Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (34): 5116-5121.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.34.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pelvic floor reconstruction using Gynemesh
Yang Lan1, Wang Juan1, Xu Lan-lan1, Wang Li-feng1, Li Yan-fang2
- 1Lianjiang People’s Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Lianjiang 524400, Guangdong Province, China; 2State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou 510060, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-06-09Online:2016-08-19Published:2016-08-19 -
Contact:Li Yan-fang, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou 510060, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yang Lan, Associate chief physician, Lianjiang People’s Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Lianjiang 524400, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Fund in the Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, No. 201411
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Lan, Wang Juan, Xu Lan-lan, Wang Li-feng, Li Yan-fang. Pelvic floor reconstruction using Gynemesh[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(34): 5116-5121.
share this article
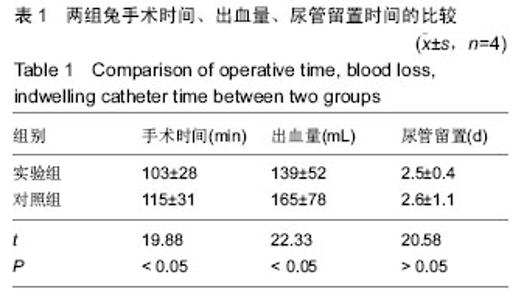
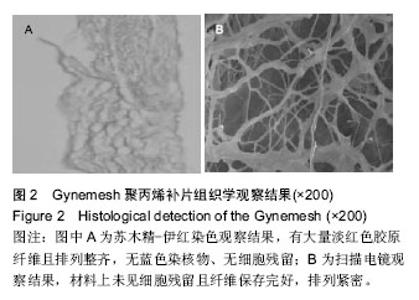
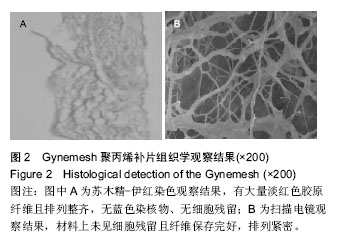
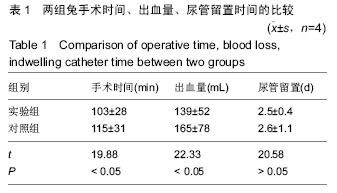
2.2 Gynemesh聚丙烯补片的生物性能 Gynemesh聚丙烯补片的厚度为(0.37±0.14)mm,断裂伸长率为(25.35±2.68)%,抗拉强度为(7.69±1.17)MPa,弹性模量为(0.007±0.008)GPa。 2.3 动物实验结果 2.3.1 实验动物数量分析 8只新西兰大白兔全部进入结果分析。 2.3.2 大体观察结果 入选新西兰大兔均取得手术成功,术后均未出现其他并发症或不良反应。实验组补片置入后未出现侵蚀反应,术后30 d取出时补片完整,未在体内发生降解。 2.3.3 两组手术时间、出血量、尿管留置时间的比较 两组尿管留置时间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),实验组手术时间、出血量显著少于对照组(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.3.4 两组术后并发症发生情况 实验组发生感染1只,并发症发生率为25%;对照组发生感染1只,化脓1只,并发症发生率为50%,两组间并发症发生率比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 "
| [1] 莫中福,吕英璞,刘彦丽,等.Prolift网片和Gynemesh聚丙烯补片用于盆底重建术的临床观察[J].河北医药, 2011, 33(4):507-509.
[2] 皋岚雅,焦成文,王坚,等.复合型人工胆管实验研究[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2010,22(6): 450-452.
[3] Kaneyama H,Kaise M,Arakawa H,et al. Gastroesophageal flap valve status distinguishes clinical phenotypes of large hiatal hernia.World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(47):6010-6015.
[4] 陈洪流,刘万红.无张力疝修补在老年腹股沟复发疝中的应用[J].湖北民族学院学报:医学版,2010,27(3):38-39.
[5] 李多孚,杜静,吴才良,等.血清H科在诊断妇女盆腔疾病中的应用[J].西部医学,2012,24(5):982-984.
[6] 陈芳,张建娟,张春仙,等.新型补片联合应用于改良盆底重建术的手术期护理[J].中华现代护理杂志, 2013,19(6):674-676.
[7] 王雯,王美玉,刘小妮.盆底重建联合全子宫切除术治万重度子宫脱垂患者围手术期护理[J].护士进修杂志, 2013, 28(19):1765-1766.
[8] Mantovani F, Tondelli E, Cozzi G, et al.Reconstructive urethro plasty using porcine acellular matrix (SIS) : evolution of the grafting technique and results of 10-year experience.Urologia.2011;78(2):92-97.
[9] 马绍英,李宝明,王旭昇,等.异种(猪)脱细胞真皮基质修复大鼠全层皮肤缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(2):156-160.
[10] Paparella R,Marturano M,Pelino L,et al.Prospective randomized trial comparing synthetic vs biological out-in transobturator tape: a mean 3-year follow-up study.Int Urogynecol J.2010;21(11):1327-1336.
[11] Menefee SA,Dyer KY,Lukacz ES,et al.Colporrhaphy compared with mesh or graft-reinforced vaginal paravaginal repair for anterior vaginal wall prolapse a randomized controlled tria.Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 118(6):1337-1344.
[12] Culligan PJ,Salamon C,Priestley JL,et al.Porcine dermis compared with polypropylene mesh for laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol.2013;121(1):143-151.
