个体化兼具标准化治疗,这将有助于优化富血小板血浆的临床应用效果。 2.2 细胞类型和功能 富血小板血浆成分复杂,数量最多的细胞类型是血小板,它是富血小板血浆的作用核心所在。富血小板血浆作用的效果不仅取决于血小板计数,还取决于其他血小板非依赖性分子[35]。富血小板血浆中包含白细胞(中性粒细胞、单核细胞和淋巴细胞)、红细胞、纤维蛋白、纤维连接蛋白、骨连接蛋白、玻连蛋白等[36]。富血小板血浆中的各种成分与创面内的细胞和内环境之间存在着复杂的相互作用。白细胞参与炎症反应,释放炎症递质,如细胞因子和趋化因子,以吸引其他细胞到达受伤部位,促进创面修复。然而,部分研究也指出高浓度的白细胞可能会引起过度炎症反应,因此在富血小板血浆制备中对白细胞浓度的控制非常重要。富血小板血浆中含有少量的红细胞,可以帮助输送氧气和营养物质到受伤组织,但大量的红细胞注入可能导致组织的炎症反应,引起局部肿胀、发红和疼痛等症状。纤维蛋白是一种重要的细胞外基质成分,有助于创面周围的细胞黏附和迁移。纤维蛋白、纤维连接蛋白、骨连接蛋白、玻连蛋白等成分对于细胞的黏附、迁移、信号传导和分化等方面起着重要作用,从而促进创面的愈合和组织的修复。 富血小板血浆对参与创面愈合的各种细胞类型,包括表皮细胞、血管内皮细胞、成纤维细胞、干细胞和炎症细胞等都有一定影响。这些细胞在愈合过程中的功能和相互作用都可以受到富血小板血浆的调节[37-44]。富血小板血浆能够促进表皮细胞的增殖和迁移,并刺激上皮细胞的再生和修复,有助于加速创面上皮化,提高创面愈合的速度和质量;富血小板血浆对成纤维细胞、平滑肌细胞的增殖、胶原蛋白合成和基质形成具有促进作用,这有助于加强创面的结构支撑和组织修复;富血小板血浆能够促进内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,进而促进新血管的形成,这有助于加强血管网的重建和血液供应,为创面提供足够的氧和营养物质。对于伤口的创面愈合,新生的毛细血管是必不可少的,内皮细胞作为参与毛细血管生成的重要细胞,其功能状态会直接影响到伤口愈合。在高水平的活性氧作用下血管内皮细胞受损会阻碍新血管形成,线粒体转移可以减少病理条件下细胞内活性氧的损伤。JIN等[45]研究表明血小板是线粒体的重要供体,血小板来源线粒体可以通过减少血管内皮细胞氧化应激引起的细胞凋亡来促进伤口愈合,并提出超声是激活血小板释放呼吸线粒体的更合适方法。另外,血小板释放的这些线粒体可以转移到间充质干细胞中,通过代谢重编程提高间充质干细胞的成血管诱导能力[46]。血小板来源线粒体同样可以和中性粒细胞结合促进中性粒细胞与血管壁的滚动黏附加强,促进炎症细胞的活化和迁移,从而调控炎症反应和伤口愈合[47],见图4。这些结果进一步扩展了对血小板功能的认识,并为血小板源性线粒体在伤口愈合中的作用提供了新的见解。总之,富血小板血浆在创面愈合中的细胞影响机制已经得到广泛关注。然而,对于不同细胞类型的具体响应机制以及它们之间的相互作用,仍需要进一步的研究来深入探索。"
上皮间质转化是一种细胞状态的转变过程,指的是上皮细胞从极性和细胞间附着状态转变为间质细胞样的状态,在上皮间质转化过程中,上皮细胞通过失去细胞间附着、极性和上皮特征,获得间质细胞样的形态和功能,如增强细胞迁移、侵袭和抗凋亡能力。同时,细胞表型也发生改变,表现出间质细胞的标志性特征,如表达间质细胞标记物、产生胶原蛋白等[48]。富血小板血浆中含有的多种活性物质,如转化生长因子β、表皮生长因子等被认为可能参与了上皮间质转化的调控,这些生长因子可以影响细胞的增殖、迁移和分化,从而可能影响上皮间质转化过程,促进上皮细胞、角质形成细胞向间质细胞转化影响伤口愈合[49]。但目前尚无研究支持富血小板血浆中的活性物质对上皮间质转化可能产生影响,需要更多的实验研究来充分理解其作用机制以及在临床应用中的潜在效果。 2.3 细胞信号通路 富血小板血浆对细胞信号通路的调控作用,包括与细胞表面受体的相互作用、信号传导通路的激活和抑制等。富血小板血浆中的生长因子和细胞因子可以与细胞表面上的受体结合,触发下游信号传导通路的激活。 现有研究表明,富血小板血浆可以通过以下信号通路促进创面愈合,见表3。 "
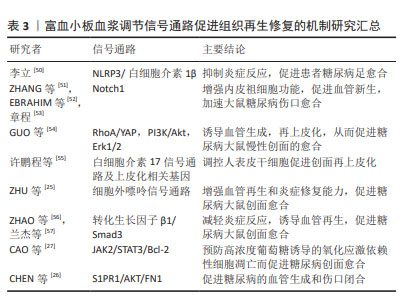

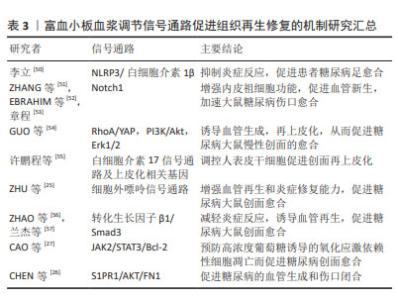
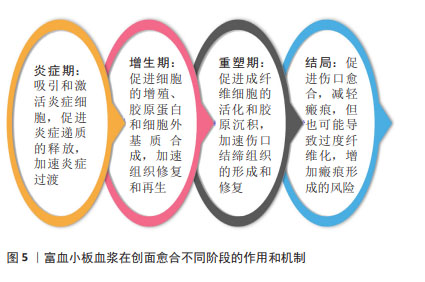
2.3.1 NLRP3/白细胞介素1β 信号通路 NLRP3是一种炎症小体感应受体,在炎症反应和免疫调节中发挥重要作用。当创面受损时,NLRP3可以被激活并启动炎症小体的形成,进而促进白细胞介素1β的释放。富血小板血浆可以抑制NLRP3 信号通路的过度激活,从而减少白细胞介素1β的释放,并调节炎症反应,促进创面愈合过程[50]。 2.3.2 Notch 信号通路 Notch信号通路是一种重要的细胞信号传导通路,参与调控多种细胞行为和功能,对于细胞增殖、分化、命运决定以及组织形成和再生过程具有重要作用。富血小板血浆中的生长因子和细胞因子可以激活Notch信号通路,从而促进干细胞的增殖和分化,加速创面愈合[51-53]。Notch信号通路的激活还可以影响新组织的再生和修复过程,提高创面愈合的效率和质量。 2.3.3 RhoA/YAP,PI3K/Akt和Erk1/2 信号通路 RhoA/YAP参与皮肤修复和上皮再形成。GUO等[54]研究表明,富血小板血浆来源外泌体比富血小板血浆更大程度地促进人微血管内皮细胞、成纤维细胞的增殖和迁移。富血小板血浆释放的外泌体可能通过激活PI3K/Akt和Erk信号通路来促进内皮细胞增殖。同时,通过激活Rho/YAP信号通路诱导再上皮化,从而促进糖尿病大鼠慢性创面的愈合。 2.3.4 白细胞介素17信号通路 白细胞介素17是一种重要的免疫系统调节因子,它参与调节炎症反应和组织修复过程。在创面修复中,白细胞介素17可能通过影响炎症反应、细胞增殖和再生等途径发挥作用。许鹏程等[55]研究显示富血小板血浆调节人表皮干细胞功能促进创面再上皮化涉及角蛋白19、角蛋白10等多个基因的转录调控,同时可能与白细胞介素17信号通路相关。 2.3.5 细胞外嘌呤信号通路 细胞外嘌呤信号通路的激活和抑制对于细胞增殖、迁移、分化和合成胶原蛋白等过程具有重要作用,从而促进创面愈合和组织修复。最新的一项研究表明富血小板血浆中的生长因子和ATP、ADP等嘌呤类物质可以与周围细胞表面的嘌呤受体结合,触发细胞外嘌呤信号通路,增强血管再生和炎症修复能力,促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合[25]。 2.3.6 转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路 转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路在创面愈合中起着重要作用,促进纤维母细胞的活化和胶原蛋白的合成,从而促进伤口愈合。