Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 103-110.doi: 10.12307/2024.737
Previous Articles Next Articles
Endothelial cell-specific bone morphogenetic protein 2 affects angiogenesis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Yan Ru1, 2, 3, Wang Kairu2, 3, Zhang Feiyan1, 2, 3, Jia Shaobin1, 2, 3, Cong Guangzhi1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Cardiology, 2Institute of Medicine, 3Institute of Cardiology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-09-16Accepted:2023-11-17Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-18 -
Contact:Cong Guangzhi, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Cardiology, and Institute of Medicine, and Institute of Cardiology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yan Ru, Master, Attending physician, Department of Cardiology, and Institute of Medicine, and Institute of Cardiology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2022AAC03479 (to YR); Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2023AAC02071 (to CGZ); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060057, 82260086 (to JSB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Ru, Wang Kairu, Zhang Feiyan, Jia Shaobin, Cong Guangzhi. Endothelial cell-specific bone morphogenetic protein 2 affects angiogenesis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 103-110.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

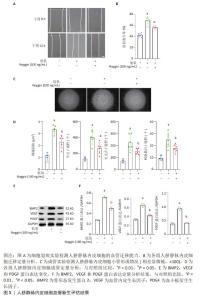
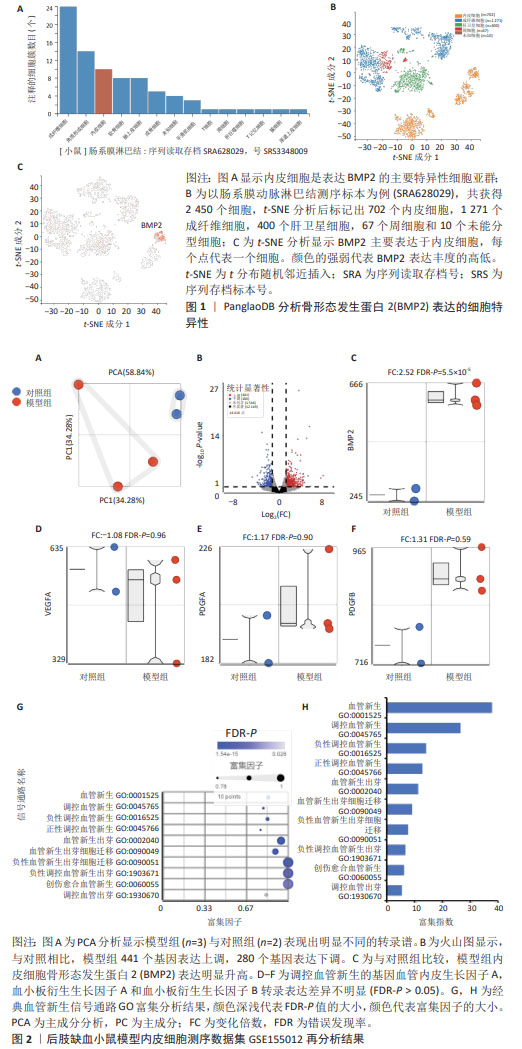
2.1 生物信息学分析结果 2.1.1 单细胞测序分析显示内皮细胞是骨形态发生蛋白 2 表达的主要细胞亚群 通过PanglaoDB数据库单细胞测序数据集进行荟萃分析显示,共纳入42个表达骨形态发生蛋白 2 的小鼠单细胞测序样本,分析标记出18个细胞簇,显示内皮细胞是骨形态发生蛋白 2 表达的主要细胞亚群。其中10个内皮细胞簇表达骨形态发生蛋白 2 。以样本SRS3348009为例,共测序出2 450个细胞,t-SNE降维分析标记出14个细胞簇,其中702个为内皮细胞,内皮细胞簇高表达骨形态发生蛋白 2 ,见图1。 2.1.2 后肢缺血模型内皮细胞骨形态发生蛋白 2 表达明显升高,激活血管新生通路 通过对后肢缺血小鼠模型分离出的内皮细胞Bulk RNA测序数据集GSE155012再分析,PCA显示模型组与对照组内皮细胞表现出完全不同的转录组特征,见图2A。火山图分析显示,与对照组比较,上调基因为441个,下调基因为280个,见图2B。模型组内皮细胞骨形态发生蛋白 2 表达明显升高,见图2C,调控血管新生的基因血管内皮生长因子A,血小板衍生生长因子A和血小板衍生生长因子B转录表达差异不明显(FDR-P > 0.05),见图2D-F。将差异基因进行28个经典血管新生信号通路GO富集分析可见,共10个血管新生通路明显富集,见图2G-H,依次为血管新生(GO:0001525),调控血管新生(GO:0045765),负性调控血管新生(GO:0045765),正性调控血管新生(GO:0045766),血管新生出芽(GO:0002040),血管新生出芽细胞迁移(GO:0090049),负性血管新生出芽细胞迁移(GO:0090051),负性调控血管新生出芽(GO:1903671),创伤愈合血管新生(GO:0060055)和调控血管出芽(GO:1930670)。以上结果显示:在后肢缺血小鼠模型内皮细胞高表达骨形态发生蛋白 2 ,同时血管新生通路明显激活,骨形态发生蛋白 2 高表达可能与血管新生通路激活有关。"

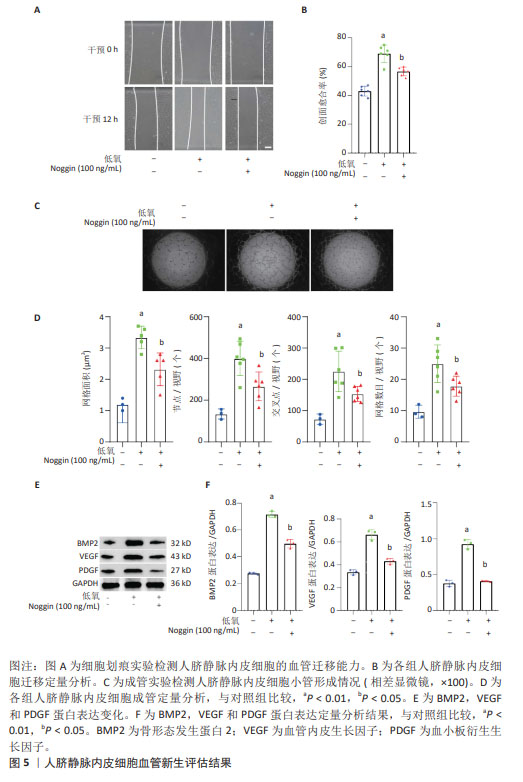
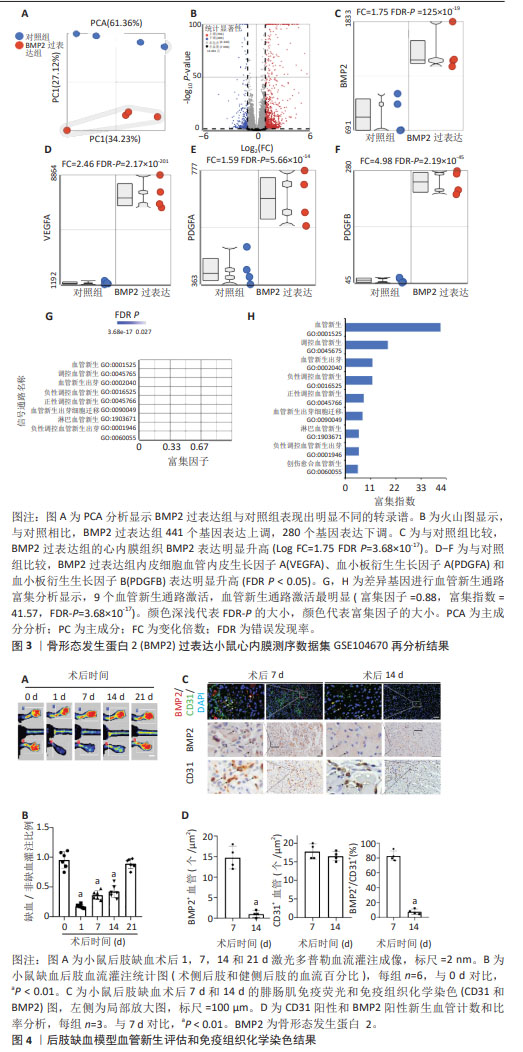