[13] Dahlgren E,Kjolhede P,Group R-PS.Long-term outcome of porcine skin graft in surgical treatment of recurrent pelvic organ prolapse. An open randomized controlled multicenter study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90(12):1393-1401.
[14] 王燕翔,孙鹏,王小云,等.不同分娩方式对产后盆底功能影响及康复治疗的效果研究[J].陕西中医, 2011,32(8): 887-889.
[15] 李玉梅,李环,肖爱民,等.低频电刺激预防宫颈癌术后尿潴留32例临床分析[J].罕少疾病杂志,2010,17(2):25-27.
[16] 赖俏红,黄惠芳.120例产后盆底康复治疗的临床效果观察[J].当代医学,2011,17(7):7-8.
[17] 黄剑青,尹玲英,黄亦文.盆底肌训练联合电刺激对产后盆底复健的效果观察[J].中国现代医药杂志, 2010,12(7): 25-27.
[18] 彭其才,许成芳,吴玲玲,等.肌电刺激联合生物反馈盆底肌训练治疗产后压力性尿失禁[J].中国实用医药, 2010, 25(9): 41-42.
[19] Raizada N,Mittal P,Suri J,et al.Comparative study to evaluate the inter- system association and reliability between standard pelvic organ prolapse quantification system and simplified pelvic organ prolapse scoring system. J Obstet Gynaecol India.2014;64(6):421-424.
[20] 张坤,韩劲松,朱馥丽,等.经阴道网片植入盆底重建术治疗盆腔器官脱垂术后并发症分析[J].中华妇产科杂志, 2012, 47(9):669-671.
[21] 莫中福,吕英璞,刘彦丽.Prolift网片和Gynemesh聚丙烯补片用于盆底重建术的临床观察[J].河北医药, 2011, 33(4):507-509.
[22] 李炳琪,郑春兰,王春昱.盆底重建术治疗盆腔器官脱垂的术后短期疗效观察[J].中国妇幼保健, 2013,28(20): 3365-3367.
[23] 朱兰,娄文佳,郎景和,等.无穿刺加用网片盆底重建术治疗症状性Ⅱ-Ⅲ度盆腔器官脱垂的近期疗效分析[J].实用妇产科杂志,2011,27(3):201-203.
[24] 陈红香,白生宾,哈提古丽•阿也提.盆底重建术治疗盆腔器官脱垂的治疗效果评价[J].中国妇幼保健, 2012,27(2): 294-296.
[25] 马宁,王凤玫,黄惠娟,等.改良Prolift网片盆底重建术对压力性尿失禁防治作用的探讨[J].中华妇产科杂志, 2012, 47(7):505-509.
[26] 许歌,王玲,李荷莲,等.应用不可吸收网片盆底重建术治疗Ⅲ-Ⅳ度盆腔器官脱垂的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(16):4555-4557.
[27] Jinkins JR.Acquired degenerative changes of the intervertebral segments at and suprajacent to the lumbosacral junction.A radioanatomic analysis of the nondiscal structures of the spinal column and perispinal soft tissues.Eur J Radiol.2004;50(2): 134-158.
[28] 吴建贤,王斌,石淑霞.下腰痛生物力学特点的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2014,8(24):4449-4453.
[29] 向君彦,罗艺,韩小容.经会阴超声诊断盆底功能障碍性疾病研究进展[J].临床超声医学杂志,2013,15(9):632-634.
[30] Eftekhar T,Sohrabi M,Haghollahi F,et al. Comparison effect of physiotherapy with surgery on sexual function in patients with pelvic floor disorder: A randomized clinical trial.Iran J Reprod Med.2014;12(1):7-14.
[31] 谢佳佳,朱才义,林小影.经会阴三维超声在女性盆底疾病诊断中的应用进展[J].临床超声医学杂志, 2014,16(1): 45-48.
[32] Espua-Pons M.Fillol M.Pascual MA.et al. Pelvic floor symptoms and severity of pelvic organ prolapse in women seeking care for pelvic floor problems. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.2014;6(177):141-145.
[33] 姚志成,胡昆鹏,钟跃思,等.应用新型生物补片减轻术后炎性反应的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2013,30(6): 1213-1215.
[34] 肖立俊,苏畅,陆景峰,等.脱细胞真皮基质与聚丙烯补片治疗腹股沟疝对比研究[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志:电子版. 2014.8(1):30-32.
[35] 罗旭,辛国华,曾逃方,等.微孔化猪脱细胞真皮基质与大鼠骨髓间充质细胞对裸鼠皮肤附件细胞再生的作用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(6):541-547.
[36] Formigli L,Benvenuti S,Mercalelli R,et al.Dermal matrix scaffold engineered with adult mesenchymal stem cells and plateletrich plasma as a potential tool for tissue repair and regeneration.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(2):125-134.
[37] Krishnan NM,Chatterjee A,Rosenkranz KM,et al.The cost effectiveness of acellular dermal matrix in expandereimplant immediate breast reconstruction.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.2014;67(4):468-476.
[38] 黄成,欧阳山蓓.脱细胞真皮基质移植联合固体硅胶假体在隆鼻术中的应用[J].中国美容医学, 2014,23(3): 194-196.
[39] 王乾锋,刘宏伟.脱细胞真皮基质作为GTR屏障膜治疗Ⅱ度根分叉缺损的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2013, 23(5):347-351.
[40] Balusubramanya K,Ramya R,Govindaraj SJ.Clinical and radiological evaluation of human osseous defects (mandibular grade Ⅱ furcation involvement)treated with bioresorbable membrane: vicryl mesh.J Contemp Dent Pract.2012;13(6):806-811. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||