此外,转化生长因子β还可以调节炎症反应、细胞凋亡和基质重塑等过程,对创面愈合的不同阶段都具有调节作用。富血小板血浆中一些成分可以影响转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路的活性,促进伤口愈合所需的胶原合成、细胞迁移和新血管生成等过程[56-57]。 2.3.7 S1PR1/AKT/FN1信号通路 S1P是血管稳态和血管生成的关键调节因子。 来自富血小板血浆来源外泌体的S1P以高水平存在,与糖尿病患者和动物皮肤中的S1PR2和S1PR3相比,S1PR1表达显著升高,富血小板血浆来源外泌体S1P可以通过S1PR1/AKT/FN1信号通路促进血管生成和伤口闭合[26]。 2.3.8 JAK2/STAT3/Bcl-2信号通路 CAO等[27]发现高葡萄糖通过活性氧依赖性激活JNK和p38 MAPK信号通路抑制细胞增殖和迁移并诱导细胞凋亡。富血小板血浆来源外泌体可能通过PDGF-BB/JAK2/STAT3/Bcl-2信号通路抑制高葡萄糖诱导的活性氧依赖性细胞凋亡,从而激活成纤维细胞功能并加速糖尿病伤口愈合。 此外,富血小板血浆还可以调节其他多种信号通路,包括NF-κB[58]、NRF2/HO-1通路[59]、Wnt信号通路[60]、HIF-α信号通路[61]、ERK/MAPK信号通路、TLR信号通路等[62],但对于富血小板血浆是否可以通过调节这些信号通路来促进创面愈合尚不明确。作者推测富血小板血浆调节创面愈合的过程可能是动态的,在不同的时期对同一信号通路的作用也不同,可以是抑制该信号通路,也可以是激活该信号通路。总之,目前对富血小板血浆影响的相关通路缺乏全面的研究,很多研究仅仅关注单一的信号通路,没有同时对多种信号通路影响创面的动态过程进行研究,需要更多深入的实验和临床研究来验证其具体机制和疗效[63]。 2.4 细胞外基质调节 富血小板血浆对创面细胞外基质合成和降解发挥调节作用,从而影响伤口愈合过程中基质重建[64-68]。富血小板血浆可以促进细胞在细胞外基质中的生长、迁移和分化,并增强其合成细胞外基质的能力。例如,富血小板血浆中的胶原生长因子和转化生长因子β可以刺激纤维母细胞合成大量的胶原和其他细胞外基质成分,从而促进细胞外基质的重建。富血小板血浆也可以降低细胞外基质的降解速度,延长其存在时间。例如,富血小板血浆中的组织抑制物可以抑制金属蛋白酶的活性,从而减少细胞外基质的降解。此外,富血小板血浆中的转化生长因子β和血小板衍生生长因子等也可以通过影响细胞内的钙离子浓度和ATP合成等方式,降低基质金属蛋白酶的表达和活性,从而减少细胞外基质的降解。富血小板血浆可以刺激伤口周围细胞的生长、迁移和分化,促进细胞外基质的重建,从而加速伤口愈合。富血小板血浆中的生长因子可以促进血管内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,从而促进新血管的生成。这对于优化创面的血液供应和营养物质的输送至关重要,有助于促进细胞外基质合成和修复。但也有研究认为富血小板血浆中的白细胞会阻碍细胞外基质重塑[69]。富血小板血浆对细胞外基质的具体作用机制仍在研究中不断探索和验证。 2.5 炎症和免疫调节 富血小板血浆在创面愈合中可以调节炎症和免疫反应,减轻氧化应激对细胞的损伤。富血小板血浆可以调节炎症反应的发生和持续时间。例如,富血小板血浆中的趋化因子如血小板衍生生长因子、白细胞介素1和白细胞介素8等,可以吸引和激活炎症相关细胞,如中性粒细胞、单核细胞和巨噬细胞等。同时,富血小板血浆中的转化生长因子β和干扰素γ等则可以抑制炎症反应,减少炎症细胞的释放和活化。富血小板血浆可以调节免疫细胞的活性和功能,从而影响免疫反应。例如,富血小板血浆中的转化生长因子β和白细胞介素10等能够抑制免疫细胞的活化和炎症反应,减轻创面的免疫介导损伤。另外,富血小板血浆中的血小板衍生生长因子和转化生长因子β等还可以促进免疫细胞的增殖和分化,提高其对创面感染的清除能力。 巨噬细胞是免疫系统中的一类重要细胞,主要负责吞噬和清除体内的病原体、细胞垃圾和损伤组织等。从功能上可以将巨噬细胞分类成M1型和M2型,M1型为促炎型,M2型为抑炎型。促进巨噬细胞向 M2 型转化,是抑制慢性炎症反应、促进创面修复的重要手段。富血小板血浆含有多种生长因子,其中包括促进巨噬细胞增殖和活化的因子。研究表明,富血小板血浆可以促进巨噬细胞的趋化、活化和分泌细胞因子,从而增强巨噬细胞的免疫功能和修复能力[70-72]。近年来,富血小板血浆在巨噬细胞相关研究领域取得了一些进展。一些研究表明,富血小板血浆可以促使巨噬细胞从M1型向M2型转变,即从促炎状态转变为抗炎和修复状态[73-76]。这种转变能够促进组织修复和改善炎症反应。此外,富血小板血浆还能够增强巨噬细胞的吞噬能力和细胞外基质降解能力,有助于修复受损组织。目前的研究显示,富血小板血浆在调节炎症和免疫反应方面具有潜在的益处。然而,针对富血小板血浆对炎症和免疫反应的详细作用机制及其在不同临床应用中的疗效,仍需要更多的临床和实验研究来验证和完善。 2.6 创面愈合不同阶段 创面愈合是指伤口或创口的生物学修复过程,通常包括3个阶段:炎症期、增生期和重塑期。富血小板血浆促进伤口的细胞增殖、新血管生成和胶原沉积,从而加速创面愈合的不同阶段。在炎症期,伤口周围的血管会发生收缩和扩张,引起局部充血和水肿以及白细胞和其他免疫细胞的聚集。在该阶段应用富血小板血浆,能够募集生长因子和激活炎症细胞,促进炎症递质的释放,从而加速炎症反应的清除和控制,促进炎症期的快速过渡[77]。在增生期,伤口周围的细胞开始增殖和迁移,以填补伤口缺损。在该阶段应用富血小板血浆能够刺激伤口多种细胞的增殖,促进胶原蛋白和基质合成,有助于加速组织修复和再生。在重塑期,伤口周围的细胞开始重新排列和重建支撑结构,并形成新的皮肤和组织。在该阶段应用富血小板血浆可促进成纤维细胞的活化和胶原沉积,通过促进胶原合成和纤维化,加速伤口结缔组织的形成和修复。总的来说,富血小板血浆可作为愈合级联的引发剂加速整个创面愈合过程。见图5。但理论上,富血小板血浆也并非没有风险,在伤口愈合的重塑期和瘢痕特别是病理性瘢痕的治疗中使用富血小板血浆并没有令人信服的证据支持。一方面,富血小板血浆所释放的转化生长因子β可以调控炎症递质的释放和炎症反应,促进新生血管生成和胶原合成,促进成纤维细胞的活化和胶原沉积,从而促进伤口结缔组织的形成和修复,减少瘢痕[78];另一方面,但过高的转化生长因子β浓度可能导致过度纤维化,增加瘢痕形成的风险[79],因此将富血小板血浆应用于增生性瘢痕或瘢痕疙瘩治疗时仍需谨慎[80]。"
