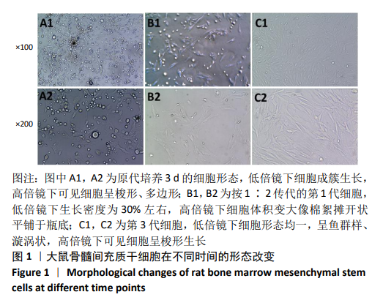
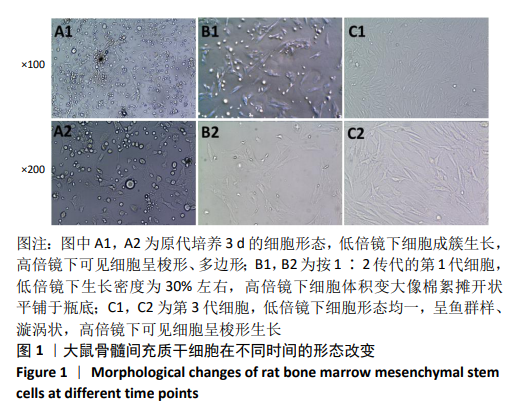
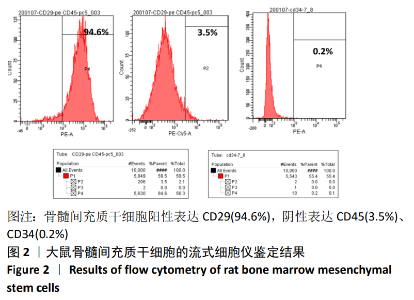
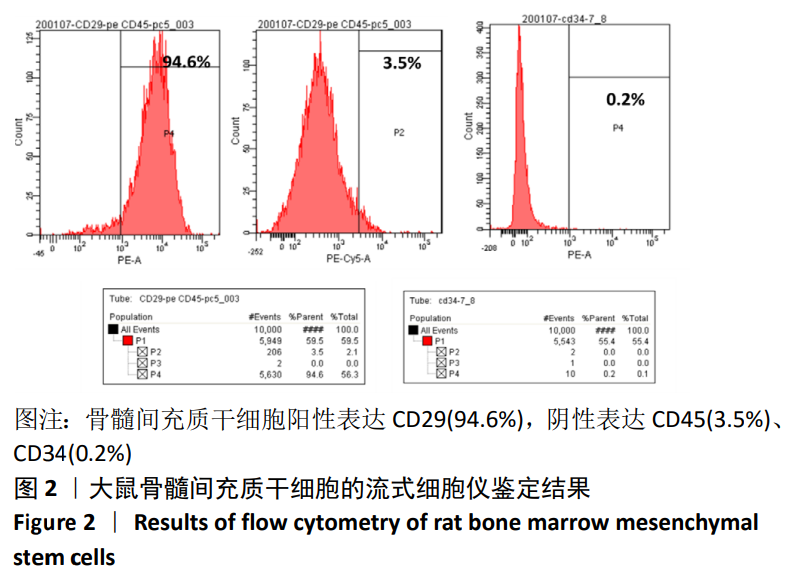
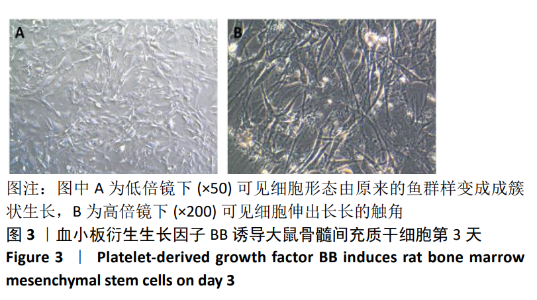
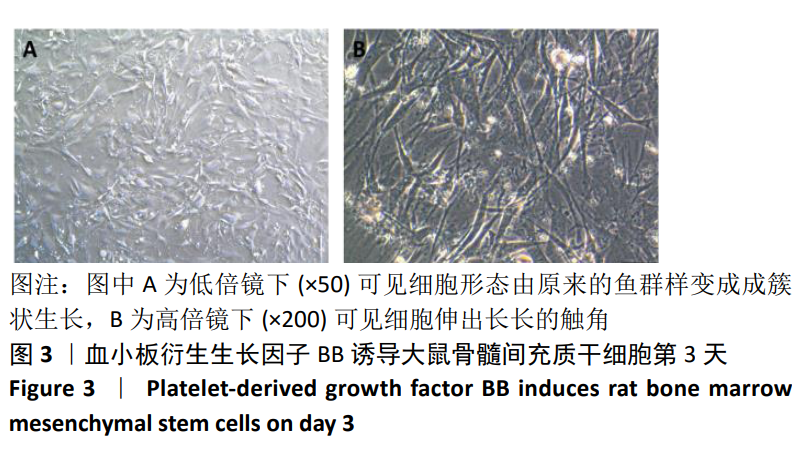
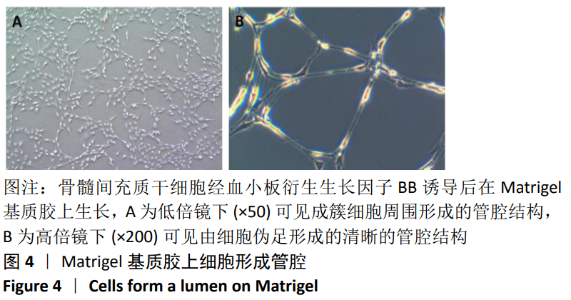
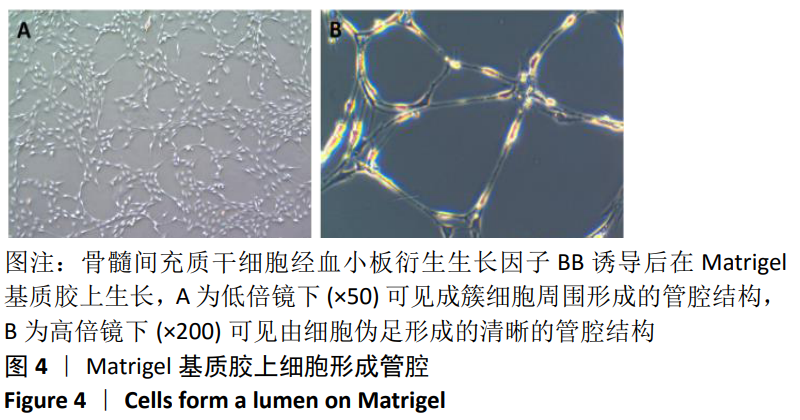
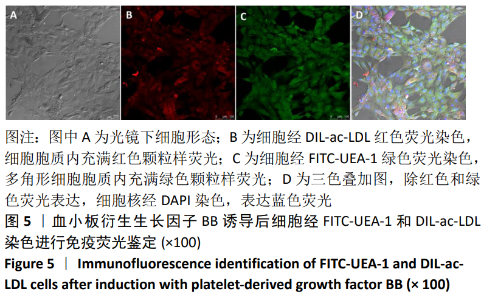
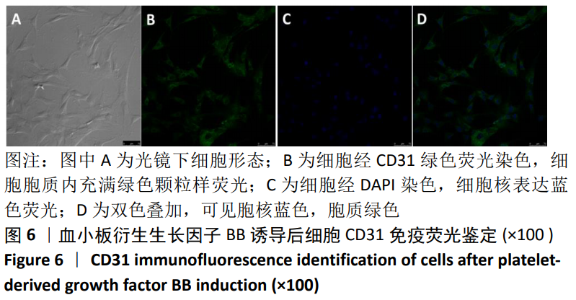
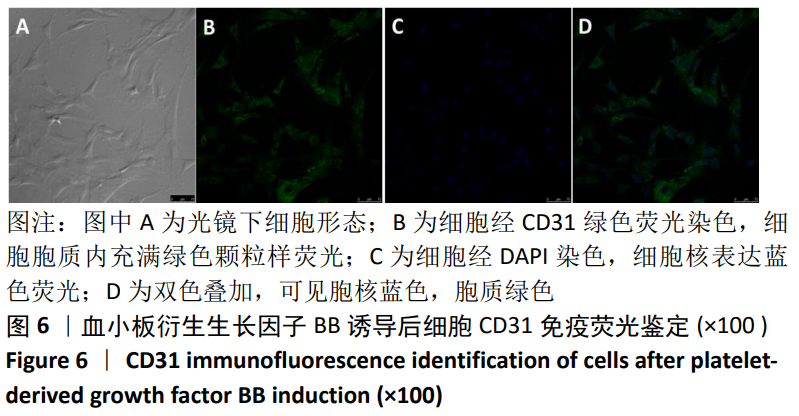
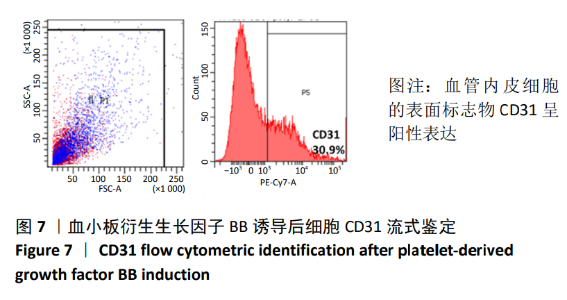
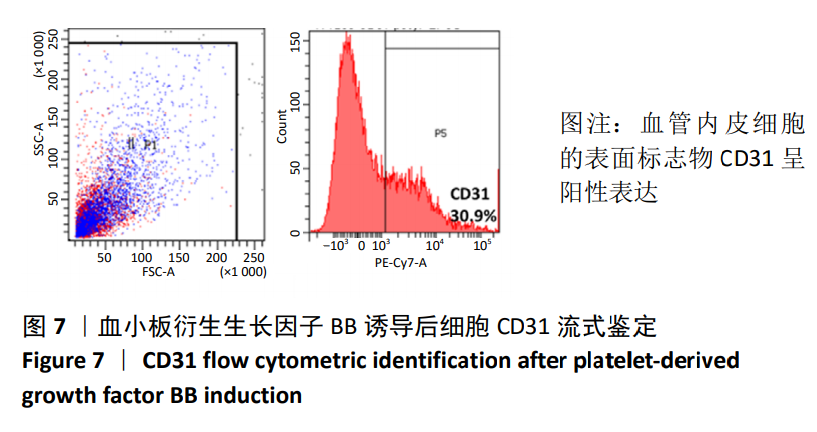
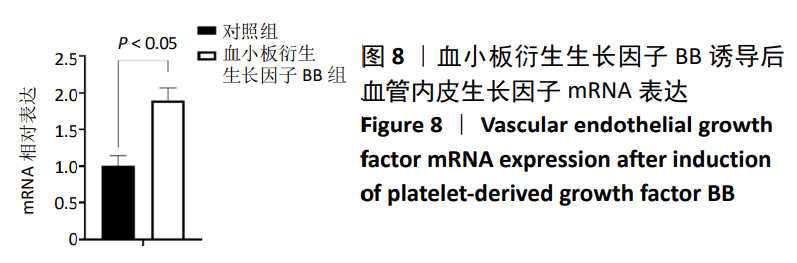
[1] TSUDA H, WADA T, YAMASHITA T, et al. Enhanced osteoinduction by mesenchymal stem cells transfected with a fiber-mutant adenoviral BMP2 gene. J Gene Med. 2005;7(10):1322-1334.
[2] HYSLOP LA, ARMSTRONG L, STOJKOVIC M, et al. Human embryonic stem cells: biology and clinical implications. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2005; 7(19):1-21.
[3] YANG J, ZHOU W, ZHENG W, et al. Effects of myocardial transplantation of marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected with vascular endothelial growth factor for the improvement of heart function and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Cardiology. 2007;107(1): 17-29.
[4] HE J, HAN X, WANG S, et al. Cell sheets of co-cultured BMP-2-modified bone marrow stromal cells and endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone regeneration in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(5):3333-3340.
[5] LIU Y, LI M, YIN Z, et al. SUMO-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promoted the repair of articular cartilage in rats. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(2):560-568.
[6] WANG Y, CHANG T, WU T, et al. M2 macrophages promote vasculogenesis during retinal neovascularization by regulating bone marrow-derived cells via SDF-1/VEGF. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;380(3): 469-486.
