Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (37): 5496-5503.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.37.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of joint immobilization on the repair of articular cartilage of the rat knee
Xu Li-yan1, Ma Jian-xiong2, Wang Ying2, Sun Lei2, Zhang Chun-qiu3, Ma Xin-long1, 2
- 1Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Orthopedics Research Institute, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300050, China; 3Tianjin University of Technology, Tianjin 300384, China
-
Online:2016-09-09Published:2016-09-09 -
Contact:Ma Xin-long, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
About author:Xu Li-yan, Master, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11172208
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Li-yan, Ma Jian-xiong, Wang Ying, Sun Lei, Zhang Chun-qiu, Ma Xin-long. Effects of joint immobilization on the repair of articular cartilage of the rat knee[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(37): 5496-5503.
share this article
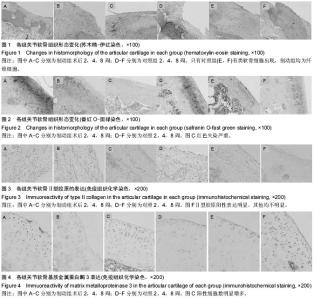
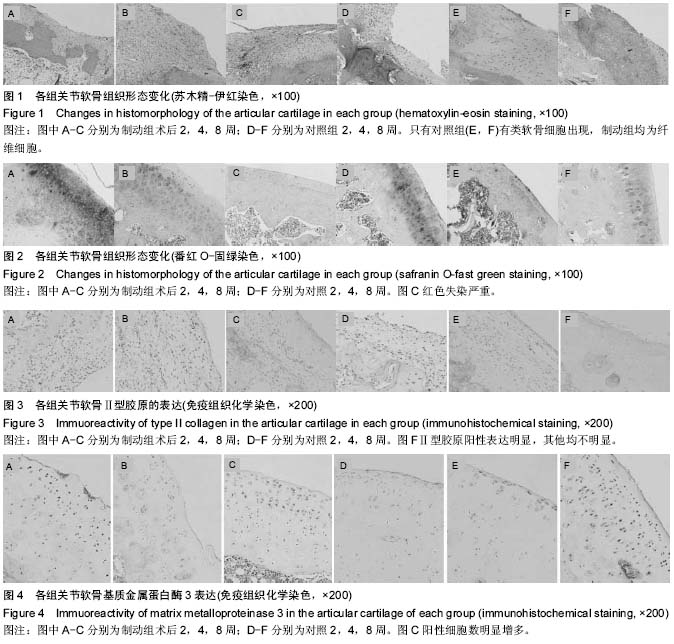
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入大鼠36只,无死亡,2只出现关节融合现象,2只出现针道感染,最终共32只进入结果分析,每组16只。 2.2 各组关节软骨一般形态 术后2周,制动组和对照组一般形态无显著差异,关节内无粘连、挛缩,周围未见血肿,关节液清亮,软骨缺损区部分填充,有凹陷,缺损处有暗红色纤维肉芽组织填充,未见软骨样组织的存在。缺损平面明显低于周围正常软骨,周围软骨表面光滑,色泽光亮。术后4周,制动组软骨缺损区被修复组织基本填平,散在比较浅的小凹陷,有部分高出周围关节面,表面不平整,能观察到与周围组织分界,周围软骨表面粗糙,色泽黯淡;对照组动物膝关节内关节液清亮,未见粘连或挛缩,软骨缺损区基本被再生组织充填完全,再生组织表面与周围软骨基本持平,边缘分界较模糊。周围软骨无异常改变。术后8周,制动组部分出现膝关节粘连,关节融合表现,关节液浑浊,可见明显凹陷,未出现粘连的软骨缺损区修复组织基本填平,周围软骨表面较粗糙,色泽较黯;对照组动物关节内关节液清亮,未见粘连或挛缩,软骨缺损区被再生组织完全充填,再生组织呈米白色半透明状,表面平坦,与周围组织无明显分界,周围软骨无异常改变。 2.3 各组关节软骨组织学变化 见图1,2。术后2周,制动组的缺损可见纤维组织填充,有明显凹陷,可见梭形成纤维细胞增殖,但细胞密度较低,未见软骨细胞,软骨基质含量很低或无基质着色(图1A),缺损周围软骨表面平整,无裂隙,软骨基质轻度失染或无失染,软骨细胞排列有序,潮线正常(图2A)。同样的对照组在术后2周后缺损区被新生组织部分填充,修复面不平整,有明显的凹陷,大量梭形的成纤维细胞增殖,未见软骨细胞(图1D)。周围软骨细胞呈圆形或椭圆形,轻度肥大,形态饱满,基质蕃红-O染色呈粉红色,表层轻度失染(图2D)。术后4周,制动组缺损基本修复,部分修复表面要高于相邻关节软骨面,修复组织仍以纤维组织为主。再生组织外周可见散在类软骨细胞,中心部分主要是成纤维细胞,细胞排列紊乱、密集,基质染色较淡或失染(图1B)。周围软骨表层裂隙形成,软骨细胞肥大,形状不规则,基质着色不均,失染退变明显(图2B)。对照组缺损基本完全填充,再生组织表面变平滑并且和周围软骨整合较好,几乎一致或非常接近。修复组织为纤维组织,可见散在小而圆的类软骨细胞排列整齐,基质均匀着色,但着色淡(图1E)。周围软骨细胞散在肥大,基质深染或失染,失染下移到软骨中下层,可见潮线不完整(图2E)。术后8周缺损处填充完整,主要为纤维组织,有裂隙以及小血管存在,可见下层有圆形类软骨细胞生成(图1C)。周围软骨层变薄,细胞簇集明显,排列紊乱,层次不清,重度失染,潮线不完整或上移(图2C)。同时期在对照组观察到缺损区充填完整,再生组织表面平滑且与周围组织整合较好,与周围软骨高度相同,修复组织有片状软骨样组织出现,细胞外基质着色不均一(图1F)。周围软骨表层纤维化,细胞肥大,细胞排列规则,分层明显,基质异染明显、均匀,有小血管侵入(图2F)。 2.4 各组组织学染色评分变化 见表1。术后2周,制动组与对照组缺损修复较差,两组Wakitani评分都很高,但两组相比差异无显著性意义。周围软骨轻微退变,两组Mankin评分较低,两组比较差异无显著性意义。术后4周,软骨缺损有所修复,但主要是纤维组织,两组Wakitani评分相比差异无显著性意义。对照组组内比较术后4周Wakitani评分显著低于术后2周,制动组组内比较术后4周评分也显著低于2周。周围软骨退变程度加重,两组Mankin评分增大,但两组比较差异无显著性意义,而组内比较发现无论对照组还是制动组术后4周Mankin评分都高于2周(P < 0.05)。术后8周,软骨缺损进一步修复,对照组和制动组术后8周Wakitani评分显著低于4周,但差"
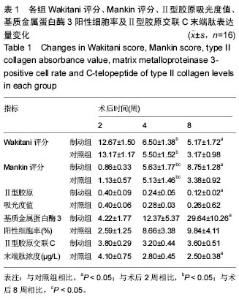
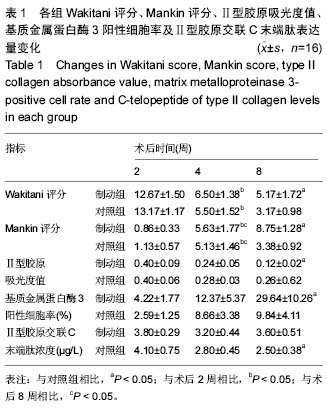
异无显著性意义。组间比较发现制动组的Wakitani评分高于对照组(P < 0.05);制动组周围软骨进一步退变,术后8周Mankin评分显著高于术后4周,而对照组有所恢复,所以对照组8周评分低于术后4周(P < 0.05)。组间比较制动组的Mankin评分高于对照组(P < 0.05)。 2.5 各组关节软骨免疫组织化学染色结果 制动组术后2周Ⅱ型胶原呈阴性表达(图3 A),4周时少量表达或几乎无阳性表达(图3B),8周阳性表达增多,散在分布,不集中(图3C)。对照组2周几乎是阴性表达,偶可见黄染的小颗粒(图3D),4周可见部分阳性表达区,大部分还是阴性表达为主(图3E),8周阳性表达明显增多,颜色分布均匀,但颜色较淡(图3F)。两组Ⅱ型胶原染色的吸光度值见表1。 基质金属蛋白酶3免疫组织化学阳性细胞为黄褐色,在对照组呈轻度表达(图4A-C),术后第2,4,8周阳性细胞率呈递增趋势,术后第2周阳性细胞数显著低于术后第4,8周与术后第4周相比差异无显著性意义;制动组阳性细胞表达明显(图4D-F),术后第2,4,8周阳性细胞率呈递增趋势,术后4周组高于2周组,术后8周组高于4周组,且均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。同时间段相比,术后第2,4周制动组均值大于对照组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),第8周制动组阳性表达率高于制动组(P < 0.05;表1)。 2.6 各组关节软骨代谢标志物Ⅱ型胶原交联C末端肽浓度变化 软骨代谢标志物检测结果显示,与对照组相比,大鼠制动8周后尿样中Ⅱ型胶原交联羧基端肽水平显著提高(P < 0.05),其他时间段Ⅱ型胶原交联羧基端肽的表达量差异无显著性意义。组内比较发现对照组2周升高,4周到8周逐渐降低趋势。而制动组内比较发现2周时Ⅱ型胶原交联羧基端肽表达升高,4周比2周时降低,但8周时比4周表达量要高。见表1。"
