Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 614-620.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2332
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis
Liu Fei1, Cui Yutao2, Liu He2
- 1Yixing Shanjuan Orthopedic Hospital, Yixing 214233, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-21Revised:2020-02-10Accepted:2020-03-18Online:2021-02-08Published:2020-11-24 -
Contact:Liu He, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Liu Fei, Associate chief physician, Yixing Shanjuan Orthopedic Hospital, Yixing 214233, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
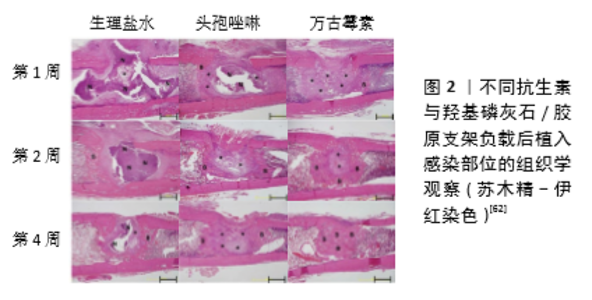
2.1 抗菌药物的选择 在慢性骨髓炎的长期治疗过程中,有效的抗菌药物治疗是成功治疗的关键。局部抗生素递送系统的原位植入为消除该区域的细菌、减少病灶部位死骨形成提供了很好的思路方法[17-18]。目前多种抗生素均已被成功应用于骨髓炎的预防及治疗。对于局部药物缓释系统中抗生素的选择,应当根据导致感染致病菌的种类及载体材料的性质进行确定。引起慢性骨髓炎最常见的微生物是金黄色葡萄球菌、A组β-溶血性链球菌和革兰阴性菌,特别是沙门氏菌、结核分枝杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[19-20]。根据慢性骨髓炎中的细菌学特征,局部药物递送系统中最常应用的药物是氨基糖苷类药物,其次是各种β-内酰胺类药物和喹诺酮类药物[21]。此外,研究显示抗生素的联合应用有助于减少个体毒性的产生,还可降低菌株出现耐药性的可能,并且可以治疗混合感染性骨髓炎[22]。 应用于局部缓释的抗生素还应适应于载体材料,药物应在与载体的复合过程中保持稳定性,例如PMMA骨水泥聚合的高温环境需要与之复合的抗生素有着较好的热稳定性。这其中的氨基糖苷类抗生素,包括链霉素、庆大霉素、丁胺卡那霉素和妥布霉素在高温下具有较好的稳定性,因此是较为理想的抗生素而常与PMMA骨水泥相结合,其他抗生素如头孢菌素类β-内酰胺类药物、环丙沙星和糖肽(万古霉素)也可与PMMA复合形成局部缓释系统[23-24]。相应的,药物的复合也能对载体产生不良的影响,比如利福平在与PMMA复合时会干扰到PMMA的聚合,因此无法与之联合应用[25]。羟基磷灰石是常用的抗生素载体,其晶体结构中具有2种不同的结合位点,即带正电荷的钙位点和带负电荷的磷位点,因此羟基磷灰石表面对许多物质如蛋白质、抗生素和生长因子具有很高的吸附能力[26-27]。大多数含羧基的抗生素如环丙沙星可通过羧基与羟基磷灰石晶体的钙离子结合而负载于羟基磷灰石载体,除此之外,环丙沙星中的氟离子也可与羟基磷灰石相结合而增强其与羟基磷灰石的结合力,因此环丙沙星可作为羟基磷灰石载体的良好选择之一[28-29]。除此之外,万古霉素、替加环素、头孢曲松、舒巴坦钠等也是羟基磷灰石载体的常用选择[30]。但同样的,抗生素在与羟基磷灰石复合后也会对羟基磷灰石晶体结构产生一定的影响,当抗生素浓度过大时,更多的药物可与羟基磷灰石发生相互作用,从而抑制羟基磷灰石结晶,导致晶粒尺寸和结晶度的减小[31]。 在药物递送系统中,大多数药物是通过自由扩散的方式从载体材料基质中释放到局部环境中,因此所选择的抗生素应当是水溶性的,并且在正常体温及体液环境下是可以稳定存在的[32]。对于慢性骨髓炎的长期治疗,局部药物缓释系统需要在较长时间内保持较高的药物浓度,但大多数药物释放系统在初期都存在爆发性的高浓度释放,因此在选择合适浓度的抗生素时应当考虑到初期较高浓度的药物是否会产生药物毒性而加剧局部骨坏死[33-34]。此外,局部应用的抗生素应具有不易进入循环系统而影响其他器官功能的能力[11]。 2.2 局部药物释放系统 材料工程和骨组织工程的发展,使得多种载体材料负载抗生素组成的局部药物缓释系统在骨髓炎治疗中得到了广泛应用。这些材料的成功应用是由于他们具有良好的生物相容性及药物负载能力,可在局部提供持续高浓度的药物。这一方法所提供的药物浓度可以达到10倍于系统用药,并且可以减少系统性并发症的发生[35-36]。目前,用于局部药物缓释系统的生物材料可主要分为不可分解材料及可分解材料。 2.2.1 不可降解性PMMA载体 药物释放:PMMA是目前最为常用的抗生素的药物载体,具有良好的生物相容性及令人满意的力学性能,可为骨髓炎局部提供良好的支撑[37]。PMMA粒子较大的表面积为抗生素药物的结合提供了充足空间,并且其具有优良的药物洗脱性能,为PMMA药物释放系统的应用奠定了良好基础[38]。在PMMA骨水泥中,抗生素的释放是通过在骨水泥表面直接溶解和扩散来实现的,因此载药PMMA中药物的释放速率主要取决于体液到达PMMA基质的方式[39-40]。PMMA由较为紧凑的基质组成,在植入体内后的初期仅有少量体液进入其基质外层,但是由于表层的药物结合通常较为不牢靠,造成药物释放的初期通常会出现爆发释放。这种爆发性释放可能来源于结合于载体表面和亚表面的药物,其可能会导致随后的持续释放阶段药物量减少,局部无法维持最低抑菌浓度,不能起到治疗效果,并且还可能增加耐药性致病菌的产生[41-42]。另一方面,在随后的药物释放期间,体液很难进入到PMMA基质内部,使得负载的药物无法充分释放。SCHURMAN等[43]的研究显示,负载庆大霉素的PMMA复合载体中具有药物释放能力的部分仅有100 μm的深度。