Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2252-2258.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3796
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential of Nel-like molecule 1 to treat osteoarthritis by promoting cartilage formation and anti-inflammatory effects
Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming
- First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-03Revised:2020-04-14Accepted:2020-05-13Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:Li Weiming, MD, Chief physician, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Tang Xiaokai, Master candidate, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2016M601449 (to LWM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Potential of Nel-like molecule 1 to treat osteoarthritis by promoting cartilage formation and anti-inflammatory effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2252-2258.
share this article
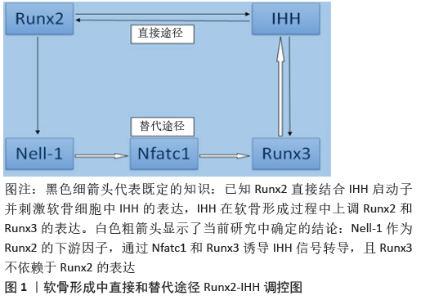
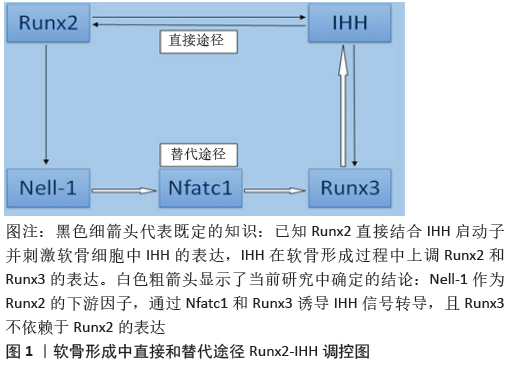
2.1 骨性关节炎发病机制的新见解 骨关节炎是一种完整的关节疾病,涉及透明关节软骨、软骨下骨、韧带、关节囊、滑膜和关节周围肌肉的结构改变[21]。骨关节炎的复杂发病机制涉及机械、炎症和代谢因素,最终导致滑膜关节的结构破坏和功能失效。这种疾病是由于关节组织修复和破坏之间的不平衡而引起的一种主动的动态改变,而不是通常所描述的被动退行性疾病或所谓的磨损疾病[22]。 在骨关节炎发生发展过程中,软骨成分发生变化,软骨失去完整性[23]。软骨成分变化改变了软骨材料的性质,增加了其对物理力量破坏的敏感性,最初侵蚀只出现在表面,后来伴随更深的软骨裂隙而来的是钙化软骨区的扩张。在试图修复过程中,肥大的软骨细胞表现出更高的合成活性,但在此过程中会产生基质降解产物和促炎递质,从而放松对软骨细胞功能的调节,并作用于邻近的滑膜,刺激增殖和促炎反应,增生的滑膜细胞也会释放促炎产物,这一过程伴随着组织肥大和血管增多。在软骨下骨中血管生成增多,并侵入关节软骨深层,造成软骨下骨骨改建增加,这种骨重建和修复也与软骨下骨髓病变的发展有关。软骨内骨化形成关节边缘的骨赘受到炎性生物因素的影响,但也受到异常关节运动学的影响[24]。 骨关节炎通常被描述为一种具有广泛潜在途径的异质性疾病,这会导致相似的关节破坏结果[25]。HUNTER等[26]认为骨关节炎是一种综合征,而不是一种单一的疾病。每一种常见的骨关节炎危险因素都可能激发不同的机制途径导致骨关节炎,因此促进老年人骨关节炎发展的介质可能与促进年轻人或肥胖者关节损伤后发生骨关节炎的介质不同。根据特定的病理过程提出了一些分层方法来划分不同的机制亚群,包括炎症成分增加[27]、超负荷[28]、代谢改变[29]、细胞衰老[30],这些机制可能是重叠的,需要进一步验证。 2.2 Nell-1的促软骨再生能力及其信号级联 2.2.1 Nell-1的促软骨生成能力 软骨细胞对于关节软骨结构支持、代谢活动和维持功能具有重要作用[31]。软骨生成是一个动态的细胞过程,这一过程包括间充质细胞凝聚、软骨前体细胞增殖、软骨细胞分化和软骨形成这几个复杂阶段。这些阶段的进展是由复杂的分化途径介导的,该途径涉及各种细胞外基质和转录因子的协调表达,以及生长因子和细胞因子的调节。Nell-1是关节软骨中表达的细胞外基质分子,同时也是一种新的促软骨形成分子,在体外可以促进软骨形成细胞及其前体细胞的增殖、分化和成熟[15-16],例如Nell-1能促进兔耳郭软骨细胞形成软骨结节[32],促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化[33]。已经被证明Nell-1能够在体内驱动骨、软骨组织的分化和生长[34-35],例如将Nell-1加入壳聚糖纳米粒并嵌入海藻酸钠水凝胶中,植入新西兰大白兔股骨髁软骨缺损,结果显示含有Nell-1的海藻酸钠填充缺损明显改善了软骨再生[17],经Nell-1修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞促进了山羊髁突关节软骨和软骨下骨的修复[36]。这些研究揭示并证实了Nell-1在软骨形成发育和成熟中的重要调控作用。 此外,OEGEMA等[37]研究发现钙化软骨在关节软骨中保持相对恒定,因为钙化软骨内的软骨细胞在成年期通常保持静止。LI等[18]进一步研究发现关节内注射Nell-1导致对照组和Nell基因敲除小鼠胫骨平台的钙化软骨层中度增厚。重要的是,Nell-1诱导的钙化软骨扩张并不伴随明显的透明软骨减少。这些在钙化的关节软骨中观察到Nell-1刺激的软骨再生,说明Nell-1用于治疗骨关节炎有预期的益处。 LI等[38]研究展现了生长因子Nell-1的软骨形成潜力,进而证明了它在各种动物模型中是有效的。Nell-1功能丧失会导致细胞外基质蛋白的基因表达减少[39],例如 Nell-1基因敲除小鼠表现出矮小和早熟、骨质疏松、发育迟缓、次级骨化中心矿化减少等特点[40],以及Nell-1基因敲除小鼠不能在围产期存活,肋骨明显变形和变短,椎体椎间隙压缩,软骨基质减少[41]。所有这些发现揭示了Nell-1在小鼠软骨细胞分化、成熟和再生过程中的重要作用。 Nell-1的促软骨形成能力以及关节软骨细胞再生对于骨关节炎治疗的重要性,为Nell-1成为一种新的改善骨关节炎药物提供了可能性。 2.2.2 Nell-1促软骨再生的分子信号级联 KIM等[42]研究表明Runx2不仅调控软骨细胞成熟,而且还参与软骨形成的启动。尽管Runx2能够直接与IHH启动子结合来刺激IHH-Gli通路[43],这是诱导软骨细胞分化和成熟的信号途径[44],但CHEN等[45]研究结果显示Runx2的核内输入和DNA结合功能不足以促进软骨细胞的分化。另外,LEE等[32]表示Nell-1是一种分泌性的细胞外基质分子,在软骨细胞的分化和成熟过程中也起着关键作用。LI等[15]研究显示Runx2敲除小鼠软骨细胞中Nell-1 mRNA的表达水平仅为WT对照组的一半。