2.1.3 过表达骨形态发生蛋白2内皮细胞明显激活血管新生通路 通过对骨形态发生蛋白 2 过表达内皮细胞(小鼠心内膜组织)Bulk RNA测序数据集GSE104670进行再分析,PCA显示骨形态发生蛋白 2 过表达组与对照组细胞表现出完全不同的转录组特征,见图3A。火山图分析显示,与对照组比较,上调基因为766个,下调基因为289个,见图3B。模型组内皮细胞骨形态发生蛋白 2 表达明显升高(Log FC=1.75 FDR P=3.68×10-17),见图3C;血管新生关键基因血管内皮生长因子A,PDGDA和PDBFB表达明显升高(FDR P < 0.05),见图3D-F;将差异基因进行28个经典血管新生信号GO通路富集分析可见,其中9个血管新生通路明显富集(FDR P < 0.05),血管新生通路富集指数为(Enrichment score)41.57,富集因子为0.88(FDRP 3.68×10-17),见图3G-H。以上结果显示:在过表达骨形态发生蛋白 2 小鼠心内膜组织,且血管新生关键基因表达明显升高,血管新生通路明显激活。 2.2 动物体内实验验证结果——后肢缺血后骨形态发生蛋白 2 主要表达于新生血管内皮细胞周围 在小鼠后肢缺血模型,术后激光多普勒血流灌注成像显示,术后1 d缺血最重,未见血流信号,术后7 d和14 d缺血逐渐恢复,至术后21 d恢复到90%以上。通过免疫组织化学标记内皮细胞特异性因子CD31,发现术后腓肠动脉明显扩张,缺血坏死的肌肉组织周围可见明显的血管新生,7 d达高峰,7-14 d后逐步下降,同时骨形态发生蛋白 2 也在坏死肌肉组织周围高表达,与新生血管的位置一致,且在7 d表达量最高,14 d降低到正常水平,提示内皮细胞骨形态发生蛋白 2 可能在后肢缺血术后血管新生中发挥重要作用,见图4。 "
| [1] JEBARI-BENSLAIMAN S, GALICIA-GARCíA U, LARREA-SEBAL A, et al. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6): 3346. [2] HEROLD J, KALUCKA J. Angiogenesis in adipose tissue: the interplay between adipose and endothelial cells. Front Physiol. 2021;11:624903. [3] XU SW, ILYAS I, LITTLE PJ, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: from mechanism to pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73(3):924-967. [4] WU XK, REBOLL MR, KORF-KLINGEBIEL M, et al. Angiogenesis after acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(5):1257-1273. [5] LI TT, LAI YW, HAN X, et al. BMP2 as a promising anticancer approach: functions and molecular mechanisms. Invest New Drugs. 2022;40(6):1322-1332. [6] YANG PR, TRONCONE L, AUGUR ZM, et al. The role of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vascular calcification. Bone. 2020; 141:115542. [7] 裴建升,杨文娟,何静,等.骨形态发生蛋白2介导同型半胱氨酸促进血管钙化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25): 4027-4033. [8] LOWERY JW, ROSEN V. Bone morphogenetic protein-based therapeutic approaches. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(4): a022327. [9] OUYANG L, SU XY, LI WX, et al. ALKBH1-demethylated DNA N-6-methyladenine modification triggers vascular calcification via osteogenic reprogramming in chronic kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(14): e146985. [10] XIE F, CUI QK, WANG ZY, et al. ILF3 is responsible for hyperlipidemia-induced arteriosclerotic calcification by mediating BMP2 and STAT1 transcription. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021;161:39-52. [11] WANG S, HU SW, WANG J, et al. Conditioned medium from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits vascular calcification through blockade of the BMP2-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):160. [12] MAJIDPOOR J, MORTEZAEE K. Angiogenesis as a hallmark of solid tumors-clinical perspectives. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021;44(4): 715-737. [13] FRANZÉN O, BJÖRKEGREN JLM. Alona: a web server for single-cell RNA-seq analysis. Bioinformatics. 2020;36(12):3910-3912. [14] FU H, SUN Y, SHAO Y, et al. Interleukin 35 delays hindlimb ischemia-induced angiogenesis through regulating ROS-extracellular matrix but spares later regenerative angiogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:595813. [15] PAPOUTSI T, LUNA-ZURITA L, PRADOS B, et al. Bmp2 and Notch cooperate to pattern the embryonic endocardium. Development. 