并且有研究表明,从PMMA骨水泥中释放出的抗生素总量仅为总负载量的10%[44]。相比于手动混合的PMMA骨水泥,商用的载药PMMA通常会具有更加优良的药物释放曲线,这是因为商用载药PMMA中的药物在载体内的分布更加均匀,其采用了真空混合方法进行复合载体的制作,这一混合方式可改善骨水泥的性能和药物分布,有效减少高黏度水泥和低黏度水泥中大空隙的数量和大小,并且真空混合水泥中的空气夹杂物更少,使得复合系统拥有更好的孔隙率和释放曲线[45]。但是目前可能由于经济或法律上的限制,或者商业产品中的不足,临床上更多应用的仍然是将未载药的PMMA与抗生素手动混合。 PMMA载体的改进:PMMA载体孔隙率与药物的释放有着直接关系,孔隙率的增加有利于药物释放,此外,材料粒子大小也是药物释放的重要决定因素,较小的粒子会使载体拥有更高的表面体积比,促进药物的释放。同样,周围组织环境和液体也会对药物的释放产生影响[21,46]。因此,目前对于PMMA载体的改进措施的方法之一是增加其孔隙率。通过在PMMA骨水泥中加入添加剂(例如羟基磷灰石、甲基丙烯酸羟乙基酯单体和聚乙烯吡咯烷酮、葡聚糖、木糖醇和甘氨酸、乳糖和羟丙基甲基纤维素)可增加骨水泥的孔隙率,改善药物在局部的释放模式,提高对感染的控制效果[47-50]。但是,KLUIN等[44]认为提高PMMA载体的孔隙率虽然改善了初期的药物爆发释放现象,弥补了一定的不足,但是药物的释放仍然是不完全的。他们提出这一改进策略对于提高药物释放效率来说是不够的,因为在药物释放后期药物释放主要取决于药物的扩散。基于这一观点,通过与其他材料的联合增加PMMA载体的亲水性是另一种有前景的改进措施。PMMA复合材料水溶性的增加有利于体液的渗透,同时也有利于抗生素的溶解,可以在溶解液和药物之间形成相互连接的水通道,改善药物的释放[51]。OH等[52]将普朗尼克F68、万古霉素与PMMA通过真空混合的方法制作成一种亲水性的载药PMMA复合材料,用于骨髓炎的治疗。对于复合系统的机械性能研究显示,PMMA骨水泥的机械强度随着添加剂的增加而逐渐降低,但在普朗尼克F68含量小于7%时该释放系统的机械性能并未发生较大降低(P > 0.05),在普朗尼克F68含量含量达到10%时PMMA机械强度明显下降(P < 0.05)。药物代谢动力学显示,含有7%和10%普朗尼克F68的PMMA可在11周内持续释放万古霉素,释放率可以达到接近100%,并且可以超过6周的时间内持续发挥抑制金黄色葡萄球菌生长的作用。将其应用于大鼠股骨骨髓炎模型中发现,相比于普通PMMA负载万古霉素系统,这一局部释放系统发挥了更好的治疗效果。因此对于PMMA载体来说,进一步改进措施的研究是亟待进行的,混合材料的制备可能是一个潜在的解决方式。但是值得注意的是,这些添加剂的加入是否会对PMMA载体材料的机械性能产生影响[53],因为某些添加剂可能是与PMMA互不相溶的,这可能会导致PMMA机械性能的下降,并且在可溶解性的添加剂发生溶解后,可能会在载体材料内形成孔隙,因此添加剂的选择应当平衡好复合系统的生物活性和机械性能的关系[51-52]。 2.2.2 可降解材料 在慢性骨髓炎治疗中,以可生物降解材料为基础的抗生素局部递送系统是一个有吸引力的选择。这些载体可消除外科清创所产生的死腔,其所负载的抗生素随着材料降解后释放至局部,而降解后的材料也不会为细菌定植留下基质。此外,由于载体材料的可生物降解性,在假体移植后一般不需要二次手术切除。可生物降解载体可分为无机材料(如硫酸钙、骨支架等)和有机材料(如胶原蛋白、合成聚合物等)[54]。 (1)药物释放:与不可降解材料相似,抗生素在可降解材料中释放也依赖于药物的自由扩散。但不同的是,环境pH值、孔隙结构、溶胀率等影响可降解材料降解速率的因素,都将对药物释放产生很大影响[55]。在大部分可降解材料的药物释放过程中,这些因素会产生综合性的影响,因此其释放效率是多因素作用的结果。在药物释放过程中药物扩散在早期发挥着主要的作用,之后材料的降解对药物释放起到了更为关键的作用[56]。在药物与材料之间的相互作用如亲水-疏水作用下,药物从材料基质内扩散至周围环境中发挥作用[56-57]。材料降解速率对药物释放的影响则主要根据材料结构及理化性质的不同而不同。在可整体降解材料中如多孔水凝胶,材料基质的降解可能是由内至外同时进行的,因此随着材料的降解其内部基质形成较多孔隙,使得材料与周围环境的接触面积增加,加速材料降解,最终导致药物释放在晚期增加。而表面侵蚀性材料的降解是逐层进行的,因此药物仅从材料的最外层释放。此外,环境的pH值、材料浓度等多种因素也可影响药物的释放,而药物释放动力学研究对于药物缓释系统而言是非常重要的,因为对于骨髓炎的治疗需要在局部较长时间内维持合适浓度的药物,发挥更加优良的治疗效果[44]。 (2)有机材料: 胶原蛋白:用于抗生素递送系统的有机材料载体可分为天然材料和合成聚合物2大类,大部分天然材料来源于各种生物组织的提取物质,其中包括胶原蛋白、壳聚糖、明胶、凝血酶和自体血栓。胶原蛋白因其较为容易获得且具有较好的生物相容性,以及较低的成本而被广泛应用[58]。目前所用的胶原蛋白主要来源于牛的皮肤或者肌腱组织,其主要成分是纤维结缔组织,因此具有良好的生物相容性,药物可通过与胶原分子的游离氨基或羧基直接结合而与胶原复合[59]。尽管不同的灭菌方式会对胶原的降解特性产生一定的影响,但无论何种使用灭菌方式,胶原的降解时间至少也为8周左右。因此在胶原药物释放系统中,抗生素的释放主要取决于药物的扩散,因为在大多数复合系统中药物的扩散速率要大于降解速率[60-61]。此外,不同抗生素在胶原支架中的吸附效率不同,也会影响治疗效果,因此抗生素的选择也尤为重要。 EGAWA等[62]将羟基磷灰石与胶原结合制作成复合支架,用于骨髓炎治疗的研究。他们用8种不同的抗生素溶液通过浸泡震荡的方法与复合支架结合,研究不同抗生素的吸附效率差异,并随后研究了其抗菌治疗效果。结果显示在植入大鼠皮下14 d后,吸附率较高的二甲胺四环素、替考拉宁和万古霉素显示出了更好的抗菌作用,而吸附能力降低的抗生素包括头孢唑啉、头孢替安、哌拉西林的抗菌效果下降。