| [1] 金路,左蕊,刘丽,等.自体富血小板血浆促糖尿病足溃疡愈合机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2021,61(14):112-115. [2] 李文娟,张树超.富血小板血浆在慢性难愈性创面治疗中的临床研究进展[J].中国输血杂志,2022,35(10):1092-1296. [3] MEZNERICS FA, FEHÉRVÁRI P, DEMBROVSZKY F, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Wound Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(24):7532. [4] LI S, XING F, YAN T, et al. The Efficiency and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Pers Med. 2023;13(3):430. [5] QU S, HU Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Clinical Studies on Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Chronic Cutaneous Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2022;11(2):56-69. [6] 程飚.浓缩血小板产品在创伤外科应用中的问题与思考[J].创伤外科杂志,2018,20(11):801-805. [7] ALVES R, GRIMALT R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018;4(1):18-24. [8] WU J, PIAO Y, LIU Q, et al. Platelet-rich plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: A superior alternative in regenerative medicine? Cell Prolif. 2021;54(12):e13123. [9] MOCHIZUKI T, USHIKI T, SUZUKI K, et al. Characterization of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Plasma Derived from Female Collage Athletes: A Cross-Sectional Cohort Study Focusing on Growth Factor, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(17):13592. [10] DEJNEK M, WITKOWSKI J, MOREIRA H, et al. Content of blood cell components, inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in autologous platelet-rich plasma obtained by various methods. World J Orthop. 2022;13(6):587-602. [11] SMITH OJ, TALAAT S, TOMOUK T, et al. An Evaluation of the Effect of Activation Methods on the Release of Growth Factors from Platelet-Rich Plasma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(2):404-411. [12] DOS SANTOS RG, SANTOS GS, ALKASS N, et al. The regenerative mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma: A review. Cytokine. 2021;144: 155560. [13] CECERSKA-HERYĆ E, GOSZKA M, SERWIN N, et al. Applications of the regenerative capacity of platelets in modern medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022;64:84-94. [14] MOCHIZUKI T, USHIKI T, WATANABE S, et al. The levels of TGFβ1, VEGF, PDGF-BB, and PF4 in platelet-rich plasma of professional soccer players: a cross-sectional pilot study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):465. [15] EVERTS P, ONISHI K, JAYARAM P, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7794. [16] HOU Y, WEN X, ZHOU L, et al. The value of platelet-rich plasma-derived extracellular vesicles in modern medicine. Ann Med. 2023; 55(2):2287705. [17] VARON D, HAYON Y, DASHEVSKY O, et al. Involvement of platelet derived microparticles in tumor metastasis and tissue regeneration. Thromb Res. 2012;130 Suppl 1:S98-99. [18] SHU QH, ZUO RT, CHU M, et al. Fiber-reinforced gelatin/β-cyclodextrin hydrogels loaded with platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes for diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2023;154:213640. [19] LOVISOLO F, CARTON F, GINO S, et al. Platelet rich plasma-derived microvesicles increased in vitro wound healing. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(18):9658-9664. [20] 袁霆,何能斌,丁坚,等.胞外囊泡在富血小板血浆修复组织中的作用[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(6):661-664. [21] HAO PC, BURNOUF T, CHIANG CW, et al. Enhanced diabetic wound healing using platelet-derived extracellular vesicles and reduced graphene oxide in polymer-coordinated hydrogels. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):318. [22] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, LI T, et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Promote Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Embedded in Collagen/Platelet-Rich Plasma Scaffold and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(40):e2303642. [23] MILLER CM, L ENNINGA EA, RIZZO SA, et al. Platelet-derived exosomes induce cell proliferation and wound healing in human endometrial cells. Regen Med. 2022;17(11):805-817. [24] SUADES R, PADRÓ T, VILAHUR G, et al. Platelet-released extracellular vesicles: the effects of thrombin activation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022; 79(3):190. [25] ZHU W, DONG Y, XU P, et al. A composite hydrogel containing resveratrol-laden nanoparticles and platelet-derived extracellular vesicles promotes wound healing in diabetic mice. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:212-230. [26] CHEN T, SONG P, HE M, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate derived from PRP-Exos promotes angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing via the S1PR1/AKT/FN1 signalling pathway. Burns Trauma. 2023;11:tkad003. [27] CAO W, MENG X, CAO F, et al. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promote diabetic wound healing via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. iScience. 2023;26(11):108236. [28] 李娇,李晓丰,李剑平.富血小板血浆来源的血小板细胞外囊泡分离技术与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(1):156-163. [29] 罗开云,王淑君,毛平平,等.不同保存方式对PRP相关生长因子影响的研究[J].临床输血与检验,2022,24(1):70-73. [30] 杨域,张卫,程飚.不同激活剂对人富血小板血浆形成凝胶及释放活性物质影响的实验研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2017,33(1):12-17. [31] 祁凤英,王蕾,李东东,等.可缓释富血小板血浆生长因子的新型自组装多肽水凝胶制备及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(15):2364-2370. [32] LI S, DONG Q, PENG X, et al. Self-Healing Hyaluronic Acid Nanocomposite Hydrogels with Platelet-Rich Plasma Impregnated for Skin Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2022;16(7):11346-11359. [33] ZHANG P, ZHOU L, WANG L, et al. A Novel Nanofiber Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma Promotes Wound Healing Through Enhancing the Survival of Fibroblasts. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25: 8712-8721. [34] BAKADIA BM, QAED AHMED AA, LAMBONI L, et al. Engineering homologous platelet-rich plasma, platelet-rich plasma-derived exosomes, and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-based dual-crosslinked hydrogels as bioactive diabetic wound dressings. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:74-94. [35] BEITIA M, DELGADO D, MERCADER J, et al. Action of Platelet-Rich Plasma on In Vitro Cellular Bioactivity: More than Platelets. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5367. [36] 王婧薷,杨荣华,陈晓东.自体富血小板血浆在糖尿病足治疗中的应用进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2018,13(2):139-141. [37] BABA K, YAMAZAKI Y, SONE Y, et al. An in vitro long-term study of cryopreserved umbilical cord blood-derived platelet-rich plasma containing growth factors-PDGF-BB, TGF-β, and VEGF. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(4):668-675. [38] 张铁凝,李全,巴特,等.富血小板血浆对人慢性难愈创面肉芽组织成纤维细胞体外增殖和迁移的影响[J].广西医学,2021,43(2): 205-208. [39] 李可可.负载脂肪来源干细胞和富血小板血浆的水凝胶用于压疮修复的研究[D].广州:广州医科大学,2021. [40] 田雅光,张倩,王洪一,等.富血小板血浆促进成纤维细胞的生长和迁移[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2019,30(8):487-490. [41] 张明宇,任博,杨镇,等.不同体积分数富血小板血浆对血管内皮细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(28): 4469-4474. [42] 林春博,姚军,农桔安,等.不同浓度富血小板血浆促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及向软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2020,37(12):2147-2152. [43] 郑波,申传安.富血小板血浆水凝胶增强脂肪源性干细胞的体内外血管再生潜能[J].中华烧伤杂志,2019,35(4):276. [44] 谭金娣,陈福扬,史欣,等.富血小板血浆对干细胞增殖及分化作用的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2017,37(8):743-745. [45] JIN P, PAN Q, LIN Y, et al. Platelets Facilitate Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer and Reducing Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023;2023:2345279. [46] LEVOUX J, PROLA A, LAFUSTE P, et al. Platelets Facilitate the Wound-Healing Capability of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Mitochondrial Transfer and Metabolic Reprogramming. Cell Metab. 2021;33(2): 283-299.e9. [47] BOUDREAU LH, FOULEM RD, LÉGER JL. The effects of functional platelet-derived extracellular mitochondria on the inflammatory phenotype of neutrophils. J Immunol. 2020; 204 (1_Supple): 67.23. [48] LAMBERT AW, WEINBERG RA. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21(5):325-338. [49] TIAN J, SHI D, LONG C, et al. Platelet concentrates may affect the formation of pathological scars by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Med Hypotheses. 2024;182:111227. [50] 李立.富血小板血浆通过NLRP3/IL-1β通路对糖尿病创面愈合的影响[D].上海:上海交通大学,2016. [51] ZHANG C, ZHU Y, LU S, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma with Endothelial Progenitor Cells Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing in Rats by Upregulating the Notch1 Signaling Pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2019; 2019:5920676. [52] EBRAHIM N, DESSOUKY AA, MOSTAFA O, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma accelerate diabetic wound healing by modulating the Notch pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):392. [53] 章程.富血小板血浆通过上调内皮祖细胞的Notch1信号通路促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合[D].上海:上海交通大学,2020. [54] GUO SC, TAO SC, YIN WJ, et al. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promote the re-epithelization of chronic cutaneous wounds via activation of YAP in a diabetic rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1): 81-96. [55] 许鹏程,贺伟峰,程飚.