此外,小鼠软骨细胞过度表达Runx2之后显著刺激Nell-1 mRNA的表达,并呈病毒剂量依赖性。在不同Nell-1基因型的小鼠软骨细胞中,Runx2 mRNA的表达保持在相似的水平。这些结果表明软骨细胞中Runx2调节Nell-1的表达,而Nell-1不改变Runx2的表达。虽然Nell-1的表达高度依赖于Runx2,但Nell-1的前软骨形成功能在Runx2敲除小鼠中持续存在,表明了管理软骨形成的Runx2→Nell-1调控网络的复杂性,特别是Nell-1至少部分通过不依赖于Runx2的核输入和DNA结合功能的另一条途径促进软骨形成。 那Nell-1是通过何种途径促进软骨形成的呢?检测Runx2的下游功能调节因子Nell-1[15],是否也通过IHH信号通路发挥作用,展示其前软骨形成特性,对于辨别这2种调节因子的相互作用至关重要。YOSHIDA等[44]研究结果表明,在发育后期Runx2基因敲除小鼠四肢近端(股骨和肱骨)的软骨细胞肥大被完全阻断,但四肢远端(桡骨、腓骨和胫骨)的软骨细胞分化仅轻微障碍。然而,Runx2和Runx3的双敲除导致整个骨骼中完全没有肥大的软骨细胞。此外,Runx3敲除小鼠在发育过程中软骨细胞成熟略有延迟,但在新生期大体骨骼发育正常。这些现象表明,Runx3是软骨细胞完全分化和成熟所必需的[46]。此外,新生小鼠软骨细胞中IHH的表达仅在Runx2敲除新生小鼠中部分降低,而在年龄匹配的Runx2和Runx3同时敲除的动物中检测不到[44],这一发现表明,除了Runx2之外,Runx3还可以有效地调节软骨细胞中IHH的表达。Nell-1招募了一条绕过Runx2-IHH启动子结合的替代途径,以刺激IHH信号并显示前软骨活性。 那Nell-1与Runx3的关系是什么呢?Runx2敲除小鼠模型中Nell-1缺乏导致小鼠软骨细胞Runx3 mRNA和Runx3蛋白在新生小鼠股骨增殖区、肥大区的表达显著降低。短期给予Nell-1不仅增加了小鼠成软骨ATDC5细胞系和小鼠原代软骨细胞中Runx3的表达,而且还诱导了Runx2敲除小鼠软骨细胞中Runx3信号转导,表现为Runx3和Runx3下游靶基因Acan30的转录上调,以及Runx3核积累的增加。此外,巨细胞病毒驱动的Nell-1过表达重建了新生Runx2敲除小鼠股骨中Runx3的强烈染色。因此,至少在Runx2敲除小鼠模型中,Runx3被确定为Nell-1的下游靶点[19]。 还有研究发现,Runx3不是Nell-1调控软骨形成过程中的早期反应基因之一[47]。LI等[20]研究首先筛选连接Nell-1→ Runx3信号转导的关键转录因子,再利用RNA干扰技术进一步验证了这些发现,最后用染色质免疫沉淀方法识别Nell-1诱导的关键转录因子在Runx3启动子上的结合位点,结果成功地确定并从功能上证实了Nfatc1是连接Nell-1和Runx3的关键转录因子。Nfatc1是Nell-1早期反应靶点,通过与Runx3?833?810区域的启动子结合进而上调Runx3的表达,从而激活Runx3-IHH信号转导级联,诱导软骨细胞分化成熟。 综上所述,除了固有的Runx2→IHH信号转导级联诱导软骨分化成熟外,Nell-1还通过Runx2→Nell-1→Nfatc1→Runx3→ IHH信号转导级联诱导软骨分化成熟,见图1,从而表现出促进损伤关节软骨愈合的能力。 "
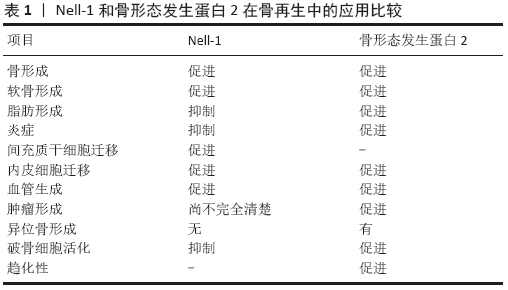
2.3 Nell-1的抗炎作用及其分子信号级联 2.3.1 Nell-1的抗炎作用 LI等[18]发现在关节炎关节软骨病变中Nell-1的表达较低,Nell-1单倍体功能不全易发生骨关节炎样病理改变,并伴有促炎症细胞因子水平增加。关节软骨细胞局部分泌促炎细胞因子,包括白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子可以激活其自分泌环[48],这对骨关节炎的发生和发展至关重要[49];这些促炎细胞因子的调节作用至少部分独立于滑膜和免疫细胞的调节作用[50]。白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α是骨关节炎进展过程中促进细胞外基质降解的主要促炎症细胞因子[51]。白细胞介素1β等促炎细胞因子可以在体外诱导关节软骨细胞发生骨关节炎样的生物学变化[50]。ALLEN等[52]证实啮齿动物膝关节中白细胞介素1β的局部升高已被证明能诱发骨关节炎样症状,进一步阐明了促炎细胞因子与骨关节炎的相关性。 软骨细胞是分泌Nell-1的细胞来源[19]。软骨细胞功能失衡可由外界刺激(如炎性细胞因子的存在)诱导,从而导致退行性疾病(如骨关节炎)的进展。SHEN等[53]通过体内股骨嵌合模型,首次表明Nell-1具有抗炎特性,其能够降低促炎标志物肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平。LI 等[18]最近的一项研究显示关节内注射白细胞介素1β可引起Nell-1缺失小鼠膝关节比对照组更严重的炎症和软骨退化,在Nell-1给药后明显恢复。此外,外源性Nell-1显著减轻了对照组和Nell-1敲除小鼠膝关节的炎症反应和关节软骨损伤。通过使用Nell-1敲除小鼠模型,证明了Nell-1除了先前表现出的促软骨生成作用外,还进一步阐明了具有抗炎作用,以保护关节软骨免受骨关节炎进展的影响,以及关节炎关节软骨中促炎标志物和Nell-1之间存在负相关,Nell-1缺乏可以加速和加重骨关节炎的进展。 综上所述, Nell-1至少可以部分减轻白细胞介素1β等炎症因子刺激引起的软骨源性细胞外基质降解和炎症反应。当Nell-1被研究并用于治疗骨质疏松症时,全身给药和化学修饰显著延长了它的半衰期和在肌肉骨骼系统中的分布[54]。因此,从有效性和安全性的角度来看,Nell-1有希望作为一种新的和有前途的骨关节炎治疗候选药物的潜力,以应对未满足的骨关节炎治疗需求[14]。 2.3.2 Nell-1抗炎作用的分子机制 到目前为止,用于软骨形成的Nell-1下游效应器中,对Nfatc1和Nfatc2的研究是最多的。Nfatc1和Nfatc2都被发现在维持软骨健康和抑制自发性骨性关节炎方面发挥重要作用[55]。Nfatc2敲除小鼠在12-24个月时发生骨关节炎[56],但是给予钙调神经磷酸酶可降低骨关节炎的严重程度[57],给予糖原合成酶激酶3β可诱导小鼠骨关节炎[58],以及还发现白细胞介素1β可诱导原代成人关节软骨细胞中Nfatc1的表达[59],这些观察结果与先前报道的Nfatc分子的抗关节炎作用不同[60]。目前对Nfatc蛋白在关节炎中的作用尚不清楚。 LI 等[20]研究表明Nfatc1通过激活IHH信号通路介导Nell-1促软骨再生中起重要作用。Nfatc1和Runx1是软骨细胞中响应Nell-1的主要基因。AINI等[61]研究结果显示Runx1和Nfatc1在关节炎条件下都是炎症的负调节因子。LI等[18]建立了稳定的Nfatc1敲除小鼠ATDC5细胞和Runx1敲除小鼠ATDC5细胞来验证。通过进一步研究发现:在与干扰ATDC5细胞相同的级别上,Nell-1的抗炎作用在Nfatc1敲除小鼠ATDC5细胞中是保守的;相反,Runx1敲除小鼠中几乎完全消除了Nell-1在ATDC5细胞中的抗炎生物活性。