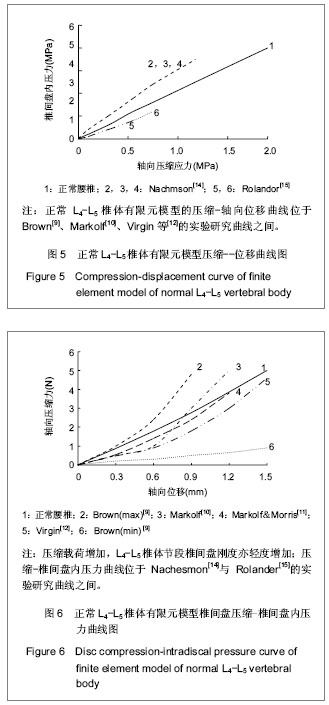
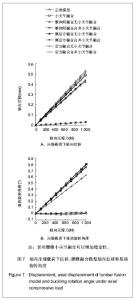
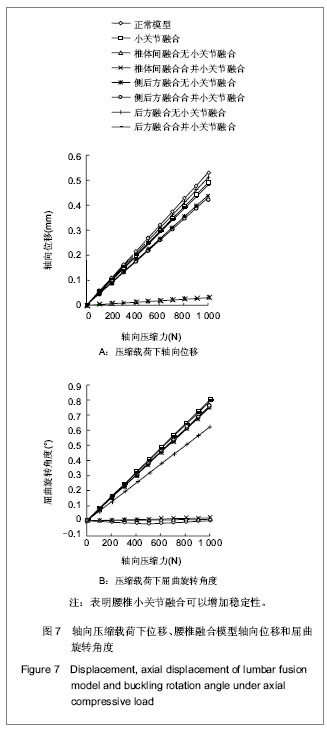
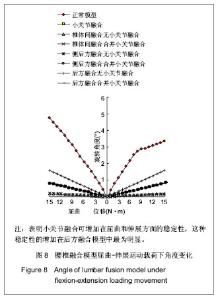
| [1] Goel VK, Kong W, Han JS, et al.A combined finite element and optimization investigation of lumbar spine mechanics with and without muscles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 1;18(11):1531-1541.[2] Rybicki EF, Simonen FA, Weis EB Jr. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur.J Biomech.1972; 5: 203.[3] Huiskes R,Chao EY. Asurvey of Finite element analysis in orchopedic biomechanicsi the first fecade. J Biomech. 1983;16(6):385-409.[4] Liu YK, Ray G, Hirsch C. The resistance of the lumbar spine to direct shear. Orthop Clin North Am. 1975;6(1):33-49.[5] Chen CS,Cheng CK,Liu CL,et al.Stress analysis of the disc adjacent to interbody fusion in lumbar spine. Med Eng Phys.2001; 23:483-491.[6] Yoganandan N, Kumaresan S, Voo L,et al. Finite element of the human lower cervical spine. Parametric analysis of the C4 -C6 unit. J Biomech Eng. 1997;119(1):87-92.[7] Wu JS , Chen JH.Clarification of th mechanial behaviour of spinal motion segments through a three dimensional poroe2lastic mixed finite element model. Med Eng Phys. 1996 ;18(3):215-224.[8] Gilbertson LG, Goel VK, Kong W, et al. Fininte element methods in spine biomenanics research Crilt. Crit Rev Biomed Eng.1995;23(5-6):411-473.[9] Brown T, Hansten RJ, Yorra AJ. Some mechanical tests on the lumbosacral spine with particular reference to intervertebral discs. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1957; 39(5):1135 - 1164.[10] Markolf KL. Deformation of the thoracolumbar intervertebral joints in response to external load : a biomechanical study using autopsy material. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1972;54(3) : 511- 533.[11] Markolf KL, Morris JM. The structural components of the intervertebral disc. A study of their contributions to the ability of the disc to withstand compressive forces. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1974;56(4):675-687. [12] Virgin WJ. Experimental investigations into the physical properties of the intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1951;33(4):607 - 611.[13] Nachemson A.Mechanical stresses on lumbar disks. Curr Pract Orthop Surg. 1966;3:208-224. [14] Rolander SD. Motion of the lumbar spine with special reference to the stabilizing effect of posterior fusion. An experimental study on autopsy specimens. Acta Orthop Scand. 1966:Suppl 90:1-144. [15] Saito T ,Tamatouro T ,Shikara J ,et al. Analysis and prevention of spinal column deformity following cervical laminectomy , pathogenic analysis of post laminectomy deformities. Spine, 1991;16 :494-502. [16] Kleinberger M. Application of finite element techniques to the study of cervical spine mechanics. In : Proceedings of the 37th Steppe Car Crash Conference. San Antonio Tesas,1993; 7-8.[17] Bozic KJ, Keyak JH, Skinner HB, et al. Three dimensional finite element modeling of a cervical vertebra : An inverstigation of burst fracture mechanism. J Spinal Disorders.1994; 7:102-110.[18] Voo L,Denman J, Kumaresan S ,et al. Development of 3-D finite element model of cervical spine. Adv Bioengineer Development of finite element model of cervical spine. Avd Bioeng.1995;31:13-14. [19] Kumaresan S,Yoganadan N,Pintar FA,et al. Finite element model of cervical laminectomy with graded facetectomy. Spinal Disorder.1997; 10 (1) :40 - 46.[20] Kumaresan S, Yoganandan N, Pintar FA. Finite element analysis of anterior cervical spine interbody fusion. Biomed Mater Eng.1997; 7:221-230.[21] 刘耀升,陈其昕,廖胜辉,等.椎问盘高度降低及退变对腰椎生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2006,24(5): 566-570.[22] Lee CK,Langrana NA.Lumbosacral spinal fusion.A biomechanical study.Spine.1984;9:574-581. |