| [1] Kunz RI, Coradini JG, Silva L, et al. Effects of immobilization and remobilization on the ankle joint in wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(10):842-849. [2] Lamb SE, Marsh JL, Hutton JL, Nakash R, Cooke MW. Mechanical supports for acute, severe ankle sprain: a pragmatic, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373:575-581. [3] Jones RK, Chapman GJ, Findlow AH, et al. A new approach to prevention of knee osteoarthritis: reducing medial load in the contralateral knee. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(3):309-315. [4] Stumpfe ST, Pester JK, Steinert S, et al. Is there a correlation between biophotonical, biochemical, histological, and visual changes in the cartilage of osteoarthritic knee-joints? Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013;3(3):157-165. [5] Brandt KD. Response of joint structures to inactivity and to reloading after immobilization. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(2):267-271. [6] Arakaki K, Kitamura N, Kurokawa T, et al. Joint immobilization inhibits spontaneous hyaline cartilage regeneration induced by a novel doublenetwork gel implantation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22:417-425. [7] Bedi A, Feeley BT, Williams RJ III. Management of articularcartilage defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:994-1009. [8] Vanwanseele B, Eckstein F, Knecht H, et al. Knee cartilage of spinal cord-injured patients displays progressive thinning in the absence of normal joint loading and movement. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46(8): 2073-2078. [9] Haapala J, Arokoski J P, Ronkko S, et al. Decline after immobilisation and recovery after remobilisation of synovial fluid IL1, TIMP, and chondroitin sulphate levels in young beagle dogs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60(1):55-60. [10] Trudel G, Himori K, Uhthoff HK. Contrasting alterations of apposed and unapposed articular cartilage during joint contracture formation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86(1):90-97. [11] 顾延,戴克戎,裘世静,等.应力降低导致关节软骨退变机理的形态学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(9):631-633. [12] Mollon B, Kandel R, Chahal J, et al. The clinical status of cartilage tissue regeneration in humans. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1824-1833. [13] Gu XI, Leong DJ, Guzman F, et al. Development and validation of a motion and loading system for a rat knee joint in vivo. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38:621-631. [14] Convery FR, Akeson WH, Keown GH. The repair of large osteochondral defects. An experimental study in horses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;82:253-262. [15] 马信龙,马剑雄.可调节动物实验用全环外固定架:中国, CN203468785U[P].2014-03-12. [16] Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4): 579-592. [17] van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ, et al. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1):58-61. [18] Angele P, Yoo JU, Smith C, et al. Cyclic hydrostatic pressure enhances the chondrogenic phenotype of human mesenchymal progenitor cells differentiated in vitro. J Orthop Res,2003,21(3):451-457. [19] Harada Y, Tomita N, Wakitani S, et al. Use of controlled mechanical stimulation in vivo to induce cartilage layer formation on the surface of osteotomized bone. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(6):969-978. [20] Loening AM, James I E, Levenston M E, et al. Injurious mechanical compression of bovine articular cartilage induces chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;381(2):205-212. [21] van Valburg AA, van Roy HL, Lafeber FP, et al. Beneficial effects of intermittent fluid pressure of low physiological magnitude on cartilage and inflammation in osteoarthritis. An in vitro study. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25(3):515-520. [22] Mobasheri A, Mobasheri R, Francis MJ, et al. Ion transport in chondrocytes: membrane transporters involved in intracellular ion homeostasis and the regulation of cell volume, free [Ca2+] and pH. Histol Histopathol. 1998;13(3):893-910. [23] Hung SC, Nakamura K, Shiro R, et al. Effects of continuous distraction on cartilage in a moving joint: an investigation on adult rabbits. J Orthop Res. 1997; 15(3): 381-390. [24] Leong DJ, Gu XI, Li Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in articular cartilage is upregulated by joint immobilizationand suppressed by passive joint motion. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:420-426. [25] Billinghurst RC, Dahlberg L, Ionescu M, et al. Enhanced cleavage of type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1997; 99(7):1534-1545. [26] Qi C, Changlin H, Zefeng H. Matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitor in knee synovial fluid as cartilage biomarkers in rabbits: the effect of high-intensity jumping exercise. J Surg Res. 2007;140(1):149-157. [27] 刘志翔,张柳,张楠.降钙素对兔骨关节炎软骨基质金属蛋白酶1的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(22):1741-1743. [28] Ando A, Suda H, Hagiwara Y, et al. Reversibility of immobilization-induced articular cartilage degeneration after remobilization in rat knee joints. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2011;224:77-85. [29] Sowers MF, Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Yosef M, et al. Longitudinal changes of serum COMP and urinary CTX-II predict X-ray defined knee osteoarthritis severity and stiffness in women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(12):1609-1614. [30] Lohmander LS, Atley LM, Pietka TA, Eyre DR. The release of crosslinked peptides from type II collagen into human synovial fluid is increased soon after joint injury and in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48(11):3130-3139. [31] Catterall JB, Stabler TV, Flannery CR, Kraus VB. Changes in serum and synovial fluid biomarkers after acute injury (NCT00332254). Arthritis Res Ther. 2010; 12(6):R229. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [5] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [6] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [7] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [11] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [12] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [13] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [14] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [15] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||