关节内注射Nell-1上调了小鼠膝关节软骨中的Runx1蛋白,而不受白细胞介素1β刺激的影响,也不受Nell-1单倍体不足的影响。综上所述,这些数据表明:Nell-1在软骨细胞中是通过关键下游介质Runx1的介导来发挥抗炎生物活性的,而不是NFATc1。 2.4 现阶段Nell-1在应用于骨关节炎治疗的不足之处 第一:以往实验使用的重复关节内注射和体外培养策略显然不是临床治疗的最佳给药途径。在Nell-1应用于临床之前,需要对Nell-1的给药剂量、治疗方案以及给药途径进行进一步优化。KWAK等[62]研究表明Nell-1在体内的半衰期只有 5.5 h,因此还需要开发合适的递送载体和/或化学修饰(如聚乙二醇化)来保护Nell-1免受内源性酶消化,从而延长其在体内的生物效力。第二:目前的发现证明了Nell-1和Runx2之间相互作用的复杂性。除了Runx3→IHH途径外,调控软骨分化的Runx2和Nell-1的确切相互作用在很大程度上仍不清楚。研究表明Nell-1不能调节软骨细胞中Runx2的表达,但Nell-1是否调节Runx2的翻译后修饰,如磷酸化[63],还没有确定。虽然非规范的wnts(例如wnt5a)通过G蛋白偶联受体激活细胞内钙释放来诱导早期软骨形成,但wnt5a也可以通过刺激磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B而起到抑制软骨细胞肥大的作用。在软骨形成调控中,Runx2也是典型和非典型Wnt通路的关键分子,提示其在软骨形成的功能调控中可能是多条信号通路的汇合点。鉴于Nell-1已被认为是典型Wnt信号通路在成骨过程中的一种新的激活剂[64],推测Nell-1在调控Runx2下游软骨形成中的作用也可能是通过IHH和Wnt信号通路之间的复杂串扰而发生的。因此,需要进一步的研究来解释这种复杂的相互作用,以全面了解Nell-1在软骨形成中的重要作用。第三:从现已发表的文献来看,目前依然没有动物模型被用作骨关节炎的黄金标准[65]。在目前的研究中,自然发生的骨关节炎模型最能代表人类原发性骨关节炎,而化学诱导的模型用来模拟人类继发性骨关节炎,以证明Nell-1作为改善骨关节炎病情的重要性。化学诱导的骨关节炎模型是阐明遗传和分子发病机制和确定药物治疗靶点的首选模型,因为它们与创伤后骨关节炎没有相关性[66]。从临床角度来看,Nell-1的抗关节炎效果应该在创伤后骨关节炎模型中得到进一步证实,因为创伤后骨关节炎占所有症状性骨关节炎病例的12%[67]。例如,前十字韧带横断术模型是最早也是最常用的模拟创伤后骨关节炎的外科模型[66]。与大鼠等小动物相比,大型动物在解剖学和生物力学上与人类有更多相似之处[65]。特别值得一提的是,山羊的膝盖在解剖学上与人类的膝盖最相似[68],因此,山羊前十字韧带横断术模型可能有助于验证Nell-1的抗关节炎效力,并提供更多临床相关数据。此外骨关节炎在女性中的发生率明显更高[66],所以性别和生殖状况的影响也应该在未来的研究中进行评估。第四:目前的研究对Nell-1→Runx1→IL-1β功能轴的理解不完整。首先,从Nell-1到Runx1的信号转导在很大程度上是未知的,这可能是由于对Nell-1的特异性细胞表面受体、相关蛋白和下游激活物的了解有限。Nell-1通过不同的细胞表面受体或辅助受体以依赖于细胞类型和发育阶段的方式提供其功能[69]。同时,Runx1在关节炎中的具体作用机制尚不清楚[70]。此外,骨关节炎是一种全关节的疾病,涉及关节软骨、软骨下骨、韧带、关节囊、滑膜和关节周围肌肉的结构改变[71],因此还应评估Nell-1对附近滑膜和免疫细胞的影响,以充分阐明Nell-1在骨关节炎治疗中的益处。 2.5 Nell-1在临床应用的最新进展 2.5.1 Nell-1在颅面骨再生中的应用进展 Nell-1在小鼠模型中具有与骨形态发生蛋白类似的成骨能力,并且还可能与骨形态发生蛋白协同作用,促进质量更好的局部骨形成[72]。最近,一项临床前研究将pDNA-Nell-1与骨髓间充质干细胞和三维打印生物活性玻璃/壳聚糖纳米复合材料联合应用于恒河猴牙槽骨再生,显著促进了牙槽骨的再生,而且再生的新骨组织在质量上与正常骨非常接近[73]。 2.5.2 Nell-1在脊柱融合中的应用进展 脱钙骨基质传递的Nell-1对脊柱融合的影响已经在大鼠和绵羊模型中得到了广泛的验证[72]。联合应用Nell-1蛋白和人血管周围干细胞可以显著提高骨质疏松大鼠的脊柱融合率[74]。值得注意的是,在非人灵长类动物模型中给予Nell-1剂量为1.7 g/L的情况下,术后3个月的融合率为100%,没有不良反应[75]。NELL-1刚刚获得人类研究伦理委员会批准,成为澳大利亚一项多中心试点临床试验的首个中心,以评估Nell-1和脱钙骨基质对成年退行性椎间盘疾病患者的安全性和有效性。 2.5.3 Nell-1在骨组织工程中的应用进展 骨形态发生蛋白2在当前骨科手术中的应用越来越广泛。然而,骨形态发生蛋白2在临床应用中的不良反应也引起了该领域的广泛关注。例如:大剂量骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的大骨块具有成熟的骨边缘和充满主要脂肪骨髓组织的中心腔[76]。Nell-1已经被证明具有抗脂肪生成作用,并且当Nell-1与骨形态发生蛋白结合时,Nell-1可以逆转骨形态发生蛋白的促脂肪作用,以提高再生骨的质量;在股骨模型中,Nell-1还可以抑制骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的炎症[77]。此外,Nell-1还可在骨再生早期刺激血管生成,并促进间充质干细胞迁移[78],见表1。 2.5.4 Nell-1在肿瘤中的应用进展 Nell-1的高甲基化在胃癌以及Barrett食管中已被证实[79-80]。此外,在霍奇金淋巴瘤和肾细胞癌中发现Nell-1表达缺失[81-82]。相反,在横纹肌肉瘤中发现了Nell-1的过度表达[83]。值得注意的是,在所有类型的骨肿瘤和软骨形成肿瘤中也检测到了Nell-1的表达。在良性骨肿瘤中,Nell-1呈强而弥漫的染色;在骨肉瘤中,Nell-1染色相对减少,肿瘤间差异较大[84]。此外,Nell-1的表达并没有因软骨形成肿瘤的类型和分级而显著变化[85]。这些Nell-1表达与肿瘤组织的关系使得Nell-1在肿瘤发生中的作用没有定论。然而,Nell-1增加了95-D肺癌干细胞的化疗敏感性并抑制肾细胞癌细胞迁移和黏附[82,86]。因此,需要进一步确定Nell-1与恶性肿瘤相关的功能特性,特别是它在促进人类骨肉瘤患者切除后骨再生方面的利弊。 2.5.5 Nell-1在神经发育与神经疾病中的应用进展 LI等[69]研究发现Nell-1在神经母细胞瘤细胞系、胶质母细胞瘤细胞系和成人大脑中表达;新近发现Nell-1单核苷酸多态性与孤独症[69]、双相情感障碍以及抑郁症的关系[87-88],进一步强调了Nell-1在神经系统中的潜在重要性。因此,预计Nell-1在神经科学和神经细胞生物学领域的研究将取得重大进展。 "
