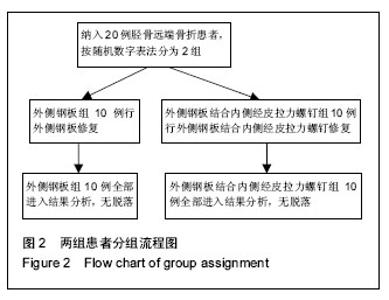
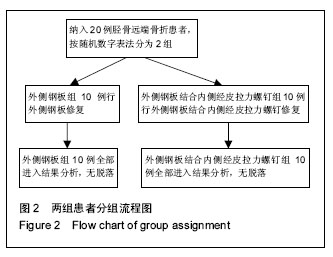
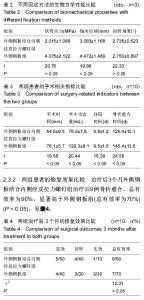
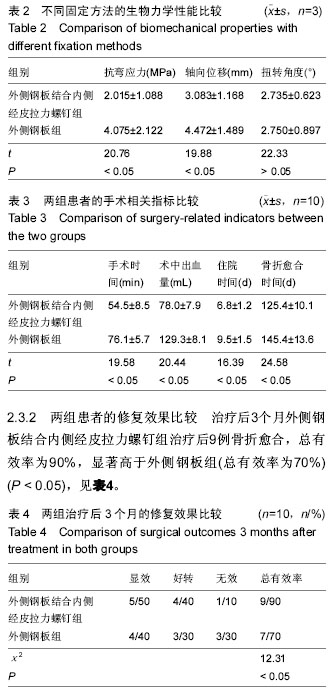
| [1] 郭宗彩,徐基亭,赵玉琴. 胫骨远端关节外骨折的治疗进展[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(16): 7524-7527.
[2] Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22: 307-311.
[3] 汤志辉,王良勇,张俊,等.经关节镜空心加压螺钉内固定治疗胫骨髁间隆起骨折[J].基层医学论坛,2014,18(22): 2980-2981.
[4] 李健伟,陈能,粟志辉,等.L型解剖板踝前横切口微创治疗胫骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014, 16(5):457-459.
[5] 张峻玮,孙磊,毕宏政,等.胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗进展.中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(14):1280-1283.
[6] 麦胡强.切开复位胫骨远端解剖钢板内固定术治疗胫骨Pilon骨折的临床效果[J]. 实用医学杂志,2014,30(14): 2256-2257.
[7] 林焱斌,林伟,林任,等.改良组合术式治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(7):632-635.
[8] 王立坤,孙正考,于腾波,等.三柱理论在复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(6):495-498.
[9] 包远祥,苏忠林,刘悦臣,等.胫骨远端骨折患者的手术治疗方案研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2014,24(22):92-95.
[10] 刘伟军,王俊文,黄玉成,等.专家型胫骨髓内钉治疗复杂性胫骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(3): 265-267.
[11] 曾荣铭,洪加源,林达生,等.后内侧解剖钢板微创治疗胫骨远端骨折的解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012, 30(1):29-32.
[12] Holcomb TM,Temple EW,Barp EA, et al. Surgical correction of checkrein deformity after malunited distal tibia fracture: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014; 53(5):631-634.
[13] Zou J,Zhang W,Zhang CQ. Comparison of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis with open reduction and internal fixation for treatment of extra-articular distal tibia fractures. Injury. 2013; 44(8):1102-1106.
[14] Aslani H,Tabrizi A,Sadighi A,et al. Treatment of open pediatric tibial fractures by external fixation versus flexible intramedullary nailing: a comparative study. Arch Trauma Res. 2013;2(3):108-112.
[15] 茆军,王培民,张惠法,等.Ilizarov环形外固定支架外固定治疗胫腓骨开放性骨折[J].中医正骨,2012,24(9):30-31.
[16] Lindvall E,Sanders R,Dipasquale T,et al. Intramedullarynailing versus percutaneous locked plating of extra -artieular proximal tibialfractures: comparison of 56 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(7):485-492.
[17] Isik M,Subasi M,Karsli B,et al. Intramedullary nailing and angulation prevention in distal metaphyseal tibial fractures.Orthopedics. 2012;35(12):1765-1768.
[18] Xavier F,Goldwyn E,Hayes W,et al. A comparison of the compressive strength of various distal locking screw options in the treatment of tibia fractures with intramedullary nails. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2011;21(3):185-192.
[19] El Attal R,Hansen M,Rosenberger R,et al. Intramedullary nailing of the distal tibia illustrated with the Expert (TM) tibia nail. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2011;23(5):397-410.
[20] Gelbke MK,Coombs D,Powell S,et al. Suprapatellar versus infra patellar intramedullary nail insertion of the tibia: A cadaveric model for comparison of patellofemoral contact pressures and forces. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(11):665-671.
[21] 蔡康,邓新昌,罗增文.锁定钢板治疗胫骨远端Pilon骨折的手术疗效观察[J].当代医学,2013,19(11):84-85.
[22] 张立军,马正儒,张华杰,等.锁定钢板治疗56例胫骨远端Pillon骨折的临床疗效观察[J].中国医学创新, 2013, 10(14): 105-106.
[23] 高展军,阚世廉,丁尔勤,等.解剖型钢板和锁定钢板内固定修复胫骨远端Pilon骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(17):3111-3115.
[24] 马童,蔡珉巍,涂意辉,等.经皮微创钢板固定技术Meta接骨板治疗胫骨远端干骺端骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(3):30-34.
[25] 赵勇,申才佳,李勇,等.胫骨远端前外侧解剖型钢板治疗不稳定性Pilon骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,15(6):666-667.
[26] 高翔,徐南伟,戚有成,等.胫骨远端前外侧锁定钢板内固定治疗Pilon骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2): 159-160.
[27] Frank M,Dedek T,Trlica J,et al. Percutaneous fixation of anterior column acetabular fractures-first experience. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010;77(2): 99-104.
[28] 张聪林,屈小鹏,刘志斌,等.髋臼前柱骨折诊疗方法的研究现状及进展[J].微创医学杂志,2011,6(3): 248-249.
[29] Den RK,Tripathy SK,Aggarwal S,et al. A safe technique of anterior column lag screw fixation in acetabular fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36(11): 2333-2340.
[30] Chen KN,Wang G,Cao LG,et al. Differences of percutaneous retrograde screw fixation of anterior column acetabular fractures between male and female: A study of 164 virtual three-dimensional models. Injury. 2009,40(10): 1067-1072.
[31] 周海波,郭晓山.经皮固定骨盆环和髋臼损伤技术的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(9): 720-721.
[32] 高洪,罗从风,胡承方,等.透视导航下经皮螺钉置入内固定髋臼骨折18例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(17):3201-3204.
[33] 李卫华,王晓,张永乐,等.前后联合入路治疗髋臼双柱骨折[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2011,3(1):47-50.
[34] 朱仕文,孙旭,杨明辉,等.经不同手术入路治疗髋臼双柱骨折的疗效分析[J].山东医药,2011,51(28):23-25.
[35] 黄进成,刘曦明.髋臼双柱骨折手术入路的研究进展[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(8):799-800.
[36] Starr AJ,Jones AL,Reinert CM,et al. Preliminary results and complications following limited open reduction and percutaneous screw fixation of displaced fractures of the acetabulum. Injury. 2001;32(1): 45-50. |