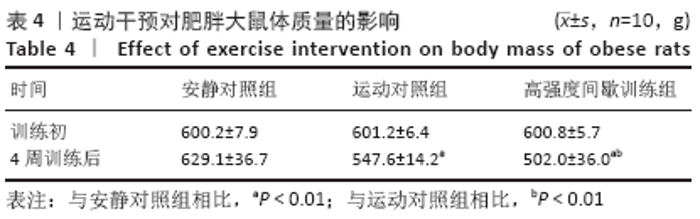
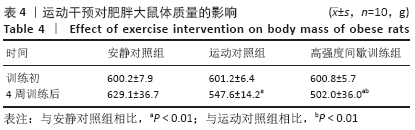
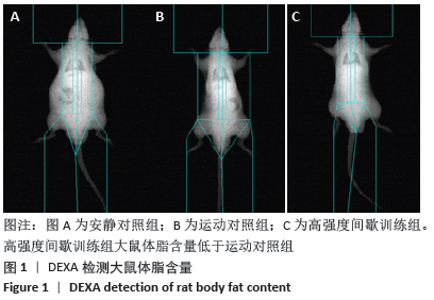
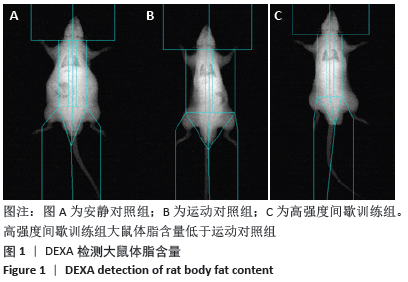
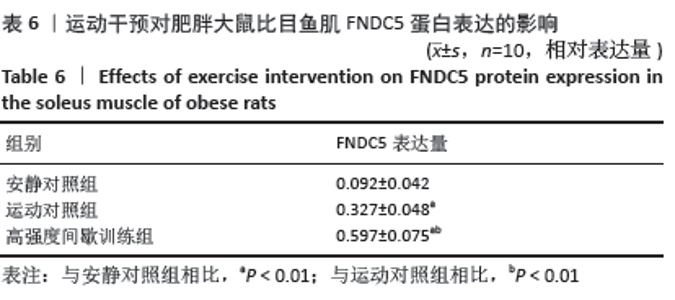
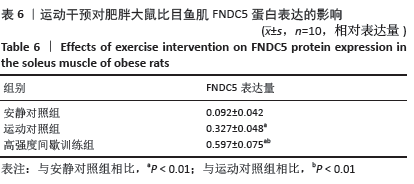
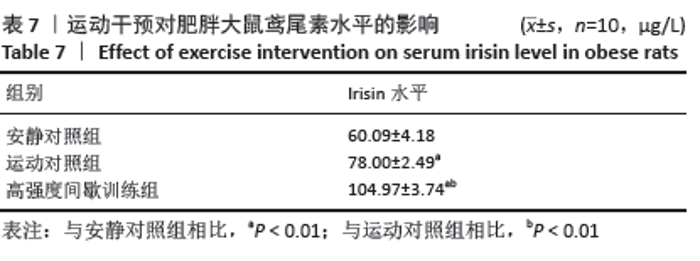
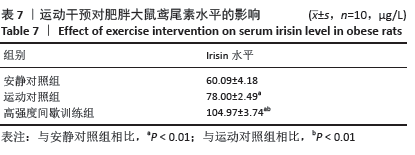
[1] 范保柱,韩梦杰.大强度间歇训练对肥胖人群减脂效果的影响研究[J].体育科技文献通报,2020,28(2):85-88.
[2] 张赛. HIIT跑台运动对肥胖小鼠UCP-1的激活作用[D]. 石家庄:河北师范大学, 2019.
[3] Zhang YJ, Li J, Huang W, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with treadmill exercise on body weight and expression of PGC-1α, Irisin and AMPK in skeletal muscle of diet-induced obesity rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019;44(7):476-480.
[4] Lu Y, Li H, Shen SW, et al. Swimming exercise increases serum irisin level and reduces body fat mass in high-fat-diet fed Wistar rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2016;15(1):93.
[5] Goh Q, Song T, Petrany MJ, et al. Myonuclear accretion is a determinant of exercise-induced remodeling in skeletal muscle. 2019;8:e44876.
