Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (30): 4882-4888.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2838
Previous Articles Next Articles
Involvement and significance of large transmembrane protein Piezo1 in orthopedic related diseases
He Qi1, Zhang Gangyu1, Wang Haibin2, Chen Peng2
- 1First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-17Revised:2020-02-24Accepted:2020-04-03Online:2020-10-28Published:2020-09-22 -
Contact:Chen Peng, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:He Qi, Master candidate, First Clinical Medicine School, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2017, No. 81774339; the Youth Science Foundation Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2017, No. 81603641; the Science and Technology Plan Project of Guangdong Province in 2017, No. 2017A020213030
CLC Number:
Cite this article
He Qi, Zhang Gangyu, Wang Haibin, Chen Peng. Involvement and significance of large transmembrane protein Piezo1 in orthopedic related diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4882-4888.
share this article
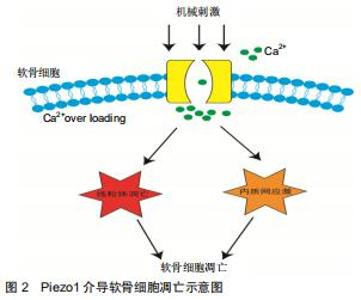
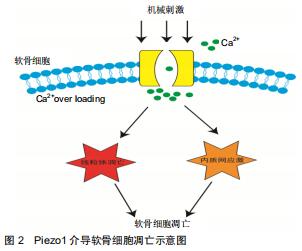
2.2 Piezo1离子通道的门控特点 作为细胞表达一系列的力传感器,在细胞机械转导时,Piezo1的门控特点在细胞质膜内外部所受力的过程中不可或缺,见图2。当Piezo1机械敏感离子通道在生理条件下感受机械应力刺激后产生内向电流, 这种门控功能介导的机械-电转导非常迅速,在胞膜去极化的同时伴随胞内正电荷增加,从而在2 ms内即可将机械刺激转化为一系列下游细胞信号[14]。Piezo1通道通过直接的膜张力进行门控, 所以任何改变膜张力的生理作用力理论上都可激活通道,如戳刺、拉伸、流体剪切力等[15]。Piezo1通道对阳离子具有非选择渗透性,对Na+,K+,Ca2+,Mg2+全部渗透,但更偏向Ca2+[16]。通过双层膜结构重建技术[17],当膜表面的张力足够大,便可引起Piezo1通道的激活,引起钙内流;当使用细胞松弛素D干预细胞破坏细胞骨架后,可观察到细胞上Piezo1通道激活的频率增加,从而验证了Piezo1是一种成孔通道亚基,它对机械性刺激敏感,但也会受到细胞骨架因素的影响[22-24],这证明了Piezo1通道的门控性。人造液滴脂质双分子层实验表明,Piezo1响应机械力的过程不需要任何其他细胞组分, 说明Piezo1的机械敏感性是固有的,不需要其他蛋白质或第二信使信号激活[25]。另外有研究发现,除了机械刺激之外Piezo1通道也受电压调控, 甚至可以切换到纯电压门控模式[26]。某些引起人类疾病的突变[27](如干瘪细胞增多症及淋巴发育不良)会极大改变Piezo1通道对静息膜电位的电压敏感性,并强烈促进电压门控。 "
|
[1] ANISHKIN A, LOUKIN SH, TENG J, et al. Feeling the hidden mechanical forces in lipid bilayer is an original sense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(22):7898-7905.
[2] GUHARAY F, SACHS F. Stretch-activated single ion channel currents in tissue-cultured embryonic chick skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1984;352:685-701.
[3] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct Mechanically Activated Cation Channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60.
[4] BORBIRO I, ROHACS T. Regulation of Piezo Channels by Cellular Signaling Pathways.Curr Top Membr. 2017;79: 245-261.
[5] ZHAO Q, ZHOU H, LI X, et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel: a three-bladed propeller-like structure and a lever-like mechanogating mechanism. FEBS J. 2019;286(13): 2461-2470.
[6] SAOTOME K, MURTHY SE, KEFAUVER JM, et al. Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature. 2018;554(7693):481-486.
[7] GUO YR, MACKINNON R. Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. Elife. 2017;6. pii: e33660.
[8] RU YW, ZHANG WB. Advances in the Role of Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 in Cellular Mechanotransduction. Chin J Cell Biol. 2019;41(8):1622-1627.