在急性骨髓炎大鼠模型中,他们通过细菌数量、骨破坏程度和骨再生能力研究证实了负载万古霉素的羟基磷灰石/胶原复合支架比头孢唑啉具有更好的疗效(图2)。 合成聚合物:生物可降解合成聚合物作为局部抗生素给药系统越来越受欢迎,因为其具有更好的药物释放曲线和更持久的作用,并且在骨和软组织感染中具有良好的渗透性。目前常用的聚合物包括聚乳酸和聚乙醇酸,以及无定形聚二乳酸和聚乳酸与聚乙醇酸共聚物等[63]。体内聚合物的降解主要是通过水解发生的,本质上是一个整体腐蚀过程。聚合物转化为单体乳酸和乙醇酸,并引起局部pH值的下降。乳酸和乙醇酸在柠檬酸循环中氧化形成二氧化碳和水,乙醇酸在尿液中直接或间接排泄[64]。如今,聚乳酸与聚乙醇酸共聚物和无定形聚二乳酸由于其良好的降解和释放特性,已取代聚乳酸和聚乙醇酸植入物用于抗生素的递送。这些非晶态聚酯在2个阶段降解:首先,水扩散到非晶态聚合物基质中,水解开始,而聚合物保持机械惰性;然后,单体浓度的增加引起pH值升高,使得增加水解速率指数增加,导致结晶部分降解及聚合物解体[65]。无定形聚二乳酸需要1年以上的时间才能降解,因此大多数抗生素通过基质扩散而释放,而聚乳酸与聚乙醇酸共聚物在1-6个月内完全降解(取决于成分),其主要以微球、微胶囊、纳米球或纳米纤维的形式用于抗生素递送载体[66]。 与整体腐蚀的合成聚合物相比,采用表面腐蚀的聚合物可以更好地调节释放速率。聚(三甲基碳酸酯)是一个很好的选择,其具有良好的生物相容性。相比于聚乳酸与聚乙醇酸共聚物或无定形聚二乳酸载体,聚(三甲基碳酸酯)可在不释放酸性产物的情况下降解,其降解模式是由巨噬细胞介导的胆固醇酯酶和超氧阴离子自由基的酶促表面侵蚀模式,聚(三甲基碳酸酯)可在体内完全降解,并有助于促进骨再生[67-68]。体外数据表明,聚(三甲基碳酸酯)的分子量可以调节以控制各种抗生素的释放速率,并且可以获得理想的零级缓释曲线[69]。ZHANG等[70]通过搅拌混匀的方法将万古霉素/壳聚糖纳米颗粒与聚(三甲基碳酸酯)混合成均一的复合物用于骨髓炎的治疗。该复合系统可在36 d内持续缓慢释放大约(83.57±0.02)%的万古霉素,并且没有初期的爆发性释放。体外研究显示该复合系统具有良好的生物相容性,并且具有很好的抗菌性能,将其植入金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的兔骨髓炎模型后发挥了优秀的抗菌和促进成骨作用。 (3)无机材料:慢性骨髓炎患者在大量坏死骨的根治性清创后需要进行骨移植,以防感染部位出现大的骨缺损。在这些情况下可以选择应用含有抗生素的无机骨移植材料进行填充,常用的植骨材料有自体骨、同种异体骨和骨替代物。自体骨具有良好的成骨诱导和成骨特性,可促进新骨形成,但同时自体骨移植也因为供区的多种并发症而受到限制[71]。在慢性骨髓炎的治疗中,松质骨可能是一种更好的载体,因为它比皮质骨具有更多结合抗生素的表面积,而且其多孔结构有利于新骨的生长。在制备的抗生素溶液中浸渍移植物后即可实现抗生素与移植物的结合,而复合材料的抗生素释放特点是快速的扩散性释放,特别是在最初的几个小时内[72-73]。 硫酸钙是骨替代物中最为常用的可降解载体材料,它是一种天然的生物陶瓷。半水硫酸钙因具有更加纯净的α-半水晶体而具有很好的机械性能,从而被应用于慢性骨髓炎的长期治疗。硫酸钙可负载水溶性抗生素,因此氨基糖苷类、万古霉素、达托霉素和替考拉宁是常见的抗生素选择[74]。负载硫酸钙的复合系统在应用于局部后通过材料的降解而释放抗生素,并且其降解产物还可以提供一个促进血管生长和成骨的骨传导环境。但负载药物的硫酸钙支架同样存在初期的爆发性释放问题,并且可能比PMMA支架更加严重[75]。为了解决这一问题,在支架表面增加涂层可延缓药物的释放。BEENKEN等[76]将硫酸钙支架与达托霉素混合后在其表面涂覆壳聚糖,研究了有机涂层对于药物释放曲线的影响。结果表明与未涂层的硫酸钙支架相比,涂层所提供的物理屏障明显减缓了抗生素的初期释放,并且有效延长了抗生素释放时间,达托霉素可在局部保持在100 g/L以上的药物浓度,并持续超过10 d。而相比于未涂层支架,该涂层系统具有更加良好的抗菌效果。"

| [1] BHATTACHARYA R, KUNDU B, NANDI SK, et al. Systematic approach to treat chronic osteomyelitis through localized drug delivery system: bench to bed side.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2013;33(7): 3986-3993. [2] LINDFORS NC, HYVONEN P, NYYSSONEN M, et al. Bioactive glass S53P4 as bone graft substitute in treatment of osteomyelitis.Bone. 2010; 47(2):212-218. [3] 刘继权, 刘玙平, 王玉辉, 等.载抗生素硫酸钙混合髂骨植骨联合穿支皮瓣移植治疗胫骨慢性骨髓炎[J].中医正骨,2019,31(2): 67-71. [4] FRANK D, MONTSKO G, JURICSKAY I, et al. Clindamycin release determined by high performance liquid chromatography from a novel low-cost local drug delivery system: a new potential treatment option for chronic osteomyelitis.J Chemother.2011;23(5):282-284. [5] 靳国强,赵蕾,韩宗昌,等.感染骨段切除、短缩外固定结合载敏感抗生素硫酸钙骨粉局部填塞治疗尺桡骨骨髓炎[J].中医正骨, 2019,31(11): 59-63. [6] GITELIS S, BREBACH GT. The treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with a biodegradable antibiotic-impregnated implant.