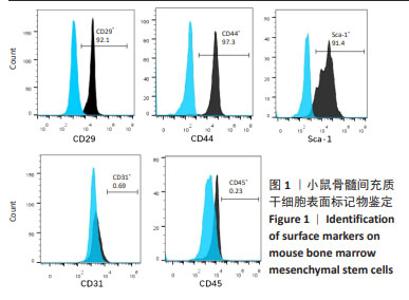
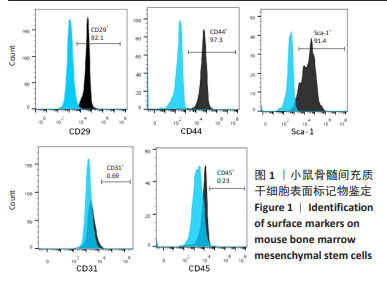
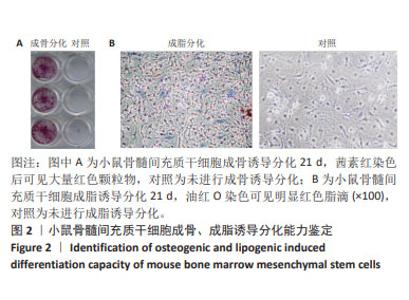
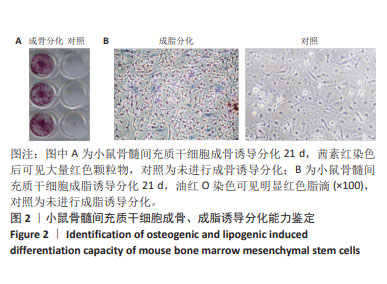
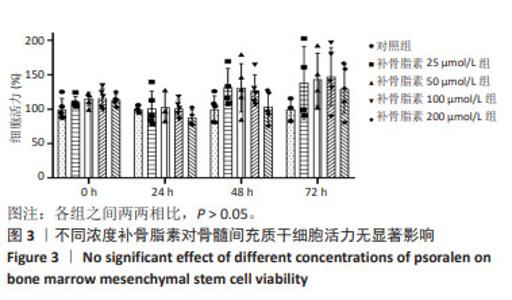
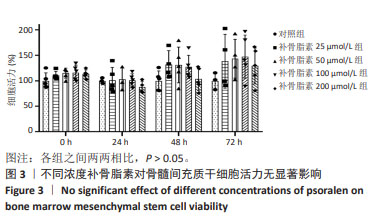
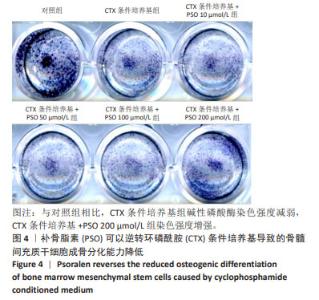
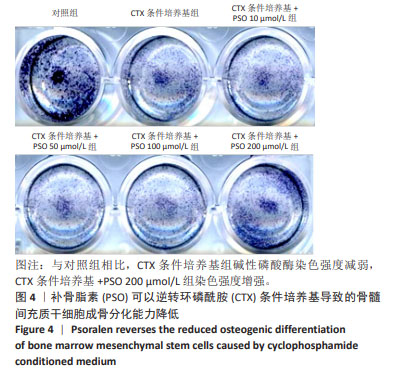
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 16-23.doi: 10.12307/2024.730
Previous Articles Next Articles
Restoration of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in mice inhibited by cyclophosphamide with psoralen
Wang Chenglong1 , Yang Zhilie2 , Chang Junli 2 , Zhao Yongjian2 , Zhao Dongfeng2 , Dai Weiwei 1 , Wu Hongjin1 , Zhang Jie1 , Wang Libo1 , Xie Ying3 , Tang Dezhi 2 , Wang Yongjun2 , Yang Yanping2
- 1 Central Laboratory for Science and Technology, 2 Institute of Spinal Disease, 3 Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Surgery, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China
-
Received:2023-09-09Accepted:2023-11-13Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-18 -
Contact:Yang Yanping, Researcher, Institute of Spinal Disease, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China -
About author:Wang Chenglong, PhD, Assistant researcher, Central Laboratory for Science and Technology, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China Yang Zhilie, Master, Institute of Spinal Disease, Longhua Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200032, China Wang Chenglong and Yang Zhilie contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Program), No. 81202708 (to WCL); National Key Research and Development Program, No. 2018YFC1704300 (to YYP); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81973877 and No. 82174408 (to YYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Chenglong , Yang Zhilie , Chang Junli , Zhao Yongjian , Zhao Dongfeng , Dai Weiwei , Wu Hongjin , Zhang Jie , Wang Libo , Xie Ying , Tang Dezhi , Wang Yongjun , Yang Yanping. Restoration of osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in mice inhibited by cyclophosphamide with psoralen[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 16-23.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
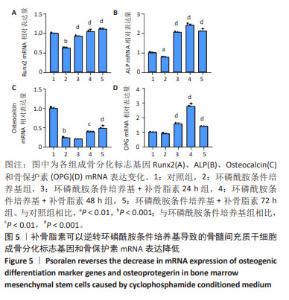
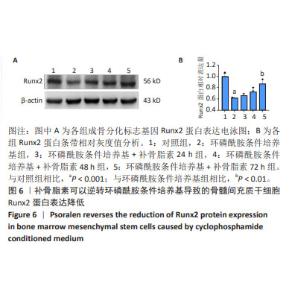
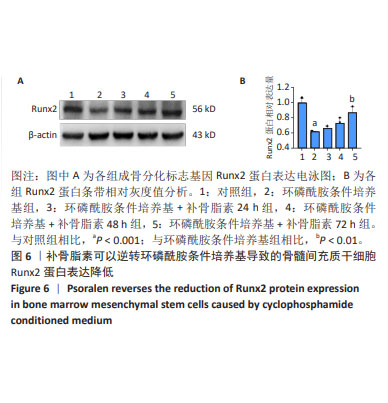
2.5 补骨脂素可以逆转环磷酰胺条件培养基导致的骨髓 间充质干细胞成骨分化标志基因 mRNA 和蛋白表达降 低 为了检测补骨脂素逆转骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能 力的机制,用 RT-qPCR 法检测了各组成骨分化标志基因 Runx2、ALP、Osteocalcin 和骨保护素 mRNA 表达变化,发 现与对照组相比,环磷酰胺条件培养基组 Runx2、ALP、 Osteocalcin成骨标志基因mRNA表达都显著降低(P < 0.01)。与环磷酰胺条件培养基组相比,环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补 骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组干预 24,48,72 h 的 Runx2、ALP 和 骨保护素 mRNA 表达均显著升高 (P < 0.001);干预 48, 72 h 的 Osteocalcin mRNA 表 达 显 著 升 高 (P < 0.01,P < 0.001),见图 5。Western blot 法检测各组成骨分化标志基 因 Runx2 蛋白表达变化,发现与对照组相比,环磷酰胺条 件培养基组 Runx2 蛋白表达显著降低 (P < 0.001)。与环磷 酰胺条件培养基组相比,环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组干预 72 h 的 Runx2 蛋白表达显著升高 (P < 0.01),见图 6,表明补骨脂素通过促进 Runx2、ALP 和 Osteocalcin mRNA 表达和 Runx2 蛋白表达而逆转骨髓间充 质干细胞的成骨分化能力。"