[9] LI J, HOU B, TUMOVA S, et al. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature. 2014;515(7526): 279-282.
[10] RANADE SS, QIU Z, WOO SH, et al. Piezo1, a mechanically activated ion channel, is required for vascular development in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(28):10347-10352.
[11] MIYAMOTO T, MOCHIZUKI T, NAKAGOMI H, et al. Functional Role for Piezo1 in Stretch-evoked Ca(2+) Influx and ATP Release in Urothelial Cell Cultures. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(23):16565-16575.
[12] PATHAK MM, NOURSE JL, TRAN T, et al. Stretch-activated ion channel Piezo1 directs lineage choice in human neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(45): 16148-16153.
[13] COOPER G. Genetics and lymphoedema: a future yet to be fully discovered. Br J Community Nurs. 2017;22(1):646-648.
[14] JIN Y, LI J, WANG Y, et al. Functional role of mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 in human periodontal ligament cells. Angle Orthod. 2015;85(1):87-94.
[15] MURTHY SE, DUBIN AE, PATAPOUTIAN A. Piezos thrive under pressure: mechanically activated ion channels in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(12):771-783.
[16] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct Mechanically Activated Cation Channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60.
[17] COSTE B. Piezo proteins form a new class of mechanically activated ion channels. Med Sci (Paris). 2012;28(12): 1056-1057.
[18] GNANASAMBANDAM R, BAE C, GOTTLIEB PA, et al. Ionic Selectivity and Permeation Properties of Human PIEZO1 Channels. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e125503.
[19] 康婷.机械敏感性离子通道 Piezo 在正畸牙周组织中表达和功能的研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2014.
[20] 李鹏.新型机械敏感离子通道Piezo在成牙本质细胞表达和功能研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.
[21] ZHANG YY, HUANG YP, ZHAO HX, et al. Cementogen-esis is inhibited under a mechanical static compressiveforce via Piezo1. Angle Orthod. 2017;87(4):618-624.
[22] LEE KL, GUEVARRAMD, NGUYEN AM, et al. The pri-mary cilium functions as a mechanical and calcium signa-ling nexus. Cilia. 2015;4:7.
[23] SHARIF-NAEINI R, FOLGERING JH, BICHET D, et al. Polycystin-1 and -2 dosage regulates pressure sensing. Cell. 2009;139(3):587-596.
[24] PEYRONNET R, MARTINS JR, DUPRAT F, et al. Piezo1-dependent stretch-activated channels are inhibited by Polycystin-2 in renal tubular epithelial cells. EMBO Rep. 2013; 14(12):1143-1148.
[25] SYEDA R, FLORENDO MN, COX CD, et al. Piezo1 channels are inherently mechanosensitive. Cell Rep. 2016;17(7): 1739-1746.
[26] KAESTNER L, EGEE S. Commentary: Voltage Gating of Mechanosensitive PIEZO Channels.Front Physiol.2018;9: 1565.
[27] ZARYCHANSKI R, SCHULZ VP, HOUSTON BL, et al. Mutations in the mechanotransduction protein PIEZO1 are associated with hereditary xerocytosis. Blood. 2012;120(9): 1908-1915.
[28] JUSTESEN J, STENDERUP K, EBBESEN EN, et al. Adipocyte tissue volume in bone marrow is increased with aging and in patients with osteoporosis. Biogerontology. 2001; 2(3):165-171.
[29] LV H, LI L, SUN M, et al. Mechanism of regulation of stem cell differentiation by matrix stiffness. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6: 103.
[30] DING H, CHEN S, YIN JH, et al. Continuous hypoxia regulates the osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in a time-dependent manner. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(4):2184-2190.
[31] MOZDZEN LC, THORPE SD, SCREEN HR, et al. The Effect of Gradations in Mineral Content, Matrix Alignment, and Applied Strain on Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Morphology within Collagen Biomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(14):1731-1739.
[32] LUND P, PILGAARD L, DUROUX M, et al. Effect of growth media and serum replacements on the proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(2):189-197.
[33] BERARD A, BRAVO G, GAUTHIER P. Meta-analysis of the effectiveness of physical activity for the prevention of bone loss in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(4): 331-337.
[34] KIM H, IWASAKI K, MIYAKE T, et al. Changes in bone turnover markers during 14-day 6 degrees head-down bed rest. J Bone Miner Metab. 2003;21(5):311-315.