2018;145(13):dev163378. [16] NIIYAMA H, HUANG NF, ROLLINS MD, et al. Murine model of hindlimb ischemia. J Vis Exp. 2009;(23):1035. [17] HE WX, CHEN PX, CHEN QQ, et al. Cytokine storm: behind the scenes of the collateral circulation after acute myocardial infarction. Inflamm Res. 2022;71(10-11): 1143-1158. [18] SPADACCIO C, NENNA A, ROSE D, et al. The role of angiogenesis and arteriogenesisin myocardial infarction and coronary revascularization. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2022;15(5):1024-1048. [19] ZENG Q, MOUSA M, NADUKKANDY AS, et al. Understanding tumour endothelial cell heterogeneity and function from single-cell omics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23(8): 544-564. [20] YUAN F, PAN X, ZENG T, et al. Identifying cell-type specific genes and expression rules based on single-cell transcriptomic atlas data. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:350. [21] HEINKE J, JUSCHKAT M, CHARLET A, et al. Antagonism and synergy between extracellular BMP modulators Tsg and BMPER balance blood vessel formation. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(14):3082-3094. [22] DIVBAND B, AGHAZADEH M, AL-QAIM ZH, et al. Bioactive chitosan biguanidine-based injectable hydrogels as a novel BMP-2 and VEGF carrier for osteogenesis of dental pulp stem cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;273:118589. [23] KIM DS, LEE JK, KIM JH, et al. Advanced PLGA hybrid scaffold with a bioactive PDRN/BMP2 nanocomplex for angiogenesis and bone regeneration using human fetal MSCs. Sci Adv. 2021;7(50):eabj1083. [24] AL-SHABRAWEY M, HUSSEIN K, WANG F, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces non-canonical inflammatory and oxidative pathways in human retinal endothelial cells. Front Immunol. 2021;11:568795. [25] ZUO WH, ZENG P, CHEN X, et al. Promotive effects of bone morphogenetic protein 2 on angiogenesis in hepatocarcinoma via multiple signal pathways. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 37499. [26] KWON MH, RHO BY, CHOI MJ, et al. BMP2 restores erectile dysfunction through neurovascular regeneration and fibrosis reduction in diabetic mice. Andrology. 2023. doi: 10.1111/andr.13475. [27] LEE JH, PARTHIBAN P, JIN GZ, et al. Materials roles for promoting angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Prog Mater Sci. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100732. [28] UEMURA A, FRUTTIGER M, D’AMORE PA, et al. VEGFR1 signaling in retinal angiogenesis and microinflammation. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021; 84:100954. [29] YU J, DARDIK A. A murine model of hind limb ischemia to study angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2018; 1717:135-143. [30] BAI Y, LENG Y, YIN G, et al. Effects of combinations of BMP-2 with FGF-2 and/or VEGF on HUVECs angiogenesis in vitro and CAM angiogenesis in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;356(1):109-121. [31] MI BB, CHEN L, XIONG Y, et al. Saliva exosomes-derived UBE2O mRNA promotes angiogenesis in cutaneous wounds by targeting SMAD6. Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):68. [32] VISHWAKARMA S, KAUR I. Molecular mediators and regulators of retinal angiogenesis. Semin Ophthalmol. 2023; 38(2):124-133. [33] OMORPHOS NP, GAO CY, TAN SS, et al. Understanding angiogenesis and the role of angiogenic growth factors in the vascularisation of engineered tissues. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(1):941-950. [34] ZHANG W, ZHU C, WU YM, et al. VEGF and BMP-2 promote bone regeneration by facilitating bone marrow stem cell homing and differentiation. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;27:1-11; discussion 11-12. [35] RADY AAM, HAMDY SM, ABDEL-HAMID MA, et al. The role of VEGF and BMP-2 in stimulation of bone healing with using hybrid bio-composite scaffolds coated implants in animal model. Bull Natl Res Cent. 2020; 44(1):131. [36] NOVAK S, MADUNIC J, SHUM L, et al. PDGF inhibits BMP2-induced bone healing. NPJ Regen Med. 2023;8(1):3. [37] SCARFI S. Use of bone morphogenetic proteins in mesenchymal stem cell stimulation of cartilage and bone repair. World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(1):1-12. |
| [1] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [3] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [4] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [5] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [6] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [7] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [8] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [9] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [10] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [11] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [12] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [13] | Ba Yanhong, Gao Minghong, Chen Yingxin. Impact of graft thickness on corneal endothelial decompensation following simple Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1199-1207. |
| [14] | Ji Huihui, Jiang Xu, Zhang Zhimin, Xing Yunhong, Wang Liangliang, Li Na, Song Yuting, Luo Xuguang, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei. SR9009 combined with indolepropionic acid alleviates inflammation in C2C12 myoblasts through the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1220-1229. |
| [15] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||