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).2002;10(1):53-60. [7] 姜楠,覃承诃,余斌.骨折内固定术后感染抗生素治疗的新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(16):1489-1492 [8] MENG E, HOANG T. Micro-and nano-fabricated implantable drug-delivery systems.Ther Deliv.2012;3(12):1457-1467. [9] DING H, ZHAO CJ, CUI X, et al. A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement as an antibiotic delivery vehicle for treating osteomyelitis. PLoS One.2014;9(1):e85472. [10] 崔宇韬,刘贺,冀璇,等.智能响应性水凝胶作为药物递送系统的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5508-5515. [11] NANDI SK, BISWANATH KUNDU B, DE DK, et al. Local antibiotic delivery systems for the treatment of osteomyelitis–A review.Mat Sci Eng C. 2009;29(8):2478-2485. [12] NEUT D, VAN DE BELT H, VAN HORN JR, et al. Residual gentamicin- release from antibiotic-loaded polymethylmethacrylate beads after 5 years of implantation.Biomaterials. 2003;24(10):1829-1831. [13] KIRAN ASK, KIZHAKEYIL A, RAMALINGAM R, et al. Drug loaded electrospun polymer/ceramic composite nanofibrous coatings on titanium for implant related infections.Ceram Int.2019; 45(15): 18710-18720. [14] KRISHNAN AG, JAYARAM L, BISWAS R, et al. Evaluation of antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of ciprofloxacin loaded gelatin-hydroxyapatite scaffolds as a local drug delivery system for osteomyelitis treatment.Tissue Eng Part A.2015;21(7-8):1422-1431. [15] PAPAGELOPOULOS PJ, MAVROGENIS AF, TSIODRAS S, et al. Calcium sulphate delivery system with tobramycin for the treatment of chronic calcaneal osteomyelitis.J Int Med Res.2006;34(6):704-712. [16] VAN VUGT TAG, WALRAVEN JMB, GEURTS JAP, et al. Arts.Antibiotic-Loaded Collagen Sponges in Clinical Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(24):2153-2161. [17] NAIR MB, KRETLOW JD, MIKOS AG, et al. Infection and tissue engineering in segmental bone defects--a mini review.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011;22(5):721-725. [18] 葛茶娜,黎飞猛,林周胜,等.抗生素缓释系统载体在慢性骨髓炎治疗中的应用研究进展[J].成都医学院学报,2016,11(1):134-137. [19] RISSING JP. Antimicrobial therapy for chronic osteomyelitis in adults: role of the quinolones.Clin Infect Dis.1997;25(6):1327-1333. [20] GALANAKIS N, GIAMARELLOU H, MOUSSAS T, et al. Chronic osteomyelitis caused by multi-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: evaluation of treatment with newer quinolones after prolonged follow-up. J Antimicrob Chemother.1997;39(2):241-246. [21] NANDI SK, BANDYOPADHYAY S, DAS P, et al. Understanding osteomyelitis and its treatment through local drug delivery system. Biotechnol Adv.2016;34(8):1305-1317. [22] RUSHTON N. Applications of local antibiotic therapy.Eur J Surg Suppl. 