| [1] PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, JUDGE A, JAVAID MK, et al. Incidence and risk factors for clinically diagnosed knee, hip and hand osteoarthritis: influences of age, gender and osteoarthritis affecting other joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(9):1659-1664. [2] HUNTER DJ, SCHOFIELD D, CALLANDER E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(7):437-441. [3] MARCUS DM. Pharmacologic interventions for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(9):672. [4] INTERNATIONAL ORS. Osteoarthritis: A serious disease. Osteoarthritis Research Society International. 2016:1-103. [5] RUNCIMAN WB, HUNT TD, HANNAFORD NA, et al. CareTrack: assessing the appropriateness of health care delivery in Australia. Med J Aust. 2012;197(2):100-105. [6] DA COSTA BR, REICHENBACH S, KELLER N, et al. RETRACTED: Effectiveness of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of pain in knee and hip osteoarthritis: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;387(10033):2093-2105. [7] SCOTT DL. CHAPTER 70 – Arthritis in the Elderly. Brocklehurst’s Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology (SEVENTH EDITION), 2010:566-576. [8] APPLETON CT. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):296-303. [9] COOPER C, BARDIN T, BRANDI ML, et al. Balancing benefits and risks of glucocorticoids in rheumatic diseases and other inflammatory joint disorders: new insights from emerging data. An expert consensus paper from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016; 28(1):1-16. [10] MAZZIOTTI G, ANGELI A, BILEZIKIAN JP, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: an update. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17(4):144-149. [11] CHEVALIER X, RAVAUD P, MAHEU E, et al. Adalimumab in patients with hand osteoarthritis refractory to analgesics and NSAIDs: a randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(9):1697-1705. [12] VAN LAAR M, PERGOLIZZI JV JR, MELLINGHOFF HU, et al. Pain treatment in arthritis-related pain: beyond NSAIDs. Open Rheumatol J. 2012;6:320-330. [13] LI C, ZOU M, ZHENG Z. Current medication for osteoarthritis. Acta Scientific Orthopaedics. 2018;1:9-12. [14] LI C, ZHENG Z. What’s the future of osteoarthritis treatment. Acta Scientific Orthopaedics. 2018;1:1-2. [15] LI C, JIANG J, ZHENG Z, et al. Neural EGFL-Like 1 Is a Downstream Regulator of Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 in Chondrogenic Differentiation and Maturation. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(5):963-972. [16] LI CS, ZHANG X, PÉAULT B, et al. Accelerated Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Perivascular Stem Cells with NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(3-4):272-285. [17] SIU RK, ZARA JN, HOU Y, et al. NELL-1 promotes cartilage regeneration in an in vivo rabbit model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(3-4):252-261. [18] LI C, ZHENG Z, HA P, et al. Neural EGFL like 1 as a potential pro-chondrogenic, anti-inflammatory dual-functional disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119541. [19] LI C, ZHENG Z, JIANG J, et al. Neural EGFL-Like 1 Regulates Cartilage Maturation through Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3-Mediated Indian Hedgehog Signaling. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(2):392-403. [20] LI C, ZHENG Z, ZHANG X, et al. Nfatc1 Is a Functional Transcriptional Factor Mediating Nell-1-Induced Runx3 Upregulation in Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):168. [21] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [22] FU K, ROBBINS SR, MCDOUGALL JJ. Osteoarthritis: the genesis of pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4):iv43-iv50. [23] LOESER RF, COLLINS JA, DIEKMAN BO. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420. [24] HSIA AW, EMAMI AJ, TARKE FD, et al. Osteophytes and fracture calluses share developmental milestones and are diminished by unloading. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):699-710. [25] DEVEZA LA, LOESER RF. Is osteoarthritis one disease or a collection of many? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4):iv34-iv42. [26] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759. [27] SCANZELLO CR. Role of low-grade inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(1):79-85. [28] BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, VAN MIDDELKOOP M. Osteoarthritis: In search of phenotypes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(12):705-706. [29] COURTIES A, SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. Metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(2):214-222. [30] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781. [31] AKKIRAJU H, NOHE A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2015;3(4):177-192. [32] LEE M, SIU RK, TING K, et al. Effect of Nell-1 delivery on chondrocyte proliferation and cartilaginous extracellular matrix deposition. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(5):1791-1800. [33] WANG C, HOU W, GUO X, et al. Two-phase electrospinning to incorporate growth factors loaded chitosan nanoparticles into electrospun fibrous scaffolds for bioactivity retention and cartilage regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:507-515. [34] LI W, ZARA JN, SIU RK, et al. Nell-1 enhances bone regeneration in a rat critical-sized femoral segmental defect model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127(2):580-587. [35] SIU RK, LU SS, LI W, et al. Nell-1 protein promotes bone formation in a sheep spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1123-1135. [36] ZHU S, ZHANG B, MAN C, et al. NEL-like molecule-1-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells/poly lactic-co-glycolic acid composite improves repair of large osteochondral defects in mandibular condyle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(6):743-750. [37] OEGEMA TR JR, CARPENTER RJ, HOFMEISTER F, et al. The interaction of the zone of calcified cartilage and subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Microsc Res Tech. 1997;37(4):324-332. [38] LI W, LEE M, WHANG J, et al. Delivery of lyophilized Nell-1 in a rat spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(9):2861-2870. [39] PAN J, ZHOU X, LI W, et al. In situ measurement of transport between subchondral bone and articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10): 1347-1352. [40] QI H, KIM JK, HA P, et al. Inactivation of Nell-1 in Chondrocytes Significantly Impedes Appendicular Skeletogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(3):533-546. [41] DESAI J, SHANNON ME, JOHNSON MD, et al. Nell1-deficient mice have reduced expression of extracellular matrix proteins causing cranial and vertebral defects. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(8):1329-1341. [42] KIM EJ, CHO SW, SHIN JO, et al. Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate early chondrogenesis: a mouse model. PLoS One. 2013; 8(2):e55296. [43] KIM IS, OTTO F, ZABEL B, et al. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by Cbfa1. Mech Dev. 1999;80(2):159-170. [44] YOSHIDA CA, YAMAMOTO H, FUJITA T, et al. Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation, and Runx2 regulates limb growth through induction of Indian hedgehog. Genes Dev. 2004;18(8):952-963. [45] CHEN H, GHORI-JAVED FY, RASHID H, et al. Runx2 regulates endochondral ossification through control of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(12):2653-2665. [46] WIGNER NA, SOUNG DO Y, EINHORN TA, et al. Functional role of Runx3 in the regulation of aggrecan expression during cartilage development. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(11):2232-2242. [47] CHEN W, ZHANG X, SIU RK, et al. Nfatc2 is a primary response gene of Nell-1 regulating chondrogenesis in ATDC5 cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(6):1230-1241. [48] SOKOLOVE J, LEPUS CM. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: latest findings and interpretations. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013;5(2):77-94. [49] PEARSON MJ, HERNDLER-BRANDSTETTER D, TARIQ MA, et al. IL-6 secretion in osteoarthritis patients is mediated by chondrocyte-synovial fibroblast cross-talk and is enhanced by obesity. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):3451. [50] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(5):471-478. [51] WANG M, SAMPSON ER, JIN H, et al. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(1):R5. [52] ALLEN KD, ADAMS SB JR, MATA BA, et al. Gait and behavior in an IL1β-mediated model of rat knee arthritis and effects of an IL1 antagonist. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):694-703. [53] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZARA JN, et al. BMP2-induced inflammation can be suppressed by the osteoinductive growth factor NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(21-22):2390-2401. [54] JAMES AW, SHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. NELL-1 in the treatment of osteoporotic bone loss. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7362. [55] Beier F. NFATs are good for your cartilage! Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(7):893-895. [56] WANG J, GARDNER BM, LU Q, et al. Transcription factor Nfat1 deficiency causes osteoarthritis through dysfunction of adult articular chondrocytes. J Pathol. 