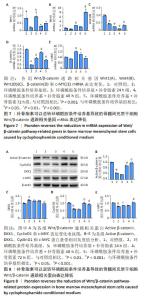
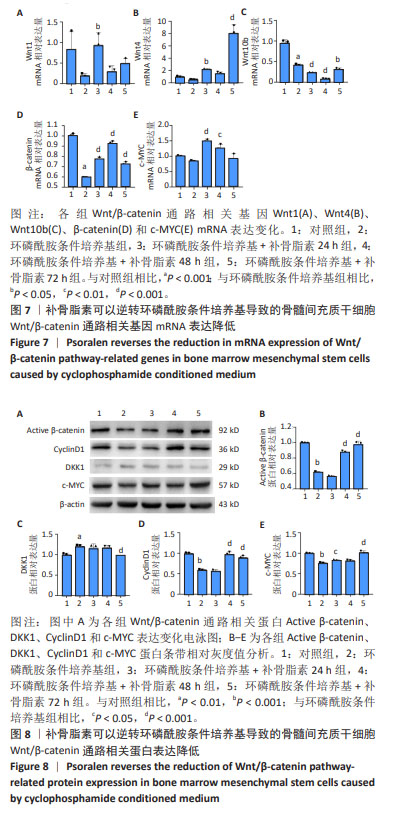
2.6 补骨脂素可以逆转环磷酰胺条件培养基导致的骨 髓间充质干细胞 Wnt/β-catenin 通路相关基因 mRNA 和 蛋白表达变化 为了进一步检测补骨脂素逆转骨髓间充 质干细胞成骨分化能力的机制,用 RT-qPCR 法检测了各 组 Wnt/β-catenin 通路相关基因 Wnt1、Wnt4、Wnt10b、 β-catenin 和 c-MYC mRNA 表 达 变 化, 与 对 照 组 相 比, 环 磷 酰 胺 条 件 培 养 基 组 β-catenin 和 Wnt10b mRNA 表 达都显著降低 (P < 0.001);与环磷酰胺条件培养基组相 比,环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组干 预 24,48,72 h 的 β-catenin mRNA 表达均显著升高 (P < 0.001);环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组 干预 24 h 使 Wnt1 和干预 24,72 h 使 Wnt4 mRNA 表达 均显著升高 (P < 0.05,P < 0.05,P < 0.001);环磷酰胺条 件 培 养 基 + 补 骨 脂 素 200 μmol/L 组 干 预 24,48,72 h 的 Wnt10b mRNA 表达均显著降低 (P < 0.001,P < 0.001, P < 0.05);环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组干预24,48 h的c-MYC mRNA表达均显著升高(P < 0.001, P < 0.01),见图 7。 Western blot 检测各组 Wnt/β-catenin 通路相关蛋白 表达变化,与对照组相比,环磷酰胺条件培养基组 Acttve β-catenin、c-MYC和CyclinD1蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.001), DKK1 蛋白表达显著升高 (P < 0.01)。与环磷酰胺条件培养 基组相比,环磷酰胺条件培养基 + 补骨脂素 200 μmol/L 组干预 48,72 h 的 Acttve β-catenin 和 CyclinD1 蛋白表达 均显著升高 (P < 0.001);干预 24,72 h 的 c-MYC 蛋白表达 均显著升高 (P < 0.05,P < 0.001);干预 72 h 的 DKK1 蛋白 表达显著降低 (P < 0.001),见图 8。表明补骨脂素对环磷 酰胺条件培养基导致的骨髓间充质干细胞 Wnt/β-catenin 通路相关基因 mRNA 和蛋白表达变化有逆转作用,推测补 骨脂素可能通过调节 Wnt/β-catenin 通路相关蛋白 ( 促进 Wnt1、Wnt4、β-catenin、c-MYC mRNA 和 Acttve β-catenin、 c-MYC、CyclinD1 蛋白表达,抑制 DKK1 蛋白表达 ) 而促进 成骨分化标志基因表达,最终达成恢复骨髓间充质干细 胞成骨分化能力的效果。 "
| [1] ADLER RA. Cancer treatment-induced bone loss. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2007;14(6):442-445. [2] PFEILSCHIFTER J, DIEL IJ. Osteoporosis due to cancer treatment: pathogenesis and management. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(7):1570-1593. [3] STAVA CJ, JIMENEZ C, HU MI, et al. Skeletal sequelae of cancer and cancer treatment. J Cancer Surviv. 2009;3(2):75-88. [4] COLEMAN RE, RATHBONE E, BROWN JE. Management of cancer treatment-induced bone loss. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 20139(6):365-374. [5] MICHAUD LB, GOODIN S. Cancer-treatment-induced bone loss, part 1. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(5):419-430. [6] DIANA A, CARLINO F, GIUNTA EF, et al. Cancer Treatment-Induced Bone Loss (CTIBL): State of the Art and Proper Management in Breast Cancer Pattents on Endocrine Therapy. Curr Treat Opttons Oncol. 2021;22(5):45. [7] WANG TM, SHIH C. Study of histomorphometric changes of the mandibular condyles in neonatal and juvenile rats affer administratton of cyclophosphamide. Acta Anat (Basel). 1986;127(2):93-99. [8] ZHAO D, WANG C, ZHAO Y, et al. Cyclophosphamide causes osteoporosis in C57BL/6 male mice: suppressive effects of cyclophosphamide on osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98163-98183. [9] NAJI A, EITOKU M, FAVIER B, et al. Biological functtons of mesenchymal stem cells and clinical implicattons. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(17): 3323-3348. [10] 吴铭 , 张岩 . 调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的 Wnt/β-catenin 信 号通路及相关因素 [J]. 中国组织工程研究 ,2021,25(1):116-122. [11] 李晋蒙 , 王新涛 .Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路在骨质疏松症和非骨质 疏松症环境下促进成骨的研究进展 [J]. 医学综述 ,2021,27(12): 2301-2305. [12] 李智奎 , 孔俊博 , 赵王林 . 淫羊藿苷调控 Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路 干预大鼠 MSCs 成脂成骨双向分化实验研究 [J]. 中国免疫学杂志 , 2019,35(24):2985-2990. [13] 马忠平 , 杨云 , 张志峰 , 等 . 芝麻素通过 Wnt/β-catenin 通路调控大 鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨细胞分化预防骨质疏松的作用研究 [J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志 , 2021,27(1):50-54+59. [14] 王一凤 , 樊国峰 , 陈胜乐 . 西红花苷对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠 Wnt/ β-Catenin 信号通路的影响 [J]. 临床和实验医学杂志 ,2022,21(1): 8-13. [15] REN Y, SONG X, TAN L, et al. A Review of the Pharmacological Properttes of Psoralen. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:571535. [16] 杨阔 , 高茸 , 马亚中 , 等 . 补骨脂素药理作用及肝毒性机制的研究 进展 [J]. 中草药 ,2021,52(1):289-298. [17] 董熠 , 刘丽佳 , 韩潞雯 , 等 . 香豆素类化学成分的药理作用及毒性 机制研究进展 [J]. 中草药 ,2023,54(16):5462-5472. [18] WANG X, XU C, HUA Y, et al. Psoralen induced cell cycle arrest by modulattng Wnt/β-catenin pathway in breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14001. [19] LI S, TU H. Psoralen inhibits the proliferatton and promotes apoptosis through endoplasmic rettculum stress in human osteosarcoma cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022;60(1):101-109. [20] WU Y, ZHANG YZ, LI MJ, et al. The In Vitro Effect of Psoralen on Glioma Based on Network Pharmacology and Potenttal Target Research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:1952891. [21] ZHENG W, LIN P, MA Y, et al. Psoralen promotes the expression of cyclin D1 in chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(5):1377-1384. [22] HUANG Y, LIAO L, SU H, et al. Psoralen accelerates osteogenic differenttatton of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by acttvattng the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(3):940. [23] 杨志烈 , 王成龙 , 赵东峰 , 等 . 淫羊藿苷对环磷酰胺化疗导致小鼠 骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化障碍的保护作用 [J]. 中国组织工程研 究 ,2016,20(6):777-784. [24] OGINO MH, TADI P. Cyclophosphamide. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2023. [25] SUN S, GUO Z, XIAO X, et al. Isolatton of mouse marrow mesenchymal progenitors by a novel and reliable method. Stem Cells. 2003;21(5): 527-535. [26] LI F, LI Q, HUANG X, et al. Psoralen sttmulates osteoblast proliferatton through the acttvatton of nuclear factor-κB-mitogen-acttvated protein kinase signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3):2385-2391. [27] HUANG Y, HOU Q, SU H, et al. miR-488 negattvely regulates osteogenic differenttatton of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by psoralen by targettng Runx2. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3746-3754. [28] YIN BF, LI ZL, YAN ZQ, et al. Psoralen alleviates radiatton-induced bone injury by rescuing skeletal stem cell stemness through AKTmediated upregulatton of GSK-3β and NRF2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):241. [29] ZHANG Q, PAN Y, JI J, et al. Roles and actton mechanisms of WNT4 in cell differenttatton and human diseases: a review. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):287. [30] ZHOU P, LI Y, DI R, et al. H19 and Foxc2 synergisttcally promotes osteogenic differenttatton of BMSCs via Wnt-β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8): 13799-13806. [31] LI X, LI Z, WANG J, et al. Wnt4 signaling mediates protecttve effects of melatonin on new bone formatton in an inffammatory environment. FASEB J. 2019;33(9):10126-10139. [32] CHANG J, SONOYAMA W, WANG Z, et al. Noncanonical Wnt-4 signaling enhances bone regeneratton of mesenchymal stem cells in craniofacial defects through acttvatton of p38 MAPK. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(42):30938-30948. [33] YU B, CHANG J, LIU Y, et al. Wnt4 signaling prevents skeletal aging and inffammatton by inhibittng nuclear factor-κB. Nat Med. 2014;20(9): 1009-1017. [34] CHAI L, ZHOU K, WANG S, et al. Psoralen and Bakuchiol Ameliorate M-CSF Plus RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differenttatton and Bone Resorptton Via Inhibitton of AKT and AP-1 Pathways in Vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2123-2133. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [3] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [4] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [5] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [6] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [7] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [8] | Lang Mecuo, Zhang Yilin, Wang Li. MiR-338-3p affects proliferation and apoptosis of alveolar bone osteoblasts by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 899-907. |
| [9] | Xiang Pan, Che Yanjun, Luo Zongping. Compressive stress induces degeneration of cartilaginous endplate cells through the SOST/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
| [10] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [11] | Ge Xiao, Zhao Zhuangzhuang, Guo Shuyu, Xu Rongyao. HOXA10 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7701-7708. |
| [12] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [13] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [14] | Liu Chengyuan, Guo Qianping. Differential effects of kartogenin on chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of rat and rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7490-7498. |
| [15] | Tang Haoxu, Liang Yingjie, Li Ce, Ding Penglin, Qian Minlong, Yuan Lingli. Deferoxamine alleviates the inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6821-6827. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||