1997;(578):27-30. [23] REGIS D, SANDRI A, SAMAILA E, et al. Release of gentamicin and vancomycin from preformed spacers in infected total hip arthroplasties: measurement of concentrations and inhibitory activity in patients’ drainage fluids and serum.ScientificWorldJournal.2013:752184. [24] CHEN DW, CHANG Y, HSIEH PH, et al. The influence of storage temperature on the antibiotic release of vancomycin-loaded polymethylmethacrylate.ScientificWorldJournal.2013:573526. [25] ANGUITA-ALONSO P, ROUSE MS, PIPER KE, et al. Comparative study of antimicrobial release kinetics from polymethylmethacrylate. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2006;445:239-244. [26] HILBRIG F, FREITAG R. Isolation and purification of recombinant proteins, antibodies and plasmid DNA with hydroxyapatite chromatography. Biotechnol J.2012;7(1):90-102. [27] HONG MH, SON JS, KIM KM, et al. Drug-loaded porous spherical hydroxyapatite granules for bone regeneration.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(2):349-355. [28] DEVANAND VENKATASUBBU G, RAMASAMY S, RAMAKRISHNAN V, et al. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite as carrier material for controlled delivery of ciprofloxacin.3 Biotech. 2011;1(3):173-186. [29] IVASHCHENKO OU, BAHLEY NM, PROTSENKO LS, et al. Kinetics of Rifampicin Release In Vitro from Iron(III) Oxide and Hydroxyapatite Nanopowders. Adv Sci Lett.2010;3(2):168-173. [30] JOOSTEN U, JOIST A, GOSHEGER G, et al. Effectiveness of hydroxyapatite-vancomycin bone cement in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus induced chronic osteomyelitis.Biomaterials. 2005;26(25):5251-5258. [31] KUMAR GS, GOVINDAN R, GIRIJA EK. In situ synthesis, characterization and in vitro studies of ciprofloxacin loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for the treatment of osteomyelitis.J Mater Chem B.2014;2:5052-5060. [32] CUI Y, ZHU T, LI D, et al. Bisphosphonate-Functionalized Scaffolds for Enhanced Bone Regeneration.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(23): e1901073. [33] GALVEZ-LOPEZ R, PENA-MONJE A, ANTELO-LORENZO R, et al. Elution kinetics, antimicrobial activity, and mechanical properties of 11 different antibiotic loaded acrylic bone cement.