转录组水平探讨人富血小板血浆调控人表皮干细胞促创面再上皮化的机制[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020,36(10): 915-922. [56] ZHAO Q, XU J, HAN X, et al. Growth differentiation factor 10 induces angiogenesis to promote wound healing in rats with diabetic foot ulcers by activating TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;13:1013018. [57] 兰杰,孔来法,张得意.富血小板血浆对糖尿病大鼠难愈感染创面的作用机制[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2023,33(2):233-237. [58] 李名禄,马兵.富血小板血浆通过NF-κB p65/BMP-7信号通路促进骨髓基质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022, 38(2):78-81. [59] 王应辉,张娅,王自林,等.PRP通过NRF2/HO-1通路对LPS诱导的BV2小胶质细胞神经炎症的保护作用[J].中国输血杂志,2023, 36(1):19-25. [60] LIU Y, JIANG J, YE Y, et al. Stromal Vascular Fraction and Platelet-Rich Plasma Upregulate Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression to Promote Hair Growth via the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett. 2019;11(12): 1685-1692. [61] YANG J, GUO A, LI Q, et al. Platelet-rich plasma attenuates interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-2α. Tissue Cell. 2021;73: 101646. [62] LU HT, LU JW, LEE CH, et al. Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts. J Clin Med. 2021;10(19):4496. [63] TIAN J, HE X, LONG C, et al. Hypothesis: Platelet-rich plasma accelerate diabetic wound healing via dynamic modulation of multiple signaling pathways. Med Hypotheses. 2023;176:111097. [64] DEVEREAUX J, DARGAHI N, FRASER S, et al. Leucocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma Enhances Fibroblast and Extracellular Matrix Activity: Implications in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6519. [65] MOROZ A, DEFFUNE E. Platelet-rich plasma and chronic wounds: remaining fibronectin may influence matrix remodeling and regeneration success. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(11):1436-1439. [66] AKEDA K, AN HS, PICHIKA R, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) stimulates the extracellular matrix metabolism of porcine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus cells cultured in alginate beads. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):959-966. [67] 吴文伯,陈敏亮,吴焱秋,等.富血小板血浆(PRP)对大鼠光老化皮肤胶原蛋白、TGF-β及MMP-1表达的影响[J].中国美容医学, 2019,28(4):64-67. [68] ROTHAN HA, DJORDJEVIC I, BAHRANI H, et al. Three-dimensional culture environment increases the efficacy of platelet rich plasma releasate in prompting skin fibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix formation. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(10):1029-1038. [69] ANITUA E, ZALDUENDO M, TROYA M, et al. The inclusion of leukocytes into platelet rich plasma reduces scaffold stability and hinders extracellular matrix remodelling. Ann Anat. 2022;240:151853. [70] 施琳颖,李艳辉,许京菁,等.富血小板血浆通过调控AMPK信号通路刺激巨噬细胞向M2型转化的作用研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2023,31(5):1486-1491. [71] 刘瑜琳,汪德清,肖潘,等.