[6] Chin EC, Yu AP, Lai CW, et al. Low-Frequency HIIT Improves Body Composition and Aerobic Capacity in Overweight Men. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020;52(1):56-66.
[7] Beetham KS, Howden EJ, Fassett RG, et al. High-intensity interval training in chronic kidney disease: A randomized pilot study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(8):1197-1204.
[8] Fiorenza M, Gunnarsson TP, Ehlers TS, et al. High-intensity exercise training ameliorates aberrant expression of markers of mitochondrial turnover but not oxidative damage in skeletal muscle of men with essential hypertension. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;225(3):13208.
[9] Moniz SC, Islam H, Hazell TJ, et al. Mechanistic and methodological perspectives on the impact of intense interval training on post-exercise metabolism. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(4):638-651.
[10] Huh JY, Siopi A, Mougios V, et al. Irisin in response to exercise in humans with and without metabolic syndrome.Clin Endocrinol Metab.2015;100(3):453-457.
[11] Guo Q, Wei X, Hu H, et al. The saturated fatty acid palmitate induces insulin resistance through Smad3-mediated down-regulation of FNDC5 in myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;520(3):619-626.
[12] 邓鑫磊,吴凌云,李婧嘉,等.鸢尾素对高脂膳食小鼠血脂水平的影响[J].海南医学,2018,29(10):1337-1340.
[13] Elizondo-Montemayor L, Mendoza-Lara G, Gutierrez-Delbosque G, et al. Relationship of Circulating Irisin with Body Composition, Physical Activity and Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorders in the Pediatric Population. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):3727.
[14] Bi J, Zhang J, Ren Y, et al. Irisin reverses intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction during intestinal injury via binding to the integrin αVβ5 receptor. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(1):996-1009.
[15] Ren YF, Wang MZ, Bi JB, et al. Irisin attenuates intestinal injury, oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice with L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(45):6653-6667.
[16] Jin Z, Guo P, Li X, et al. Neuroprotective effects of irisin against cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion injury via Notch signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;120:109452.
[17] Samy DM, Ismail CA, Nassra RA, et al. Circulating irisin concentrations in rat models of thyroid dysfunction - effect of exercise.Metabolism. 2015; 64(7):804-813.
[18] Kang YS, Kim JC, Kim JS, et al. Effects of Swimming Exercise on Serum Irisin and Bone FNDC5 in Rat Models of High-Fat Diet-Induced Osteoporosis. Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(4):596-603.
[19] Natalicchio A, Marrano N, Biondi G, et al. Irisin Increases the Expression of Anorexigenic and Neurotrophic Genes in Mouse Brain.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(3):e3238.
[20] 刘子铭,于亮,李琳,等.有氧运动及膳食干预对肥胖大鼠减脂效果及Irisin调控的研究[J].中国体育科技, 2018,54(6):90-96.
[21] Archundia-Herrera C, Macias-Cervantes M, Ruiz-Muñoz B, et al.Muscle irisin response to aerobic vs HIIT in overweight female adolescents. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9(1):101.
[22] Shirvani H, Delpasand A, Bazgir B, et al. The data on the aerobic training with or without calorie restriction and muscular levels of Irisin and muscular FNDC5 concentration in obese male Wistar rats. Data Brief. 2018;21:888-892.
[23] Dehghani M, Kargarfard M, Rabiee F, et al. A comparative study on the effects of acute and chronic downhill running vs uphill running exercise on the RNA levels of the skeletal muscles PGC1-&alpha, FNDC5 and the adipose UCP1 in BALB/c mice. Gene. 2018;679:369-376.
[24] Abedi-Taleb E, Vahabi Z, Sekhavati-Moghadam E, et al. Upregulation of FNDC5 gene expression in C2C12 cells after single and combined treatments of resveratrol and ATRA. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):181.
[25] 苏坤霞.不同强度耐力运动影响高脂诱导肥胖模型小鼠血清Irisin含量、骨骼肌PGC-1α、FNDC5、PPARδ蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(3):427-434.
[26] 李灵杰,张靓,赵大林,等.跑台运动对高脂饮食喂养的肥胖小鼠心肌及骨骼肌Irisin表达的影响[J].西安体育学院学报,2018,35(2):212-217.
|