[7] JIA H, WANG Y, CHEN J, et al. Combination of BMSCs-laden acellular nerve xenografts transplantation and G-CSF administration promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. Synapse. 2019;73(7):e22093.
[8] PAN J, DENG J, LUO Y, et al. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Delivery of Human Periodontal Stem Cells Overexpressing Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Enhances Alveolar Bone Defect Repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2019; 28(24):1620-1631.
[9] XU T, LUO Y, KONG F, et al. GIT1 is critical for formation of the CD31hiEmcnhi vessel subtype in coupling osteogenesis with angiogenesis via modulating preosteoclasts secretion of PDGF-BB. Bone. 2019;122:218-230.
[10] CHENG X, JIN Z, JI X, et al. ETS variant 5 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis by targeting platelet-derived growth factor BB. Int J Cancer. 2019;145(1):179-191.
[11] LIU H, CHEN H, DENG X, et al. Knockdown of TRIM28 inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;311:108772.
[12] ZHANG M, CHANG Z, ZHANG P, et al. Protective effects of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid on pulmonary arterial hypertension via regulation of Rho A/Rho kinsase pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2019; 311:108749.
[13] PRASAD A, LIN F, CLARK RAF. Fibronectin-derived Epiviosamines enhance PDGF-BB-stimulated human dermal fibroblast migration in vitro and granulation tissue formation in vivo. Wound Repair Regen. 2019;27(6):634-649.
[14] CAI Z, XIANG W, PENG X, et al. MicroRNA-145 Involves in the Pathogenesis of Renal Vascular Lesions and May Become a Potential Therapeutic Target in Patients with Juvenile Lupus Nephritis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019;44(4):643-655.
[15] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278.
[16] 姜涛,吴硕,李志强,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB促进SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13): 1976-1981.
[17] 曹波,马创,魏琴,等.血小板衍生因子促进血管内皮细胞血管化的实验研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(24):2393-2397.
[18] ZHOU ZC, CHE L, KONG L, et al. CKIP-1 silencing promotes new bone formation in rat mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017;123(1):e1-e9.
[19] DENG J, PAN J, HAN X, et al. PDGFBB-modified stem cells from apical papilla and thermosensitive hydrogel scaffolds induced bone regeneration. Chem Biol Interact. 2020;316:108931.
[20] 任志勇,邱世超,黄现峰. 骨形态发生蛋白 2 基因修饰自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进兔胫骨牵张成骨的实验研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(5):453-457.
[21] VAN GASTEL N, TORREKENS S, ROBERTS SJ, et al. Engineering vascularized bone: osteogenic and proangiogenic potential of murine periosteal cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(11):2460-2471.
[22] KAMEI N, ATESOK K, OCHI M. The Use of Endothelial Progenitor Cells for the Regeneration of Musculoskeletal and Neural Tissues. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:1960804.
[23] WANG H, YIN Y, LI W, et al. Over-expression of PDGFR-β promotes PDGF-induced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of EPCs through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30503.
[24] FIEDLER J, ETZEL N, BRENNER RE. To go or not to go: Migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells stimulated by isoforms of PDGF. J Cell Biochem. 2004;93(5):990-998.
[25] CAPLAN AI, CORREA D. PDGF in bone formation and regeneration: new insights into a novel mechanism involving MSCs. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(12):1795-1803.
[26] PHILP D, CHEN SS, FITZGERALD W, et al. Complex extracellular matrices promote tissue-specific stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 2005;23(2):288-296.
[27] DU WJ, CHI Y, YANG ZX, et al. Heterogeneity of proangiogenic features in mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and placenta. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):163.
[28] 张斌斌,高全文,李冰,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在 Matrigel 凝胶支架上的生长与变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(13):1993-1998.
[29] 刘竹影,陈颖,刘倩,等.血管内皮祖细胞改善骨质疏松大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(14): 1999-2006.
[30] GIANNI-BARRERA R, BUTSCHKAU A, UCCELLI A, et al. PDGF-BB regulates splitting angiogenesis in skeletal muscle by limiting VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation. Angiogenesis. 2018;21(4):883-900.
[31] LÉVESQUE JP, WINKLER IG, HENDY J, et al. Hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization results in hypoxia with increased hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A in bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8):1954-1965. |