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.2014;78(1):70-74. [34] PARK KW, YUN YP, KIM SE, et al. The Effect of Alendronate Loaded Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds on Bone Regeneration in a Rat Tibial Defect Model.Int J Mol Sci.2015;16(11):26738-26753. [35] ZHANG X, JIA W, GU Y, et al. Teicoplanin-loaded borate bioactive glass implants for treating chronic bone infection in a rabbit tibia osteomyelitis model.Biomaterials.2010;31(22):5865-5874. [36] KANELLAKOPOULOU K, GALANOPOULOS I, SORANOGLOU V, et al. Treatment of experimental osteomyelitis caused by methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a synthetic carrier of calcium sulphate (Stimulan) releasing moxifloxacin.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33(4):354-359. [37] 贾崇哲,唐海,陈浩,贾璞,包利.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的基础研究进展[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(5):519-521. [38] LALIDOU F, KOLIOS G, DROSOS GI. Bone infections and bone graft substitutes for local antibiotic therapy.Surg Technol Int. 2014;24: 353-362. [39] VAN DE BELT H, NEUT D, SCHENK W, et al. Infection of orthopedic implants and the use of antibiotic-loaded bone cements. A review.Acta Orthop Scand.2001;72(6):557-571. [40] KHOURY AE, LAM K, ELLIS B, et al. Prevention and control of bacterial infections associated with medical devices.ASAIO J. 1992;38(3): M174-M178. [41] LEWIS G. Properties of antibiotic-loaded acrylic bone cements for use in cemented arthroplasties: a state-of-the-art review.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;89(2):558-574. [42] VAN DE BELT H, NEUT D, SCHENK W, et al. Gentamicin release from polymethylmethacrylate bone cements and Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation.Acta Orthop Scand.2000;71(6):625-629. [43] SCHURMAN DJ, TRINDADE C, HIRSHMAN HP, et al. Antibiotic-acrylic bone cement composites. Studies of gentamicin and Palacos.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1978;60(7):978-984. [44] KLUIN OS, VAN DER MEI HC, BUSSCHER HJ, et al. Biodegradable vs non-biodegradable antibiotic delivery devices in the treatment of osteomyelitis.Expert Opin Drug Deliv.2013;10(3):341-351. [45] NEUT D, VAN DE BELT H, VAN HORN JR, et al. The effect of mixing on gentamicin release from polymethylmethacrylate bone cements. Acta Orthop Scand.2003;74(6):670-676. [46] PITHANKUAKUL K, SAMRANVEDHYA W, VISUTIPOL B, et al. The effects of different mixing speeds on the elution and strength of high-dose antibiotic-loaded bone cement created with the hand-mixed technique.J Arthroplasty.2015;30(5):858-863. [47] PADILLA S, DEL REAL RP, VALLET-REGI M. In vitro release of gentamicin from OHAp/PEMA/PMMA samples.J Control Release. 2002;83(3): 343-352. [48] RASYID HN, VAN DER MEI HC, FRIJLINK HW, et al. Concepts for increasing gentamicin release from handmade bone cement beads. Acta Orthop.2009;80(5):508-513. [49] MCLAREN AC, MCLAREN SG, SMELTZER M. Xylitol and glycine fillers increase permeability of PMMA to enhance elution of daptomycin. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2006;451:25-28. [50] VIRTO MR, FRUTOS P, TORRADO S, et al. Gentamicin release from modified acrylic bone cements with lactose and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose.Biomaterials.2003;24(1):79-87. [51] FRUTOS P, DIEZ-PENA E, FRUTOS G, et al. Release of gentamicin sulphate from a modified commercial bone cement. Effect of (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) comonomer and poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) additive on release mechanism and kinetics. Biomaterials.2002;23(18):3787-3797. [52] OH EJ, OH SH, LEE IS, et al. Antibiotic-eluting hydrophilized PMMA bone cement with prolonged bactericidal effect for the treatment of osteomyelitis.J Biomater Appl.2016;30(10):1534-1544. [53] 梁佩清,全昌云,康婷,等.改性PMMA骨水泥的临床研究进展[J].功能材料,2017,48(2):2048-2054. [54] MCLAREN AC. Alternative materials to acrylic bone cement for delivery of depot antibiotics in orthopaedic infections.Clin Orthop Relat R.2004; (427):101-106. [55] SIEPMANN J, GOPFERICH A. Mathematical modeling of bioerodible, polymeric drug delivery systems.Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2001;48(2-3): 229-247. [56] POSADOWSKA U, PARIZEK M, FILOVA E, et al. Injectable nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel system for local delivery of sodium alendronate.Int J Pharmaceut.2015;485(1-2):31-40. [57] BOSE S, TARAFDER S. Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering:A review. Acta Biomater.2012;8(4):1401-1421. [58] ZILBERMAN M, ELSNER JJ. Antibiotic-eluting medical devices for various applications. J Control Release.2008;130(3):202-215. [59] RUSZCZAK Z, FRIESS W. Collagen as a carrier for on-site delivery of antibacterial drugs.Adv Drug Deliver Rev.2003;55(12):1679-1698. [60] STEMBERGER A, GRIMM H, BADER F, et al. Local treatment of bone and soft tissue infections with the collagen-gentamicin sponge.Eur J Surg Suppl.1997;(578):17-26. [61] RUTTEN HJ, NIJHUIS PH. Prevention of wound infection in elective colorectal surgery by local application of a gentamicin-containing collagen sponge.Eur J Surg Suppl.1997(578):31-35. [62] EGAWA S, HIRAI K, MATSUMOTO R, et al. Efficacy of Antibiotic-Loaded Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Composites Is Dependent on Adsorbability for Treating Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis in Rats.J Orthop Res. 2020;38(4):843-851. [63] GARVIN K, FESCHUK C. Polylactide-polyglycolide antibiotic implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;(437):105-110. [64] DING AG, SCHWENDEMAN SP. Acidic microclimate pH distribution in PLGA microspheres monitored by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Pharm Res.2008;25(9):2041-2052. [65] ULERY BD, NAIR LS, LAURENCIN CT. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polymers.J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 2011;49(12): 832-864. [66] UEDA H, TABATA Y. Polyhydroxyalkanonate derivatives in current clinical applications and trials.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2003;55(4):501-518. [67] ZHANG Z, KUIJER R, BULSTRA SK, et al. The in vivo and in vitro degradation behavior of poly(trimethylene carbonate).Biomaterials. 2006;27(9):1741-1748. [68] BAT E, VAN KOOTEN TG, FEIJEN J, et al. Macrophage-mediated erosion of gamma irradiated poly(trimethylene carbonate) films. Biomaterials.2009;30(22):3652-3661. [69] KLUIN OS, VAN DER MEI HC, BUSSCHER HJ, et al. A surface-eroding antibiotic delivery system based on poly-(trimethylene carbonate). Biomaterials.2009;30(27):4738-4742. [70] ZHANG Y, LIANG RJ, XU JJ, et al. Efficient induction of antimicrobial activity with vancomycin nanoparticle-loaded poly(trimethylene carbonate) localized drug delivery system.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12:1201-1214. [71] MARTIN V, BETTENCOURT A. Bone regeneration: Biomaterials as local delivery systems with improved osteoinductive properties.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;82:363-371. [72] BUTTARO M, COMBA F, PICCALUGA F. Vancomycin-supplemented cancellous bone allografts in hip revision surgery.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;461:74-80. [73] WITSØ E, PERSEN L, BENUM P, et al .High local concentrations without systemic adverse effects after impaction of netilmicin-impregnated bone.Acta Orthop Scand.2004;75(3):339-346. [74] WEBB ND, MCCANLESS JD, COURTNEY HS, et al. Daptomycin eluted from calcium sulfate appears effective against Staphylococcus. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;466(6):1383-1387. [75] THOMAS DB, BROOKS DE, BICE TG, et al. Tobramycin-impregnated calcium sulfate prevents infection in contaminated wounds.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;441:366-371. [76] BEENKEN KE, SMITH JK, SKINNER RA, et al. Chitosan coating to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of calcium sulfate-based antibiotic therapy in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis.J Biomater Appl. 2014;29(4): 514-523. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||