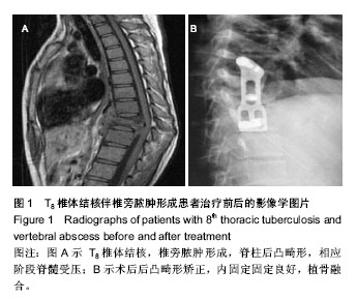
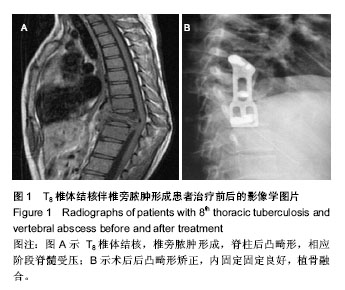
| [1] 严碧涯,端木宏.结核病学[M].北京:北京出版社, 2003:689-702.
[2] 张忠民,付忠泉,尹刚辉,等.胸椎结核外科治疗的长期临床随访[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2012,10(4): 198-201.
[3] 范扬航,吴智勇,李卓毅.中断肋骨后外侧开胸切口施行食管、贲门癌切除术[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2006, 13(4):282- 283.
[4] 李永庆.中断肋骨后外侧切口在胸外手术中的应用[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志, 2003,19(2):125-126.
[5] 吴肇汉,王国民.临床外科学[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社, 2000: 300.
[6] 陈满荫,何建行,杨运有,等.改良胸后外侧小切口与传统开胸手术的肺功能对比[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2000,16(6):362.
[7] 张宏其,郭虎兵,陈筱,等.单纯一期后路病灶清除椎体间植骨融合内固定治疗胸椎结核的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 9(1): 34-40.
[8] Wewers ME, Lowe NK. A critical review of visual analogue scales in the measurement of clinical phenomena. Res Nurs Health. 1990;13(4): 227-236.
[9] Upadhyay SS, Saji MJ, Yau AC, et al. Duration of antituberculosis chemotherapy in conjunction with radical surgery in the management of spinal tuberculosis.Spine. 1996;21:1898-1903.
[10] Zhang HQ,Wang YX.One-stage posterior focus debridement,fusion,and instrumentation in the surgical treatment of cervicothoracic spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis in children:a preliminary report. Child Nervous Syst. 2010;1:8.
[11] Harms J,Jeszenszky D,Stolze D,et al.True spondylolithesis reduction and more segmental fusion in spondylolisthesis// The textbook of spinal surgery.2nd ed.Philadelphia,PA: Lippincott-Raven, 1997:1337-1347.
[12] 王自立. 病灶清除单节段融合固定治疗脊柱结核[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009,19(11): 807.
[13] 张宏其,唐明星,葛磊,等.单纯经后路一期前方病灶清除植骨内固定矫形治疗伴后凸畸形的高胸段脊柱结核[J].医学临床研究, 2008,25(11): 1948-1951.
[14] Ha KY,Chung YG,Ryoo SJ.Adherence and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis on various spinal implants. Spine. 2005;30: 38-43.
[15] Talu u,Gogus A,Oturk C,et al.The role of posterior instumentation and fusion after anterior radical debride-ment and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: experience of 127 case.Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(8): 554-559.
[16] 黄志强,黎鳌,张肇祥,主编.外科手术学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1996: 355.
[17] 吴肇汉,王国民.临床外科学[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社,2000: 300.
[18] 谢富荣,林春博,梁伟国,等.不断肋并保留肋骨经肋间隙入路治疗胸椎疾患的体会[J].广西医科大学学报,2010, 27(2):303-304.
[19] 贺青卿,姜军,杨新华,等.经肋间隙人路行内乳淋巴结活检的探讨[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2006,21(9):634-636.
[20] 闫本流.不断肋经肋间隙手术入路治疗下胸椎疾患的临床观察[D].广西:广西中医学院,2012.
[21] 王文己,王建民.保留肋骨、肋间神经的胸椎结核手术入路[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(9):925-926.
[22] Benli IT, Kaya A, Acaroglu E. Anterior instrumentation in tuberculous spondylitis: is it effective and safe? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460: 108-116.
[23] Ozdemir HM, Us AK, Ogun T. The role of anterior spinal instrumentation and allograft fibula for the treatment of pott disease. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(5): 474-479.
[24] 卢旭华,陈德玉,赵定麟.脊柱结核的外科治疗现状及进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2004,25(5):363-366.
[25] Currier BL,Eismon FJ. Infections of the spine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders. 1992: 1319. |