富血小板血浆对巨噬细胞表型的作用及其影响因素研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2023,31(4):1155-1163. [72] YUNIATI R, INNELYA I, RACHMAWATI A, et al. Application of Topical Sucralfate and Topical Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Wound Healing in Diabetic Ulcer Rats Wound Model. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021;13:797-806. [73] PARK G, QIAN W, ZHANG MJ, et al. Platelet-rich plasma regulating the repair of ultraviolet B-induced acute tissue inflammation: adjusting macrophage polarization through the activin receptor-follistatin system. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):3125-3136. [74] UCHIYAMA R, TOYODA E, MAEHARA M, et al. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(5):2336. [75] ZHANG J, LUO Q, HU Q, et al. An injectable bioactive dressing based on platelet-rich plasma and nanoclay: Sustained release of deferoxamine to accelerate chronic wound healing. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(10):4318-4336. [76] ZHANG T, XIANG Z, LIU L, et al. Bioinspired Platelet-Anchored Electrospun Meshes for Tight Inflammation Manipulation and Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(10):e2300036. [77] ZHOU S, LI L, CHEN C, et al. Injectable gelatin microspheres loaded with platelet rich plasma improve wound healing by regulating early inflammation. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(9):1910-1920. [78] NAM SM, KIM YB. The effects of platelet-rich plasma on hypertrophic scars fibroblasts. Int Wound J. 2018;15(4):547-554. [79] SUN Q, GUO S, WANG CC, et al. Cross-talk between TGF-β/Smad pathway and Wnt/β-catenin pathway in pathological scar formation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):7631-7639. [80] EBRAHIMI Z, ALIMOHAMADI Y, JANANI M, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of scars, to suggest or not to suggest? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;16(10): 875-899. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [3] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [4] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [5] | De Ji, Suo Langda, Wei Yuchen, Wang Bin, Awangcuoji, Renqingcuomu, Cui Jiuzeng, Zhang Lei, Ba Gui. Comprehensive analysis of genes related to endometrial receptivity and alternative splicing events in northwest Tibetan cashmere goats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1429-1436. |
| [6] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [7] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [8] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [9] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [10] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [11] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [12] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [13] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [14] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [15] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||