[35] WAMOTO J, TAKEDA T, SATO Y. Interventions to prevent bone loss in astronauts during space flight. Keio J Med. 2005;54(2):55-59.
[36] GREGL A, HEITMANN D, KRACK U, et al. Das Gesetz der Transformation der Knochen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1893;19(47):1222-1224.
[37] SUGIMOTO A, MIYAZAKI A, KAWARABAYASHI K, et al. Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 functions as a regulator of the cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17696.
[38] SYEDA R, XU J, DUBIN AE, et al. Chemical activation of the mechanotransduction channel Piezo1. Elife. 2015. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07369.
[39] SUN W, CHI S, LI Y, et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation. Elife. 2019. doi:10.7554/eLife.47454.
[40] WANG L, YOU X, LOTINUN S, et al. Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast- osteoclast crosstalk. Nat Commun.2020;11(1):282.
[41] LAWRENCE RC, FELSON DT, HELMICK CG, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58(1):26-35.
[42] D'LIMA DD, PATIL S, STEKLOV N, et al. In vivo knee moments and shear after total knee arthroplasty. J Biomech. 2007;40 Suppl 1:S11-S17.
[43] FREGLY BJ, BESIER TF, LLOYD DG, et al. Grand challenge competition to predict in vivo knee loads. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(4):503-513.
[44] KOIKE M, NOJIRI H, OZAWA Y, et al. Mechanical overloading causes mitochondrial superoxide and SOD2 imbalance in chondrocytes resulting in cartilage degeneration. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11722.
[45] ONITSUKA K, MURATA K, KOKUBUN T, et al. Effects of Controlling Abnormal Joint Movement on Expression of MMP13 and TIMP-1 in Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2018: 941195303.
[46] GRIFFIN TM, GUILAK F. The role of mechanical loading in the onset and progression of osteoarthritis. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2005;33(4):195-200.
[47] LAWRENCE KM, JONES RC, JACKSON TR, et al. Chondroprotection by urocortin involves blockade of the mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 5147.
[48] LEE W, LEDDY HA, CHEN Y, et al. Synergy between Piezo1 and Piezo2 channels confers high-strain mechanosensitivity to articular cartilage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(47): E5114-5122.
[49] ROCIO SM, MORONI M, LEWIN GR, et al. Direct measurement of TRPV4 and PIEZO1 activity reveals multiple mechanotransduction pathways in chondrocytes. Elife. 2017; 6. pii: e21074.
[50] LI XF, ZHANG Z, CHEN Z K, et al. Piezo1 protein induces the apoptosis of human osteoarthritis-derived chondrocytes by activating caspase-12, the signaling marker of ER stress. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(3):845-853.
[51] 鲁玉来.腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(23): 1901-1904.
[52] LI XF, LENG P, ZHANG Z, et al. The Piezo1 protein ion channel functions in human nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial dysfunction and the endoplasmic reticulum stress signal pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2017;358(2): 377-389.
[53] 殷涛,邵进,张岩,等.机械敏感性离子通道蛋白Piezo1在椎间盘髓核细胞中的表达及意义[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(12):77-80.
[54] PASZEK MJ, WEAVER VM. The tension mounts: mechanics meets morphogenesis and malignancy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004;9(4):325-342.
[55] YANG JH, SAKAMOTO H, XU EC, et al. Biomechanical regulation of human monocyte/macrophage molecular function. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(5):1797-1804.
[56] WELLS RG, DISCHER DE. Matrix elasticity, cytoskeletal tension, and TGF-beta: the insoluble and soluble meet. Sci Signal. 2008;1(10):e13.
[57] JIANG L, ZHAO YD, CHEN WX. The function of the novel mechanical activated ion channel Piezo1 in the human osteosarcoma cells.Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:5070-5082.
[58] LEWIECKI EM, COMPSTON JE, MILLER PD, et al. Official Positions for FRAX® Bone Mineral Density and FRAX® Simplification: From Joint Official Positions Development Conference of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and International Osteoporosis Foundation on FRAX®. J Clin Densitom. 2011;14(3):226-236.
[59] LEBLANC AD, SPECTOR ER, EVANS HJ, et al. Skeletal responses to space flight and the bed rest analog: a review. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2007;7(1):33-47. [60] 李晓飞,张钊,王天宝,等.Piezo1蛋白经MAPK/ERK5信号通路介导软骨细胞凋亡的机制研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(12): 795-803. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [5] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [6] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [7] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||