2009;219(2):163-172. [57] YOO SA, PARK BH, YOON HJ, et al. Calcineurin modulates the catabolic and anabolic activity of chondrocytes and participates in the progression of experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7):2299-2311. [58] MICLEA RL, SIEBELT M, FINOS L, et al. Inhibition of Gsk3β in cartilage induces osteoarthritic features through activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(11):1363-1372. [59] YAYKASLI KO, OOHASHI T, HIROHATA S, et al. ADAMTS9 activation by interleukin 1 beta via NFATc1 in OUMS-27 chondrosarcoma cells and in human chondrocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009;323(1-2):69-79. [60] GREENBLATT MB, RITTER SY, WRIGHT J, et al. NFATc1 and NFATc2 repress spontaneous osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(49):19914-19919. [61] AINI H, ITAKA K, FUJISAWA A, et al. Messenger RNA delivery of a cartilage-anabolic transcription factor as a disease-modifying strategy for osteoarthritis treatment. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18743. [62] KWAK JH, ZHANG Y, PARK J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and osteogenic potential of PEGylated NELL-1 in vivo after systemic administration. Biomaterials. 2015;57:73-83. [63] VIMALRAJ S, ARUMUGAM B, MIRANDA PJ, et al. Runx2: Structure, function, and phosphorylation in osteoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;78:202-208. [64] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZHANG X, et al. Novel Wnt Regulator NEL-Like Molecule-1 Antagonizes Adipogenesis and Augments Osteogenesis Induced by Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(2):419-434. [65] GREGORY MH, CAPITO N, KUROKI K, et al. A review of translational animal models for knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis. 2012;2012:764621. [66] KUYINU EL, NARAYANAN G, NAIR LS, et al. Animal models of osteoarthritis: classification, update, and measurement of outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:19. [67] PUNZI L, GALOZZI P, LUISETTO R, et al. Post-traumatic arthritis: overview on pathogenic mechanisms and role of inflammation. RMD Open. 2016;2(2):e000279. [68] PROFFEN BL, MCELFRESH M, FLEMING BC, et al. A comparative anatomical study of the human knee and six animal species. Knee. 2012;19(4):493-499. [69] LI C, ZHENG Z, HA P, et al. Neurexin Superfamily Cell Membrane Receptor Contactin-Associated Protein Like-4 (Cntnap4) Is Involved in Neural EGFL-Like 1 (Nell-1)-Responsive Osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(10):1813-1825. [70] LEE YH, BAE SC, KIM JH, et al. Meta-analysis of SLC22A4 and RUNX1 polymorphisms : Associations with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Z Rheumatol. 2015;74(4):351-358. [71] BRANDT KD, RADIN EL, DIEPPE PA, et al. Yet more evidence that osteoarthritis is not a cartilage disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(10): 1261-1264. [72] ZHANG X, ZARA J, SIU RK, et al. The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration. Version 2. J Dent Res. 2010;89(9):865-878. [73] ZHANG J, CHEN Y, XU J, et al. Tissue engineering using 3D printed nano-bioactive glass loaded with NELL1 gene for repairing alveolar bone defects. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(4):213-220. [74] LEE S, ZHANG X, SHEN J, et al. Brief Report: Human Perivascular Stem Cells and Nel-Like Protein-1 Synergistically Enhance Spinal Fusion in Osteoporotic Rats. Stem Cells. 2015;33(10):3158-3163. [75] JAMES AW, SHEN J, TSUEI R, et al. NELL-1 induces Sca-1+ mesenchymal progenitor cell expansion in models of bone maintenance and repair. JCI Insight. 2017;2(12):e92573. [76] JAMES AW, LACHAUD G, SHEN J, et al. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016; 22(4):284-297. [77] PAKVASA M, ALVERDY A, MOSTAFA S, et al. Neural EGF-like protein 1 (NELL-1): Signaling crosstalk in mesenchymal stem cells and applications in regenerative medicine. Version 2. Genes Dis. 2017;4(3):127-137. [78] FAHMY-GARCIA S, VAN DRIEL M, WITTE-BUOMA J, et al. NELL-1, HMGB1, and CCN2 Enhance Migration and Vasculogenesis, But Not Osteogenic Differentiation Compared to BMP2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(3-4):207-218. [79] GAO C, ZHANG Q, KONG D, et al. MALDI-TOF Mass Array Analysis of Nell-1 Promoter Methylation Patterns in Human Gastric Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:136941. [80] WANG Z, KAMBHAMPATI S, CHENG Y, et al. Methylation Biomarker Panel Performance in EsophaCap Cytology Samples for Diagnosing Barrett’s Esophagus: A Prospective Validation Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(7):2127-2135. [81] SLOVAK ML, BEDELL V, HSU YH, et al. Molecular karyotypes of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells at disease onset reveal distinct copy number alterations in chemosensitive versus refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(10):3443-3454. [82] NAKAMURA R, OYAMA T, TAJIRI R, et al. Expression and regulatory effects on cancer cell behavior of NELL1 and NELL2 in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015;106(5):656-664. [83] TOMBOLAN L, POLI E, MARTINI P, et al. NELL1, whose high expression correlates with negative outcomes, has different methylation patterns in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(20):33086-33099. [84] SHEN J, LACHAUD G, KHADARIAN K, et al. NELL-1 expression in benign and malignant bone tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015; 460(2):368-374. [85] SHEN J, LACHAUD G, SHRESTHA S, et al. NELL-1 expression in tumors of cartilage. J Orthop. 2015;12(Suppl 2):S223-229. [86] ZHAI Y, WEI R, SHA S, et al. Effect of NELL1 on lung cancer stem‑like cell differentiation. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1817-1826. [87] MATHIEU F, ETAIN B, DIZIER MH, et al. Genetics of emotional reactivity in bipolar disorders. J Affect Disord. 2015;188:101-106. [88] LIN E, KUO PH, LIU YL, et al. A Deep Learning Approach for Predicting Antidepressant Response in Major Depression Using Clinical and Genetic Biomarkers. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:290. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [5] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [12] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [13] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [14] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [15] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||